Structure and Catalytic Properties of Carboxylesterase Isozymes Involved in Metabolic Activation of Prodrugs
Abstract
:Introduction
Classification and Nomenclature of CES Superfamily
Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of CES Isozymes

| Substrate | Alcohol Substituent | Acyl Substituent | Substrate Specficity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cocaine (methyl ester) | CH3OH | 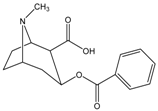 | CES1 |
| Meperidine | CH3CH2OH | 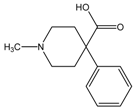 | CES1 |
| Methylphenidate | CH3OH | 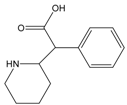 | CES1 |
| Temocapril | C2H5OH | 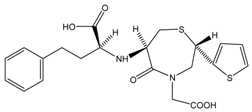 | CES1 |
| Oseltamivir | C2H5OH | 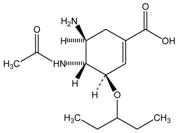 | CES1 |
| Cocaine (benzoyl ester) | 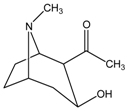 |  | CES2>>CES1 |
| CPT-11 | 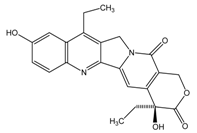 | 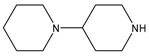 | CES2>>CES1 |
| Heroin | 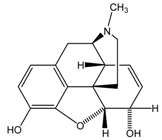 | CH3COOH | CES2>>CES1 |
| Methylprednisolone 21-Hemisuccinate | 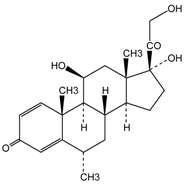 | HOOC-CH2-CH2-COONa | CES2>>CES1 |
Structure-activity Relationships of Substrates with CES1 and CES2 Families
| Species | Isozyme | Liver | Small intestine | Kidney | Lung |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse | CES1 CES2 | +++ +++ | - +++ | +++ +++ | +++ - |
| Rat | CES1 CES2 | +++ - | - +++ | +++ - | +++ - |
| Hamster | CES1 CES2 | +++ +++ | - +++ | +++ - | NT NT |
| Guinea Pig | CES1 CES2 | +++ - | +++ + | ++ - | NT NT |
| Beagle Dog | CES1 CES2 | +++ ++ | - - | NT NT | +++ + |
| Monkey | CES1 CES2 | +++ + | ++ +++ | - + | NT NT |
| Human | CES1 CES2 | +++ + | - +++ | + +++ | +++ - |
Gene Structure and Regulation of CES Isozymes

Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Furihata, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Koyano, N.; Nakamura, T.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Identification of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced carboxylesterase 1 in C57BL/6 mouse liver microsomes: purification, cDNA cloning, and baculovirus-mediated expression. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1170–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furihata, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Nakata, F.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Purification, molecular cloning, and functional expression of inducible liver acylcarnitine hydrolase in C57BL/6 mouse, belonging to the carboxylesterase multigene family. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 416, 101–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Maki, T.; Satoh, T. Characterization of molecular species of liver microsomal carboxylesterases of several animal species and humans. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 277, 219–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Satoh, T. Molecular aspect of the inter-species variation in carboxylesterase, 7th North American ISSX Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA; 1996.
- Hosokawa, M.; Suzuki, K.; Takahashi, D.; Mori, M.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Purification, molecular cloning, and functional expression of dog liver microsomal acyl-CoA hydrolase: a member of the carboxylesterase multigene family. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 389, 245–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Satoh, T.; Sato, K. Changes in carboxylesterase isoenzymes of rat liver microsomes during hepatocarcinogenesis. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1991, 82, 800–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentlein, R.; Berge, R. K.; Heymann, E. Identity of purified monoacylglycerol lipase, palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase and aspirin-metabolizing carboxylesterase from rat liver microsomal fractions. A comparative study with enzymes purified in different laboratories. Biochem. J. 1985, 232, 479–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein, R.; Heiland, S.; Heymann, E. Simultaneous purification and comparative characterization of six serine hydrolases from rat liver microsomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1980, 200, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentlein, R.; Heymann, E. Hydrolysis of ester- and amide-type drugs by the purified isoenzymes of nonspecific carboxylesterase from rat liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1984, 33, 1243–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, M.; Furihata, T.; Yaginuma, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Koyano, N.; Fujii, A.; Nagahara, Y.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Genomic structure and transcriptional regulation of the rat, mouse, and human carboxylesterase genes. Drug Metab. Rev. 2007, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, T.; Hosokawa, M. The mammalian carboxylesterases: from molecules to functions. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1998, 38, 257–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Hosokawa, M. Structure, function and regulation of carboxylesterases. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 162, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Hirata, K.; Nakata, F.; Suga, T.; Satoh, T. Species differences in the induction of hepatic microsomal carboxylesterases caused by dietary exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate, a peroxisome proliferator. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1994, 22, 889–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, M.; Maki, T.; Satoh, T. Multiplicity and regulation of hepatic microsomal carboxylesterases in rats. Mol. Pharmacol. 1987, 31, 579–84. [Google Scholar]
- Brzezinski, M. R.; Abraham, T. L.; Stone, C. L.; Dean, R. A.; Bosron, W. F. Purification and characterization of a human liver cocaine carboxylesterase that catalyzes the production of benzoylecgonine and the formation of cocaethylene from alcohol and cocaine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 48, 1747–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, M. R.; Spink, B. J.; Dean, R. A.; Berkman, C. E.; Cashman, J. R.; Bosron, W. F. Human liver carboxylesterase hCE-1: binding specificity for cocaine, heroin, and their metabolites and analogs. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25((9)), 1089–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ellinghaus, P.; Seedorf, U.; Assmann, G. Cloning and sequencing of a novel murine liver carboxylesterase cDNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1397, 175–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroetz, D. L.; McBride, O. W.; Gonzalez, F. J. Glycosylation-dependent activity of baculovirus-expressed human liver c arboxylesterases: cDNA cloning and characterization of two highly similar enzyme forms. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 11606–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, K.; Seko, T.; Tanaka, S.; Shikata, Y.; Ando, T.; Ida, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Satoh, T.; Yuzuriha, T.; Horie, T. Purification and characterization of monkey liver amidohydrolases and it's relationship to a metabolic polymorphism of E6123, a platelet activating factor receptor antagonist. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1996, 24, 1186–91. [Google Scholar]
- Langmann, T.; Aslanidis, C.; Schuierer, M.; Schmitz, G. Differentiation-dependent expression of a human carboxylesterase in monocytic cells and transcription factor binding to the promoter. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 230, 215–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E. W.; Yan, B.; Greenway, D.; Petersen, D. R.; Parkinson, A. Purification and characterization of two rat liver microsomal carboxylesterases (hydrolase A and B). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 315, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yang, D.; Brady, M.; Parkinson, A. Rat kidney carboxylesterase. Cloning, sequencing, cellular localization, and relationship to rat liver hydrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29688–96. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Yang, D.; Brady, M.; Parkinson, A. Rat testicular carboxylesterase: cloning, cellular localization, and relationship to liver hydrolase A. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 316, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yang, D.; Bullock, P.; Parkinson, A. Rat serum carboxylesterase. Cloning, expression, regulation, and evidence of secretion from liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 19128–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yang, D.; Parkinson, A. Cloning and expression of hydrolase C, a member of the rat carboxylesterase family. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 317, 222–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prueksaritanont, T.; Gorham, L. M.; Hochman, J. H.; Tran, L. O.; Vyas, K. P. Comparative studies of drug-metabolizing enzymes in dog, monkey, and human small intestines, and in Caco-2 cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1996, 24, 634–42. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, M.; Morikawa, M.; Tsuboi, M.; Sugiura, M. Species difference and characterization of intestinal esterase on the hydrolizing activity of ester-type drugs. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1979, 29, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Taketani, M.; Shii, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Chiba, K. Substrate specificity of carboxylesterase isozymes and their contribution to hydrolase activity in human liver and small intestine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1734–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansbach, C. M., 2nd; Nevin, P. Intracellular movement of triacylglycerols in the intestine. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 963–8. [Google Scholar]
- Schwer, H.; Langmann, T.; Daig, R.; Becker, A.; Aslanidis, C.; Schmitz, G. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel putative carboxylesterase, present in human intestine and liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 233, 117–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbel, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Satoh, T. Differences in the induction of carboxylesterase RL4 in rat liver microsomes by various perfluorinated fatty acids, metabolically inert derivatives of fatty acids. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 19, 765–767. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, K.; Igarashi, M.; Itoh, M.; Tomisawa, H.; Tateishi, M. Specific induction by glucocorticoids of steroid esterase in rat hepatic microsomes and its release into serum. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 1921–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Endo, Y.; Fujisawa, M.; Hara, S.; Iwata, N.; Sato, Y.; Satoh, T. Interindividual variation in carboxylesterase levels in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1995, 23, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, M.; Hattori, K.; Igarashi, M.; Satoh, T.; Ohkawara, S.; Igarashi, T.; Ueno, K.; Ohshima, T.; Kitagawa, H. Effects of pituitary hormones on carboxylesterase and drug metabolizing enzymes in rat liver microsomes. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1984, 36, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Satoh, T. Differences in the induction of carboxylesterase isozymes in rat liver microsomes by perfluorinated fatty acids. Xenobiotica 1993, 23, 1125–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, R.; Kuksis, A. Purification of an acyl-CoA hydrolase from rat intestinal microsomes. A candidate acyl-enzyme intermediate in glycerolipid acylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24726–33. [Google Scholar]
- Mentlein, R.; Schumann, M.; Heymann, E. Comparative chemical and immunological characterization of five lipolytic enzymes (carboxylesterases) from rat liver microsomes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1984, 234, 612–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Kayano, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamamoto, I.; Yoshimura, H. Purification and characterization of a novel 46.5-kilodalton esterase from mouse hepatic microsomes. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1993, 31, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Geshi, E.; Kimura, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Suzuki, H.; Koba, S.; Sakai, T.; Saito, T.; Koga, A.; Muramatsu, M.; Katagiri, T. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the carboxylesterase gene is associated with the responsiveness to imidapril medication and the promoter activity. Hypertens. Res. 2005, 28, 719–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Ogasawara, Y.; Tsukada, E.; Chiba, K. cDNA cloning, characterization and stable expression of novel human brain carboxylesterase. FEBS Lett. 1999, 458, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, S.; Matsuda, A.; Usami, Y.; Adachi, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Katagiri, Y.; Tatematsu, M.; Hirano, K. Hydrolytic profile for ester- or amide-linkage by carboxylesterases pI 5.3 and 4.5 from human liver. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 20, 869–73. [Google Scholar]
- Danks, M. K.; Morton, C. L.; Pawlik, C. A.; Potter, P. M. Overexpression of a rabbit liver carboxylesterase sensitizes human tumor cells to CPT-11. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 20–2. [Google Scholar]
- Guichard, S. M.; Morton, C. L.; Krull, E. J.; Stewart, C. F.; Danks, M. K.; Potter, P. M. Conversion of the CPT-11 metabolite APC to SN-38 by rabbit liver carboxylesterase. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 3089–94. [Google Scholar]
- Humerickhouse, R.; Lohrbach, K.; Li, L.; Bosron, W. F.; Dolan, M. E. Characterization of CPT-11 hydrolysis by human liver carboxylesterase isoforms hCE-1 and hCE-2. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1189–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, A.; Hackett, N. R.; Ohwada, A.; Crystal, R. G. In vivo human carboxylesterase cDNA gene transfer to activate the prodrug CPT-11 for local treatment of solid tumors. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 101, 1789–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, P. M.; Pawlik, C. A.; Morton, C. L.; Naeve, C. W.; Danks, M. K. Isolation and partial characterization of a cDNA encoding a rabbit liver carboxylesterase that activates the prodrug irinotecan (CPT-11). Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2646–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghani, S. P.; Quinney, S. K.; Fredenburg, T. B.; Sun, Z.; Davis, W. I.; Murry, D. J.; Cummings, O. W.; Seitz, D. E.; Bosron, W. F. Carboxylesterases expressed in human colon tumor tissue and their role in CPT-11 hydrolysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4983–91. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Atsumi, R.; Suzuki, W.; Hakusui, H.; Nagai, E. Metabolic activation of CPT-11, 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1- piperidino]carbonyloxycamptothecin, a novel antitumor agent, by c arboxylesterase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 17, 662–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tabata, T.; Katoh, M.; Tokudome, S.; Nakajima, M.; Yokoi, T. Identification of the cytosolic carboxylesterase catalyzing the 5'-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine formation from capecitabine in human liver. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1103–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamendulis, L. M.; Brzezinski, M. R.; Pindel, E. V.; Bosron, W. F.; Dean, R. A. Metabolism of cocaine and heroin is catalyzed by the same human liver carboxylesterases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 279, 713–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Burnell, J. C.; Dumaual, N.; Bosron, W. F. Binding and hydrolysis of meperidine by human liver carboxylesterase hCE-1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 290, 314–8. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, T.; Yoshigae, Y.; Hosokawa, M.; Chiba, K.; Otagiri, M. Evidence for the involvement of a pulmonary first-pass effect via carboxylesterase in the disposition of a propranolol ester derivative after intravenous administration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 1234–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuka, K.; Inoue, S.; Kameyama, M.; Kanetoshi, A.; Fujimoto, T.; Takaoka, K.; Araya, Y.; Shida, A. Intracellular conversion of irinotecan to its active form, SN-38, by native carboxylesterase in human non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2003, 41, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Pindel, E. V.; Kedishvili, N. Y.; Abraham, T. L.; Brzezinski, M. R.; Zhang, J.; Dean, R. A.; Bosron, W. F. Purification and cloning of a broad substrate specificity human liver carboxylesterase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of cocaine and heroin. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 14769–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, G.; McLeod, H. L. Comprehensive evaluation of carboxylesterase-2 expression in normal human tissues using tissue array analysis. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2002, 10, 374–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, W. N. The esterases: perspectives and problems. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1993, 87, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschunke, F.; Salmassi, A.; Kreipe, H.; Buck, F.; Parwaresch, M. R.; Radzun, H. J. cDNA cloning and characterization of human monocyte/macrophage serine esterase-1. Blood 1991, 78, 506–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ovnic, M.; Tepperman, K.; Medda, S.; Elliott, R. W.; Stephenson, D. A.; Grant, S. G.; Ganschow, R. E. Characterization of a murine cDNA encoding a member of the carboxylesterase multigene family. Genomics 1991, 9, 344–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbi, M.; Beaufay, H. Biosynthesis of rat liver pI-6.1 esterase, a carboxylesterase of the cisternal space of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. J. 1987, 248, 545–50. [Google Scholar]
- Robbi, M.; Beaufay, H.; Octave, J. N. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA coding for rat liver pI 6.1 esterase (ES-10), a carboxylesterase located in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. J. 1990, 269, 451–8. [Google Scholar]
- Robbi, M.; Van Schaftingen, E.; Beaufay, H. Cloning and sequencing of rat liver carboxylesterase ES-4 (microsomal palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase). Biochem. J. 1996, 313, 821–6. [Google Scholar]
- Taketani, M.; Shii, M.; Ohura, K.; Ninomiya, S.; Imai, T. Carboxylesterase in the liver and small intestine of experimental animals and human. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 924–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, D.; Yang, D.; Song, X.; Yan, B. Interleukin-6 alters the cellular responsiveness to clopidogrel, irinotecan, and oseltamivir by suppressing the expression of carboxylesterases HCE1 and HCE2. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 686–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furihata, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Fujii, A.; Derbel, M.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Dexamethasone-induced methylprednisolone hemisuccinate hydrolase: Its identification as a member of the rat carboxylesterase 2 family and its unique existence in plasma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 1287–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozols, J. Isolation, properties, and the complete amino acid sequence of a second form of 60-kDa glycoprotein esterase. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 12533–12545. [Google Scholar]
- Sone, T.; Isobe, M.; Takabatake, E.; Wang, C. Y. Cloning and sequence analysis of a hamster liver cDNA encoding a novel putative carboxylesterase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1207, 138–42. [Google Scholar]
- Aida, K.; Moore, R.; Negishi, M. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a novel, male-predominant carboxylesterase in mouse liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1174, 72–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghani, S. P.; Quinney, S. K.; Fredenburg, T. B.; Davis, W. I.; Murry, D. J.; Bosron, W. F. Hydrolysis of irinotecan and its oxidative metabolites, 7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic acid)-1-piperidino]carbonyloxy camptothecin and 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-amino]- carbonyloxy camptothecin, by human carboxylesterases CES1A1, CES2, and a newly expressed carboxylesterase isoenzyme, CES3. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 505–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Yamashita, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Taira, H.; Suzuki, A. Species-, sex-, and age-dependent urinary excretion of cauxin, a mammalian carboxylesterase. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 145, 270–7. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, M.; Yamashita, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Saito, Y.; Soeta, S.; Taira, H.; Suzuki, A. A major urinary protein of the domestic cat regulates the production of felinine, a putative pheromone precursor. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1071–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, M. R.; Beer, M.; Beer, D.; Jeno, P.; Meyer, U. A.; Gasser, R. Human liver arylacetamide deacetylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 21650–21656. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, M. R.; Jeno, P.; Meyer, U. A. Purification and characterization of a human liver arylacetamide deacetylase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 177, 453–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelham, H. R. The retention signal for soluble proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbi, M.; Beaufay, H. The COOH terminus of several liver carboxylesterases targets these enzymes to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 20498–503. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B. K.; Kalow, W. Variable activation of lovastatin by hydrolytic enzymes in human plasma and liver. 4. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 449–51. [Google Scholar]
- Korza, G.; Ozols, J. Complete covalent structure of 60-kDa esterase isolated from 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced rabbit liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 3486–3495. [Google Scholar]
- Robbi, M.; Beaufay, H. Cloning and sequencing of rat liver carboxylesterase ES-3 (egasyn). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 1404–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medda, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Devore-Carter, D.; von Deimling, O.; Heymann, E.; Swank, R. T. An accessory protein identical to mouse egasyn is complexed with rat microsomal beta-glucuronidase and is identical to rat esterase-3. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 7248–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ovnic, M.; Swank, R. T.; Fletcher, C.; Zhen, L.; Novak, E. K.; Baumann, H.; Heintz, N.; Ganschow, R. E. Characterization and functional expression of a cDNA encoding egasyn (esterase-22): the endoplasmic reticulum-targeting protein of beta- glucuronidase. Genomics 1991, 11, 956–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, F.; Takagi, Y.; Kitajima, M.; Kuroda, T.; Omura, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human carboxylesterase gene. Genomics 1993, 17, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Heijne, G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur. J. Biochem. 1983, 133, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cygler, M.; Schrag, J. D.; Sussman, J. L.; Harel, M.; Silman, I.; Gentry, M. K.; Doctor, B. P. Relationship between sequence conservation and three-dimensional structure in a large family of esterases, lipases, and related proteins. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 366–82. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, PA; Whitt, SA; Tobin, JB. A low-barrier hydrogen bond in the catalytic triad of serine proteases. Science 1994, 264, 1927–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Vance, D. E.; Lehner, R. Structure-function analysis of human triacylglycerol hydrolase by site-directed mutagenesis: identification of the catalytic triad and a glycosylation site. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6679–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencharit, S.; Morton, C. L.; Howard-Williams, E. L.; Danks, M. K.; Potter, P. M.; Redinbo, M. R. Structural insights into CPT-11 activation by mammalian carboxylesterases. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 9, 337–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencharit, S.; Morton, C. L.; Hyatt, J. L.; Kuhn, P.; Danks, M. K.; Potter, P. M.; Redinbo, M. R. Crystal structure of human carboxylesterase 1 complexed with the Alzheimer's drug tacrine: from binding promiscuity to selective inhibition. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 341–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencharit, S.; Morton, C. L.; Xue, Y.; Potter, P. M.; Redinbo, M. R. Structural basis of heroin and cocaine metabolism by a promiscuous human drug-processing enzyme. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 349–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.; Schotz, M. C. The lipase gene family. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 993–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T. J.; Ghosh, S.; McLean Grogan, W. Molecular cloning and expression of rat lung carboxylesterase and its potential role in the detoxification of organophosphorus compounds. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 1999, 20, 1201–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M. Differences in the functional roles of hepatic microsomal carboxylesterase isozymes in various mammals and humans. Xenobiotic Metab. Dispos. 1990, 5, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, T. Human carboxylesterase isozymes: catalytic properties and rational drug design. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 21, 173–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Taylor, P.; Bosron, W. F.; Sanghani, S. P.; Hosokawa, M.; La Du, B. N. Current progress on esterases: from molecular structure to function. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 488–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Murry, D. J.; Sanghani, S. P.; Davis, W. I.; Kedishvili, N. Y.; Zou, Q.; Hurley, T. D.; Bosron, W. F. Methylphenidate is stereoselectively hydrolyzed by human carboxylesterase CES1A1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 469–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, D.; LeCluyse, E. L.; Black, C.; You, L.; Akhlaghi, F.; Yan, B. Anti-influenza prodrug oseltamivir is activated by carboxylesterase human carboxylesterase 1, and the activation is inhibited by antiplatelet agent clopidogrel. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 1477–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmann, T.; Becker, A.; Aslanidis, C.; Notka, F.; Ullrich, H.; Schwer, H.; Schmitz, G. Structural organization and characterization of the promoter region of a human carboxylesterase gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1350, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Furihata, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Synergistic role of specificity proteins and upstream stimulatory factor 1 in transactivation of the mouse carboxylesterase 2/microsomal acylcarnitine hydrolase gene promoter. Biochem. J. 2004, 384, 101–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furihata, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Masuda, M.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha plays pivotal roles in the regulation of mouse carboxylesterase 2 gene transcription in mouse liver. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 447, 107–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Furihata, T.; Yaginuma, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Watanabe, N.; Tsukada, E.; Ohhata, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, K. Structural organization and characterization of the regulatory element of the human carboxylesterase (CES1A1 and CES1A2) genes. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 23, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Contact the author.
© 2008 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Hosokawa, M. Structure and Catalytic Properties of Carboxylesterase Isozymes Involved in Metabolic Activation of Prodrugs. Molecules 2008, 13, 412-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13020412
Hosokawa M. Structure and Catalytic Properties of Carboxylesterase Isozymes Involved in Metabolic Activation of Prodrugs. Molecules. 2008; 13(2):412-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13020412
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosokawa, Masakiyo. 2008. "Structure and Catalytic Properties of Carboxylesterase Isozymes Involved in Metabolic Activation of Prodrugs" Molecules 13, no. 2: 412-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13020412
APA StyleHosokawa, M. (2008). Structure and Catalytic Properties of Carboxylesterase Isozymes Involved in Metabolic Activation of Prodrugs. Molecules, 13(2), 412-431. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13020412






