Apocynin: Chemical and Biophysical Properties of a NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
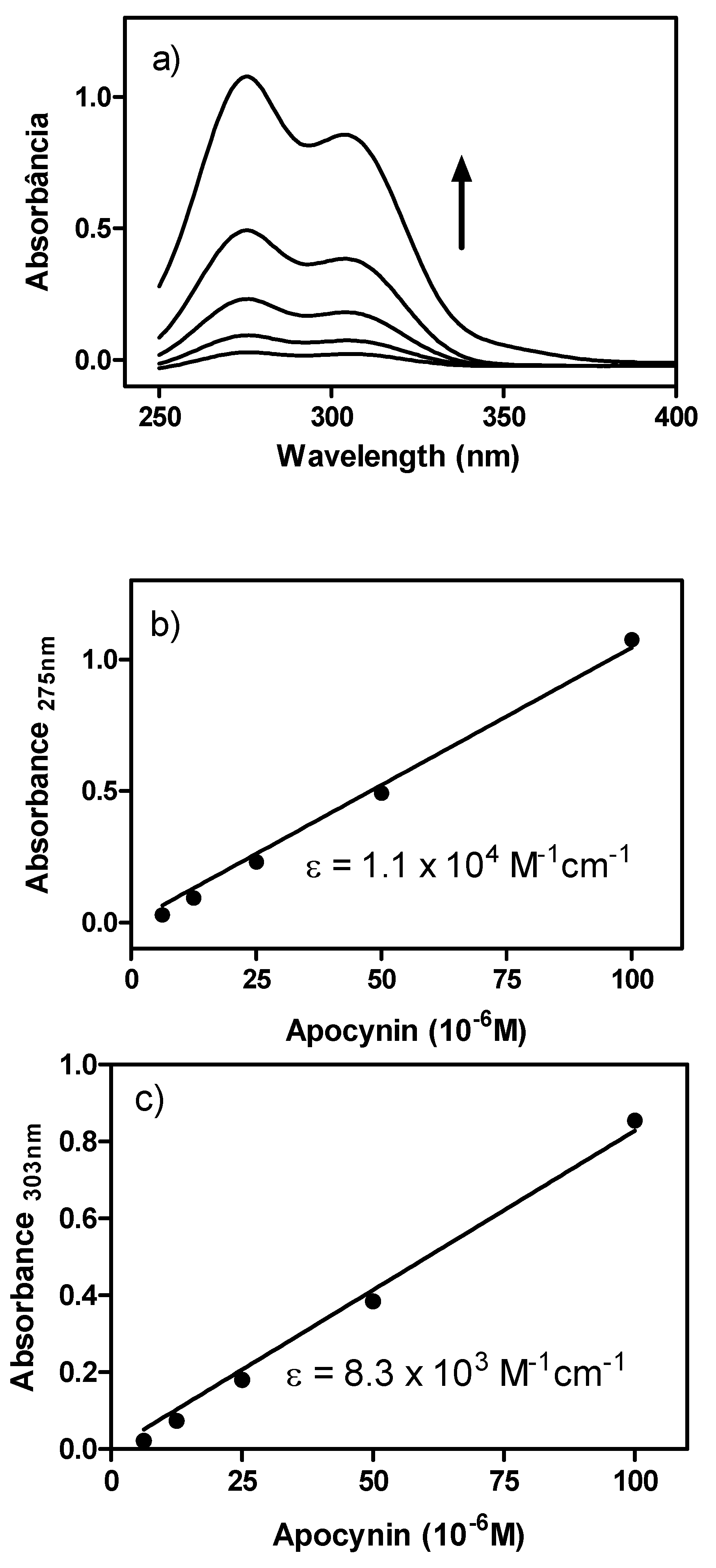
2. Results and Discussion










3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Estimation of Logarithm of Partition Coefficient (log P)
3.3. Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements
3.4. Reactivity with DPPH
3.5. Reactivity with Peroxyl Radicals: Conjugated Autoxidizable Triene Assay
3.6. Reactivity with Nitric Oxide
3.7. Reactivity with Hydrogen Peroxide
3.8. Reactivity with Hypochlorous Acid
3.9. Fluorescence, Quenching Studies and Apparent Binding Constant Determination
3.10. Displacement Studies Using Fluorescent Ligands
3.11. Circular Dichroism Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Kleniewska, P.; Piechota, A.; Skibska, B.; Gorąca, A. The NADPH oxidase family and its inhibitors. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2012, 60, 277–294. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuyama, M.; Matsuno, K.; Yabe-Nishimura, C. Physiological roles of NOX/NADPH oxidase, the superoxide-generating enzyme. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 50, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Nauseef, W.M. Biological roles for the NOX family NADPH oxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16961–16965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolk, J.; Hiltermann, T.J.; Dijkman, J.H.; Verhoeven, A.J. Characteristics of the inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation in neutrophils by apocynin, a methoxy-substituted catechol. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1994, 11, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Riganti, C.; Costamagna, C.; Bosia, A.; Ghigo, D. The NADPH oxidase inhibitor apocynin (acetovanillone) induces oxidative stress. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 212, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejrazka, M.; Mícek, R.; Stípek, S. Apocynin inhibits NADPH oxidase in phagocytes but stimulates ROS production in non-phagocytic cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1722, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, T.; Steinbach, A.C.; Steffen, A.; Rettig, R.; Grisk, O. Apocynin-induced vasodilation involves Rho kinase inhibition but not NADPH oxidase inhibition. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 80, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heumuller, S.; Wind, S.; Barbosa-Sicard, E.; Schmidt, H.H.; Busse, R.; Schroder, K.; Brandes, R.P. Apocynin is not an inhibitor of vascular NADPH oxidases but an antioxidant. Hypertension 2008, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldieri, E.; Riganti, C.; Polimeni, M.; Gazzano, E.; Lussiana, C.; Campia, I.; Ghigo, D. Classical inhibitors of NOX NAD(P)H oxidases are not specific. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Davidson, B.P.; Yue, Q.; Belcik, T.; Xie, A.; Inaba, Y.; McCarty, O.J.; Tormoen, G.W.; Zhao, Y.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; et al. Molecular Imaging of Inflammation and Platelet Adhesion in Advanced Atherosclerosis: Effects of Antioxidant Therapy with NADPH Oxidase Inhibition. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 6, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.Y.; Yao, X.C.; Xue, X.; Zhang, Q.C.; Wang, X.X.; Ding, L.L.; Wu, C.F. Oligomeric Aβ-Induced Microglial Activation is Possibly Mediated by NADPH Oxidase. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 38, 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.Z.; Han, W.Q.; Chen, J.; Zhu, D.L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, P.J. Anti-stiffness effect of apocynin in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats via inhibition of oxidative stress. Hypertens. Res. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Kanthasamy, A.; Joseph, J.; Anantharam, V.; Srivastava, P.; Dranka, B.P.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of an orally active apocynin derivative in pre-clinical models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhuan, L.; Wang, T.; Rao, K.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Quan, W.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z. Apocynin Improves Erectile Function in Diabetic Rats through Regulation of NADPH Oxidase Expression. J. Sex. Med. 2012, 9, 3041–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, T.K.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, J.K.; Han, P.L. NADPH oxidase mediates depressive behavior induced by chronic stress in mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9690–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanska, J.; Sarniak, A.; Wlodarczyk, A.; Sokolowska, M.; Doniec, Z.; Bialasiewicz, P.; Nowak, D.; Pawliczak, R. Hydrogen peroxide and nitrite reduction in exhaled breath condensate of COPD patients. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 25, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.K.; Schillinger, K.L.; Kwait, D.M.; Hughes, C.V.; McNamara, E.J.; Ishmael, F.; O’Donnell, R.W.; Chang, M.M.; Hogg, M.G.; Dordick, J.S.; et al. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation in endothelial cells by ortho-methoxy-substituted catechols. Endothelium 2002, 9, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhuan, L.; Wang, T.; Guo, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z. Effects of apocynin on oxidative stress and expression of apoptosis-related genes in testes of diabetic rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Lee, P.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, Y.W. Ischemia-activated microglia induces neuronal injury via activation of gp91phox NADPH oxidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1526–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximenes, V.F.; Kanegae, M.P.; Rissato, S.R.; Galhiane, M.S. The oxidation of apocynin catalyzed by myeloperoxidase: Proposal for NADPH oxidase inhibition. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 457, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanegae, M.P.; Condino-Neto, A.; Pedroza, L.A.; de Almeida, A.C.; Rehder, J.; da Fonseca, L.M.; Ximenes, V.F. Diapocynin versus apocynin as pretranscriptional inhibitors of NADPH oxidase and cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Pale, M.; Weïwer, M.; Yu, J.; Linhardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S. Inhibition of human vascular NADPH oxidase by apocynin derived oligophenols. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5146–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masella, R.; Santangelo, C.; D’Archivio, M.; LiVolti, G.; Giovannini, C.; Galvano, F. Protocatechuic acid and human disease prevention: Biological activities and molecular mechanisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2901–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeh, I.F.; Ohman, L.O.; Sjoberg, S. Equilibrium and structural studies of silicon(IV) and aluminum(III) in aqueous-solution. Aqueous complexation between silicic-acid and some ortho-diphenolic and triphenolic compounds. Acta Chem. Scand. 1992, 46, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Crippen, G.M. Atomic physicochemical parameters for threedimensional-structure-directed quantitative structureactivity relationships. Modeling dispersive and hydrophobic interactions. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1987, 27, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguerre, M.; López-Giraldo, L.J.; Lecomte, J.; Baréa, B.; Cambon, E.; Tchobo, P.F.; Barouh, N.; Villeneuve, P. Conjugated autoxidizable triene (CAT) assay: A novel spectrophotometric method for determination of antioxidant capacity using triacylglycerol as ultraviolet probe. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 380, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Worm, E.; Beukelman, C.J.; van den Berg, A.J.; Kroes, B.H.; Labadie, R.P.; van Dijk, H. Effects of methoxylation of apocynin and analogs on the inhibition of reactive oxygen species production by stimulated human neutrophils. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 433, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, C.M.; Nazaré, A.C.; Petrônio, M.S.; Paracatu, L.C.; Zeraik, M.L.; Regasini, L.O.; Silva, D.H.; da Fonseca, L.M.; Ximenes, V.F. Protocatechuic acid alkyl esters: Hydrophobicity as a determinant factor for inhibition of NADPH oxidase. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4885–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.C.; Francini, F.; Schinella, G.; Caldiz, C.I.; Zubiría, M.G.; Gagliardino, J.J.; Massa, M.L. Apocynin administration prevents the changes induced by a fructose-rich diet on rat liver metabolism and the antioxidant system. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2012, 123, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, G.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Weber, G. Quenching of fluorescence by oxygen. A probe for structural fluctuations in macromolecules. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 4161–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.N.; Chimatadar, S.A.; Nandibewoor, S.T. Interaction between a potent corticosteroid drug—Dexamethasone with bovine serum albumin and human serum albumin: A fluorescence quenching and fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy study. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2010, 100, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zuo, Y.; Bi, Y.; Gao, S. Spectroscopic Studies on the Interaction of Vitamin C with Bovine Serum Albumin. J. Solution Chem. 2012, 38, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Cao, H.; Zhu, S.; Lu, Y.; Shang, Y.; Wang, M.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, L. Investigation of the binding of Salvianolic acid B to human serum albumin and the effect of metal ions on the binding. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 81, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, Y. Spectroscopic analyses on interaction of Naphazoline hydrochloride with bovine serum albumin. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 98, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, E.A.; Vedenkina, N.S.; Ivkova, M.N. Fluorescence and the location of tryptophan residues in protein molecules. Photochem. Photobiol. 1973, 18, 263–279. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Su, S.; Kokot, S. Spectrofluorimetric studies on the binding of salicylic acid to bovine serum albumin using warfarin and ibuprofen as site markers with the aid of parallel factor analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 580, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, N.; Lapicque, F.; Drelon, E.; Netter, P. Binding sites of fluorescent probes on human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximenes, V.F.; Paino, I.M.; Faria-Oliveira, O.M.; Fonseca, L.M.; Brunetti, I.L. Indole ring oxidation by activated leukocytes prevents the production of hypochlorous acid. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Ximenes, V.F.; Maghzal, G.J.; Turner, R.; Kato, Y.; Winterbourn, C.C.; Kettle, A.J. Serotonin as a physiological substrate for myeloperoxidase and its superoxide-dependent oxidation to cytotoxic tryptamine-4,5-dione. Biochem. J. 2009, 425, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, C.N.; Vajdos, F.; Fee, L.; Grimsley, G.; Gray, T. How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein. Sci. 1995, 4, 2411–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraik, M.L.; Ximenes, V.F.; Regasini, L.O.; Dutra, L.A.; Silva, D.H.; Fonseca, L.M.; Coelho, D.; Machado, S.A.; Bolzani, V.S. 4'-aminochalcones as novel inhibitors of the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5405–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Singh, N.; Saini, B.S.; Rao, H.S. In vitro antioxidant activity of pet ether extract of black pepper. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2008, 40, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S. Fluorescence quenching methods to study protein-nucleic acid interactions. Methods Enzymol. 2004, 379, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Haigh, S.; Barman, S.; Fulton, D.J. From form to function: The role of Nox4 in the cardiovascular system. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrônio, M.S.; Zeraik, M.L.; Fonseca, L.M.d.; Ximenes, V.F. Apocynin: Chemical and Biophysical Properties of a NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor. Molecules 2013, 18, 2821-2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032821
Petrônio MS, Zeraik ML, Fonseca LMd, Ximenes VF. Apocynin: Chemical and Biophysical Properties of a NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor. Molecules. 2013; 18(3):2821-2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032821
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrônio, Maicon S., Maria Luiza Zeraik, Luiz Marcos da Fonseca, and Valdecir F. Ximenes. 2013. "Apocynin: Chemical and Biophysical Properties of a NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor" Molecules 18, no. 3: 2821-2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032821
APA StylePetrônio, M. S., Zeraik, M. L., Fonseca, L. M. d., & Ximenes, V. F. (2013). Apocynin: Chemical and Biophysical Properties of a NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor. Molecules, 18(3), 2821-2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18032821




