Abstract
In an effort to study the effects of flexibility on enzyme recognition and activity, we have developed several different series of flexible nucleoside analogues in which the purine base is split into its respective imidazole and pyrimidine components. The focus of this particular study was to synthesize the truncated neplanocin A fleximers to investigate their potential anti-protozoan activities by inhibition of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHase). The three fleximers tested displayed poor anti-trypanocidal activities, with EC50 values around 200 μM. Further studies of the corresponding ribose fleximers, most closely related to the natural nucleoside substrates, revealed low affinity for the known T. brucei nucleoside transporters P1 and P2, which may be the reason for the lack of trypanocidal activity observed.
1. Introduction
Modified nucleosides, in particular carbocyclic nucleosides, are potent inhibitors of S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase (SAHase) [1]. SAHase is a critical enzyme that hydrolyzes S-adenosyl homocysteine, the byproduct of biomethylations that utilize S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) [2,3]. By inhibiting SAHase, an excess of SAH is produced, which in turn exhibits potent inhibitory effects on methyltransferases [4]. Thus, inhibition of SAHase leads to incomplete methylation of nucleic acids, phospholipids, proteins, and other small molecules, disrupting various biochemical pathways [5]. As a result, carbocyclic nucleosides have proven useful in a number of chemotherapeutic applications [6,7,8].
Neplanocin A (NpcA, Figure 1) and aristeromycin (Ari) are both naturally occurring carbocyclic adenosine analogues that have shown significant antiviral, antiparasitic and anticancer properties [4,7,9,10]. Unfortunately, NpcA and Ari both exhibit deleterious cytotoxicity due to intracellular conversion to their triphosphate forms by adenosine kinase as well as their recognition and metabolism by adenosine deaminase [11,12,13]. Removal of the 4'-CH2OH from Ari and NpcA, as shown in the truncated analogues shown in Figure 1 (R = H), significantly lowers the cytotoxicity [14].
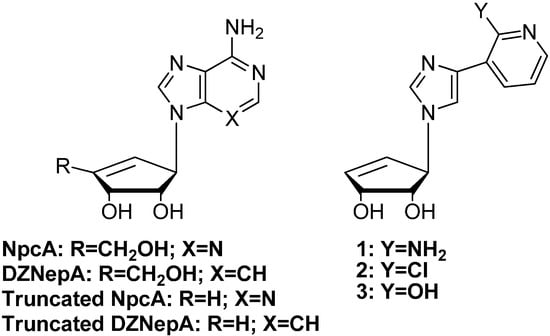
Figure 1.
Neplanocin A (NpcA) and analogues and the target NcpA fleximers (1–3).
Figure 1.
Neplanocin A (NpcA) and analogues and the target NcpA fleximers (1–3).
Interestingly, nucleosides with base modifications such as 3-deazaadenosine have also been found to act as substrates, with similar Km’s found for adenosine and 3-deazaadenosine [7,10,15]. To date, the truncated 3-deaza analogues of Ari and NpcA (truncated DZNepA, Figure 1) lacking the 4'-hydroxy-methyl group have both exhibited greater levels of inhibition than their parent counterparts [5,6,13,16].
More importantly, these compounds have also shown potent inhibition against chloroquine-resistant and chloroquine-susceptible strains of P. falciparum [5]. In protozoan parasites, methylation of the four nucleosides present in the “cap-four” terminal end of mRNA requires SAM as the methyl donor. This cap structure is important for RNA recognition and stability, is highly conserved across almost all protozoan species, and is critical for replication [17,18,19]. Thus, inhibition of SAHase results in an accumulation of SAH, causing methylations to cease, which then disrupts the methylation of the cap structure, thereby providing an important target for the development of potential antiparasitic chemotherapeutics [5].
The Seley-Radtke group has long been interested studying the effects of flexibility on the nucleobase. This flexibility is achieved by “splitting” the purine base into its respective imidazole and pyrimidine (or pyridine) components, which remain connected by a single carbon-carbon bond between the two heteroaromatic moieties. This connectivity allows for free rotation, while still retaining the elements essential for base pairing and molecular recognition [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. This modification has led to enhanced enzyme binding and recognition, as well as the ability to overcome point mutations in enzyme binding sites [29,30]. These analogues have also been studied for their potential therapeutic properties [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Interestingly, when the fleximer analogues of adenosine (Flex-A), inosine (Flex-I) and guanosine (Flex-G) were studied in SAHase, which is a flexible enzyme, Flex-A and Flex-I acted as substrates, whereas Flex-G proved to be an inhibitor [22]. This is significant because it is, to our knowledge, the only report of a G-nucleoside inhibiting an adenosine metabolizing enzyme. It has been postulated that this is due to an intramolecular hydrogen bond between the pyrimidine and the 5'-OH of the sugar, which then positions the amino group into the binding site where the amino group on adenosine would normally reside, thus essentially creating an adenosine mimic [22].
Historically, a number of nucleoside analogues have been evaluated for trypanocidal activity [31,32,33,34]. For example, Cai et al. showed that the antiviral drug ribavirin was an inhibitor of Trypanosoma cruzi SAHase [33]. Additionally, 7-deaza-5'-noraristeromycin was shown to be a potent inhibitor of four strains of Trypanosoma brucei [34]. To further explore the potential of base flexibility and antiparasitic activity, we combined the fleximer base with the carbocyclic nucleoside scaffold, to determine whether the flexible base motif would enhance the biological results previously observed with carbocyclic analogues such as NpcA and Ari. Thus, a series of 3-deaza fleximers (compounds 1–3, Figure 1) were designed and synthesized to evaluate their anti-parasitic properties.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
As shown in Scheme 1, cyclopentenol 5 was available from known literature procedures starting from d-cyclopentenone 4 [35], which can be obtained following stereospecific reduction to the “down” hydroxyl using Luche reduction conditions [36]. Alcohol 5 was then coupled to 4,5-diiodoimidazole [29] using standard Mitsunobu [37] conditions to give 6. Initially the Mitsunobu reaction was attempted with diisopropylazodicarboxylate (DIAD) and triphenylphosphine (TPP) in dichloromethane at room temperature to yield 5, however only in a 12% yield. Attempts at heating the reaction only served to give additional side products, as well as to lower the yield even further. Changing the solvent to THF increased the solubility of the diiodoimidazole and subsequently resulted in an improved yield of 40%. Unfortunately, contaminates from the byproduct, triphenylphospine oxide (TPPO), still proved to be problematic during purification. Altering the phosphine reagent to DPPE (1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane) drastically improved the ease in purification. Other coupling methods were also tried, such as using Hendrickson’s “POP” reagent, bis(triphenyl)oxodiphosphonium trifluoromethanesulfonate [38], or using bases such as NaH or K2CO3 [39] to form the imidazole nucleophile, proved unsuccessful when compared to the Mitsunobu coupling using DPPE.
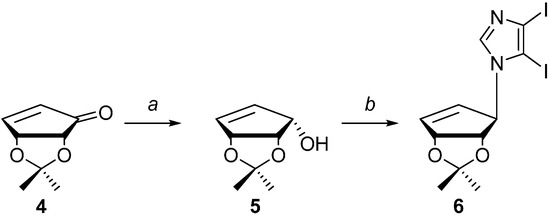
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of compound 6.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of compound 6.
Reagents and Conditions: a. CeCl3·7H2O, MeOH, NaBH4; b. DPPE, DIAD, 4,5-diiodoimidazole, THF, rt.
Next, as shown below in Scheme 2, removal of the 5-iodo group of 6 to give compound 7 was achieved via selective deiodination using ethyl magnesium bromide (EtMgBr) followed by quenching with water. Coupling to the pyridine ring was then accomplished using Stille [40] coupling.
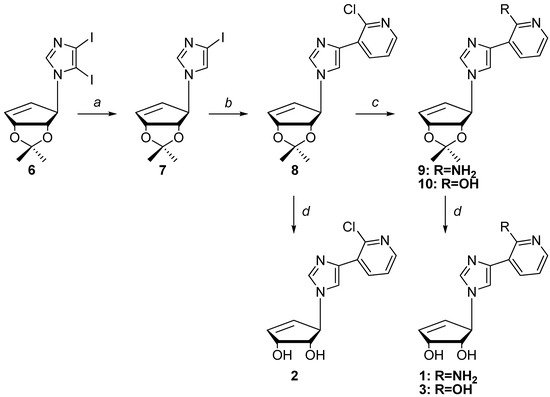
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of compounds 1–3.
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of compounds 1–3.
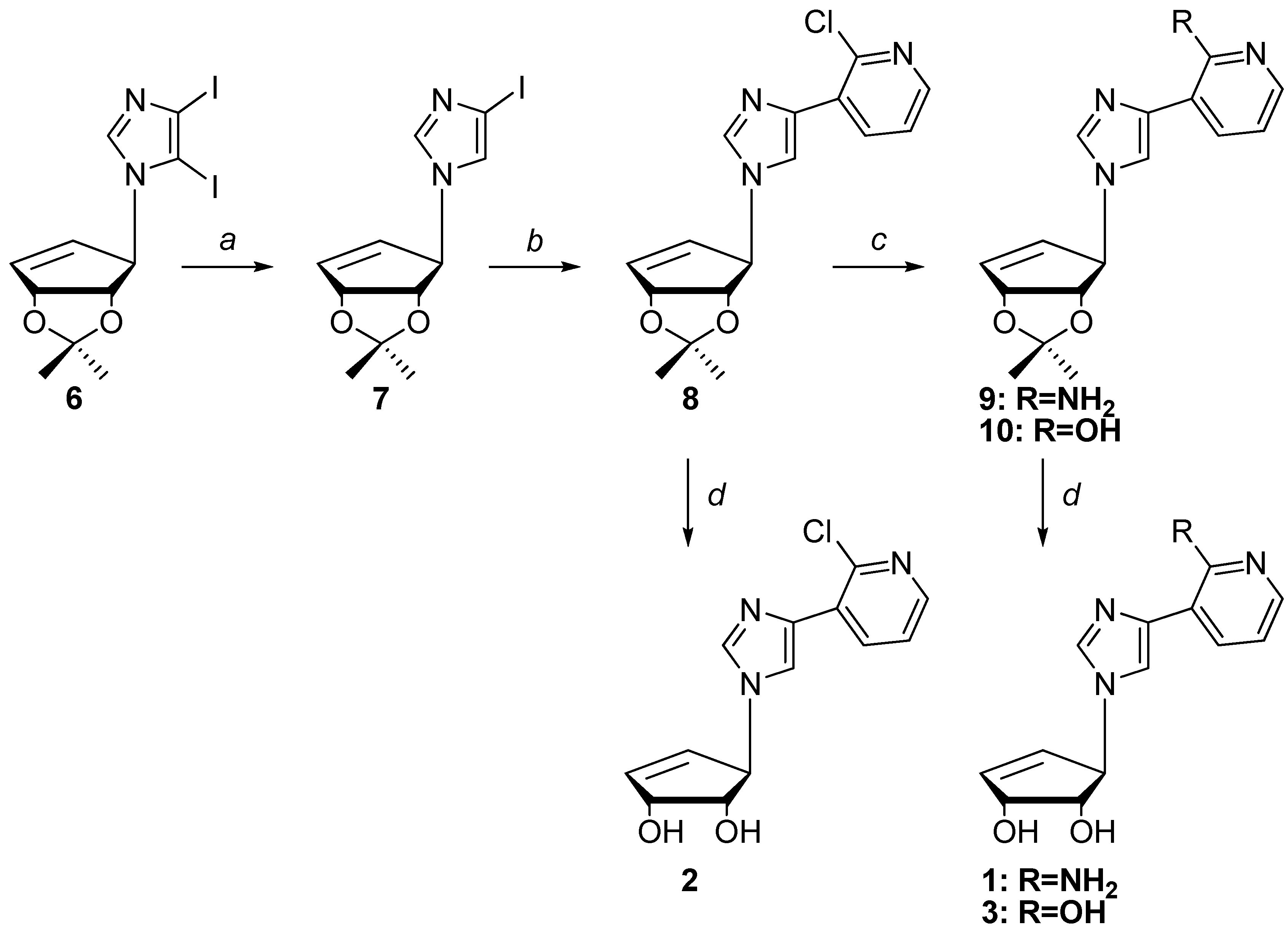
Reagents and Conditions: a. EtMgBr, THF, 0 °C; b. 3-tributyltin-2-chloropyridine, Pd(PPh3)4, Cu(I) Br, 1,4-dioxane, reflux; c. for compound 9: (i) hydrazine neat, 80 °C; (ii) TiCl3; for compound 10: concentrated acetic acid neat, 110 °C; d. TFA/H2O (1/1) in THF.
The 3-tributyltin-2-chloropyridine was prepared from the commercially available 3-bromo-2-chloropyridine. Stille coupling of 7 with the 3-tributyltin-2-chloropyridine provided 8 in a 23% yield, however when copper (I) bromide was used, the yield improved to 71%. Following Stille coupling, transformation of the chloro group into the exocyclic amine group was necessary. Standard procedures using MeOH/NH3 or converting the chloro to an azide using sodium or lithium azide proved unsuccessful. A literature search revealed a palladium-assisted method developed by Hartwig using sodium t-butoxide in ammonia saturated 1,4-dioxane [41]. Unfortunately this method also proved unsuccessful.
Related to this latter route, Buchwald developed a similar method, where the catalyst is made in situ using a more common phosphine ligand [42]. This method seemed promising since one of the examples utilized 2-chloropyridine, which was successfully converted in a 96% yield [28], but it too proved to be unsuccessful. Use of NaNH2 in ammonia was also tried but the conditions proved to be too harsh and decomposition ensued [43]. Another approach involved converting the chloro group using hydrazine followed by reduction. Initial attempts at reducing the hydrazine employed zinc in acetic acid, but this resulted in a complex mixture that could not be purified. Using titanium chloride (TiCl3) [44] proved to be successful, although there was evidence of some isopropylidene deprotected product(s) as well as protected products, thus treatment of the mixture with dilute TFA in THF gave the desired final product 1.
Next, deaminated compound 10 was obtained from 8 using concentrated acetic acid at high temperature. Although this conversion also led to partial deprotection of the isopropylidene on the 2'- and 3'-hydroxyls, the protected pyridine 10 was the major product. Subsequent deprotection of the isopropylidene of 10 led to the fleximer inosine 3.
2.2. Trypanosomiasis Screening
The three NpcA fleximers (1–3) were tested for trypanocidal activity against the laboratory Trypanosoma brucei brucei strain Lister 427, using a standard protocol based on the fluorescent format of 23 doubling dilutions, starting at 500 μM, in 96-well plates. All three fleximers tested displayed very similar activities against this strain, with EC50 values around 200 μM; in contrast, the control drug pentamidine displayed activity in the low nM range (Table 1), consistent with previous results [45,46].

Table 1.
Trypanosomiasis results.
| Compound | Average EC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 216 ± 21 |
| 2 | 212 ± 31 |
| 3 | 287 ± 24 |
| pentamidine | 0.0044 ± 0.0001 |
EC50 = concentration of drug required to give a 50% response. Data are the average of three independent experiments and SEM.
We considered that the relatively low activity might be related to a lack of recognition of these molecules by the T. brucei nucleoside transporters. We therefore investigated whether fleximers in general display reduced uptake kinetics in these parasites, compared to their fixed-ring counterparts (Figure 2). Using the fleximers [21] most closely related to the original nucleoside substrates, it is clear from Table 2 that fleximers indeed show low affinity for the known T. brucei nucleoside transporters P1 and P2 [47].
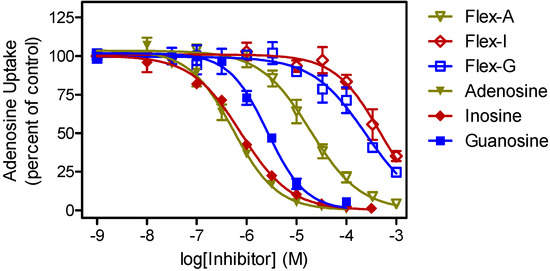
Figure 2.
Transport of 0.1 µM [3H]-adenosine by Trypanosoma brucei brucei bloodstream form parasites.
Figure 2.
Transport of 0.1 µM [3H]-adenosine by Trypanosoma brucei brucei bloodstream form parasites.
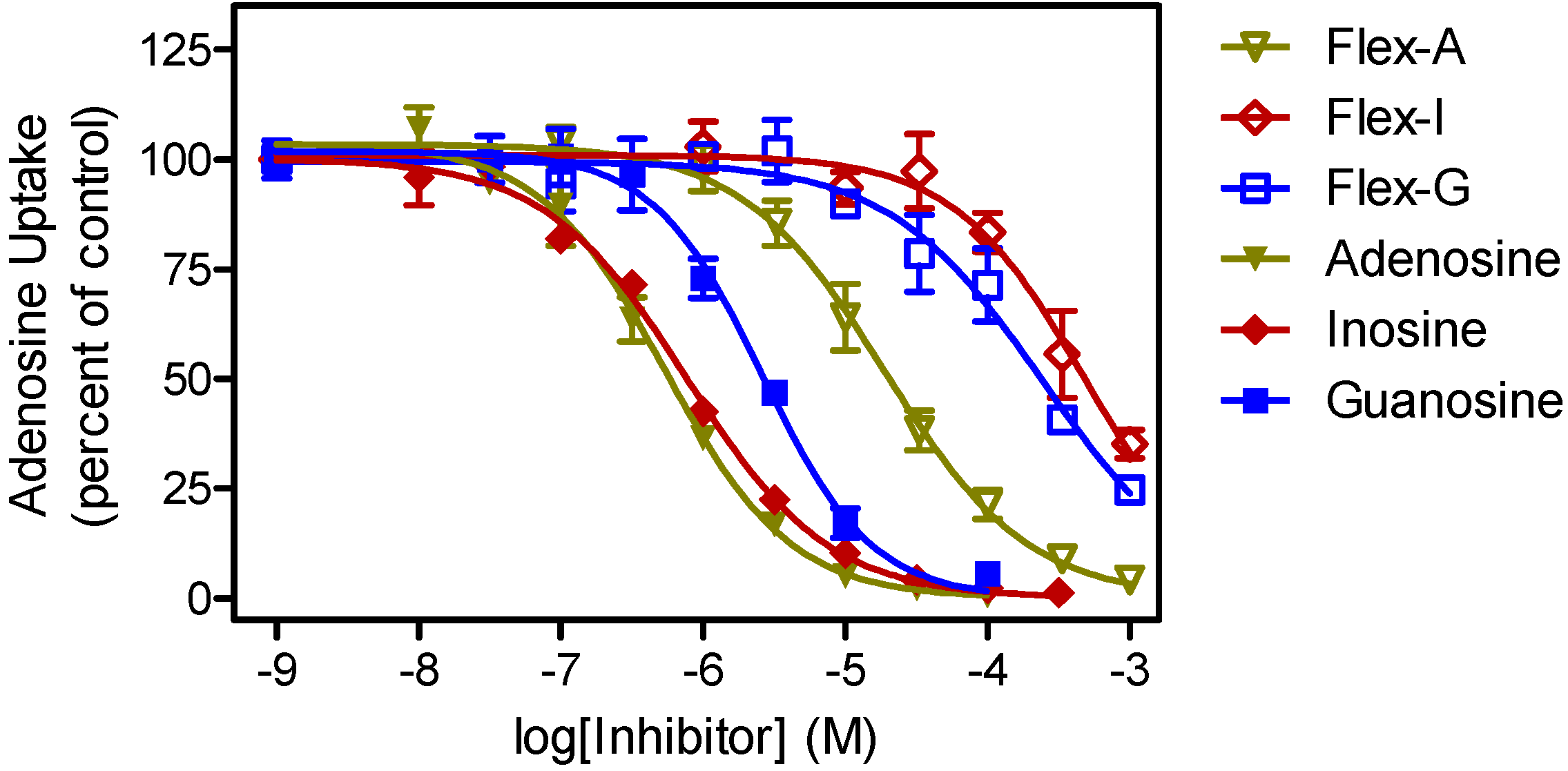

Table 2.
Comparison of affinity of purine nucleosides and corresponding fleximers for T. brucei transporters. 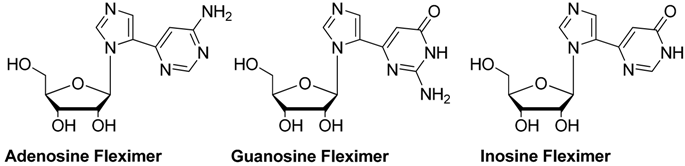

| P1 Ki (μM) | P2 Ki (µM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleoside 1 | Fleximer | δ(ΔG0) | Nucleoside 1 | Fleximer | δ(ΔG0) | |
| Adenosine | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 35 ± 11 | 11.4 | 0.91 ± 0.29 | 37 ± 3 | 9.2 |
| Guanosine | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 251 ± 75 | 12.2 | >500 | >500 | |
| Inosine | 0.44 ± 0.10 | 387 ± 30 | 16.8 | >500 | >500 | |
Data are the average inhibition constants (Ki) and SEM of at least three independent experiments; Values for adenosine are Michaelis-Menten constants (Km). 1 values were taken from previous findings of De Koning [47] and included here for comparison; δ(ΔG0) is the difference in Gibbs free energy of interaction of the nucleoside and the fleximer with the transporter, given in kJ/mol.
Transport, mediated by the P1 nucleoside transporter, was measured in the presence or absence of various concentrations of nucleosides (filled symbols) or their corresponding fleximers (open symbols), in the presence of 100 µM adenine to block potential adenosine transport through the P2 transporter. Data shown are the average and SEM of triplicate determinations in a single experiment, representative of three independent experiments with essentially identical outcomes.
It is thus clear that the fleximers generally display about two orders of magnitude less affinity for the T. brucei nucleoside transporters than the corresponding nucleosides, limiting cellular uptake as there are no other nucleoside uptake mechanisms in these parasites than the P1 and P2 systems, although P1 consists of a cluster of multiple genes with slightly divergent sequences [48,49]. In addition, the truncated NpcA fleximers lack a 4'-hydroxymethyl group and an equivalent of the purine N3 residue, and both required for high affinity for P1 [50]. Moreover, the P2 transporter does not recognize any oxopurine nucleoside analogues [47]. The loss of approximately 10 kJ/mol in Gibbs free energy for the fleximer-transporter interaction may in part be due to the increased entropy in the orientation of the fleximer orientation in the binding pocket, as well as the slightly larger volume of the base. We thus conclude that the low effectiveness of the Npc fleximers is at least partially due to unfavorable interactions with the parasite’s nucleoside transporters. As important differences exist between nucleoside transporters of even closely related pathogenic parasites including Trypanosoma congolense [51] and Leishmania species [48], it would be worthwhile to follow this study with a wider screening of anti-parasite activity for a diverse panel of protozoa.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
All chemicals were obtained from commercial sources and used without further purification unless otherwise noted. Anhydrous DMF, MeOH, DMSO and toluene were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA, USA). Anhydrous THF, acetone, CH2Cl2, CH3CN and ether were obtained using a solvent purification system (mBraun Labmaster 130, MBRAUN, Stratham, NH, USA). 3-Bromo-2-chloropyridine was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Melting points are uncorrected. NMR solvents were purchased from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories (Andover, MA, USA). All 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were obtained on a JEOL ECX 400 MHz NMR, operated at 400 and 100 MHz respectively, and referenced to internal tetramethylsilane (TMS) at 0.0 ppm. The spin multiplicities are indicated by the symbols s (singlet), d (doublet), dd (doublet of doublets), t (triplet), q (quartet), m (multiplet), and b (broad). Reactions were monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) using 0.25 mm Whatman Diamond silica gel 60-F254 precoated plates. Column chromatography was performed using silica gel (63–200 µm) from Dynamic Adsorptions Inc. (Norcross, GA, USA), and eluted with the indicated solvent system. Yields refer to chromatographically and spectroscopically (1H- and 13C-NMR) homogeneous materials. High resolution mass spectra were recorded at the Johns Hopkins Mass Spectrometry Facility (Baltimore, MD, USA) using fast atom bombardment for ionization.
3.2. Synthesis
Preparation of (4R,5R)-4,5-O-isopropylidene-2-cyclopenten-1-ol (5): (4R,5R)-4,5-O-isopropylidene-2-cyclopentenone 4 [35] (4.63 g, 0.03 mol) was dissolved in dry methanol (20 mL) at room temperature. CeCl3·7H2O was added to the reaction followed by the portionwise addition of NaBH4 (1.36 g, 0.04 mol). Once TLC analysis showed the complete disappearance 4, the reaction was extracted into ethyl acetate (50 mL) and washed with water (10 mL). The organic layer was dried over MgSO4 and the solvent was removed under rotary evaporation. The crude oil was used in the following reaction without further purification.
Preparation of (1′R,2′S,3′R)-1-[(2′,3′-O-isopropylidene)-4′-cyclopenten-1′-yl]-4,5-diiodoimidazole (6): Thoroughly dried 5 (0.78 g, 0.05 mol) was dissolved in dry THF (100 mL) under N2. Ethylenebis(diphenylphosphine) (2.0 g, 0.05 mol) and 4,5-diiodoimidazole (3.2 g, 0.01 mol) added to the reaction, followed by the dropwise addition of diisopropyl azodicarboxylate. The reaction was allowed to stir for 48 h and then the solvent was removed using reduced pressure. The crude material was purified by silica gel column chromatography hexanes–ethyl acetate (2:1) to yield a yellow waxy solid (0.95 g, 0.02 mol, 41% yield). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ 1.32 (s, 3H), 1.45 (s, 3H), 4.44 (d, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz), 5.24 (d, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz), 5.31 (m, 1H), 5.90 (dt, 1H, J = 4.6, 5.9 Hz), 6.34 (dt, 1H, J = 1.8 Hz, 5.9 Hz), 7.38 (s, 1H). 13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ 25.9, 27.4, 70.8, 82.7, 84.2, 84.3, 97.1, 112.6, 128.9, 139.0, 139.4. HRMS calculated for C11H12I2N2O2 [M+H]+ 458.9066, found 458.9073.
Preparation of (1′R,2′S,3′R)-1-[(2′,3′-O-isopropylidene)-4′-cyclopenten-1′-yl]-4-iodoimidazole (7): Dried 6 (1.83 g, 0.004 mol) was dissolved in anhydrous THF under N2. The reaction was dropped to 0 °C, and ethyl magnesium bromide (3.0 M, 1.3 mL, 0.004 mol) was added dropwise to the reaction. After 1 h the reaction was quenched with saturated NH4Cl (5 mL) and then the solvent was removed. The crude mixture was dissolved in ethyl acetate (50 mL) and washed with water (20 mL) and then dried over MgSO4. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and purified using silica gel chromatography petroleum ether–ethyl acetate (2:1) to yield a yellow oil (1.12 g, 0.003 mol, 85% yield). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ 1.28 (s, 3H), 1.40 (s, 3H), 4.44 (d, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz), 5.15 (d, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz), 5.30 (dq, 1H, J = 1.8, 5.5 Hz), 5.87 (dt, 1H, J = 0.9, 5.5 Hz), 6.22 (dt, 1H, J = 1.8, 5.9 Hz), 6.89 (d, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz), 7.34 (d, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz). 13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ 25.7, 27.3, 68.3, 82.7, 84.2, 84.9, 112.5, 123.2, 129.8, 137.5, 138.1. HRMS calculated for C11H13IN2O2 [M+H]+ 333.0100, found 333.0010.
Preparation of 3-tributylstannyl-2-chloropyridine: Commercially available 3-bromo-2-chloropyridine (0.30 g, 0.002 mol) was dissolved in anhydrous THF (20 mL) under N2. Ethyl magnesium bromide (3.0 M, 0.5 mL, 0.002 mol) was added dropwise at room temperature. The reaction was allowed to stir for 2 h, and then tributyltin chloride (0.42 mL, 0.002 mol) was added and the reaction was left to stir overnight. The reaction was concentrated in vacuo and then purified on silica gel chromatography hexanes-ethyl acetate (15:1) to yield a colorless oil (0.40 g, 0.001 mol, 64% yield). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ 1.13 (m, 5 H), 1.30 (m, 13H), 1.56 (m, 6 H), 1.65 (m, 3 H), 7.13 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6, 7.8 Hz), 7.67 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 4.6 Hz), 8.27 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 7.8 Hz). 13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ 26.9, 27.0, 27.3, 27.9, 28.9, 29.0, 29.1, 122.2, 139.5, 146.9, 147.1, 147.2, 149.6, 159.2.
Preparation of (1′R,2′S,3′R)-3-[((2′,3′-O-isopropylidene)-4′-cyclopenten-1′-yl)-(imidazol-4-yl)]-2-chloropyridine (8): Intermediate 7 (0.34 g, 0.001 mol) and 2-chloro-3-(tributylstannyl)pyridine (3.50 g, 0.007 mol) were dissolved in 1,4-dioxane under N2. Pd(PPh3)4 (0.05 g, 0.04 mmol) and CuBr (0.08 g, 0.5 mmol) were added to the reaction and the reaction and was refluxed at 120 °C for 12 h. The reaction was cooled and filtered through a pad of Celite. The filtrate was diluted in ethyl acetate (20 mL) and washed with a saturated solution of NH4Cl (20 mL), water (20 mL), brine (20 mL) and then dried over MgSO4. The organic solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the crude material was purified using 5% MeOH in CH2Cl2 to yield a yellow oil (0.23 g, 0.7 mmol, 71% yield). 1H-NMR (CDCl3): δ 1.36 (s, 3H), 1.48 (s, 3H), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 5.5 Hz), 5.28 (d, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz), 5.40 (dt, 1H, J = 0.9, 4.6 Hz), 6.00 (dd, 1H, J = 1.2, 5.5 Hz), 6.32 (dt, 1H, J = 1.8, 5.5 Hz), 7.30 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6, 7.7 Hz), 7.55 (d, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz), 7.67 (d, 1H, J = 0.9 Hz), 8.26 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 4.6 Hz), 8.50 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 7.8 Hz). 13C-NMR (CDCl3): δ 25.7, 27.3, 68.5, 84.4, 85.1, 112.6, 118.5, 122.8, 129.4, 130.1, 132.1, 135.9, 136.9, 137.7, 137.9, 147.2. HRMS calculated for C16H16ClN3O2 [M+H 35Cl]+ 318.1009, [M+H 37Cl]+ 320.0980, found, 318.1001, 320.0976.
Preparation of (1′R,2′S,3′R)-3-[((2′,3′-O-isopropylidene)-4′-cyclopenten-1′-yl)-(imidazol-4-yl)]-2-pyrimidone (10): Analogue 9 (0.1 g, 0.3 mmol) was dissolved in concentrated acetic acid in a sealed glass tube and heated to 120 °C overnight. The acetic acid was evaporated and the crude material was extracted into ethyl acetate. Silica gel chromatography using ethyl acetate-acetone-methanol (6:1:1) yielded an off white solid (0.05 g, 0.2 mmol, 56% yield). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 1.24 (s, 3H), 1.32 (s, 3H), 4.41 (d, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz), 5.05 (d, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz), 5.98 (d, 1H, J = 5.9 Hz), 6.12 (dt, 1H, J = 2.3, 5.9 Hz), 6.26 (t, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz), 7.24 (d, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz), 7.65 (d, 1H, J = 0.9 Hz), 7.79 (d, 1H, J = 1.4 Hz), 8.07 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 7.3 Hz), 11.78 (bs, 1H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 25.5, 27.3, 67.4, 73.0, 78.9, 105.8, 117.6, 125.1, 131.0, 131.6, 132.9, 133.9, 136.7, 136.8, 136.9, 160.7. HRMS calculated for C16H17N3O3 [M+H]+ 300.1348, found 300.1342.
Preparation of (1′R,2′S,3′R)-3-[(2ʹ,3ʹ-Dihydroxy)-4ʹ-cyclopenten-1ʹ-yl]-(imidazol-4-yl)-2-amino-pyridine (1): Compound 8 (80 mg, 0.25 mmol) was refluxed in hydrazine (2 mL) for 1 h. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue dissolved in THF (5 mL). Titanium (III) chloride (1.7 mmol, 0.5 mL, 20% in 3% HCl) was neutralized using NaOH (0.5 mL, 20%), and 0.6 mL of the solution was added dropwise to the reaction. The mixture was refluxed at 70 °C for 4 h, cooled to room temperature, and brought to pH > 10 using NaOH (20%) while cooling in an ice-bath. The solvents were removed under vacuum, and the product was extracted with CH2Cl2 (10 mL × 5). The organic layer was dried over MgSO4. The solvents were evaporated, and the crude material, 3-[((2', 3'-O-isopropylidene)-4'-cyclopenten-1'-yl)-imidazol-4-yl]-2-aminopyridine (9), was used directly in preparation of 1. Crude 9 was dissolved in THF (5 mL) and TFA:H2O (1 mL:1 mL) was added dropwise. This was allowed to stir overnight at room temperature. The solvent was evaporated and co-evaporated with ethanol (3 × 5 mL) to yield an off-white solid (0.03 g, 0.1 mmol, 46% yield over 2 steps). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 3.93 (m, 1H), 4.45 (m, 1H), 4.96 (m, 1H), 5.08 (m, 1H), 5.14 (d, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz), 5.96 (dd, 1H, J = 1.4, 6.4 Hz), 6.11 (dt, 1H, J = 2.3, 6.4 Hz), 6.54 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0, 7.3 Hz), 6.95 (bs, 2H), 7.59 (d, 1H, J = 0.9 Hz), 7.70 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 7.4 Hz), 7.78 (d, 1H, J = 1.0 Hz), 7.81 (m, 1H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 67.6, 73.1, 78.6, 112.2, 112.5, 115.1, 132.9, 133.7, 136.2, 136.9, 140.1, 146.5, 156.5 HRMS calculated for C13H14N4O2 [M+H]+ 259.1195, found 259.1193.
Preparation of (1′R,2′S,3′R)-3-[(2ʹ,3ʹ-Dihydroxy)-4ʹ-cyclopenten-1ʹ-yl]-(imidazol-4-yl)-2-chloro-pyridine (2): Intermediate 8 (0.16 g, 0.5 mmol) was dissolved in THF (5 mL) and TFA:H2O (1 mL:1 mL) was added dropwise. This was allowed to stir overnight at room temperature. The solvent was evaporated and co-evaporated with ethanol (3 × 5 mL). Column chromatography in 10% MeOH in CH3CN returned an off-white solid (0.12 g, 0.4 mmol, 86% yield). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 3.90 (m, 1H), 4.42 (m, 1H), 4.98 (m, 1H), 5.08 (m, 1H), 5.17 (d, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz), 6.00 (dd, 1H, J = 1.4, 5.9 Hz), 6.11 (dt, 1H, J = 2.3, 5.9 Hz), 7.43 (dd, 1H, J = 4.6, 7.8 Hz), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.80 (s, 1H), 8.22 (dd, 1H, J = 2.3, 4.6 Hz), 7.81 (dd, 1H, J = 1.8, 7.8 Hz). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 67.6, 73.0, 78.9, 119.0, 123.8, 129.9, 132.7, 135.4, 137.1, 137.6, 137.9, 146.5, 147.5. HRMS calculated for C13H12ClN3O2 [M+H 35Cl]+ 278.0696, [M+H 37Cl]+ 280.0667, found, 278.0689, 280.0668.
Preparation of (1′R,2′S,3′R)-3-[(2ʹ,3ʹ-Dihydroxy)-4ʹ-cyclopenten-1ʹ-yl]-imidazol-4-yl)-2-hydroxypyridine (3): Intermediate 10 (0.08 g, 0.3 mmol) was dissolved in THF (5 mL) and TFA:H2O (1 mL:1 mL) was added dropwise. This was allowed to stir overnight at room temperature. The solvent was evaporated and co-evaporated with ethanol (3 × 5 mL). Column chromatography in ethyl acetate–acetone–methanol–water (6:1:1:0.5) produced an off-white solid (0.03 g, 0.1 mmol, 43% yield). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 3.82 (d, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz), 4.43 (bs, 1H), 4.95 (m, 1H), 5.05 (m, 1H), 5.11 (d, 1H, J = 7.4 Hz), 5.97 (dd, 1H, J = 1.4, 5.9 Hz), 6.12 (dt, 1H, J = 2.8, 5.9 Hz), 6.29 (t, 1H, J = 6.9 Hz), 7.23 (d, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz), 7.65 (d, 1H, J = 0.9 Hz), 7.80 (d, 1H, J = 1.4), 8.08 (dd, 1H, J = 2.3, 7.3 Hz), 11.73 (bs, 1H). 13C-NMR (DMSO-d6): δ 67.6, 73.1, 78.6, 112.2, 112.5, 115.1, 132.9, 133.7, 136.2, 136.9, 140.1, 146.5, 156.5 HRMS calculated for C13H13N3O3 [M+H]+ 260.1035, found 260.1033.
3.3. Anti-Trypanosome Activity
In vitro activity against Trypanosoma brucei was determined using the Alamar blue (resazurin) assay for cell viability exactly as described [52]. Briefly, serial dilutions of test compounds were made in 96-well plates by serial passage of 100 μL of test compound (usually at 2 mM) to 100 μL of HMI9 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen), using 2 rows, with the negative control values obtained from wells with 100 μL of medium without test compound. Serial dilutions with pentamidine isethionate (Sigma) were used as positive control. To each well, 100 μL of medium, containing 104 culture-adapted bloodstream T. b. brucei (strain Lister 427), was added and the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 48 h after which 20 μL 5 mM resazurin solution was added. Following a further incubation of 24 h at 37 °C, fluorescence was determined in a FLUOstar OPTIMA (BMG Labtech, Aylesbury, UK) fluorimeter with excitation and emission filters at 544 nm and 620 nm, respectively. EC50 values (the effective concentration reducing specific fluorescence by 50%) were calculated by nonlinear regression using the Prism 5 software package (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA).
3.4. Transport Assays
Transport assays with bloodstream forms of T. b. brucei were performed exactly as described previously [53,54]. Briefly, transport was initiated by the addition of 100 µL of T. b. brucei bloodstream forms (107 cells/mL in assay buffer [53]) to 100 µL of [2,8,5'-3H]-adenosine (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA; 54.4 Ci/mmol) pre-mixed with up to 1 mM of test inhibitor in assay buffer. After exactly 10 s the mixture was centrifuged through an oil layer in a microfuge (13,000× g) and the microfuge tubes were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen. Pellets were cut off and collected in scintillation tubes; after solubilisation in 2% SDS and addition of scintillation fluid, radioactivity was determined in a liquid scintillation counter. Inhibition data were fitted to a sigmoidal curve with variable slope (GraphPad Prism 5.0), allowing for the determination of EC50 values, from which inhibition constants (Ki) were calculated using the Cheng-Prusoff equation, and Gibbs Free Energy using ΔG0 = −RTln (Ki), as described [52].
4. Conclusions
The strategy of the work presented herein was to potentially synthesize new and more potent inhibitors of SAHases, thereby disrupting mRNA capping in protozoa as a strategy towards new antiparasitic therapeutics. To this end, characteristics of known SAHase inhibitors such as neplanocin and Aristeromycin were combined, and the nucleoside analogue was given enhanced flexibility using the “fleximer” approach, and added specificity by omitting the N3 equivalent nitrogen residue in the pyrimidine half of the fleximer base group. In addition, the 4'-CH2OH moiety was omitted to reduce general cytotoxicity [10,14]. The data, however, show that the resulting 3-deazaneplanocin fleximers (1–3) displayed only moderate activity in a standardized anti-protozoal test, against Trypanosoma brucei, despite the possibility of this species being vulnerable to inhibition of SAHase [55].
We have previously shown that the trypanocidal action of nucleoside and nucleobase analogues is either enabled or limited by their rate of uptake by specific transport proteins [52,53,54,56,57], and therefore investigated the effect of the fleximer modification on nucleoside transport. We found that the introduction of this modification of the purine ring reduces affinity, and thus presumably translocation rates, for both of the transport systems expressed in bloodstream T. brucei, and conclude that the lack of suitable transporters for these molecules causes (or at least contributes to) the observed lack of trypanocidal potency. However, we have also shown that purine transporters in other protozoan parasites, e.g., Toxoplasma gondii [58], Plasmodium falciparum [59], Leishmania donovani [48], and Trichomonas vaginalis (Natto and De Koning, unpublished data) all have very different substrate-specificity characteristics. Further studies with additional parasites, and the optimization of the inhibitors for enhanced uptake by the parasites, are in progress.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (R01 CA97634 to KSR, NIH T32 GM066706 CBI Fellowship to SCZ) and Wellcome Trust (grant to HPdK). We are also grateful to Phil Mortimer (Johns Hopkins Mass Spectrometry Facility) for his invaluable assistance with the HRMS analysis. We also thank Therese Ku for her help with compound characterizations and editorial assistance.
Author Contributions
KLS was responsible for the oversight of the project and supervision of the students, SCZ and EO, while HdK was responsible for supervision of GUE and LW. KLS and SCZ designed the synthesis; SCZ and EO performed the synthesis and characterization of the compounds; GUE, LW and HdK were responsible for the parasite testing and adenosine uptake assays. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
References
- Tseng, C.K.; Marquez, V.E.; Fuller, R.W.; Goldstein, B.M.; Haines, D.R.; McPherson, H.; Parsons, J.L.; Shannon, W.M.; Arnett, G.; Hollingshead, M.; et al. Synthesis of 3-deazaneplanocin A, a powerful inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase with potent and selective in vitro and in vivo antiviral activities. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, G. The centrality of S-adenosylhomocysteinase in the regulation of the biological utilization of S-adenosylmethionine. In Biological Methylation and Drug Design; Borchardt, R.T., Creveling, C.R., Ueland, P.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Clifton, NJ, USA, 1986; pp. 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Cantoni, G.L.; Scarano, E. The formation of S-adenosylhomocysteine in enzymatic transmethylation reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchardt, R.T.; Keller, B.T.; Patel-Thombre, U.; Neplanocin, A. A potent inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and of vaccinia virus multiplication in mouse L929 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 4353–4358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bujnicki, J.M.; Prigge, S.T.; Caridha, D.; Chiang, P.K. Structure, evolution, and inhibitor interaction of S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase from Plasmodium falciparum. Proteins 2003, 52, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, P.K. Biological effects of inhibitors of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 77, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E. John Montgomery’s legacy: Carbocyclic adenosine analogues as SAH hydrolase inhibitors with broad-spectrum antiviral activity. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2005, 24, 1395–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Marquez, V.E. Carbocyclic nucleosides. Adv. Antivir. Drug Des. 1996, 2, 89–146. [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt, R.T.; Wu, Y.-S. S-Aristeromycinyl-l-homocysteine, a potent inhibitor of S-adenosylmethionine-dependent transmethylations. J. Med. Chem. 1976, 19, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guranowski, A.; Montgomery, J.A.; Cantoni, G.L.; Chiang, P.K. Adenosine analogues as substrates and inhibitors of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Brummelen, A.C.; Olszewski, K.L.; Wilinski, D.; Llinas, M.; Louw, A.I.; Birkholtz, L.M. Co-inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase/ornithine decarboxylase reveals perturbation-specific compensatory mechanisms by transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome analyses. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4635–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, M.S.; Borchardt, R.T. S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase as a target for antiviral chemotherapy. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 34, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasobe, M.; Liang, H.; Ault-Riche, D.B.; Borcherding, D.R.; Wolfe, M.S.; Borchardt, R.T. (1'R,2'S,3'R)-9-(2',3'-Dihydroxycyclopentan-1'-yl)-adenine and -3-deaza-adenine: Analogs of aristeromycin which exhibit potent antiviral activity with reduced cytotoxicity. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1993, 4, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, M.S.; Lee, Y.; Bartlett, W.J.; Borcherding, D.R.; Borchardt, R.T. 4'-Modified analogs of aristeromycin and neplanocin A: Synthesis and inhibitory activity toward S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, H.H.; Chiang, P.K.; Cantoni, G.L. Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Crystallization of the purified enzyme and its properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 4476–4480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hasobe, M.; McKee, J.G.; Borcherding, D.R.; Borchardt, R.T. 9-(trans-2',trans-3'-Dihydroxycyclopent-4'-enyl)-adenine and -3-deazaadenine: Analogs of neplanocin A which retain potent antiviral activity but exhibit reduced cytotoxicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.P.; Shen, S.; Ullu, E.; Tschudi, C. Evidence for a capping enzyme with specificity for the trypanosome spliced leader RNA. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007, 156, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mair, G.; Ullu, E.; Tschudi, C. Cotranscriptional Cap 4 Formation on the Trypanosoma brucei spliced leader RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28994–28999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamudio, J.R.; Mittra, B.; Campbell, D.A.; Sturm, N.R. Hypermethylated cap 4 maximizes Trypanosoma brucei translation. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 72, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seley, K.L.; Zhang, L.; Hagos, A. “Fleximers”. Design and synthesis of two novel split nucleosides. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3209–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seley, K.L.; Zhang, L.; Hagos, A.; Quirk, S. “Fleximers”. Design and synthesis of a new class of novel shape-modified nucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seley, K.L.; Quirk, S.; Salim, S.; Zhang, L.; Hagos, A. Unexpected inhibition of S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase by a guanosine nucleoside. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 1985–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak, M.; Seley, K.L.; Plavec, J. Conformational properties of shape modified nucleosides—Fleximers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8159–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seley, K.L.; Salim, S.; Zhang, L. “Molecular chameleons”. Design and synthesis of C-4-substituted imidazole fleximers. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seley, K.L.; Salim, S.; Zhang, L.; O’Daniel, P.I. “Molecular chameleons”. Design and synthesis of a second series of flexible nucleosides. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, S.C.; Sadler, J.M.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; Balzarini, J.; Seley-Radtke, K.L. Carbocyclic 5'-nor “reverse” fleximers. Design, synthesis, and preliminary biological activity. Med. Chem. Commun. 2011, 2, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauchope, O.R.; Velasquez, M.; Seley-Radtke, K. Synthetic routes to a series of proximal and distal 2'-deoxy fleximers. Synthesis (Stuttg.) 2012, 44, 3496–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.C.; Sadler, J.M.; O’Daniel, P.I.; Kim, N.T.; Seley-Radtke, K.L. “Reverse” carbocyclic fleximers: Synthesis of a new class of adenosine deaminase inhibitors. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2013, 32, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirk, S.; Seley, K.L. Identification of catalytic amino acids in the human GTP fucose pyrophosphorylase active site. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13172–13178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirk, S.; Seley, K.L. Substrate discrimination by the human GTP fucose pyrophosphorylase. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 10854–10863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, J.; Scott-Finnigan, T.J. Trypanocidal activity of antitumor antibiotics and other metabolic inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1978, 13, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sufrin, J.R.; Rattendi, D.; Spiess, A.J.; Lane, S.; Marasco, C.J., Jr.; Bacchi, C.J. Antitrypanosomal activity of purine nucleosides can be enhanced by their conversion to O-acetylated derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Li, Q.S.; Borchardt, R.T.; Kuczera, K.; Schowen, R.L. The antiviral drug ribavirin is a selective inhibitor of S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine hydrolase from Trypanosoma cruzi. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 7281–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seley, K.L.; Schneller, S.W.; Rattendi, D.; Bacchi, C.J. (+)-7-deaza-5'-noraristeromycin as an anti-trypanosomal agent. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Ye, W.; Schneller, S.W. Preparation of carbocyclic S-adenosylazamethionine accompanied by a practical synthesis of (−)-aristeromycin. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 3993–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luche, J.-L. Lanthanides in organic chemistry. 1. Selective 1,2 reductions of conjugated ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 2226–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, K.C.; Kumar, N.N.; Balaraman, E.; Kumar, K.V. Mitsunobu and related reactions: Advances and applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2551–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, Z. The Hendrickson ‘POP’ reagent and analogues thereof: Synthesis, structure, and application in organic synthesis. ARKIVOC 2012, 432–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.O.; Lee, K.M.; Chun, M.W.; Moon, H.R.; Jeong, L.S. Asymmetric synthesis of homo-apioneplanocin A from d-ribose. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 6339–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, J.; Sevignon, M.; Gozzi, C.; Schulz, E.; Lemaire, M. Aryl-aryl bond formation one century after the discovery of the Ullmann reaction. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 1359–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, G.D.; Hartwig, J.F. Palladium-catalyzed coupling of ammonia with aryl chlorides, bromides, iodides, and sulfonates: A general method for the preparation of primary arylamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11049–11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Buchwald, S.L. New ammonia equivalents for the Pd-catalyzed amination of aryl halides. Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3417–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkeser, R.A.; Buting, W.E. The preparation of aromatic amines with sodium amide in liquid ammonia. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 3011–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Luo, M. Reduction of hydrazines to amines with aqueous solution of titanium(iii) trichloride. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4977–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matovu, E.; Stewart, M.L.; Geiser, F.; Brun, R.; Maser, P.; Wallace, L.J.; Burchmore, R.J.; Enyaru, J.C.; Barrett, M.P.; Kaminsky, R.; et al. Mechanisms of arsenical and diamidine uptake and resistance in Trypanosoma brucei. Eukaryot. Cell 2003, 2, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.C.; Eze, A.A.; Baker, N.; Glover, L.; Clucas, C.; Aguinaga Andres, D.; Natto, M.J.; Teka, I.A.; McDonald, J.; Lee, R.S.; et al. Trypanosoma brucei aquaglyceroporin 2 is a high-affinity transporter for pentamidine and melaminophenyl arsenic drugs and the main genetic determinant of resistance to these drugs. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koning, H.P.; Jarvis, S.M. Adenosine transporters in bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei brucei: Substrate recognition motifs and affinity for trypanocidal drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Koning, H.P.; Bridges, D.J.; Burchmore, R.J.S. Purine and pyrimidine transport in pathogenic protozoa: From biology to therapy. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 987–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Salabi, M.I.; Wallace, L.J.; Luscher, A.; Maser, P.; Candlish, D.; Rodenko, B.; Gould, M.K.; Jabeen, I.; Ajith, S.N.; de Koning, H.P. Molecular interactions underlying the unusually high adenosine affinity of a novel Trypanosoma brucei nucleoside transporter. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koning, H.P. Transporters in African trypanosomes: Role in drug action and resistance. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.C.; Rojas Lopez, K.E.; Eze, A.A.; Delespaux, V.; van den Abbeele, J.; Rowan, T.; Barrett, M.P.; Morrison, L.J.; de Koning, H.P. Functional expression of TcoAT1 reveals it to be a P1-type nucleoside transporter with no capacity for diminazene uptake. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2013, 3, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, L.J.; Candlish, D.; de Koning, H.P. Different substrate recognition motifs of human and trypanosome nucleobase transporters. Selective uptake of purine antimetabolites. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26149–26156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natto, M.J.; Wallace, L.J.; Candlish, D.; Al-Salabi, M.I.; Coutts, S.E.; de Koning, H.P. Trypanosoma brucei: Expression of multiple purine transporters prevents the development of allopurinol resistance. Exp. Parasitol. 2005, 109, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, J.A.; Creek, D.J.; Burgess, K.; Allison, H.C.; Field, M.C.; Maser, P.; de Koning, H.P. Pyrimidine salvage in Trypanosoma brucei bloodstream forms and the trypanocidal action of halogenated pyrimidines. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, N.B.; Yang, X.; Hanke, J.; Mason, K.A.; Schowen, R.L.; Borchardt, R.T.; Yin, D.H. Trypanosoma cruzi: Molecular cloning and characterization of the S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Exp. Parasitol. 2003, 105, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiser, F.; Luscher, A.; de Koning, H.P.; Seebeck, T.; Maser, P. Molecular pharmacology of adenosine transport in Trypanosoma brucei: P1/P2 revisited. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vodnala, S.K.; Lundbäck, T.; Yeheskieli, E.; Sjöberg, B.; Gustavsson, A.-L.; Svensson, R.; Olivera, G.C.; Eze, A.A.; de Koning, H.P.; Hammarström, L.G.J.; et al. Structure-activity relationships of synthetic cordycepin analogues as experimental therapeutics for African Trypanosomiasis. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9861–9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koning, H.P.; Al-Salabi, M.I.; Cohen, A.M.; Coombs, G.H.; Wastling, J.M. Identification and characterisation of high affinity nucleoside and nucleobase transporters in Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quashie, N.B.; Dorin-Semblat, D.; Bray, P.G.; Biagini, G.A.; Doerig, C.; Ranford-Cartwright, L.C.; de Koning, H.P. A comprehensive model of purine uptake by the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: Identification of four purine transport activities in intraerythrocytic parasites. Biochem. J. 2008, 411, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors at this time.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
