Biocatalytic Behaviour of Immobilized Rhizopus oryzae Lipase in the 1,3-Selective Ethanolysis of Sunflower Oil to Obtain a Biofuel Similar to Biodiesel
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Efficiency of Different Lipase Immobilization Procedures


| pH | rnat 102 (mmol/min) | rfil 102 (mmol/min) | rimm 102 (mmol/min) | Eimm (%) | Eres (%) | Espe (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14.28 | 2.9 | 1.8 | 79.7 | 12.6 | 15.8 |
| 9 | 12.5 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 20.0 | 72.0 | 360.0 |
| pH | rnat 102 (mmol/min) | rfil 102 (mmol/min) | rimm 102 (mmol/min) | Eimm (%) | Eres (%) | Espe (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14.3 | 12.8 | 4.6 | 10.4 | 32.2 | 310.8 |
| 9 | 12.5 | 7.0 | 5.9 | 44.0 | 47.2 | 107.0 |

| pH | rnat 102 (mmol/min) | rfil 102 (mmol/min) | rimm 102 (mmol/min) | Eimm (%) | Eres (%) | Espe (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14.7 | 6.1 | 7.8 | 58.5 | 53.0 | 90.6 |
| 9 | 14.2 | 4.7 | 9.2 | 66.9 | 64.8 | 96.9 |
| pH | rnat 102 (mmol/min) | rfil 102 (mmol/min) | rimm 102 (mmol/min) | Eimm (%) | Eres (%) | Espe (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 14.1 | 12.8 | 0.6 | 9.2 | 4.3 | 46.7 |
| 9 | 14.5 | 13.5 | 1.2 | 6.9 | 8.3 | 120.3 |
2.2. Reusability of the Different Systems of Immobilized Lipases
| N° Reuse | Conversion (%) | Selectivity (%) | DG (%) | TG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 84.3 | 59.1 | 25.2 | 15.7 |
| 2 | 83.7 | 53.2 | 30.5 | 16.3 |
| 3 | 83.1 | 52.9 | 30.2 | 16.9 |
| 4 | 83.6 | 54.3 | 29.3 | 16.4 |
| 5 | 77.8 | 42.8 | 35.0 | 22.2 |
| 6 | 61.3 | 36.3 | 25.0 | 38.7 |
| 7 | 40.1 | 28.9 | 11.2 | 59.9 |
| 8 | 34.2 | 22.3 | 11.9 | 65.8 |
| 9 | 21.4 | 15.6 | 5.8 | 78.6 |
| N° Reuse | Conversion (%) | Selectivity (%) | DG (%) | TG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90.2 | 60.3 | 29.9 | 9.8 |
| 2 | 83.7 | 58.1 | 25.6 | 16.3 |
| 3 | 73.2 | 43.1 | 30.1 | 26.8 |
| 4 | 61.1 | 37.8 | 23.3 | 38.9 |
| 5 | 60.6 | 32.3 | 28.3 | 39.4 |
| 6 | 49.5 | 29.9 | 19.6 | 50.5 |
| 7 | 33.3 | 20.1 | 13.7 | 66.2 |
| 8 | 21.2 | 16.7 | 4.5 | 78.8 |
| 9 | 18.1 | 12.3 | 5.8 | 81.9 |


3. Experimental Section
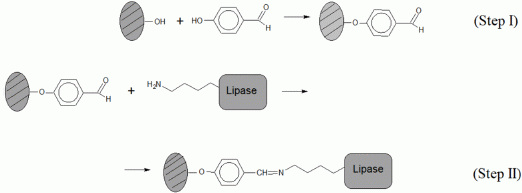
3.1. Support Activation and Functionalization of Sepiolite for Covalent Lipase Immobilization
3.2. Demineralized Sepiolite System Used for Physical Retention of Lipases
3.3. Immobilization of Biolipase R on Different Sepiolite Activated Supports
3.4. Alcoholysis Reactions
3.5. Analytical Method
3.6. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Different Lipase Immobilization Procedures
3.7. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Reuse of the Immobilized Systems
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demirbas, A. Political, economic and environmental impacts of biofuels: A review. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, S108–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Herrero-Davila, L.; Campelo, J.M.; Clark, J.H.; Hidalgo, J.M.; Luna, D.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A. Biofuels: A technological perspective. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 542–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, D.; Calero, J.; Sancho, E.D.; Luna, C.; Posadillo, A.; Bautista, F.M.; Romero, A.A.; Berbel, J.; Verdugo, C. Technological challenges for the production of biodiesel in arid lands. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 102, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, P.P.; Lau, H.L.N.; Chen, J.H.; Chong, M.F.; Choo, Y.M. A review on conventional technologies and emerging process intensification (PI) methods for biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 5131–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, D.; Rajendran, A.; Thangavelu, V. An overview on the recent advances in the transesterification of vegetable oils for biodiesel production using chemical and biocatalysts. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 367–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilham, Z.; Saka, S. Two-step supercritical dimethyl carbonate method for biodiesel production from jatropha curcas oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Jung, S.M.; Park, Y.C.; Park, K. Lipase catalyzed transesterification of soybean oil using ethyl acetate, an alternative acyl acceptor. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2007, 12, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.T.; Lee, K.T.; Mohamed, A.R. A glycerol-free process to produce biodiesel by supercritical methyl acetate technology: An optimization study via response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, A.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ramos, M.J.; Perez, A. Effects of triacetin on biodiesel quality. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4481–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Production, purification, characterization, and applications of lipases. Biotechnol. Adv. 2001, 19, 627–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Hameed, A. Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, A.; Kademi, A.; Leblanc, D. Lipases and their industrial applications—An overview. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2004, 118, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gog, A.; Roman, M.; Tosa, M.; Paizs, C.; Irimie, F.D. Biodiesel production using enzymatic transesterification—Current state and perspectives. Renew. Energy 2012, 39, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario, A.; Giordano, G. Catalytic conversion of renewable sources for biodiesel production: A comparison between biocatalysts and inorganic catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2013, 143, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.M.; Rancke-Madsen, A. Enzymatic large-scale production of biodiesel. Lipid Technol. 2011, 23, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, N.N.A.N.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Yaakub, Z. Overview on the current trends in biodiesel production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabani, A.E.; Silitonga, A.S.; Badruddin, I.A.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Masjuki, H.H.; Mekhilef, S. A comprehensive review on biodiesel as an alternative energy resource and its characteristics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 2070–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Medina, A.; Gonzalez-Moreno, P.A.; Esteban-Cerdan, L.; Molina-Grima, E. Biocatalysis: Towards ever greener biodiesel production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.W.; Lu, J.K.; Nie, K.L.; Deng, L.; Wang, F. Biodiesel production with immobilized lipase: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 937–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Diego, T.; Manjon, A.; Lozano, P.; Iborra, J.L. A recyclable enzymatic biodiesel production process in ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6336–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornscheuer, U.T. Lipase-catalyzed syntheses of monoacylglycerols. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1995, 17, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, V.; Bautista, F.M.; Campelo, J.M.; Luna, D.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A.; Hidalgo, J.M.; Luque, R.; Macario, A.; Giordano, G. Sustainable preparation of a novel glycerol-free biofuel by using pig pancreatic lipase: Partial 1,3-regiospecific alcoholysis of sunflower oil. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, C.; Luque, R.; Luna, D.; Hidalgo, J.M.; Posadillo, A.; Sancho, E.D.; Rodriguez, S.; Ferreira-Dias, S.; Bautista, F.; Romero, A.A. A comprehensive study of reaction parameters in the enzymatic production of novel biofuels integrating glycerol into their composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6657–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, D.; Posadillo, A.; Caballero, V.; Verdugo, C.; Bautista, F.M.; Romero, A.A.; Sancho, E.D.; Luna, C.; Calero, J. New biofuel integrating glycerol into its composition through the use of covalent immobilized pig pancreatic lipase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10091–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, C.; Sancho, E.; Luna, D.; Caballero, V.; Calero, J.; Posadillo, A.; Verdugo, C.; Bautista, F.M.; Romero, A.A. Biofuel that keeps glycerol as monoglyceride by 1, 3-selective ethanolysis with pig pancreatic lipase covalently immobilized on AlPO4 support. Energies 2013, 6, 3879–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, C.; Luna, D.; Posadillo, A.; Sancho, E.D.; Rodriguez, S.; Bautista, F.; Luque, R.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A. Production of a new second generation biodiesel with a low cost lipase derived from Thermomyces lanuginosus: Optimization by response surface methodology. Catal. Today 2011, 167, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadumesthrige, K.; Ara, M.; Salley, S.O.; Ng, K.Y.S. Investigation of lubricity characteristics of biodiesel in petroleum and synthetic fuel. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Wang, Q.J.; Hu, X.G.; Li, C.; Zhu, X.F. Characterization of the lubricity of bio-oil/diesel fuel blends by high frequency reciprocating test rig. Energy 2010, 35, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, A.; Sia, S.Y.; Fazal, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H. Effect of temperature on tribological properties of palm biodiesel. Energy 2010, 35, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelikten, I. The effect of biodiesel, ethanol and diesel fuel blends on the performance and exhaust emissions in a DI diesel engine. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2011, 24, 341–346. [Google Scholar]
- Cheenkachorn, K.; Fungtammasan, B. Biodiesel as an additive for diesohol. Int. J. Green Energy 2009, 6, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganjac, M.; Prah, I.O.; Cipak, A.; Cindric, M.; Mrakovcic, L.; Tatzber, F.; Ilincic, P.; Rukavina, V.; Spehar, B.; Vukovic, J.P.; et al. Effects of bioreactive acrolein from automotive exhaust gases on human cells in vitro. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 27, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, C.; Verdugo, C.; Sancho, E.D.; Luna, D.; Calero, J.; Posadillo, A.; Bautista, F.M.; Romero, A.A. A biofuel similar to biodiesel obtained by using a lipase from Rhizopus oryzae, optimized by response surface methodology. Energies 2014, 7, 3383–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero, J.; Verdugo, C.; Luna, D.; Sancho, E.D.; Luna, C.; Posadillo, A.; Bautista, F.M.; Romero, A.A. Selective ethanolysis of sunflower oil with Lipozyme RM IM, an immobilized Rhizomucor miehei lipase, to obtain a biodiesel-like biofuel, which avoids glycerol production through the monoglyceride formation. New Biotechnol. 2014. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt (accessed on 8 Februry 2014).
- Bautista, F.M.; Bravo, M.C.; Campelo, J.M.; Garcia, A.; Luna, D.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A. Covalent immobilization of porcine pancreatic lipase on amorphous alpo4 and other inorganic supports. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1998, 7, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, F.M.; Bravo, M.C.; Campelo, J.M.; Garcia, A.; Luna, D.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A. Covalent immobilization of acid phosphatase on amorphous AlPO4 support. J. Mol. Catal. B—Enzym. 1999, 6, 473–481. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, F.M.; Campelo, J.M.; Garcia, A.; Jurado, A.; Luna, D.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A. Properties of a glucose oxidase covalently immobilized on amorphous AlPO4 support. J. Mol. Catal. B-Enzym. 2001, 11, 567–577. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, F.M.; Caballero, V.; Campelo, J.M.; Luna, D.; Marinas, J.M.; Romero, A.A.; Romero, I.; Serrano, I.; Llobet, A. Heterogeneization of a new Ru(II) homogeneous asymmetric hydrogenation catalyst containing binap and the n-tridentate bpea ligand, through covalent attachment on amorphous AlPO4 support. Top. Catal. 2006, 40, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, C.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Improvement of enzyme activity, stability and selectivity via immobilization techniques. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Enzyme immobilization: The quest for optimum performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1289–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Torres, R.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Glutaraldehyde in bio-catalysts design: A useful crosslinker and a versatile tool in enzyme immobilization. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutarra, M.L.E.; Romero, O.; Abian, O.; Torres, F.A.G.; Freire, D.M.G.; Castro, A.M.; Guisan, J.M.; Palomo, J.M. Enzyme surface glycosylation in the solid phase: Improved activity and selectivity of candida antarctica lipase b. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Ortiz, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Torres, R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Modifying enzyme activity and selectivity by immobilization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6290–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: Why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, N.; Maeiro, I.; Luna, D.; Ferreira-Dias, S. Interesterification of fat blends rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids catalyzed by immobilized lipase on modified sepiolite. New Biotechnol. 2009, 25, S111–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.A.; Pires-Cabral, P.; Guillen, M.; Valero, F.; Luna, D.; Ferreira-Dias, S. Production of mlm-type structured lipids catalyzed by immobilized heterologous Rhizopus oryzae lipase. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macario, A.; Giordano, G.; Setti, L.; Parise, A.; Campelo, J.M.; Marinas, J.M.; Luna, D. Study of lipase immobilization on zeolitic support and transesterification reaction in a solvent free-system. Biocatal. Biotransf. 2007, 25, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of all compounds are available from the authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Luna, C.; Verdugo, C.; Sancho, E.D.; Luna, D.; Calero, J.; Posadillo, A.; Bautista, F.M.; Romero, A.A. Biocatalytic Behaviour of Immobilized Rhizopus oryzae Lipase in the 1,3-Selective Ethanolysis of Sunflower Oil to Obtain a Biofuel Similar to Biodiesel. Molecules 2014, 19, 11419-11439. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811419
Luna C, Verdugo C, Sancho ED, Luna D, Calero J, Posadillo A, Bautista FM, Romero AA. Biocatalytic Behaviour of Immobilized Rhizopus oryzae Lipase in the 1,3-Selective Ethanolysis of Sunflower Oil to Obtain a Biofuel Similar to Biodiesel. Molecules. 2014; 19(8):11419-11439. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811419
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuna, Carlos, Cristóbal Verdugo, Enrique D. Sancho, Diego Luna, Juan Calero, Alejandro Posadillo, Felipa M. Bautista, and Antonio A. Romero. 2014. "Biocatalytic Behaviour of Immobilized Rhizopus oryzae Lipase in the 1,3-Selective Ethanolysis of Sunflower Oil to Obtain a Biofuel Similar to Biodiesel" Molecules 19, no. 8: 11419-11439. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811419
APA StyleLuna, C., Verdugo, C., Sancho, E. D., Luna, D., Calero, J., Posadillo, A., Bautista, F. M., & Romero, A. A. (2014). Biocatalytic Behaviour of Immobilized Rhizopus oryzae Lipase in the 1,3-Selective Ethanolysis of Sunflower Oil to Obtain a Biofuel Similar to Biodiesel. Molecules, 19(8), 11419-11439. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules190811419