Abstract
Alkaloids are used in traditional medicine for the treatment of many diseases. These compounds are synthesized in plants as secondary metabolites and have multiple effects on cellular metabolism. Among plant derivatives with biological properties, the isoquinoline quaternary alkaloid berberine possesses a broad range of therapeutic uses against several diseases. In recent years, berberine has been reported to inhibit cell proliferation and to be cytotoxic towards cancer cells. Based on this evidence, many derivatives have been synthesized to improve berberine efficiency and selectivity; the results so far obtained on human cancer cell lines support the idea that they could be promising agents for cancer treatment. The main properties of berberine and derivatives will be illustrated.
1. Introduction
Natural compounds have been used for centuries because of their availability; those present in plants are employed in the so-called Traditional Medicine, which translates theories, beliefs and experiences into knowledge, skills and practices applied to prevent, diagnose and treat physical and mental disorders [1]. Being recognized as an integral part of the culture and traditions of populations, Traditional Medicine has been recommended by the World Health Organization as an effective complementary and alternative medicine for different diseases [2].
Plants have wide biological and medicinal properties, and are characterized by high safety, availability, accessibility and low cost, thus representing an invaluable source of chemicals with potential therapeutic effects [3,4]. Secondary metabolites of plants, such as flavonoids, saponins, tannins, steroids and alkaloids, display a number of properties, including hormonal mimicry, antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, detoxificant effects [5] and even anticancer activity [3,4,6].
2. Berberine
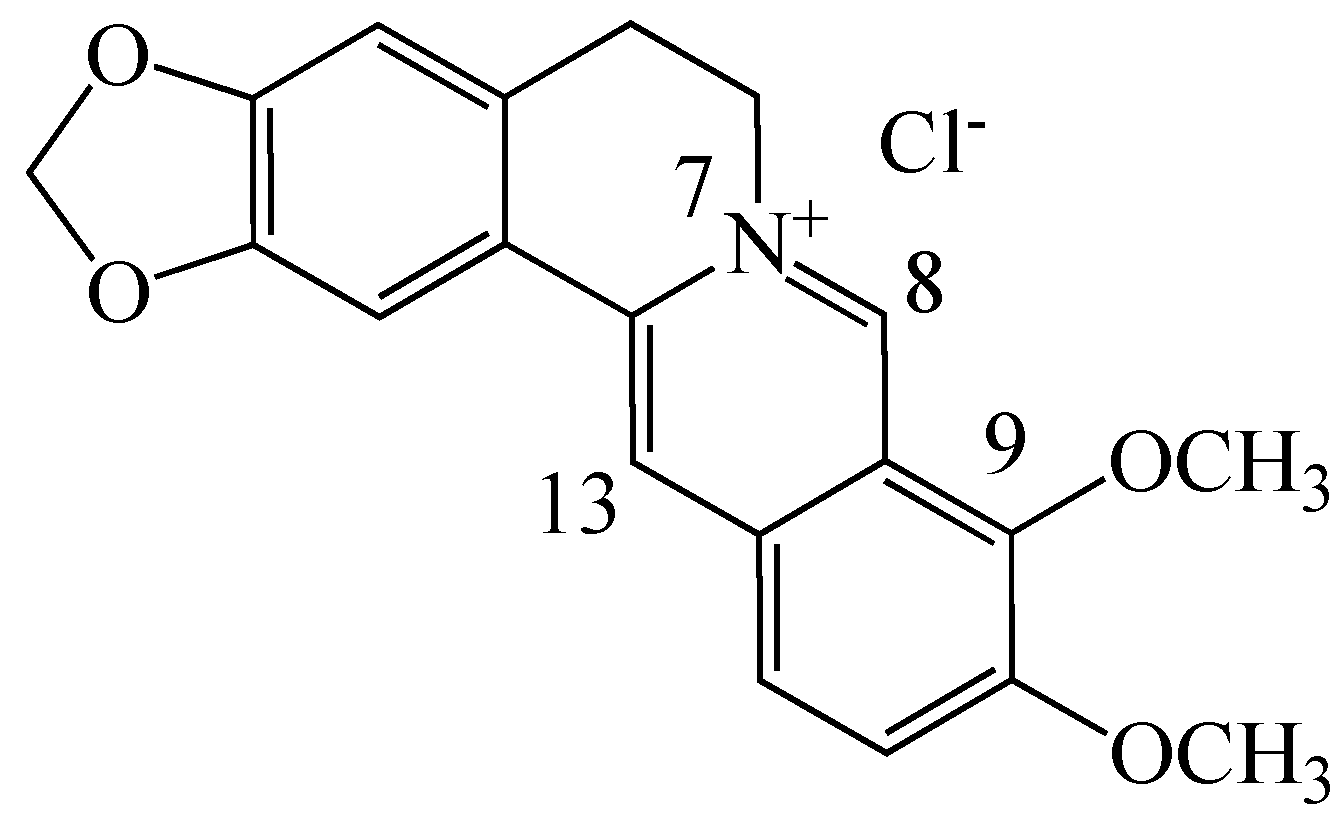
Among the several plant secondary metabolites, alkaloids possess a variety of pharmacological properties. Berberine (BBR, C20H19NO5, Figure 1, a 5,6-dihydro-dibenzo[a,g]quinolizinium derivative) is an isoquinoline quaternary alkaloid isolated from many kinds of medicinal plants such as Hydrastis canadensis, Berberis aristata, Coptis chinensis, Coptis japonica, Phellondendron amurense and Phellondendron chinense Schneid [7,8]. BBR has antioxidant effects and multiple pharmacological properties. It has been found to be effective against gastroenteritis, diarrhea, hyperlipidemia, obesity, fatty liver and coronary artery diseases, hypertension, diabetes and metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary [8,9,10,11] and Alzheimer’s disease [12,13]. Recently, in vitro studies using cancer cell lines have shown that BBR inhibits cancer cell proliferation and migration, and induces apoptosis in a variety of cancer cell lines [8,14,15,16], stimulating further development of derivatives for drug-base cancer prevention and treatment.
Many groups are actively working to depict the molecular mechanism of action of BBR; although many results suggest that the molecular structure of BBR is able to bind DNA, other nuclear and cytoplasmic targets have been identified (see below).
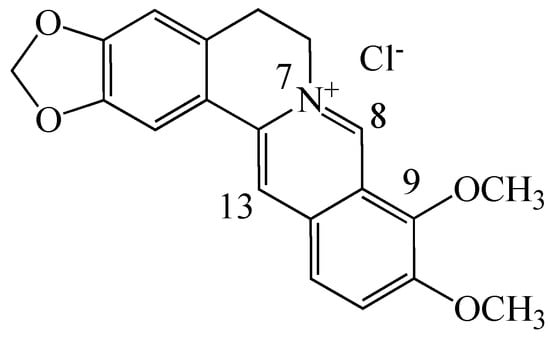
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of berberine chloride.
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of berberine chloride.
3. Molecular Targets of Berberine
BBR interacts directly with nucleic acids and with several proteins, including telomerase, DNA topoisomerase I, p53, NF-kB, MMPs and estrogen receptors. In general, BBR treatment promotes cell cycle arrest and death in human cancer cell lines, coupled to an increased expression of apoptotic factors [8,15,16]. The main known targets of BBR are below described.
3.1. DNA
Several studies have shown that BBR interacts directly with DNA, inducing double-strand breaks [16,17], and alters the spatial DNA conformation, thus suppressing gene transcription through the inhibition of the association between TBP (TATA binding protein) and the TATA box in the gene promoters [17]. Of note, BBR and derivatives (with substituents in position 9 or 13) can form DNA triplexes [18] or G-quadruplexes and block different cellular processes, including telomere elongation (see below) and DNA replication by the stabilization of the topoisomerase-mediated-DNA “cleavable complex” [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
3.2. Cell Cycle
Cell cycle arrest has been reported in human cancer cell lines as an effect of the interaction of BBR with DNA [8], as supported by the analysis of the phosphorylation of the histone H2AX [16], which impairs cell cycle progression and cell division. The net impact on cell cycle distribution depends on the cell type and treatment. In fact, an arrest at the G0/G1 phase was recorded in breast cancer MDAMB-231 and MCF-7 [27], thyroid carcinoma 8505C and TPC1 [28] and ovarian carcinoma OVCAR-3 and Skov-3 [29] cell lines. In giant cell carcinoma and prostate carcinoma cells, BBR affected the synthesis and activation of cyclins D1, D2, E, Cdk2, Cdk4 and Cdk6, inducing G0/G1 arrest and suppressing cell proliferation [7]. A cell cycle arrest in G1 phase, paralleled by decreased expression levels of cyclin B1, was observed in lung cancer H1299 and A549 cell lines [30] as well as in WM793 human melanoma cells treated with low drug concentrations. Conversely, high doses of the drug blocked cells in the G2 phase [31], indicating that the effect could change depending on drug concentrations. Interestingly, the impact could be dependent on p53 status: in human U2OS, Saos-2 and HOS osteosarcoma cells, BBR causes a cell cycle arrest in G1 (accompanied by p53-dependent upregulation of p21) and a p53-independent arrest in G2/M phase [32]. In general, the integrity of p53 is relevant because cells with p53wt were found to be very sensitive to BBR, whereas cell lines lacking functional p53 do not respond to BBR treatment [14,16]. In this respect, using 13-arylalkyl BBR derivatives, named NAX012, NAX014 and NAX018, we have demonstrated that they are more potent than BBR, and that the more susceptible cells were harboring p53wt [33].
It was also observed that BBR induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase in colorectal, breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma cells followed by apoptosis activation through the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c, inhibition of anti-apoptotic proteins (c-IAP1, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL), activation of pro-apoptotic proteins (p53, p21, caspase-3 and -9) and cleavage of PARP-1 [8,33,34,35,36,37].
3.3. GADD (DNA Damage-Inducible Gene) 153
This protein (also known as C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP-10) or DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (DDIT3), is involved in growth arrest and DNA damage, ubiquitously expressed at very low levels [38] and overexpressed under cellular stress conditions inducing nutrient deprivation and metabolic perturbations. Thus, GADD153 heterodimerizes with other C/EBP proteins to direct GADD153 dimers away from “classical” C/EBP binding sites, blocking cells at the G1/S boundary [38,39]. It has been reported that the overexpression of GADD153 can be induced by BBR in human cervical cancer cells, accompanied by the release of Ca2+ from endoplasmic reticulum (ER). An event which causes cell cycle arrest and cell death, driven by altered functions of mitochondria followed by cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation leading to apoptosis [38,39,40,41].
3.4. Cyclooxygenases (COX)
Two COX isoforms with distinct physiological functions have been described; COX-1 is constitutively expressed and has an important role in cell homeostasis, while COX-2 is an inducible enzyme activated by extracellular stimuli. Overexpression of COX-2 stimulates the production of prostaglandins, including prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which are implicated in inflammatory responses and also in carcinogenesis and metastasis [42,43,44]. BBR anti-inflammation potential is correlated with the inhibition of COX-2 transcription in human colon and melanoma cancer cells, and even macrophages, blocking in turn the transcription of PGE2 [8,43,44]. Down-regulation of COX-2 is mediated by the binding of its promoter to NF-κB, which promotes NF-κB translocation from the nucleus to the cytosol [42]. Moreover, with in vivo assays, BBR was found to lower COX-2 expression in the colon of rats treated with azoxymethane (AOM), inhibiting in turn the neoplastic transformation [34].
3.5. Mcl-1
This protein, initially isolated from the ML-1 human myeloblastic leukemia cell line, is an anti-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family which contains three Bcl-2 homology domains and inhibits apoptosis by interacting with the pro-apoptotic proteins Bim, Bak, and Bid [45]. This protein becomes activated either constitutively or after induction by oxidative stress, cytokines or growth factors, and it can promote cell growth, survival and angiogenesis by the transcriptional up-regulation of the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) [46]. Overexpression of Mcl-1 has been observed in a variety of cancers [45].
It has been reported that BBR could suppress the constitutive activation of STAT3 in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma, renal and oral cancer cells by down-regulating the activity of Mcl-1 [46], therefore, BBR can act inhibiting cell survival and leading apoptosis by suppressing Mcl-1 expression in different cancer cell types [45,46,47]. Moreover, BBR-mediated down-regulation of Mcl-1 expression was accompanied by down-regulation of c-FLIP, allowing the induction of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis [47,48,49].
3.6. Nucleophosmin/B23
Nucleophosmin/B23 is a chaperone protein that translocates from the nucleoli to the nucleoplasm in response to DNA damage, causing cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and apoptosis; the involvement of nucleophosmin/B23 in tumor development, although through an unknown mechanism, renders it a promising target for developing an anticancer strategy [50]. BBR promotes downregulation of nucleophosmin with consequent impairment of telomerase activity and induction of apoptosis [51].
3.7. Telomerase
Shortening of telomeres causes a loss of approximately 50 to 200 bp of telomeric DNA at each cell division; when telomeres are completely eroded, the ends of each strand of DNA are exposed to exonucleases and further DNA degradation [52]; then, cell cycle is arrested and the apoptotic pathway activated. Telomerase has a crucial role in cellular immortalization and tumorigenesis, being detected in 80%–90% of human cancers [52,53]. Telomerase is an enzyme that adds DNA sequence repeats to the 3' end of DNA strands in the telomere regions of chromosomes to ensure telomere elongation. Telomerase consists of a reverse transcriptase carrying its own RNA template used when it elongates telomeres [52].
BBR functions as an inhibitor of the telomere elongation by blocking the telomerase activity through formation of a G-quadruplex with telomeric DNA [54,55]. Remarkably, it interacts with the POT1 protein, an essential factor in the protection of telomeres, thus abolishing its binding to telomeric DNA and compromising cellular immortality. The inhibitory effect of BBR on lung cancer cell proliferation was described to be mediated by the decreased expression of activating enhancer-binding proteins (AP)-2α and -2β, both necessary for the hTERT expression. Under this condition, a down-regulation in the expression of telomerase was observed [42].
3.8. Wnt
BBR has the potential to modulate and regulate Wnt/β-catenin pathway [56], which in normal cells is inactivated by ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of the β-catenin protein, blocking the expression of different cell division factors. Conversely, the binding of the extracellular Wnt factor to the membrane receptor Frizzled activates the pathway and induces gene transcription. An effect of BBR on this pathway, and in a greater manner of its arylalkyl derivatives, was reported in cancer cells. The level of β-catenin increased in drug treated cancer cell lines, thus leading to an enhancement of E-cadherin and consequent cell death [56].
3.9. DAXX
The death-domain-associated protein (DAXX) regulates a wide range of cellular signaling pathways for both cell survival and death. In neuroblastoma cells it was observed that BBR binds to DNA in the DAXX core promoter region and suppressed its transcriptional activity. The down-regulation of DAXX expression resulted in the degradation of MDM2 (murine double minute 2) by ubiquitination, followed by the activation of p53 and then apoptosis [14,16].
It has been demonstrated that DAXX interacts with MDM2 and HAUSP (herpes virus-associated ubiquitin-specific protease) to form a tertiary complex. This complex reduces self-ubiquitination of MDM2, to maintain a low level of p53 under non-stress conditions. In different cancer cell types, BBR induced a dissociation of the MDM2-DAXX-HAUSP complex, resulting in enhanced MDM2 ubiquitination that increases p53 protein activity, leading to apoptosis [14].
3.10. AMPK
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a highly conserved serine/threonine kinase that serves as a metabolic sensor for the maintenance of cellular energy homeostasis and is capable to inhibit AR (androgen receptor). AMPK becomes activated in cell starvation, hypoxia, ischemia and heat shock. In prostate cancer, AR signaling is crucial for development and progression by regulating cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. After treatment with BBR, prostate cancer cells decrease their proliferation by a direct activation of AMPK, contributing to the degradation of AR and leading to apoptosis [57,58].
3.11. Enzymes Regulating Folate Cycle
Thymidylate synthase (TS) catalyzes the reductive methylation of dUMP by 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (CH2H4PteGlu), generating dTMP and dihydrofolate [59]. Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) catalyzes the reduction of folate and 7,8-dihydrofolate (DHF) to 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate (THF), utilizing NADPH as cofactor. Both reactions are essential steps in the biosynthesis of nucleotide bases of DNA and thus important targets for chemotherapy [60]. Moreover, enhanced DNA repair is a common feature of almost all resistant cell lines studied.
In this regard, a large panel of human ovarian carcinoma cell lines, in which cisplatin-resistance was associated with cross-resistance to 5-FU (5-fluorouracil) and methotrexate, showed an increase in TS and in the intracellular pools of 5,10-methylene-THF and THF [61]. These cells presented an increase in mRNA level for both DHFR and TS, which resulted in an increased enzyme activity [62]. Unlike traditional folate cycle inhibitors such as 5-FU, BBR showed an antiproliferative effect accompanied by a greater inhibition of TS and DHFR expression in cell extracts from resistant cells than from sensitive ones. Additional results showed that BBR suppresses the growth of cisplatin-resistant cells more than the sensitive counterparts, by interfering with the expression of folate cycle enzymes DHFR and TS [63].
4. Berberine and Cancer
The search for new drugs that induce apoptosis in tumors refractory to the conventional therapy is crucial to develop efficient anticancer therapies. Several mechanisms by which BBR inhibits the proliferation of different cancer cell lines have been reported. Among them, the killing of cancer cells by the activation of apoptosis is the best characterized.
In this context, several groups have reported the pro-apoptotic effect of BBR mediated by the impact on mitochondria. In fact, BBR was proved to alter the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), inhibit mitochondrial respiration leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and regulate the expression of Bcl-2 family members, as Mcl-1 [45,47]. Alterations in mitochondrial membrane stimulate the release of cytochrome c promoting the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that trigger apoptosis that requires the activation of caspases and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) cleavage [64]. Some examples of the pro-apoptotic effect of BBR are shown in Table 1 (see references therein).

Table 1.
Examples of the multiple effects of BBR leading to apoptosis in different cancer cell lines.
| Cell Line | Origin | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8505C, TPC1 | Thyroid carcinoma | Cell cycle arrest | [28] |
| OVCAR-3, Skov-3 | Ovarian carcinoma | Cell cycle arrest | [29,63] |
| SCC-4, HSC-3 | Oral squamous carcinoma | Caspase activation; MMP disruption; Cytochrome c release; Cell cycle arrest; ROS production | [64,65] |
| SK-N-SH, SK-N-MCT98G | NeuroblastomaGlioblastoma | Caspase activation; PARP-1 cleavage | [66,67] |
| A375, Hs29 | Melanoma | COX-2 downregulation | [43] |
| HONE-1, NPC, C666-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Caspase activation; PARP-1 cleavage; STAT3 inhibition; Mcl-1 downregulation | [46,47,68] |
| Panc-1 | Pancreatic cancer | TRAIL activation | [49] |
| A549, H1299 | Lung cancer | Caspase activation; MMP disruption; Bcl-2/Bcl-xL decrease; COX-2 downregulation; Cell cycle arrest | [30,42,69] |
| MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, SK-BR-3 | Breast cancer | Caspase activation; PARP-1 cleavage; Cytochrome c release; Cell cycle arrest | [27,37,49,70,71,72] |
| HepG2 | Hepatoma | Caspase activation; PARP-1 cleavage; MMP disruption; Cytochrome c release; Bcl-2/Bcl-xL decrease | [73] |
| IMCE, HCT-116, SW480, SW620, SW613 | Colorectal cancer | Caspase activation; PARP-1 cleavage; ROS production; Cytochrome c release; Cell cycle arrest | [33,74,75,76] |
| LNCaP, PC-3, DU145, C4-2B | Prostate carcinoma | Caspase activation; PARP-1 cleavage; ROS production; MMP disruption; Cytochrome c release; Bcl-2/Bcl-xL decrease | [77,78,79] |
| A431 | Epidermoid carcinoma | Caspase activation; PARP-1 cleavage; MMP disruption; Bcl-2/Bcl-xL decrease | [80] |
| U937, HL-60 | Lymphoma, leukemia | Caspase activation; ROS production | [81,82,83] |
| SiHa, HeLa | Cervical cancer | Caspase activation; Telomerase downregulation | [84] |
BBR pro-apoptotic effects could be mediated through the modulation of the HER2/PI3K/Akt [71,72] and/or JNK/p38 signaling pathway [76] an impact of BBR on the NF-kB pathway, leading to inactivation of this factor with consequent triggering of the apoptotic process, cell cycle and invasion pathway arrest, was reported [85]. The inhibition of the transcription factor AP-1 by BBR caused apoptosis in human hepatoma [86], oral [87], breast [88] and colon [89] cancer cells.
BBR modulates the activity of the Bcl-2 family members; increased expression of pro-apoptotic protein Bax (Bcl-2-associated X protein) together with decrease of Bcl-2/Bcl-xL after BBR treatment was observed not only in human prostate epithelial (PWR-1E) or carcinoma cells (DU145, PC-3 and LNCaP), but also in promyelocytic leukemia, gastric carcinoma and lung cancer cells, inducing cell death (Table 1).
Caspase-dependent apoptosis was reported in colon carcinoma cells treated with 13-arylalkyl BBR derivatives [33]. BBR has been used to treat TRAIL-sensitive breast cancer cells, and found to be able to sensitize also TRAIL-resistant breast cancer cells to apoptosis [48,49]. BBR suppresses HPV transcription in dose and time dependent manner in cervical cancer cell lines [84].
4.1. Combined Use with Drugs and Radiation
BBR has been used in combination with drugs or radiation. It was found as an adjuvant therapeutic agent in combination with taxol, a frequently used clinical chemotherapeutic drug, in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells (SKBR-3) [71]. Furthermore, administration of BBR with arsenic trioxide [90,91], cisplatin [92] and evodiamine [93] increased their cytotoxic effect on many cancer cell types. A similar effect was reported for the combined treatment of MCF-7 (estrogen receptor ER-wt) and MDA-MB-231 (ER-null) cells with BBR and ER antagonists [94]. BBR was combined with irinotecan to potentiate the cytotoxicity on colon cancer cells; the effect was due to an increased rate of apoptosis, possibly mediated by the inhibition of the NF-κB activation [95]. The use of BBR in combination with the microtubule poison vincristine has been proved to be efficient against hepatoma cell lines by potentiating the pro-apoptotic effect of the single drug [96]. Also the combination of conventional radiotherapy and BBR exerts a synergistic cytotoxic effect on different tumor cell lines [97,98]. Ionizing radiation combined with BBR treatment was applied to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines, showing that the drug could display radiosensitization properties. The same effect was recorded in vivo when tumor cells were injected into nude mice [99].
4.2. Effect on Tumor Progression and Metastasis
Of note, BBR could interfere with tumor progression and invasion, possibly through the inhibition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA), GTPase [68], PE2 receptor agonist [43], TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition [100] and Rho kinase-mediated ezrin [101]. A reduced migration in vitro could be related to the inhibition of FAK, IKK, NF-κB, u-PA, MMP-2, and MMP-9 [68,85,88,101]. The effect of BBR on the metastatic potential of cancer cells could be mediated by the activation of AMPK signaling, with the consequent reduction of ERK activity and COX-2 expression [102]. The property of BBR to exert anti-invasive and anti-metastatic effect was supported both by in vivo and in vitro analyses in B16F-10 cells, where BBR affected MMP expression through a negative regulation of ERK [103]. The activator effect of BBR on AMPK impaired the migration of colon carcinoma SW480 and HCT116 cells by interfering with the integrin β1 pathway [104]. The same signaling pathway could be responsible for the anti-migration action of BBR on chondrosarcoma cells, which are characterized by high invasion ability [105].
Metastatic lung cancer A549 cells also appeared to be blocked in tumor progression and invasion by BBR, due to the down-regulation of several transcription factors such as c-fos, c-jun and NF-κB [106]. The same cell line was used to identify the regulators of cell migration impairment by BBR; in fact, it was found that BRR impact on epithelial-to-mesenchimal factors plays a crucial role in the inhibition of lung cancer metastasis [100].
4.3. Induction of Autophagy
Autophagy contrasts cellular stress conditions including nutrient deprivation and produces recycled energy originated from macromolecule degradation, thus regulating cellular homeostasis. The function of autophagy in cancer cells is to sense the presence of damaged DNA and organelles caused by chemotherapy and to degrade them, according to its own function; in this way, continuous energy is produced, which ensures cancer cell survival [107,108,109,110]. Enforced autophagy could act as a genuine Programmed Cell Death type II [111,112].
The analysis of the potential ability of BBR to induce autophagy revealed that in non-small-cell and Lewis lung cancer cell lines as well as mice with Lewis lung carcinoma xenografts, in fact autophagic hallmarks (activation of Beclin-1, inhibition of mTOR and conversion of LC3I into LC3II) were detected [113,114]. Accordingly, human hepatocarcinoma cell survival was affected by BBR through the activation of both apoptosis and autophagy [115]. The molecular analysis of the complex network between apoptosis and autophagy [113,116] revealed that BBR acts on the interaction between Bcl-2 family members, promoting the dissociation/assembly of complexes in charge of regulating the balance between apoptosis and autophagy [116].
Several derivatives of BBR have been evaluated in the HCT116 colon carcinoma cell line and found to be capable of inducing vesicle formation at cytoplasmic level, where LC3I was converted into its lipidated form LC3II [33].
5. BBR Derivatives for Anticancer Drug Discovery
Berberine offers ready functionalization and decoration at various positions on its skeleton, and can be readily converted into derivative compounds by known synthetic methodologies [117,118,119].
In particular, arylalkyl derivatives of berberine have been investigated [33,119]. Unprecedented features of this class of analogues are aromatic groups bonded to the C-13 position of the parent berberine via a linker of variable length, in a fashion to create a propensity for additional non-covalent aromatic interactions with the cellular target. These types of interactions are ubiquitous in nature [120] and their geometry is relevant for the molecular recognition in biological systems and for a possible effect on cancer cell proliferation and migration [18,121,122,123].
6. Conclusions and New Perspectives
The above discussed evidences suggest that multiple effects of BBR are mediated by the impact on different pathways, leading essentially to cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and controlled inflammation (Figure 2). The promising data obtained on cancer cells support an active role of BBR in inhibiting cancer cell proliferation. To improve this relevant property, many derivatives (essentially with aromatic groups in the position 9 or 13 of the alkaloid skeleton) have been designed and synthesized [119]. In general, derivatives proved to be more efficient than the lead compound, thus opening new perspectives for drug discovery.
Among the multiple studies aiming at defining the mechanism of action of BBR, it is noteworthy to mention the evidence that BBR could regulate microRNAs (miRNAs), short non-coding RNA molecules (21–23 nucleotides) generated in the nucleus and involved in a variety of biological processes, including development, cell proliferation and death. Deregulated expression of miRNAs was observed in many human cancer types, where they can act either as tumor suppressor or oncogenes [124]. Recent studies have demonstrated a key role of miRNA as targets of BBR; in fact, in hepatocellular carcinoma, miRNA expression (especially of miR-21-3p) was increased by BBR, contributing to decrease cancer cell proliferation and induce apoptosis. The mechanism of action of miR-21-3p was postulated to be correlated to the expression of methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT) genes (MAT2A and MAT2B) [125]. In different experimental contexts, i.e., human multiple myeloma [126] and cisplatin-resistant SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells treated with BBR [127], a dose dependent downregulation of miRNA-21 was observed. Further experiments are required to clearly depict the impact of BBR on microRNA dynamics.
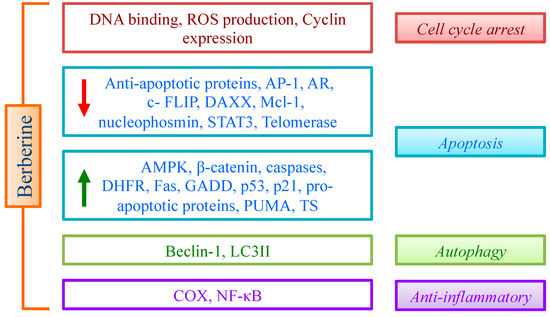
Figure 2.
Effect of BBR on cell cycle, apoptosis, autophagy and inflammation through the modulation of different targets.
Figure 2.
Effect of BBR on cell cycle, apoptosis, autophagy and inflammation through the modulation of different targets.
Acknowledgments
LMGO is a PhD student (Dottorato in Genetica, Biologia Cellulare e Molecolare, University of Pavia, Italy) supported by SENESCYT (Quito, Ecuador) and Universidad Técnica Particular de Loja (Loja, Ecuador); MT is a post-doc supported by Italian AIRC. The authors acknowledge Lucrezia Lombardi for English revision of the text.
Author Contribution
All the authors wrote the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Scovassi, A.I. Traditional medicine: An ancient remedy rediscovered. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kohler, J.C.; Baghdadi-Sabeti, G. Traditional medicines: Global situation, issues and challenges. The World Medicines Situation 2011, 3rd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Teiten, M.H.; Gaascht, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Anticancer bioactivity of compounds from medicinal plants used in European medieval traditions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlikova, B.; Legrand, N.; Panning, J.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Anti-inflammatory and anticancer drugs from nature. Cancer Treat. Res. 2014, 159, 123–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Chen, Z. Traditional Chinese medicine ZHENG and Omics convergence: A systems approach to post-genomics medicine in a global world. OMICS 2013, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.F. Natural compounds as anticancer agents: Experimental evidence. World J. Exp. Med. 2012, 2, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Di, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.W.; Li, C.G.; Zhou, S.F. Interaction of herbal compounds with biological targets: A case study with berberine. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 708292. [Google Scholar]
- Tillhon, M.; Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Berberine: New perspectives for old remedies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.L.; Lai, M.L.; Zhong, Y.F.; Wang, A.M.; Su, J.K.; Zhang, M.Q. Antinociceptive effect of berberine on visceral hypersensitivity in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4582–4589. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, C.M.; Li, J.; Meng, Z.J.; Wei, S.N.; Li, J.; Bucala, R.; Li, Y.L.; Chen, L. Berberine protects against palmitate-induced endothelial dysfunction: Involvements of upregulation of AMPK and eNOS and downregulation of NOX4. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 260464. [Google Scholar]
- Heidarian, E.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Khoshdel, A.; Bakhshesh, M. Metabolic effects of berberine on liver phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in rats fed on high lipogenic diet: An additional mechanism for the hypolipidemic effects of berberine. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, S429–S435. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, N.; Khodagholi, F. Natural products as promising drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Molecular mechanism aspect. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tang, Z.H.; Peng, J.; Liao, L.; Pan, L.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Jiang, Z.S.; Wang, G.X.; Liu, L.S. The dual behavior of PCSK9 in the regulation of apoptosis is crucial in Alzheimer’s disease progression. Biomed. Rep. 2014, 2, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Shah, N.; He, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, M. Degradation of MDM2 by the interaction between berberine and DAXX leads to potent apoptosis in MDM2-overexpressing cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9895–9904. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hao, C.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Xu, B.; Yang, Q.; et al. Berberine radiosensitizes human esophageal cancer cells by downregulating homologous recombination repair protein RAD51. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Tian, D.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, S. Berberine represses DAXX gene transcription and induces cancer cell apoptosis. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 354–364. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kheir, M.M.; Chai, Y.; Hu, J.; Xing, D.; Lei, F.; Du, L. Comprehensive study in the inhibitory effect of berberine on gene transcription, including TATA box. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23495. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmik, D.; Buzzetti, F.; Fiorillo, G.; Lombardi, P.; Suresh Kumar, G. Spectroscopic studies on the binding interaction of novel 13-phenylalkyl analogs of the natural alkaloid berberine to nucleic acid triplexes. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 120, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.; Bastow, K. The 9-position in berberine analogs is an important determinant of DNA topoisomerase II inhibition. AntiCancer Drug Des. 2000, 15, 255–264. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Pang, J.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Z.H. Inhibition of DNA topoisomerase I by natural and synthetic mono- and dimeric protoberberine alkaloids. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.A.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Muller, M.T.; Chung, I.K. Induction of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA cleavage by a protoberberine alkaloid, berberrubine. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 16316–16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, B.; Sanders, M.M.; Yu, C.; Wu, H.Y.; Makhey, D.; LaVoie, E.J.; Liu, L.F. Identification of topoisomerase I as the cytotoxic target of the protoberberine alkaloid coralyne. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2795–2800. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.R.; Chung, I.K. Down-regulation of DNA topoisomerase II alpha in human colorectal carcinoma cells resistant to a protoberberine alkaloid, berberrubine. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Fujii, N.; Takaboshi, K.; Kawakami, T.; Kawamura, M.; Mizukami, T.; Nakano, H. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerase I and II isolated from the Coptis rhizomes. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 414–418. [Google Scholar]
- Pilch, D.S.; Yu, C.; Makhey, D.; LaVoie, E.J.; Srinivasan, A.R.; Olson, W.K.; Sauers, R.R.; Breslauer, K.J.; Geacintov, N.E.; Liu, L.F. Minor groove-directed and intercalative ligand-DNA interactions in the poisoning of human DNA topoisomerase I by protoberberine analogs. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 12542–12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.M.; Liu, A.A.; Li, T.K.; Wu, H.Y.; Desai, S.D.; Mao, Y.; Rubin, E.H.; LaVoie, E.J.; Makhey, D.; Liu, L.F. Selective cytotoxicity of topoisomerase-directed protoberberines against glioblastoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Yu, J.H.; Ko, E.; Lee, K.W.; Song, A.K.; Park, S.Y.; Shin, I.; Han, W.; Noh, D.Y. The alkaloid berberine inhibits the growth of anoikis-resistant MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines by inducing cell cycle arrest. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Kim, J.B.; Bae, J.; Park, S.Y.; Jee, H.G,; Lee, K.E.; Youn, Y.K. Berberine inhibited the growth of thyroid cancer cell lines 8505C and TPC1. Yonsei Med. J. 2012, 53, 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.S.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, S.J.; Bae, J. Berberine-induced growth inhibition of epithelial ovarian carcinoma cell lines. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2012, 38, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.A.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.R.; You, M. Dietary administration of berberine or Phellodendron amurense extract inhibits cell cycle progression and lung tumorigenesis. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, T.L.; Oliveira, P.J.; Sardao, V.A.; Perkins, E.; Parke, D.; Holy, J. Different concentrations of berberine result in distinct cellular localization patterns and cell cycle effects in a melanoma cell line. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 61, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Xu, B.; Wu, J.; Guo, C.; Zhu, F.; Yang, Q.; Gao, G.; Gong, Y.; Shao, C. Berberine induces p53-dependent cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells by inflicting DNA damage. Mutat. Res. 2009, 662, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Tillhon, M.; Parks, M.; Dutto, I.; Prosperi, E.; Savio, M.; Arcamone, A.G.; Buzzetti, F.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Multiple effects of berberine derivatives on colon cancer cells. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 924585. [Google Scholar]
- Thirupurasundari, C.J.; Padmini, R.; Devaraj, S.N. Effect of berberine on the antioxidant status, ultrastructural modifications and protein bound carbohydrates in azoxymethane-induced colon cancer in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 177, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.; Prasad, S.; Sung, B.; Krishnan, S.; Guha, S. Prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer by natural agents from mother nature. Curr. Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2013, 9, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, N.K.; Ho, W.S. Berberine induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in liver cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Pierpaoli, E.; Arcamone, A.G.; Buzzetti, F.; Lombardi, P.; Salvatore, C.; Provinciali, M. Antitumor effect of novel berberine derivatives in breast cancer cells. Biofactors 2013, 39, 672–679. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.P.; Yang, J.S.; Chang, N.W.; Chiu, T.H.; Su, C.C.; Lu, K.W.; Ho, Y.T.; Yeh, C.C.; Yang, M.D.; Lin, H.J.; et al. GADD153 mediates berberine-induced apoptosis in human cervical cancer Ca Ski cells. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Sheng, M.; Xu, R.; Yu, J.; Cui, K.; Tong, J.; Shi, L.; Ren, H.; Du, H. Berberine protects human renal proximal tubular cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial stress pathways. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D.Z. CPU86017: A novel Class III antiarrhythmic agent with multiple actions at ion channels. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2006, 24, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.L.; Yu, F.; Dai, D.Z.; Zhang, G.L.; Zhang, C.; Dai, Y. Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediating downregulated StAR and 3-beta-HSD and low plasma testosterone caused by hypoxia is attenuated by CPU86017-RS and nifedipine. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Chen, W.; Guo, W.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Shi, D.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, H.; Xiao, X.; Kang, T.; et al. Berberine targets AP-2/hTERT, NF-κB/COX-2, HIF-1α/VEGF and cytochrome-c/caspase signaling to suppress human cancer cell growth. PLoS One 2013, 8, e69240. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, T.; Vaid, M.; Katiyar, N.; Sharma, S.; Katiyar, S.K. Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid, inhibits melanoma cancer cell migration by reducing the expressions of cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin E2 receptors. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, A.; Chen, X.; Pi, R.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y. Berberine attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57 BL/6 mice. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13489. [Google Scholar]
- Sugio, A.; Iwasaki, M.; Habata, S.; Mariya, T.; Suzuki, M.; Osogami, H.; Tamate, M.; Tanaka, R.; Saito, T. BAG3 upregulates Mcl-1 through downregulation of miR-29b to induce anticancer drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.M.; Cheung, Y.C.; Lui, V.W.; Yip, Y.L.; Zhang, G.; Lin, V.W.; Cheung, K.C.; Feng, Y.; Tsao, S.W. Berberine suppresses tumorigenicity and growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inhibiting STAT3 activation induced by tumor associated fibroblasts. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L.; Chi, C.W.; Liu, T.Y. Modulation of apoptosis by berberine through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 and Mcl-1 expression in oral cancer cells. In Vivo 2005, 19, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Refaat, A.; Abd-Rabou, A.; Reda, A. TRAIL combinations: The new “trail” for cancer therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Refaat, A.; Abdelhamed, S.; Yagita, H.; Inoue, H.; Yokoyama, S.; Hayakawa, Y.; Saiki, I. Berberine enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 840–844. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, E.; Alcalay, M.; Pelicci, P.G. Nucleophosmin and its complex network: A possible therapeutic target in hematological diseases. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2595–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Liu, WH.; Yung, B.Y. Berberine-induced apoptosis of human leukemia HL-60 cells is associated with down-regulation of nucleophosmin/B23 and telomerase activity. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 923–929. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardes de Jesus, B.; Blasco, M.A. Telomerase at the intersection of cancer and aging. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günes, C.; Rudolph, K.L. The role of telomeres in stem cells and cancer. Cell 2013, 152, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzicalupi, C.; Ferraroni, M.; Bilia, A.R.; Scheggi, F.; Gratteri, P. The crystal structure of human telomeric DNA complexed with berberine: An interesting case of stacked ligand to G-tetrad ratio higher than 1:1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Sun, H.; Zhou, H.; Xiang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, C. The interaction of telomeric DNA and C-myc22 G-quadruplex with 11 natural alkaloids. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012, 22, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Albring, K.F.; Weidemüller, J.; Mittag, S.; Weiske, J.; Friedrich, K.; Geroni, M.C.; Lombardi, P.; Huber, O. Berberine acts as a natural inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling-Identification of more active 13-arylalkyl derivatives. Biofactors 2013, 39, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ratnam, M.; Dou, Q.P. The interplay of AMP-activated protein kinase and androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.J.; Kim, G.W.; Chung, S.H. AMP-activated protein kinase: An emerging target for ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras, C.W.; Santi, D.V. The catalytic mechanism and structure of thymidylate synthase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 721–762. [Google Scholar]
- Costi, M.P.; Ferrari, S. Update on antifolate drugs targets. Curr. Drug Targets 2001, 2, 135–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, K.J.; Kashani-Sabet, M. Elevated expression of thymidylate synthase cycle genes in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian carcinoma A2780 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, K.J.; Wang, W.Z.; Han, H. Cyclosporin A suppresses cisplatin-induced oncogene expression in human cancer cells. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1990, 17, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marverti, G.; Ligabue, A.; Lombardi, P.; Ferrari, S.; Monti, M.G.; Frassineti, C.; Costi, M.P. Modulation of the expression of folate cycle enzymes and polyamine metabolism by berberine in cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Yang, J.S.; Chen, J.T.; Fan, S.; Yu, F.S.; Yang, J.L.; Lu, C.C.; Kao, M.C.; Huang, A.C.; Lu, H.F.; et al. Berberine induces apoptosis in human HSC-3 oral cancer cells via simultaneous activation of the death receptor-mediated and mitochondrial pathway. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3371–3378. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.T.; Lu, C.C.; Yang, J.S.; Chiang, J.H.; Li, T.C.; Ip, S.W.; Hsia, T.C.; Liao, C.L.; Lin, J.G.; Wood, W.G.; et al. Berberine induced apoptosis via promoting the expression of caspase-8, -9 and -3, apoptosis-inducing factor and endonuclease G in SCC-4 human tongue squamous carcinoma cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4063–4070. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.S.; Yuk, D.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Han, S.B.; Moon, D.C.; Hong, J.T. Berberine inhibits human neuroblastoma cell growth through induction of p53-dependent apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3777–3784. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, K.S.; Hong, J.M.; Youn, M.J.; So, H.S.; Park, R.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, T.Y. Berberine induces G1 arrest and apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G cells through mitochondrial/caspases pathway. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 558–562. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, C.M.; Lau, E.P.; Di, K.; Cheung, P.Y.; Hau, P.M.; Ching, Y.P.; Wong, Y.C.; Cheung, A.L.; Wan, T.S.; Tong, Y.; et al. Berberine inhibits Rho GTPases and cell migration at low doses but induces G2 arrest and apoptosis at high doses in human cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 24, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Meeran, S.M.; Katiyar, N.; Akhtar, S. p53 Cooperates berberine- induced growth inhibition and apoptosis of non-small cell human lung cancer cells in vitro and tumor xenograft growth in vivo. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, J.B.; Kim, J.; Jayaprakasha, G.K. Berberine induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells (MCF-7) through mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 645, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.P.; Chuang, T.C.; Yeh, M.H.; Hsu, S.C.; Way, T.D.; Chen, P.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Chang, Y.H.; Kao, M.C.; Liu, J.Y. Growth suppression of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells by berberine via modulation of the HER2/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8216–8224. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, H.P.; Chuang, T.C.; Tsai, S.C.; Tseng, H.H.; Hsu, S.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Kuo, C.L.; Kuo, Y.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Kao, M.C. Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid, inhibits the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells via Akt pathway modulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9649–9658. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Tseng, T.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Chu, C.Y. Berberine induces apoptosis through a mitochondria/caspases pathway in human hepatoma cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Cao, H.; Chaturvedi, R.; Calcutt, M.W.; Hu, T.; Ren, X.; Wilson, K.T.; Polk, D.B.; et al. Berberine induces caspase-independent cell death in colon tumor cells through activation of apoptosis-inducing factor. PLoS One 2012, 7, e36418. [Google Scholar]
- Piyanuch, R.; Sukhthankar, M.; Wandee, G.; Baek, S.J. Berberine, a natural iso-quinoline alkaloid, induces NAG-1 and ATF3 expression in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 258, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.H.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Kuo, H.C.; Teng, C.Y.; Huang, H.I.; Wang, C.J.; Yang, S.F.; Liou, Y.S.; Kuo, W.H. Berberine induces apoptosis in SW620 human colonic carcinoma cells through generation of reactive oxygen species and activation of JNK/p38 MAPK and FasL. Arch. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Jung, H.Y.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Moon, D.C.; Han, S.B.; Hong, J.T. Berberine inhibits p53-dependent cell growth through induction of apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Meeran, S.M.; Katiyar, S.; Katiyar, S.K. Berberine-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells is initiated by reactive oxygen species generation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 229, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantena, S.K.; Sharma, S.D.; Katiyar, S.K. Berberine, a natural product, induces G1-phase cell cycle arrest and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 296–308. [Google Scholar]
- Mantena, S.K.; Sharma, S.D.; Katiyar, S.K. Berberine inhibits growth, induces G1 arrest and apoptosis in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells by regulating Cdki-Cdk-cyclin cascade, disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential and cleavage of caspase 3 and PARP. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letasiova, S.; Jantova, S.; Cipak, L.; Muckova, M. Berberine-antiproliferative activity in vitro and induction of apoptosis/necrosis of the U937 and B16 cells. Cancer Lett. 2006, 239, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Jantova, S.; Cipak, L.; Letasiova, S. Berberine induces apoptosis through a mitochondrial/caspase pathway in human promonocytic U937 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2007, 21, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Kao, S.T.; Chen, G.W.; Ho, H.C.; Chung, J.G. Apoptosis of human leukemia HL-60 cells and murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells induced by berberine through the activation of caspase-3. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 227–242. [Google Scholar]
- Mahata, S.; Bharti, A.C.; Shukla, S.; Tyagi, A.; Husain, S.A.; Das, B.C. Berberine modulates AP-1 activity to suppress HPV transcription and downstream signaling to induce growth arrest and apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, M.K.; Sung, B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sethi, G.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Berberine modifies cysteine 179 of IκBαkinase, suppresses nuclear factor-κB-regulated antiapoptotic gene products, and potentiates apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5370–5379. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, K.; Hibiya, Y.; Mutoh, M.; Koshiji, M.; Akao, S.; Fujiwara, H. Inhibition of activator protein 1 activity by berberine in human hepatoma cells. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L.; Chi, C.W.; Liu, T.Y. The anti-inflammatory potential of berberine in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2004, 203, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.B.; Nam, S.J.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.E. Berberine suppresses TNF-α-induced MMP-9 and cell invasion through inhibition of AP-1 activity in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Molecules 2008, 13, 2975–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Hibiya, Y.; Mutoh, M.; Koshiji, M.; Akao, S.; Fujiwara, H. Inhibition by berberine of cyclooxygenase-2 transcriptional activity in human colon cancer cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 66, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Chou, F.P.; Lu, F.J. Berberine enhances inhibition of glioma tumor cell migration and invasiveness mediated by arsenic trioxide. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.W.; Ahan, S.H.; Kim, T.Y. Enhancement of arsenic trioxide (As2O3)-mediated apoptosis using berberine in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2007, 42, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, M.J.; So, H.S.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Sohn, J.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Chung, S.Y.; Park, R. Berberine, a natural product, combined with cisplatin enhanced apoptosis through a mitochondria/caspase-mediated pathway in HeLa cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 789–795. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.N.; Han, X.; Xu, L.N.; Yin, L.H.; Xu, Y.W.; Qi, Y.; Peng, J.Y. Enhancement of apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells through synergy of berberine and evodiamine. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, C.; Zhou, K.; Wang, J.; Kang, J.X. Coptis extracts enhance the anticancer effect of estrogen receptor antagonists on human breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Tong, X.; Qi, B.; Qu, H.; Dong, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, N.; Tang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C. Berberine enhances chemosensitivity to irinotecan in colon cancer via inhibition of NF-κB. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wei, D.; Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Fan, C.; Zhang, J.; Mo, C.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. The combinational effect of vincristine and BBR on growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in hepatoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.L.; Kuo, W.H.; Tseng, H.C.; Chou, F.P. Synergistic tumor-killing effect of radiation and berberine combined treatment in lung cancer: the contribution of autophagic cell death. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 529–542. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, J.M.; Hyun, M.S.; Lim, S.Y.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, D. The combination of berberine and irradiation enhances anti-cancer effects via activation of p38 MAPK pathway and ROS generation in human hepatoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 107, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, B.; Cai, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L.; Qin, Q.; Zhu, H.; Ma, J.; Tao, G.; et al. Berberine enhances radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cancer by targeting HIF-1α in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.W.; Xin, L.Y.; Xu, X.; Ji, X.X.; Fan, L.H. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers to predict response of Berberine in suppressing lung cancer invasion and metastasis. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Wang, D.; Duan, C.; Huang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, C.; Meng, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Berberine inhibits metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 5–8F cells by targeting Rho kinase-mediated Ezrin phosphorylation at threonine 567. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27456–27466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, E.J.; Yang, Y.; Lee, M.S.; Lim, J.S. Berberine-induced AMPK activation inhibits the metastatic potential of melanoma cells via reduction of ERK activity and COX-2 protein expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Hamsa, T.P.; Kuttan, G. Berberine inhibits pulmonary metastasis through down-regulation of MMP in metastatic B16F-10 melanoma cells. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Seo, S.M.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Ko, Y.G.; Ha, J.; Lee, M. Berberine inhibits human colon cancer cell migration via AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated downregulation of integrin β1 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Li, T.M.; Tan, T.W.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. Berberine reduces the metastasis of chondrosarcoma by modulating the αvβ3 integrin and the PKCδ, c-Src, and AP-1 signaling pathways. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.L.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Wang, C.J.; Hsu, J.L.; Chou, F.P. Inhibitory effect of berberine on the invasion of human lung cancer cells via decreased productions of urokinase-plasminogen activator and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 214, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aredia, F.; Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Giansanti, V.; Scovassi, A.I. Autophagy and cancer. Cells 2012, 1, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K.; Coffelt, S.B.; Cho, C.H.; Wang, X.J.; Lee, C.W.; Chan, F.K.; Yu, J.; Sung, J.J. The autophagic paradox in cancer therapy. Oncogene 2012, 31, 939–953. [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz, D.A. The four faces of autophagy: Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 647–651. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg-Lerner, A.; Kimchi, A. The paradox of autophagy and its implication in cancer etiology and therapy. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, G.; Niso-Santano, M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Kroemer, G. Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, B.; Engelbrecht, A.M.; Lockshin, R.A.; Klionsky, D.J.; Zakeri, Z. The variability of autophagy and cell death susceptibility: Unanswered questions. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1270–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Giansanti, V.; Tillhon, M.; Mazzini, G.; Prosperi, E.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Killing of tumor cells: A drama in two acts. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y. Berberine hydrochloride: Anticancer activity and nanoparticulate delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1773–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Tang, X.; Liu, H.; Tang, J.; Yang, Y.; Jing, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, W.; Gou, X.; Wang, Z. Berberine induces cell death in human hepatoma cells in vitro by downregulating CD147. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giansanti, V.; Torriglia, A.; Scovassi, A.I. Conversation between apoptosis and autophagy: “Is it your turn or mine?”. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Lenka, G.; Dostal, J.; Radek, M. Quaternary protoberberine alkaloids. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 150–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechepurenko, I.V.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Tolstikov, G.A. Berberine: Chemistry and biological activity. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.P.; Mahajan, S. Berberine and its derivatives: A patent review (2009–2012). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, M.L. Aromatic interactions in model systems. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 736–741. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, K.E.; Hobza, P. On the importance and origin of aromatic interactions in chemistry and biodisciplines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, D.; Hossain, M.; Buzzetti, F.; D’Auria, R.; Lombardi, P.; Kumar, G.S. Biophysical studies on the effect of the 13 position substitution of the anticancer alkaloid berberine on its DNA binding. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 2314–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmik, D.; Buzzetti, F.; Fiorillo, G.; Orzi, F.; Syeda, T.M.; Lombardi, P.; Kumar, G.S. Synthesis of new 13-diphenylalkyl analogs of berberine and elucidation of their base pair specificity and energetics of DNA binding. Med. Chem. Commun. 2014, 5, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 2, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, T.F.; Tsai, W.C.; Chen, S.T. MicroRNA-21–3p, a berberine-induced miRNA, directly down-regulates human methionine adenosyltransferases 2A and 2B and inhibits hepatoma cell growth. PLoS One 2013, 8, e75628. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.Y.; Li, K.P.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Z.G.; Dong, R.H.; Guo, H.B.; Zhang, M.X. Set9, NF-κB, and microRNA-21 mediate berberine-induced apoptosis of human multiple myeloma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fang, Y.; Shen, H.; Xu, W.; Li, H. Berberine sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin through miR-21/PDCD4 axis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 756–762. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
