Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
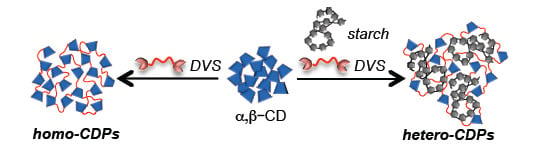
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of DVS Cross-Linked Polymers

| Polymer | Stoichiometry DVS:Glc | Elemental Analysis (% S/C) | Mass Resulting from the Reaction (gr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S-P1 a | 1:1 | 26.2 | 4.1 |
| S-P0.5 a | 0.5:1 | 19.4 | 3.7 |
| βCD-P1 a | 1:1 | 26.7 | 3.8 |
| αCDP2 a | 2:1 | 33.3 | 5.4 |
| αCDP1 a | 1:1 | 27.2 | 3.8 |
| βCD/S-P | 1:1 b | 22.6 | 3.9 |
| αCD/S-P | 1:1 b | 27.2 | 3.8 |

| Polymer | Water Content | Onset T (To) | DTG (Tp) | Residual mass |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-P1 | 1.43% | 335 °C | 365.36 °C | 10.55% |
| S-P0.5 | 1.96% | 325 °C | 335.31 °C | 11.79% |
| βCD-P1 | 2.85% | 340 °C | 376.65 °C | 10.99% |
| αCD-P2 | 1.75% | 330 °C | 352.20 °C | 10.38% |
| αCD-P1 | 2.72% | 330 °C | 373.94 °C | 12.25% |
| βCD/S-P | 2.25% | 335 °C | 354.06 °C | 8.77% |
| αCD/S-P | 1.35% | 330 °C | 361.11 °C | 9.73% |


2.2. Sorption of Representative Phenolic Pollutants β-Naphthol (III) and Bisphenol-A (IV)
| Isotherm | Parameter | S-P1 a | S-P0.5 a | βCD-P1 a | αCDP2 a | αCDP1 a | βCD/S-P a | αCD/S-P a | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | ||
| Freundlich | R2 | 0.993 | 0.999 | 0.983 | 0.987 | 0.993 | 1.000 | 0.992 | 0.998 | 0.986 | 0.994 | 0,997 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
| N | 0.887 | 0.999 | 0.857 | 1.077 | 1.507 | 1.326 | 1.430 | 1.515 | 1.863 | 1.575 | 1.1248 | 1.496 | 1.445 | 1.319 | |
| KF × 103 | 2.151 | 19.111 | 1.206 | 23.004 | 199.149 | 340.003 | 243.777 | 627.696 | 623.005 | 902.217 | 56.067 | 404.501 | 146.413 | 193.438 | |
| Langmuir | R2 | 0.088 | 0.063 | 0.383 | 0.010 | 0.844 | 0.816 | 0.895 | 0.867 | 0.858 | 0.921 | 0.771 | 0.817 | 0.807 | 0.749 |
| KL | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0.040 | 0.119 | 0.064 | 0,150 | 0.066 | 0.225 | 0.021 | 0.083 | 0.032 | 0.060 | |
| qmax (mg/g) | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 67.788 | 200.275 | 97.362 | 148.723 | 61.667 | 148.643 | 78.724 | 135.896 | 66.112 | 164.027 | |
| Solvent | Isotherm | Parameter | S-P1 a | βCD-P1 a | αCDP1 a | βCD/S-P a | αCD/S-P a | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| III | IV | III | IV | III | IV | III | IV | III | IV | |||
| MeOH | Freundlich | R2 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.970 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.998 | 0.959 | 0.996 | 0.993 | 0.993 |
| N | 0.620 | 1.016 | 1.554 | 1.457 | 1.164 | 1.451 | 1.542 | 1.383 | 1.065 | 1.240 | ||
| KF × 103 | 57.487 | 66.497 | 1417.224 | 725.786 | 339.596 | 752.014 | 1631.827 | 390.589 | 199.708 | 240.918 | ||
| Langmuir | R2 | 0.578 | 0.308 | 0.972 | 0.883 | 0.980 | 0.838 | 0.966 | 0.840 | 0.790 | 0.874 | |
| KL | n/a | n/a | 0.707 | 0.295 | 0.238 | 0.313 | 0.856 | 0.169 | 0.173 | 0.136 | ||
| qmax (mg/g) | n/a | n/a | 69.153 | 72.826 | 119.317 | 75.043 | 76.231 | 56.642 | 190.905 | 67.717 | ||
| DMSO | Freundlich | R2 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.984 | 0.996 | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.944 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 0.994 |
| N | 0.927 | 1.068 | 1.459 | 1.298 | 1.066 | 1.291 | 1.290 | 1.234 | 1.050 | 1.159 | ||
| KF × 103 | 32.998 | 43.205 | 865.455 | 309.468 | 159.151 | 360.703 | 598.517 | 161.121 | 105.484 | 117.209 | ||
| Langmuir | R2 | 0.271 | 0.872 | 0.947 | 0.902 | 0.838 | 0.944 | 0.850 | 0.822 | 0.747 | 0.944 | |
| KL | n/a | 0.035 | 0.403 | 0.135 | 0.135 | 0.192 | 0.341 | 0.838 | 0.091 | 0.076 | ||
| qmax (mg/g) | n/a | 80.137 | 69.844 | 66.944 | 185.832 | 67.727 | 88.838 | 0.838 | 256.673 | 66.944 | ||
2.3. Sorption of Bioactive Compounds

2.3.1. Sorption of Progesterone (V)
| Isotherm | Parameter | S-P1 | βCD-P1 | αCD-P1 | βCD/S-P | αCD/S-P | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | V | VI | V | V | VI | V | ||||||
| Freundlich | R2 | 0.992 | 0.993 | 0.974 | 0.992 | 0.994 | 0.999 | 0.981 | ||||
| N | 1.171 | 1.222 | 1.036 | 1.118 | 1.214 | 0.985 | 1.198 | |||||
| KF × 103 | 114.040 | 291.825 | 10,411.744 | 84.983 | 442.241 | 8.915 | 110.339 | |||||
| Langmuir | R2 | 0.751 | 0.972 | 0.275 | 0.755 | 0.974 | 0.107 | 0.647 | ||||
| KL | 0.099 | 0.281 | na | 0.077 | 0.452 | na | 0.093 | |||||
| qmax (mg/g) | 5.807 | 6.645 | na | 6.480 | 7.928 | na | 5.074 | |||||
2.3.2. Sorption of Curcumin
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of DVS Cross-Linked Homo-Polymers (S-Pn and CD-Pn)
3.3. Synthesis of DVs Cross-Linked Hetero-CDPs (CDS/S-P)
3.4. Characterization of DVS Cross-Linked Polymers
3.5. Sorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van de Manakker, F.; Vermonden, T.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Hennink, W.E. Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Pharmaceutical/Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3157–3175. [Google Scholar]
- Landy, D.; Mallard, I.; Ponchel, A.; Monflier, E.; Fourmentin, S. Remediation technologies using cyclodextrins: An overview. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2012, 10, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, D.; Mallard, I.; Ponchel, A.; Monflier, E.; Fourmentin, S. Cyclodextrins for Remediation Technologies. In Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Lichtfouse, E., Schwarzbauer, J., Robert, D., Eds.; Springer: Dondrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 47–81. [Google Scholar]
- Heidel, J.D.; Schluep, T. Cyclodextrin-Containing Polymers: Versatile Platforms of Drug Delivery Materials. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ritter, H. Cyclodextrin functionalized polymers as drug delivery systems. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 38–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Morcellet, M. Synthesis and applications of adsorbents containing cyclodextrins. J. Sep. Sci. 2002, 25, 789–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, A. Adsorption: From theory to practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 93, 135–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palem, C.R.; Siva, C.K.; Subrahmanyam, P.V.R.S.; Rao, Y.M. Cyclodextrins and their Derivatives in Drug Delivery: A Review. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2012, 6, 255–279. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.; Harikumar, S.L.; Kaur, A. Cyclodextrins: An excipient tool in drug delivery. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2012, 3, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, P.X. Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular systems for drug delivery: Recent progress and future perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, A. Cyclodextrins as Drug Carrier Molecule: A Review. Sci. Pharm. 2008, 76, 567–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, T.; Hetenyi, C.; Lv, Y.; van der Spoel, D. Cooperative Binding of Cyclodextrin Dimers to Isoflavone Analogues Elucidated by Free Energy Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 7163–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Loh, X.J. Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular architectures: Syntheses, structures, and applications for drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Crini, G. Environmental applications of water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin- epichlorohydrin polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 344–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, H.; Makihata, Y.; Fukunaga, K. Preparation of crosslinked β-cyclodextrin polymer beads and their application as a sorbent for removal of phenol from wastewater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmen, E.Y.; Sezgin, M.; Yilmaz, A.; Yilmaz, M. Synthesis of β-cyclodextrin and starch based polymers for sorption of azo dyes from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, C.-S.; Huang, W.-Q.; Hu, J.-L. Water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin polymer crosslinked by citric acid: synthesis and adsorption properties toward phenol and methylene blue. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 63, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, C.; Tian, Z.; Shen, X. Synthesis and properties of water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin polymer crosslinked by citric acid with PEG-400 as modifier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, S.; Lukasiewicz, M.; Mazela, W.; Pajda, M.; Kasprzyk, W. Chemical structure of poly(β-cyclodextrin-co-citric acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 3511–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forristal, I. The chemistry of a,β-unsaturated sulfoxides and sulfones: an update. J. Sulfur Chem. 2005, 26, 163–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, D.C.; Gervay-Hague, J. Vinyl sulfones: Synthetic preparations and medicinal chemistry applications. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 793–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Sanfrutos, J.; Lopez-Jaramillo, J.; Ortega-Munoz, M.; Megia-Fernandez, A.; Perez-Balderas, F.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Vinyl sulfone: A versatile function for simple bioconjugation and immobilization. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Jaramillo, F.J.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Vinyl sulfone: A Multi-purpose Function in Proteomics. In Integrative Proteomics; Eastwood Leung, H.-C., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 301–326. [Google Scholar]
- Santoyo-González, F.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Morales-Sanfrutos, J. Polymeric Adsorbents Based on Polysaccharides and Cyclodextrins for Water Purification. ES Patent 2334756 A1, 15 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, J.; Jimenez, V.; Belmar, J.; Mansilla, H.D.; Alderete, J.B. Inclusion Complexation of Phenol Derivatives with a β-Cyclodextrin Based Polymer. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2012, 53, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abay, I.; Denizli, A.; Biskin, E.; Salih, B. Removal and pre-concentration of phenolic species onto β-cyclodextrin modified poly(hydroxyethylmethacrylate-ethyleneglycoldimethacrylate) microbeads. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, H.; Makihata, Y.; Fukunaga, K. Efficient phenol removal of wastewater from phenolic resin plants using crosslinked cyclodextrin particles. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, A.; Peñas, F.J.; Isasi, J.R.; Garcia-Zubiri, I.X.; Gonzalez-Galiano, G. Extraction of phenols from aqueous solutions by β-cyclodextrin polymers. Comparison of sorptive capacities with other sorbents. React. Funct. Polym. 2008, 68, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, J.W.; Fan, Y.F.; Tao, S.Y. Adsorption behavior of β-cyclodextrin polymer to phenol in aqueous solution. Adv. Mat. Res. 2012, 554–556, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Han, P.; Lü, X. A facile Reremoval of phenol in wastewater using crosslinked β-cyclodextrin particles with ultrasonic treatment. Clean Soil Air Water 2012, 42, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.A.; Hansen, L.D. Thermodynamics of binding of guest molecules to α- and β-cyclodextrins. J. Chem. Soc. Perk. Trans. 2 1973, 15, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Hussain, M.; Ali, M.; Muushar, M.; Tabassan, M.A.R.; Mohsin, M.; Naisr, H.A.A. Evolution of Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm for potassium adsorption phenomena. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2013, 6, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, S.A.; Villeneuve, D.L.; Snyder, E.M.; Giesy, J.P. Identification and Quantification of Estrogen Receptor Agonists in Wastewater Effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3620–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, C.A.; Dome, P.B.; Klecka, G.M.; Oblock, S.T.; Harris, L.R. A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 2149–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howdeshell, K.L.; Peterman, P.H.; Judy, B.M.; Taylor, J.A.; Orazio, C.E.; Ruhlen, R.L.; vom Saal, F.S.; Welshons, W.V. Bisphenol A is released from used polycarbonate animal cages into water at room temperature. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-H.; Zhou, B.-X.; Cai, W.-M. The solubility behavior of bisphenol A in the presence of surfactants. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 2511–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hong, C.; Pan, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, L. Removal enhancement of 1-naphthol and 1-naphthylamine in single and binary aqueous phase by acid–basic interactions with polymer adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaoka, M.; Hayashi, K. Adsorption of bisphenol A by cross-linked β-cyclodextrin polymer. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 44, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, M.; Kawasaki, N.; Nakamura, T.; Tanada, S. Removal of bisphenol A in soil by cyclodextrin derivatives. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2001, 79, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Inclusion complexes of bisphenol A with cyclomaltoheptaose (β-cyclodextrin): solubilization and structure. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 2439–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegers-Hochschild, F.; Schwarze, J.-E.; Borrero, C. Delivery routes of progesterone in assisted reproduction. Expert Rev. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 1, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Trotta, F.; Carlotti, M.E.; Possetti, B.; Trotta, M. Nanoparticles derived from amphiphilic γ-cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memisoglu, E.; Bochot, A.; Sen, M.; Duchene, D.; Hincal, A.A. Non-surfactant nanospheres of progesterone inclusion complexes with amphiphilic β-cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 251, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, M.; Duchene, D.; Puisieux, F.; Wouessidjewe, D. Development of a new colloidal drug carrier from chemically-modified cyclodextrins: Nanospheres and influence of physicochemical and technological factors on particle size. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 129, 113–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Peira, E.; Caputo, O.; Gasco, M.R. Solid lipid nanoparticles as carriers of hydrocortisone and progesterone complexes with β-cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 182, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, B.; Cerchiara, T.; Bigucci, F.; Caponio, D.; Zecchi, V. Bovine serum albumin nanospheres carrying progesterone inclusion complexes. Drug Deliv. 2005, 12, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silveira, A.M.; Ponchel, G.; Puisieux, F.; Duchene, D. Combined poly(isobutyl cyanoacrylate) and cyclodextrins nanoparticles for enhancing the encapsulation of lipophilic drugs. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerchiara, T.; Luppi, B.; Bigucci, F.; Zecchi, V. Effect of chitosan on progesterone release from hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 258, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, I.; Bateson, M.; Bari, M.; Joshi, H.N. Synergistic effect of PEG-400 and cyclodextrin to enhance solubility of progesterone. AAPS PharmSciTech 2003, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiani-Skiba, M.; Barbot, C.; Bounoure, F.; Joudieh, S.; Skiba, M. Solubility and Dissolution Rate of Progesterone-Cyclodextrin-Polymer Systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2006, 32, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Fridfriksdottir, H.; Sigurdardottir, A.M.; Ueda, H. The effect of water-soluble polymers on drug-cyclodextrin complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 110, 169–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishiya, T.; Shibata, M.; Kakazu, M.; Asanuma, H.; Komiyama, M. Molecularly imprinted cyclodextrins as selective receptors for steroids. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 2265–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Curcumin Nanomedicine: A Road to Cancer Therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1994–2010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Lu, L.; Song, L.; Guo, S.; Huang, S. Recent progress in studying curcumin and its nano-preparations for cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1974–1993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naksuriya, O.; Okonogi, S.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Hennink, W.E. Curcumin nanoformulations: A review of pharmaceutical properties and preclinical studies and clinical data related to cancer treatment. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3365–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, E.; Grootveld, M.; Soares, G.; Henriques, M. Cyclodextrins as encapsulation agents for plant bioactive compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C. Poly(β-cyclodextrin)curcumin self-assembly: A novel approach to improve curcumin delivery and its therapeutic efficacy in prostate cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baglole, K.N.; Boland, P.G.; Wagner, B.D. Fluorescence enhancement of curcumin upon inclusion into parent and modified cyclodextrins. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2005, 173, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.D. Using XPowder: A software package for powder X-ray diffraction analysis; Spain, 2004. Available online: http://www.xpowder.com. (accessed on 10 October 2014).
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales-Sanfrutos, J.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.J.; Elremaily, M.A.A.; Hernández-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3565-3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033565
Morales-Sanfrutos J, Lopez-Jaramillo FJ, Elremaily MAA, Hernández-Mateo F, Santoyo-Gonzalez F. Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents. Molecules. 2015; 20(3):3565-3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033565
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales-Sanfrutos, Julia, Francisco Javier Lopez-Jaramillo, Mahmoud A. A. Elremaily, Fernando Hernández-Mateo, and Francisco Santoyo-Gonzalez. 2015. "Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents" Molecules 20, no. 3: 3565-3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033565
APA StyleMorales-Sanfrutos, J., Lopez-Jaramillo, F. J., Elremaily, M. A. A., Hernández-Mateo, F., & Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. (2015). Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents. Molecules, 20(3), 3565-3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20033565