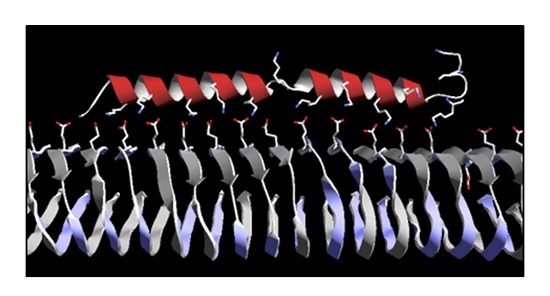
Preclinical Validation of the Heparin-Reactive Peptide p5+14 as a Molecular Imaging Agent for Visceral Amyloidosis
Abstract
Share and Cite
Wall, J.S.; Martin, E.B.; Richey, T.; Stuckey, A.C.; Macy, S.; Wooliver, C.; Williams, A.; Foster, J.S.; McWilliams-Koeppen, P.; Uberbacher, E.; et al. Preclinical Validation of the Heparin-Reactive Peptide p5+14 as a Molecular Imaging Agent for Visceral Amyloidosis. Molecules 2015, 20, 7657-7682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20057657
Wall JS, Martin EB, Richey T, Stuckey AC, Macy S, Wooliver C, Williams A, Foster JS, McWilliams-Koeppen P, Uberbacher E, et al. Preclinical Validation of the Heparin-Reactive Peptide p5+14 as a Molecular Imaging Agent for Visceral Amyloidosis. Molecules. 2015; 20(5):7657-7682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20057657
Chicago/Turabian StyleWall, Jonathan S., Emily B. Martin, Tina Richey, Alan C. Stuckey, Sallie Macy, Craig Wooliver, Angela Williams, James S. Foster, Penney McWilliams-Koeppen, Ed Uberbacher, and et al. 2015. "Preclinical Validation of the Heparin-Reactive Peptide p5+14 as a Molecular Imaging Agent for Visceral Amyloidosis" Molecules 20, no. 5: 7657-7682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20057657
APA StyleWall, J. S., Martin, E. B., Richey, T., Stuckey, A. C., Macy, S., Wooliver, C., Williams, A., Foster, J. S., McWilliams-Koeppen, P., Uberbacher, E., Cheng, X., & Kennel, S. J. (2015). Preclinical Validation of the Heparin-Reactive Peptide p5+14 as a Molecular Imaging Agent for Visceral Amyloidosis. Molecules, 20(5), 7657-7682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20057657