Validation and Application of an Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Yuanhuacine Determination in Rat Plasma after Pulmonary Administration: Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a New Drug Delivery System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of the Experimental Condition
2.2. Method Validation
2.2.1. Specificity
2.2.2. Linearity of Calibration Curves and LLOQ
2.2.3. Precision and Accuracy
2.2.4. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.2.5. Sample Stability
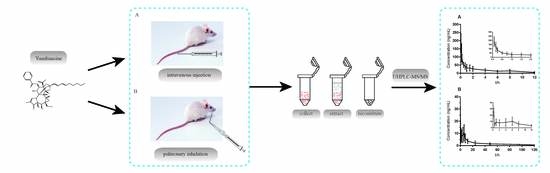
2.2.6. Application of Pharmacokinetic Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Instruments and Conditions
3.2.1. Instruments
3.2.2. UHPLC-MS/MS Conditions
3.3. Animals
3.4. Preparation of Pulmonary Inhaled Powder Samples and Intravenous Injection Samples
3.5. Preparation of Calibration Standards, Quality Control, and Internal Standard
3.6. Plasma Sample Preparation
3.7. Method Validation
3.7.1. Selectivity
3.7.2. Linearity and Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
3.7.3. Precision and Accuracy
3.7.4. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect
3.7.5. Stability
3.8. Pharmacokinetic Study
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 3rd ed.; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.Y.; Nam, J.W.; Seo, E.K.; Lee, S.K. Daphnane diterpene esters with anti-proliferative activities against human lung cancer cells from Daphne genkwa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, H.; Jin, X.Q. Determination of genkwanin in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application to a bioavailability study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 84, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.N.; Yin, L.H.; Xu, L.N.; Peng, J.Y. A simple and efficient protocol for large-scale preparation of three flavonoids from the flower of Daphne genkwa by combination of macroporous resin and counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2168–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, F.J.; Soper, C.J. The tigliane, daphnane and ingenane diterpenes, their chemistry, distribution and biological activities. A review. Lloydia 1978, 41, 193–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Guo, J.M.; Tang, Y.P.; Wu, L.; Tao, W.W.; Qian, Y.F.; Duan, J.A. Pharmacokinetic profile and metabolite identification of yuanhuapine, a bioactive component in Daphne genkwa by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 112, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Z.J.; Fan, C.Q.; Ding, J.; Yue, J.M. Novel diterpenoids with potent inhibitory activity against endothelium cell HMEC and cytotoxic activities from a well-known TCM plant Daphne genkwa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.X.; Li, X.N.; Zhang, F.H.; Yang, P.W.; Gao, X.J.; Song, Q.L. Preparation of yuanhuacine and relative daphne diterpene esters from Daphne genkwa and structure-activity relationship of potent inhibitory activity against DNA topoisomerase I. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wu, Q.L.; Sun, L.M.; Ruan, Q.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, M.; Duan, J.; Wang, D. Full Toxicity Assessment of Genkwa Flos and the Underlying Mechanism in Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Guo, J.M.; Qian, Y.F.; Guo, S.; Ma, C.H.; Duan, J.A. Toxicity of daphnane-type diterpenoids from Genkwa Flos and their pharmacokinetic profile in rat. Phytomedicine 2013, 21, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Gu, L.Q.; Zhang, R.W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.H.; Ju, P.; Ma, B.; Zhang, K.; Bi, K.; Chen, X. Evaluation of the indicative roles of seven potential biomarkers on hepato-nephrotoxicity induced by Genkwa Flos. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfagih, I.; Kunda, N.; Alanazi, F.; Dennison, S.R.; Somavarapu, S.; Hutcheon, G.A.; Saleem, I.Y. Pulmonary Delivery of Proteins Using Nanocomposite Microcarriers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 4386–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sou, T.; Meeusen, E.N.; Veer, M.D.; Morton, D.A.V.; Kaminskas, L.M.; McIntosh, M.P. New developments in dry powder pulmonary vaccine delivery. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunda, N.K.; Somavarapu, S.; Gordon, S.B.; Hutcheon, G.A.; Saleem, I.Y. Nanocarriers targeting dendritic cells for pulmonary vaccine delivery. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, B.; Bondesson, E.; Borgström, L.; Edsbäcker, S.; Eirefelt, S.; Ekelund, K.; Gustavsson, L.; Hegelund-Myrbäck, T. Pulmonary drug metabolism, clearance, and absorption. In Controlled Pulmonary Drug Delivery; Smyth, H.D.C., Hickey, A.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 21–50. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, A.; Schopf, L.; Bourassa, J.; Chen, H. Enhanced pulmonary delivery of fluticasone propionate in rodents by mucus-penetrating nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.W. Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Metabolism of Natural Anticancer Agent Yuanhuacine in Rabbits. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.X.; Yang, P.W.; Zhang, D.C.; Dong, W.Q.; Zhang, F.H.; Sun, Y.M. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and metabolism of novel DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor yuanhuacine in rabbit. Xenobiotica 2009, 39, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Guidance for Industry Bioanalytical Method Validation; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013.
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds Yuanhuacine is available from the authors.





| Compounds | Added Concentration (ng/mL) | Accuracy (%) | Presion (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | RE (%) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | ||||
| Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | ||||
| Yuanhuacine | 5 | 4.71 ± 0.42 | −5.8 | 4.71 ± 0.42 | 8.9 | 4.67 ± 0.36 | 7.8 |
| 75 | 76.58 ± 3.92 | 2.1 | 76.58 ± 3.92 | 5.1 | 74.21 ± 4.93 | 6.6 | |
| 400 | 393.53 ± 14.45 | −1.6 | 393.53 ± 14.45 | 3.7 | 401.94 ± 17.61 | 4.4 | |
| Compounds | Added Concentration (ng/mL) | Extraction Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Matrix Effect (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yuanhuacine | 5 | 80.31 ± 3.33 | 4.1 | 93.47 ± 4.60 | 4.9 |
| 75 | 77.86 ± 2.22 | 2.8 | 98.15 ± 5.11 | 5.2 | |
| 400 | 82.54 ± 4.54 | 5.5 | 99.69 ± 4.04 | 4.0 |
| Storage Condition | Added Concentration (ng/mL) | Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | RE (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term stability | 5 | 4.77 ± 0.14 | −4.6 | 2.9 |
| 75 | 74.38 ± 2.60 | −0.8 | 3.5 | |
| 400 | 395.34 ± 13.05 | −1.2 | 3.3 | |
| Long-term stability | 5 | 4.75 ± 0.40 | −5.0 | 8.3 |
| 75 | 74.77 ± 4.41 | −0.3 | 5.9 | |
| 400 | 399.14 ± 14.22 | −0.2 | 3.6 | |
| Freezing and thawing stability | 5 | 4.71 ± 0.37 | −5.8 | 7.9 |
| 75 | 74.37 ± 1.80 | −0.8 | 2.4 | |
| 400 | 392.62 ± 9.94 | −1.8 | 2.5 | |
| Post-preparative stability | 5 | 4.77 ± 0.32 | −4.6 | 6.8 |
| 75 | 74.36 ± 4.94 | −0.8 | 6.6 | |
| 400 | 397.82 ± 8.91 | −0.5 | 2.2 |
| Parameters | Intravenous Administration of Yuanhuacine | Pulmonary Administration of Yuanhuacine |
|---|---|---|
| AUC0–t (h∙ng/mL) | 252.09 ± 103.70 | 241.34 ± 106.53 |
| AUC0–∞ (h∙ng/mL) | 308.94 ± 133.42 | 302.22 ± 141.22 |
| MRT0–t (h) | 3.48 ± 0.52 | 35.38 ± 6.93 |
| MRT0–∞ (h) | 5.83 ± 2.61 | 65.38 ± 19.41 |
| t1/2 (h) | 5.28 ± 1.95 | 63.93 ± 33.08 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 185.35 ± 57.71 | 24.86 ± 6.59 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.08 | 0.25 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Liu, X.; Cai, H.; Shen, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Duan, J.; Chen, Z. Validation and Application of an Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Yuanhuacine Determination in Rat Plasma after Pulmonary Administration: Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a New Drug Delivery System. Molecules 2016, 21, 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121733
Li M, Liu X, Cai H, Shen Z, Xu L, Li W, Wu L, Duan J, Chen Z. Validation and Application of an Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Yuanhuacine Determination in Rat Plasma after Pulmonary Administration: Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a New Drug Delivery System. Molecules. 2016; 21(12):1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121733
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Man, Xiao Liu, Hao Cai, Zhichun Shen, Liu Xu, Weidong Li, Li Wu, Jinao Duan, and Zhipeng Chen. 2016. "Validation and Application of an Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Yuanhuacine Determination in Rat Plasma after Pulmonary Administration: Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a New Drug Delivery System" Molecules 21, no. 12: 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121733
APA StyleLi, M., Liu, X., Cai, H., Shen, Z., Xu, L., Li, W., Wu, L., Duan, J., & Chen, Z. (2016). Validation and Application of an Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Yuanhuacine Determination in Rat Plasma after Pulmonary Administration: Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of a New Drug Delivery System. Molecules, 21(12), 1733. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21121733