Analysis of Potential Amino Acid Biomarkers in Brain Tissue and the Effect of Galangin on Cerebral Ischemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Validation
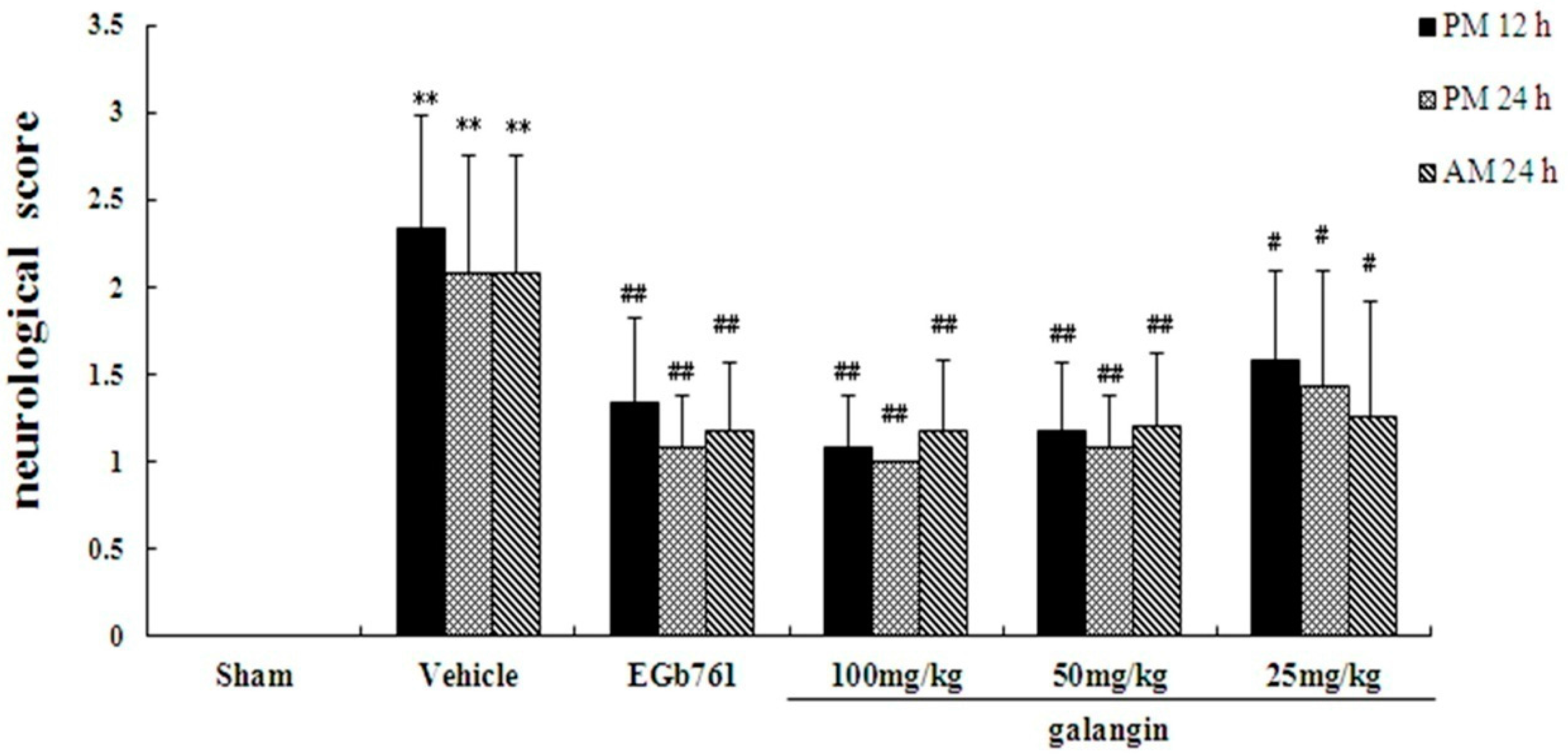
2.2. Assessment of Neurological Defects
2.3. Effect of Galangin on the Level Changes of AAs in Rat Brain Tissue and Identification of Biomarkers
2.4. Metabolite-Protein Interaction Networks
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Animal Models and Experimental Protocol
4.4. Assessment of Neurological Defects
4.5. Brain Tissue Homogenate Sampling and Preparation
4.6. Instrumentation (Chromatographic and MS Spectrum Conditions)
4.7. Identification of the Endogenous AAs
4.8. Data Analysis
4.9. Network Analysis
4.10. Molecule Docking
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciolino, H.P.; Yeh, G.C. The flavonoid galangin is an inhibitor of CYP1A1 activity and an agonist/antagonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Brit. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebringer, L.; Dobias, J.; Krajcvoic, J.; Polónyi, J.; Krizková, L.; Lahitová, N. Antimutagens reduce ofloxacin-induced bleaching in Euglena gracilis. Mutat. Res. 1996, 359, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, A.S.; Anuradha, C.V. Effect of galangin supplementation on oxidative damage and inflammatory changes in fructose-fed rat liver. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2011, 193, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.C.; Ho, F.M.; Chao, P.D.L.; Chen, C.P.; Jeng, K.C.; Hsu, H.B.; Lee, S.T.; Wen, T.W.; Lin, W.W. Inhibition of iNOS gene expression by quercetin is mediated by the inhibition of IκB kinase, Nuclear factor-kappa B and STAT1, and depends on heme oxygenase-1 induction in mouse BV-2 microglia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 521, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blonska, M.; Bronikowska, J.; Pietsz, G.; Czuba, Z.P.; Scheller, S.; Krol, W. Effects of ethanol extract of propolis (EEP) and its flavones on inducible gene expression in J774A.1 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 91, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, S.; Vellecco, V.; Alfieri, A.; Mascolo, N.; Cicala, C. Vasorelaxant effect of the flavonoid galangin on isolated rat thoracic aorta. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.L.; Sulaiman, S.A. The potential role of honey and its polyphenols in preventing heart diseases: A review. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. 2010, 7, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Wu, C.H.; Zhu, L.; Gao, J.; Fang, J.; Li, D.; Fu, M.; Liang, R.; Wang, L.; Cheng, M.; et al. By improving regional cortical blood flow, attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction and sequential apoptosis galangin acts as a potential neuroprotective agent after acute ischemic stroke. Molecules 2012, 17, 13403–13423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roessner, U.; Bowne, J. What is metabolomics all about? Biotechniques 2009, 46, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.; Gill, R.S.; Schiller, D.; Sawyer, M.B. Potential role of metabolomics in diagnosis and surveillance of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 20, 12874–12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, R.J.; Preiss, D.; Welsh, P.; Burgess, K.E.; Nelson, S.M.; Lawlor, D.A.; Sattar, N. The emergence of proton nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics in the cardiovascular arena as viewed from a clinical perspective. Atherosclerosis 2014, 237, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, P.L. Mass Spectrometry Strategies for Clinical Metabolomics and Lipidomics in Psychiatry, Neurology, and Neuro-Oncology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Zhu, L.; Lu, J.L. Application of metabolomics in autoimmune diseases: Insight into biomarkers and pathology. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 279, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.S.; Shearer, J. Metabolomics and Type 2 Diabetes: Translating Basic Research into Clinical Application. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Zhou, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Tissue amino acid profile could be used to differentiate advanced adenoma from colorectal cancer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 118, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, K.W.; Lees, K.R. Excitatory amino acid antagonists for acute stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, 3, CD001244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bame, M.; Grier, E.R.; Needleman, R.; Donadoni, C.; Salani, S.; Simone, C.; Falcone, M.; Riboldi, G.; Govoni, A.; Bresolin, N.; et al. Amino Acids as biomarkers in the SOD1G93A mouse model of ALS. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 19, 2782–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, Z.L.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Nan, J.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. System-wide assembly of pathways and modules hierarchically reveal metabolic mechanism of cerebral ischemia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, Y.; Sakaiy, R.; Kimura, Y. Metabolomics and its potential for assessment of adequacy and safety of amino acid intake. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2097S–2100S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irie, M.; Fujimura, Y.; Yamato, M.; Miura, D.; Wariishi, H. Integrated MALDI-MS imaging and LC-MS techniques for visualizing spatiotemporal metabolomic dynamics in a rat stroke model. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinzman, J.M.; DiNapoli, V.A.; Mahoney, E.J.; Gerhardt, G.A.; Hartings, J.A. Spreading depolarizations mediate excitotoxicity in the development of acute cortical lesions. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 267, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.R.; Wang, J.S.; Yang, M.H.; Kong, L.Y. Neuroprotective effects of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction on ischemic stroke rats revealed by (1)H-NMR metabolomics approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 1, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.X.; Liang, S.W.; Wang, S.W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S. 1H-NMR-based metabonomic analysis of the effect of optimized rhubarb aglycone on the plasma and urine metabolic fingerprints of focal cerebral ischemia–reperfusion rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yang, H.J.; Chen, J.X.; Fang, J.; Chen, C.; Liang, R.; Yang, G.; Wu, H.; Wu, C.; Li, S.J. Analysis of serum metabolites for the discovery of amino acid biomarkers and the effect of galangin on cerebral ischemia. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 2311–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Chen, J.X.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Wen, L.; Gao, K.; Chen, X.; Xiong, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.J. Wnt/β-catenin coupled with HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathways involved in galangin neurovascular unit protection from focal cerebral ischemia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16151–16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Fu, Q.; Leung, K.; Wong, Z.C.; Choi, R.C.; Tsim, K.W. The establishment of a sensitive method in determining different neurotransmitters simultaneously in rat brains by using liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floyd, R.A. Role of oxegen free radicals in carcinogenesis and brain ischemia. Faseb J. 1990, 4, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, P.L.; Panahian, N.; Dalkara, T.; Fishman, M.C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Effects of cerebral ischemia in mice deficient in neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Science 1994, 265, 1883–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, S.; Sjostrom, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: A basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Minguez, P.; Doerks, T.; Stark, M.; Muller, J.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, W.S.; Yu, Z.; Herder, C.; Messias, A.C.; Floegel, A.; He, Y.; Heim, K.; Campillos, M.; Holzapfel, C.; Thorand, B.; et al. Novel biomarkers for pre-diabetes identified by metabolomics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.






| AAs + I.S. | m/z | Ion Transition | Dwell Time (s) | FV (V) | CE (eV) | Mean RT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naa | 176.1 | 176.1 > 134.3 | 20 | 80 | 0 | 6.176 |
| 176.1 > 88.1 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 6.176 | ||
| Ala | 90.1 | 90.1 > 44.2 | 10 | 45 | 10 | 4.466 |
| GABA | 104.1 | 104.1 > 87.2 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 4.077 |
| Phe | 166.3 | 166.3 > 120.3 | 10 | 90 | 10 | 8.833 |
| 166.3 > 103.2 | 10 | 90 | 20 | 8.833 | ||
| Tyr | 182.3 | 182.3 > 165 | 10 | 110 | 4 | 5.579 |
| 182.3 > 136.3 | 10 | 110 | 10 | 5.579 | ||
| Gly | 76.2 | 76.2 > 48.2 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 4.432 |
| 76.2 > 30.2 | 10 | 50 | 4 | 4.432 | ||
| Met | 150.2 | 150.2 > 133 | 10 | 55 | 4 | 5.432 |
| 150.2 > 104.2 | 10 | 55 | 5 | 5.432 | ||
| Trp | 205.2 | 205.2 > 188.3 | 10 | 90 | 7 | 10.535 |
| 205.2 > 146.2 | 10 | 90 | 17 | 10.535 | ||
| Asp | 134.2 | 134.2 > 88.2 | 10 | 60 | 5 | 4.620 |
| 134.2 > 74.2 | 10 | 60 | 12 | 4.620 | ||
| Ser | 106.1 | 106.1 > 60.2 | 10 | 70 | 10 | 4.478 |
| 106.1 > 42.2 | 10 | 70 | 10 | 4.478 | ||
| Glu | 148.2 | 148.2 > 102 | 10 | 90 | 4 | 4.570 |
| 148.2 > 84.2 | 10 | 90 | 10 | 4.570 | ||
| Hcy | 136.1 | 136.1 > 90.2 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 4.966 |
| 136.1 > 56.2 | 20 | 80 | 20 | 4.966 | ||
| acrylamide-d3 | 75.1 | 75.1 > 58.1 | 10 | 40 | 8 | 6.505 |
| 75.1 > 30.2 | 10 | 40 | 8 | 6.505 |
| Chemicals | Equations | Correlation Coefficient (r2) | Linear Range a (ng·mL−1) | LOD b (ng·mL−1) | LOQ c (ng·mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ala | y = 3.0611x + 0.0165 | 0.9999 | 10–5000 | 0.53 | 1.79 |
| GABA | y = 1.1833x − 0.0018 | 0.9991 | 10–5000 | 0.31 | 1.05 |
| Ser | y = 1. 0241x + 0.0230 | 0.9997 | 10–5000 | 0.49 | 1.67 |
| Asp | y = 0.6314x + 0.0040 | 0.9997 | 10–5000 | 0.49 | 1.67 |
| Gly | y = 0.5793x + 0.0018 | 0.9990 | 10–5000 | 0.51 | 1.73 |
| Hcy | y = 0.3371x + 07.73583 × 10−4 | 0.9966 | 1–500 | 0.10 | 0.35 |
| Glu | y = 1.5217x + 0.0102 | 0.9999 | 20–10000 | 0.47 | 1.59 |
| Met | y = 1.7855x + 0.0055 | 0.9993 | 1–500 | 0.05 | 0.18 |
| Phe | y = 7.4569x + 0.0922 | 0.9981 | 1–500 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| Naa | y = 0.0789x − 2.50132 × 10−4 | 0.9994 | 20–10000 | 0.64 | 2.17 |
| Tyr | y = 0.8392x + 0.0126 | 0.9981 | 1–500 | 0.05 | 0.18 |
| Trp | y = 4.6319x + 0.0199 | 0.9996 | 1–500 | 0.13 | 0.43 |
| Chemicals | Intra-Day Precision RSD (%, n = 6) | Inter-Day Precision RSD (%, n = 6) | Recovery (%, n = 6) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Mid | High | Low | Mid | High | ||
| GABA | 0.54 | 1.69 | 8.03 | 1.69 | 3.25 | 8.18 | 98.80 |
| Gly | 3.64 | 1.81 | 6.22 | 4.31 | 3.13 | 6.13 | 97.46 |
| Ala | 2.95 | 1.72 | 8.10 | 3.62 | 2.90 | 6.36 | 96.21 |
| Ser | 3.43 | 1.64 | 8.39 | 4.55 | 3.29 | 8.20 | 108.58 |
| Glu | 1.60 | 2.47 | 8.35 | 2.33 | 3.51 | 7.05 | 100.38 |
| Asp | 6.63 | 2.39 | 8.65 | 5.32 | 4.07 | 6.62 | 85.11 |
| Hcy | 3.78 | 3.99 | 7.56 | 4.66 | 4.91 | 9.42 | 114.87 |
| Met | 7.86 | 3.02 | 7.02 | 7.89 | 4.03 | 8.91 | 78.78 |
| Tyr | 10.97 | 4.11 | 7.52 | 9.73 | 6.60 | 9.58 | 69.71 |
| Naa | 3.07 | 1.69 | 9.16 | 2.87 | 3.41 | 9.25 | 107.96 |
| Phe | 5.70 | 3.36 | 8.43 | 6.16 | 3.24 | 6.77 | 72.10 |
| Trp | 8.72 | 6.57 | 7.99 | 6.41 | 7.20 | 9.83 | 75.72 |
| Chemicals | Stability RSD (%, n = 6) | Repeatability RSD (%, n = 6) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −80 °C Freeze | Freeze-Thaw | Room Temperature | 4 °C | ||
| GABA | 6.44 | 9.37 | 11.22 | 9.54 | 5.72 |
| Gly | 11.53 | 7.16 | 15.32 | 5.08 | 3.75 |
| Ala | 12.20 | 6.45 | 15.42 | 4.33 | 3.65 |
| Ser | 12.72 | 6.73 | 15.98 | 6.13 | 3.48 |
| Glu | 6.19 | 6.89 | 13.82 | 3.63 | 3.62 |
| Asp | 9.49 | 6.66 | 13.60 | 3.43 | 2.88 |
| Hcy | 16.90 | 8.07 | 6.51 | 8.75 | 8.35 |
| Met | 14.59 | 5.54 | 13.51 | 4.81 | 3.00 |
| Tyr | 11.85 | 9.48 | 15.07 | 7.28 | 6.61 |
| Naa | 12.52 | 6.60 | 6.70 | 4.61 | 3.22 |
| Phe | 9.47 | 4.87 | 13.70 | 3.90 | 3.26 |
| Trp | 8.95 | 5.63 | 7.84 | 5.02 | 2.90 |
| Proteins | MOE Docking of Endogenous Ligands | MOE Docking Scores of Galangin | Interacting Residues | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSD | Scores | |||
| GLUD1 | 1.256284 | −22.78383 | −26.44535 | Arg 211, Val 255, Met 111, Asn 349, Lys 126, Met 169 |
| GLUL | 0.9439976 | −35.19292 | −18.74692 | Arg 355 |
| GLS | 1.326625 | −21.21566 | −17.68718 | Tyr A394, Leu A321, Phe A322, Leu A323 |
| GAD1 | 3.128657 | −16.44727 | ||
| CTH | 1.960125 | −16.61392 | −10.80142 | Lys 210, Tyr 111, Arg 372, Tyr 338 |
| ATP1B3 | 3.068527 | −13.54975 | ||
| GOT2 | 1.691135 | −21.93334 | −19.29626 | Arg 258, Lys 250, Trp 133 |
| HP | 1.764202 | −15.15395 | −19.11285 | Ser 557, Tyr 646, Val 564, Val 635 |
| Proteins | Full Name | Pdb Number |
|---|---|---|
| GLUD1 | Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, mitochondrial | 3ETD |
| GLUL | Glutamine synthetase | 1FPY |
| GLS | Glutaminase | 3VOZ |
| GAD1 | Glutamate decarboxylase 1 | 4HKP |
| CTH | cystathionase | 2FQ6 |
| ATP1B3 | ATPase | 3N23 |
| GOT2 | Aspartate aminotransferase | 1IVR |
| HP | haptoglobin | 3QUG |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Chen, K.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, P.; Duan, F.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, S. Analysis of Potential Amino Acid Biomarkers in Brain Tissue and the Effect of Galangin on Cerebral Ischemia. Molecules 2016, 21, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040438
Yang R, Chen K, Zhao Y, Tian P, Duan F, Sun W, Liu Y, Yan Z, Li S. Analysis of Potential Amino Acid Biomarkers in Brain Tissue and the Effect of Galangin on Cerebral Ischemia. Molecules. 2016; 21(4):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040438
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ruocong, Kun Chen, Yanyan Zhao, Pengpeng Tian, Feipeng Duan, Wenli Sun, Yuxin Liu, Zhiyong Yan, and Shaojing Li. 2016. "Analysis of Potential Amino Acid Biomarkers in Brain Tissue and the Effect of Galangin on Cerebral Ischemia" Molecules 21, no. 4: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040438
APA StyleYang, R., Chen, K., Zhao, Y., Tian, P., Duan, F., Sun, W., Liu, Y., Yan, Z., & Li, S. (2016). Analysis of Potential Amino Acid Biomarkers in Brain Tissue and the Effect of Galangin on Cerebral Ischemia. Molecules, 21(4), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040438





