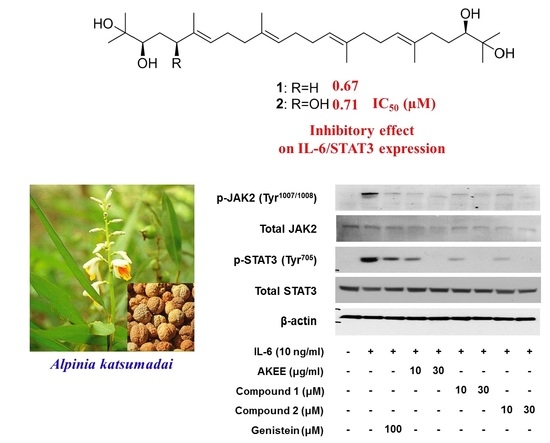
Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation
Abstract
Share and Cite
Jang, H.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.; Jung, K.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.-C. Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611
Jang H-J, Lee S-J, Lee S, Jung K, Lee SW, Rho M-C. Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation. Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Hyun-Jae, Seung-Jae Lee, Soyoung Lee, Kyungsook Jung, Seung Woong Lee, and Mun-Chual Rho. 2017. "Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611
APA StyleJang, H.-J., Lee, S.-J., Lee, S., Jung, K., Lee, S. W., & Rho, M.-C. (2017). Acyclic Triterpenoids from Alpinia katsumadai Inhibit IL-6-Induced STAT3 Activation. Molecules, 22(10), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101611