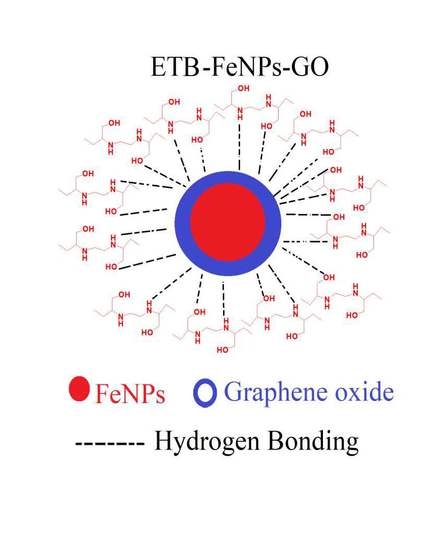
Nano-Formulation of Ethambutol with Multifunctional Graphene Oxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles Retains Its Anti-Tubercular Activity with Prospects of Improving Chemotherapeutic Efficacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization
2.1.1. Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD) of ETB-FeNPs-GO
2.1.2. Fourier Transformed Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopic Analysis
2.1.3. Raman Spectroscopy Analysis
2.1.4. HPLC and ICP Analysis
2.1.5. Transmission Electron Microscopic (TEM) Analysis
2.2. Magnetic Properties
2.2.1. In vitro Drug Release Study
2.2.2. Nano-Formulation Shows Antimycobacterial Activity
2.2.3. Biofilm Inhibition by ETB-FeNPs-GO
2.2.4. Cytotoxicity Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instrumentations
4.3. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide
4.4. Synthesis of Iron Oxide Magnetite Nanoparticles Fe3O4 (FeNPs)
4.5. Synthesis of Multifunctional Nanoparticles FeNPs-GO and Loading of Ethambutol (ETB)
4.6. Sustained Release of Nano-Formulation In Vitro
4.7. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis for ETB Loading
4.8 Biological Evaluation
4.8.1. MTT Assay for In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
4.8.2. Resazurin Microtiter Assay (REMA)
4.8.3. Modified SPOTi Assay
4.8.4. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saifullah, B.; Hussein, M.Z.; Al Ali, S.H.H. Controlled-release approaches towards the chemotherapy of tuberculosis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5451–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2016; World Health Ognization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; p. 192.
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nochehdehi, A.R.; Thomas, S.; Sadri, M.; Afghahi, S.S.S.; Hadavi, S.M. Iron Oxide Biomagnetic Nanoparticles (IO-BMNPs); Synthesis, Characterization and Biomedical Application. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Roy, I.; Yang, C.; Prasad, P.N. Nanochemistry and Nanomedicine for Nanoparticle-based Diagnostics and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2826–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Shi, X.; Cheng, L.; Luo, Y.; Dong, Z.; Gong, H.; Xu, L.; Zhong, Z.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Graphene-based nanocomposite as an effective, multifunctional, and recyclable antibacterial agent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2014, 6, 8542–8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wan, C.; Du, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Li, F. Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro evaluation of targeted gold nanoshelled poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles carrying anti p53 antibody as a theranostic agent for ultrasound contrast imaging and photothermal therapy. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saifullah, B.; Hussein, M.Z.B. Inorganic nanolayers: structure, preparation, and biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5609–5633. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, H.; Huang, D.; Feng, S.; Fujita, M.; Gao, X.-D. Chitosan-Functionalized Graphene Oxide as a Potential Immunoadjuvant. Nanomaterial 2017, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Z.H. Graphene Oxide Modified Electrodes for Dopamine Sensing. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.S.; Yi, D.K.; Kim, K. Study of antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide using Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthoosamy, K.; Abubakar, I.B.; Bai, R.G.; Loh, H.-S.; Manickam, S. Exceedingly Higher co-loading of Curcumin and Paclitaxel onto Polymer-functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide for Highly Potent Synergistic Anticancer Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorniani, D.; Saifullah, B.; Barahuie, F.; Arulselvan, P.; Hussein, M.Z.B.; Fakurazi, S.; Twyman, L.J. Graphene Oxide-Gallic Acid Nanodelivery System for Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbas, K.; Aleksandrzak, M.; Jedrzejczak, M.; Rakoczy, R.; Chen, X.; Mijowska, E. Chemical and magnetic functionalization of graphene oxide as a route to enhance its biocompatibility. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassaee, M.Z.; Motamedi, E.; Majdi, M. Magnetic Fe3O4-graphene oxide/polystyrene: Fabrication and characterization of a promising nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahuie, F.; Dorniani, D.; Saifullah, B.; Gothai, S.; Hussein, M.Z.; Pandurangan, A.K.; Arulselvan, P.; Norhaizan, M.E. Sustained release of anticancer agent phytic acid from its chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles for drug-delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2361–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Peng, C.; Luo, W.; Lv, M.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. Graphene-Based Antibacterial Paper. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4317–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotchey, G.P.; Allen, B.L.; Vedala, H.; Yanamala, N.; Kapralov, A.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Kagan, V.E.; Star, A. The Enzymatic Oxidation of Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barahuie, F.; Saifullah, B.; Dorniani, D.; Fakurazi, S.; Karthivashan, G.; Hussein, M.Z.; Elfghi, F.M. Graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for controlled release and targeted delivery of an anticancer active agent, chlorogenic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 74, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimzadeh, I.; Aghazadeh, M.; Doroudi, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Kolivand, P.H. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Coated with PEG/PEI for Biomedical Applications: A Facile and Scalable Preparation Route Based on the Cathodic Electrochemical Deposition Method. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2017, 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.K.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.W.; Min, J.J.; Kim, K.; Jon, S. Drug-loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined cancer imaging and therapy in vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 5362–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mornet, S.; Vasseur, S.; Grasset, F.; Duguet, E. Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical diagnosis and therapy. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2161–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorniani, D.; Hussein, M.Z.B.; Kura, A.U.; Fakurazi, S.; Shaari, A.H.; Ahmad, Z. Sustained Release of Prindopril Erbumine from Its Chitosan-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 23639–23653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Milani, A.S.; Stroeve, P. Synthesis, surface architecture and biological response of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for application in drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Biomed. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 1, 164–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, L.C.; Seabra, A.B.; Pelegrino, M.T.; de Araujo, D.R.; Bernardes, J.S.; Haddad, P.S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles dispersed in Pluronic F127 hydrogel: Potential uses in topical applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14496–14503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Tao, H.; Yang, K.; Feng, L.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z. A functionalized graphene oxide-iron oxide nanocomposite for magnetically targeted drug delivery, photothermal therapy, and magnetic resonance imaging. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorniani, D.; Hussein, M.Z.B.; Kura, A.U.; Fakurazi, S.; Shaari, A.H.; Ahmad, Z. Preparation of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles coated with gallic acid for drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M.; Sinitskii, A.; Sun, Z.; Slesarev, A.; Alemany, L.B.; Lu, W.; Tour, J.M. Improved Synthesis of Graphene Oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Magnetite nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and treatment monitoring: recent advances. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Ungphaiboon, S.; Srichana, T. The development of dimple-shaped chitosan carrier for ethambutol dihydrochloride dry powder inhaler. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annapurna, M.M.; Rao, M.E.B.; Kumar, B.V.V.R. Synthesis, Spectral Characterization and Evaluation of Pharmacodynamic Activity of Copper and Nickel Complexes of Ethambutol Dihydrochloride. J. Chem. 2006, 3, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Mungse, H.P.; Kumar, N.; Choudhary, S.; Jain, S.L.; Sain, B.; Khatri, O.P. Graphene oxide: An efficient and reusable carbocatalyst for aza-Michael addition of amines to activated alkenes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12673–12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.A.K.; Davies, B.R.; Noorbehesht, N.; Newman, P.; Church, T.L.; Harris, A.T.; Razal, J.M.; Minett, A.I. A New Raman Metric for the Characterisation of Graphene oxide and its Derivatives. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Kim, E.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Reduction of graphene oxide by resveratrol: A novel and simple biological method for the synthesis of an effective anticancer nanotherapeutic molecule. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbac, M.; Hsieh, Y.-P.; Farhat, H.; Kavan, L.; Hofmann, M.; Kong, J.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Defects in Individual Semiconducting Single Wall Carbon Nanotubes: Raman Spectroscopic and in Situ Raman Spectroelectrochemical Study. Nano. Lett. 2010, 10, 4619–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Jorio, A.; Hofmann, M.; Dresselhaus, G.; Saito, R. Perspectives on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Raman Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorniani, D.; Kura, A.U.; Hussein-Al-Ali, S.H.; Bin Hussein, M.Z.; Fakurazi, S.; Shaari, A.H.; Ahmad, Z. In Vitro Sustained Release Study of Gallic Acid Coated with Magnetite-PEG and Magnetite-PVA for Drug Delivery System. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahajuddin, S.A. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.A.; Dekker, L.; Kallumadil, M.; Southern, P.; Wilson, M.; Nair, S.P.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Parkin, I.P. Carboxylic acid-stabilised iron oxide nanoparticles for use in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6529–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, B.; Chrzastek, A.; Maitra, A.; Bullo, N.; Fakurazi, S. Novel Anti-Tuberculosis Nanodelivery Formulation of Ethambutol with Graphene Oxide. Molecules 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Saifullah, B.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Arulselvan, P.; Fakurazi, S.; Webster, T.J.; Geilich, B.M.; Hussein, M.Z. Synthesis, characterization, and efficacy of antituberculosis isoniazid zinc aluminum-layered double hydroxide based nanocomposites. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 2016, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadian, S.; Barar, J.; Saei, A.A.; Fakhree, M.A.A.; Omidi, Y. Cellular Toxicity of Nanogenomedicine in MCF-7 Cell Line: MTT assay. JOVE J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, N.K.; Tyagi, J.S. Resazurin reduction assays for screening of anti-tubercular compounds against dormant and actively growing Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium bovis BCG and Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Antimicrob. Chemoth. 2007, 60, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish, T.; Brown, A.C. Mycobacteria Protocols, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Danquah, C.A.; Maitra, A.; Gibbons, S.; Faull, J.; Bhakta, S. HT-SPOTi: A Rapid Drug Susceptibility Test (DST) to Evaluate Antibiotic Resistance Profiles and Novel Chemicals for Anti-Infective Drug Discovery. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2016, 17.8.1–17.8.12. [Google Scholar]
- Rizi, K.; Murdan, S.; Danquah, C.A.; Faull, J.; Bhakta, S. Development of a rapid, reliable and quantitative method—“SPOTi” for testing antifungal efficacy. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2015, 117, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, J.D.; Evangelopoulos, D.; Gupta, A.; Birchall, K.; Mwaigwisya, S.; Saxty, B.; McHugh, T.D.; Gibbons, S.; Malkinson, J.; Bhakta, S. Antitubercular specific activity of ibuprofen and the other 2-arylpropanoic acids using the HT-SPOTi whole-cell phenotypic assay. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelopoulos, D.; Bhakta, S. Rapid methods for testing inhibitors of mycobacterial growth. In Antibiotic Resistance Protocols, 2nd ed.; Gillespie, S.H., McHugh, T.D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 642, pp. 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. JOVE J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 47, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors B.S and M.Z.H. |



| Assignments | Free ETB | FeNPs | GO | ETB-FeNPsGO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-H Stretching | 3739 cm−1 | - | - | 3730 cm−1 |
| O-H Stretching | 3419 cm−1 | 3419 cm−1 | 3429 cm−1 | 3431 cm−1 |
| C-H Stretching | 2975 cm−1 | - | 2975 & 2809 cm−1 | 2924 cm−1 |
| C=O, C=C stretching | - | - | 1722 & 1629 cm−1 | 1630 cm−1 |
| C-N Stretching | 1315 cm−1 | - | - | 1384 cm−1 |
| C-O Stretching | 1060 cm−1 | 1034 cm−1 | ~1064 cm−1 | 1051 cm−1 |
| F-O stretching | - | 575 cm−1 | - | 583 cm−1 |
| Compound | REMA | Modified SPOTi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed MIC (µg/mL) | Effective MIC (µg/mL) | Observed MIC (µg/mL) | Effective MIC (µg/mL) | |
| ETB | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 |
| ETB-FeNPs-GO | 6.25 | 2.1 | 6.25 | 2.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saifullah, B.; Maitra, A.; Chrzastek, A.; Naeemullah, B.; Fakurazi, S.; Bhakta, S.; Hussein, M.Z. Nano-Formulation of Ethambutol with Multifunctional Graphene Oxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles Retains Its Anti-Tubercular Activity with Prospects of Improving Chemotherapeutic Efficacy. Molecules 2017, 22, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101697
Saifullah B, Maitra A, Chrzastek A, Naeemullah B, Fakurazi S, Bhakta S, Hussein MZ. Nano-Formulation of Ethambutol with Multifunctional Graphene Oxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles Retains Its Anti-Tubercular Activity with Prospects of Improving Chemotherapeutic Efficacy. Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101697
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaifullah, Bullo, Arundhati Maitra, Alina Chrzastek, Bullo Naeemullah, Sharida Fakurazi, Sanjib Bhakta, and Mohd Zobir Hussein. 2017. "Nano-Formulation of Ethambutol with Multifunctional Graphene Oxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles Retains Its Anti-Tubercular Activity with Prospects of Improving Chemotherapeutic Efficacy" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101697
APA StyleSaifullah, B., Maitra, A., Chrzastek, A., Naeemullah, B., Fakurazi, S., Bhakta, S., & Hussein, M. Z. (2017). Nano-Formulation of Ethambutol with Multifunctional Graphene Oxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles Retains Its Anti-Tubercular Activity with Prospects of Improving Chemotherapeutic Efficacy. Molecules, 22(10), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101697