From 2-Alkylsulfanylimidazoles to 2-Alkylimidazoles: An Approach towards Metabolically More Stable p38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
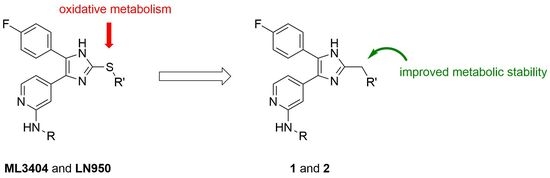
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.3. Microsomal Stability Studies
2.4. CYP Inhibition
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 2-Alkylimidzole 1
3.1.2. Synthesis of 2-Alkylimidzole 2
3.2. HLM Stability Test
3.3. CYP Inhibition Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachstetter, A.D.; Xing, B.; de Almeida, L.; Dimayuga, E.R.; Watterson, D.M.; van Eldik, L.J. Microglial p38α MAPK is a key regulator of proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation induced by toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands or beta-amyloid (Aβ). J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, K.; Floyd, R.A.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Nael, R.; Robinson, K.A.; Nguyen, X.; Pye, Q.N.; Stewart, C.A.; Geddes, J.; Markesbery, W.R.; et al. p38 Kinase is activated in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Kim, N.-J. Recent advances in the inhibition of p38 MAPK as a potential strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials. Gov Registration Number: NCT02423122. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02423122 (accessed on 17 August 2017).
- ClinicalTrials. Gov Registration Number: NCT02423200. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02423200 (accessed on 17 August 2017).
- Laufer, S.A.; Wagner, G.K.; Kotschenreuther, D.A.; Albrecht, W. Novel substituted pyridinyl imidazoles as potent anticytokine agents with low activity against hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 3230–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laufer, S.A.; Hauser, D.R.J.; Domeyer, D.M.; Kinkel, K.; Liedtke, A.J. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel Tri- and tetrasubstituted imidazoles as highly potent and specific ATP-mimetic inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase: Focus on optimized interactions with the enzyme’s surface-exposed front region. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4122–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, L.; Ramsay, E.E.; Manetsch, M.; Ge, Q.; Peifer, C.; Laufer, S.; Ammit, A.J. Novel p38 MAPK inhibitor ML3403 has potent anti-inflammatory activity in airway smooth muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 635, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziosi, L.; Mencarelli, A.; Santorelli, C.; Renga, B.; Cipriani, S.; Cavazzoni, E.; Palladino, G.; Laufer, S.; Burnet, M.; Donini, A.; et al. Mechanistic role of p38 MAPK in gastric cancer dissemination in a rodent model peritoneal metastasis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 674, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, D.A.; Silva, R.B.M.; de Souza, A.H.; Leite, C.E.; Nicoletti, N.F.; Campos, M.M.; Laufer, S.; Morrone, F.B. Efficacy and gastrointestinal tolerability of ML3403, a selective inhibitor of p38 MAP kinase and CBS-3595, a dual inhibitor of p38 MAP kinase and phosphodiesterase 4 in CFA-induced arthritis in rats. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, P.; Bäuerlein, C.; Jank, H.; Laufer, S. Targeting the ribose and phosphate binding site of p38 mitogeN-activated protein (MAP) kinase: Synthesis and biological testing of 2-alkylsulfanyl-, 4(5)-aryl-, 5(4)-heteroaryl-substituted imidazoles. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5630–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammerer, B.; Scheible, H.; Zurek, G.; Godejohann, M.; Zeller, K.P.; Gleiter, C.H.; Albrecht, W.; Laufer, S. In vitro metabolite identification of ML3403, a 4-pyridinylimidazole-type p38 MAP kinase inhibitor by LC-Qq-TOF-MS and LC-SPE-cryo-NMR/MS. Xenobiotica 2007, 37, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammerer, B.; Scheible, H.; Albrecht, W.; Gleiter, C.H.; Laufer, S. Pharmacokinetics of ML3403 ({4–5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-methylsulfanyl-3H-imidazol-4-yl-pyridin-2-yl}-(1-phenylethyl)-amine), a 4-Pyridinylimidazole-type p38 mitoge-activated protein kinase inhibitor. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, J.M.; Stahl, S.S. Highly practical copper(I)/TEMPO catalyst system for chemoselective aerobic oxidation of primary alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16901–16910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goettert, M.; Graeser, R.; Laufer, S.A. Optimization of a nonradioactive immunosorbent assay for p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 406, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansideri, F.; Lange, A.; El-Gokha, A.; Boeckler, F.M.; Koch, P. Fluorescence polarization-based assays for detecting compounds binding to inactive c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 and p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 503, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegzouti, H.; Goueli, S.A. (Eds.) Kinase Screening and Profiling: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.L.; Boehm, J.C.; Kassis, S.; Gorycki, P.D.; Webb, E.F.; Hall, R.; Sorenson, M.; Lee, J.C.; Ayrton, A.; Griswold, D.E.; et al. Pyrimidinylimidazole inhibitors of CSBP/P38 kinase demonstrating decreased inhibition of hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, T.; Price, A.L. The Effect of Cytochrome P450 metabolism on drug response, interactions, and adverse effects. Am. Fam. Phys. 2007, 76, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, P.; Jahns, H.; Schattel, V.; Goettert, M.; Laufer, S. Pyridinylquinoxalines and pyridinylpyridopyrazines as lead compounds for novel p38 alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, M.; Juchum, M.; Kelter, G.; Fiebig, H.; Laufer, S. Lung Cancer: EGFR Inhibitors with low Nanomolar activity against a therapy-resistant L858R/T790M/C797S mutant. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 10890–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1 and 2 are available from the authors. |








| Cpd | ELISA Assay p38α IC50 [nM] a | FP Assay p38α Ki [nM] a | HWB Assay TNF-α IC50 [nM] b |
|---|---|---|---|
| ML3403 | 40 ± 5 c | 38 ± 1 e | 2979 ± 874 |
| 1 | 25 ± 2 | 11 ± 3 | 2539 ± 20 |
| LN950 | 11 ± 0.9 d | 4 ± 1 e | 37 ± 4 d |
| 2 | 11 ± 5 | 1 ± 0.2 | 32 ± 1 |
| CYP | 1A2 | 2C9 | 2C19 | 2D6 | 3A4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML3403 a | 66.7 | 79.0 | 83.5 | 31.1 | 79.2 |
| 1 | 85.6 | 85.1 | 71.0 | 90.2 | 97.6 |
| LN950 | 28.0 | 91.5 | 63.0 | 41.5 | 61.0 |
| 2 | 69.4 | 61.9 | 83.6 | 78.8 | 92.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heider, F.; Haun, U.; Döring, E.; Kudolo, M.; Sessler, C.; Albrecht, W.; Laufer, S.; Koch, P. From 2-Alkylsulfanylimidazoles to 2-Alkylimidazoles: An Approach towards Metabolically More Stable p38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2017, 22, 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101729
Heider F, Haun U, Döring E, Kudolo M, Sessler C, Albrecht W, Laufer S, Koch P. From 2-Alkylsulfanylimidazoles to 2-Alkylimidazoles: An Approach towards Metabolically More Stable p38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2017; 22(10):1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeider, Fabian, Urs Haun, Eva Döring, Mark Kudolo, Catharina Sessler, Wolfgang Albrecht, Stefan Laufer, and Pierre Koch. 2017. "From 2-Alkylsulfanylimidazoles to 2-Alkylimidazoles: An Approach towards Metabolically More Stable p38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors" Molecules 22, no. 10: 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101729
APA StyleHeider, F., Haun, U., Döring, E., Kudolo, M., Sessler, C., Albrecht, W., Laufer, S., & Koch, P. (2017). From 2-Alkylsulfanylimidazoles to 2-Alkylimidazoles: An Approach towards Metabolically More Stable p38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules, 22(10), 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101729