Design, Synthesis of N-phenethyl Cinnamide Derivatives and Their Biological Activities for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Antioxidant, Beta-amyloid Disaggregating and Rescue Effects on Memory Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Pharmacology
2.2.1. Determination of Anti-Oxidant Activity Based on DPPH Assay
2.2.2. Inhibition of Cu2+-Induced Aβ Aggregation and Disaggregation
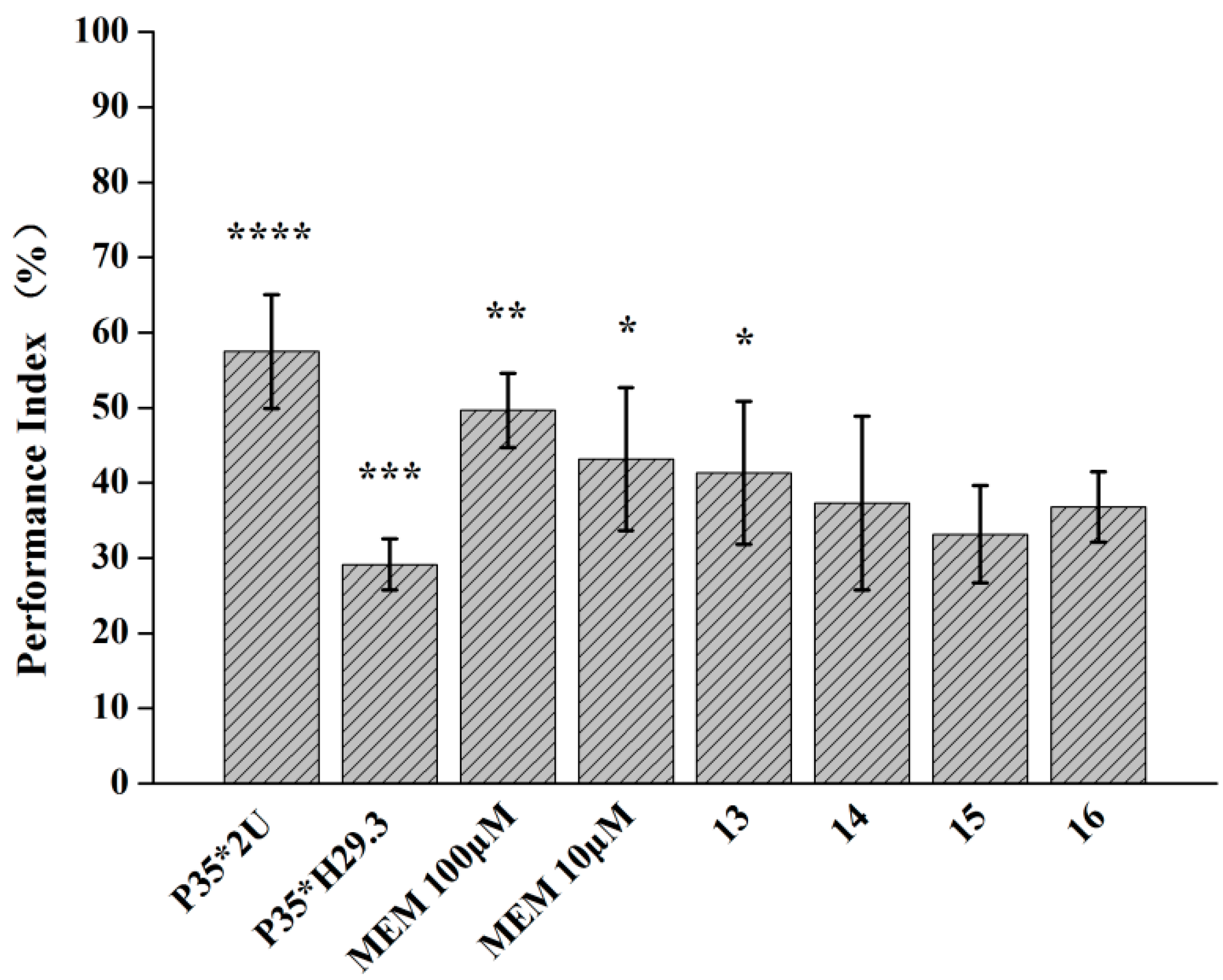
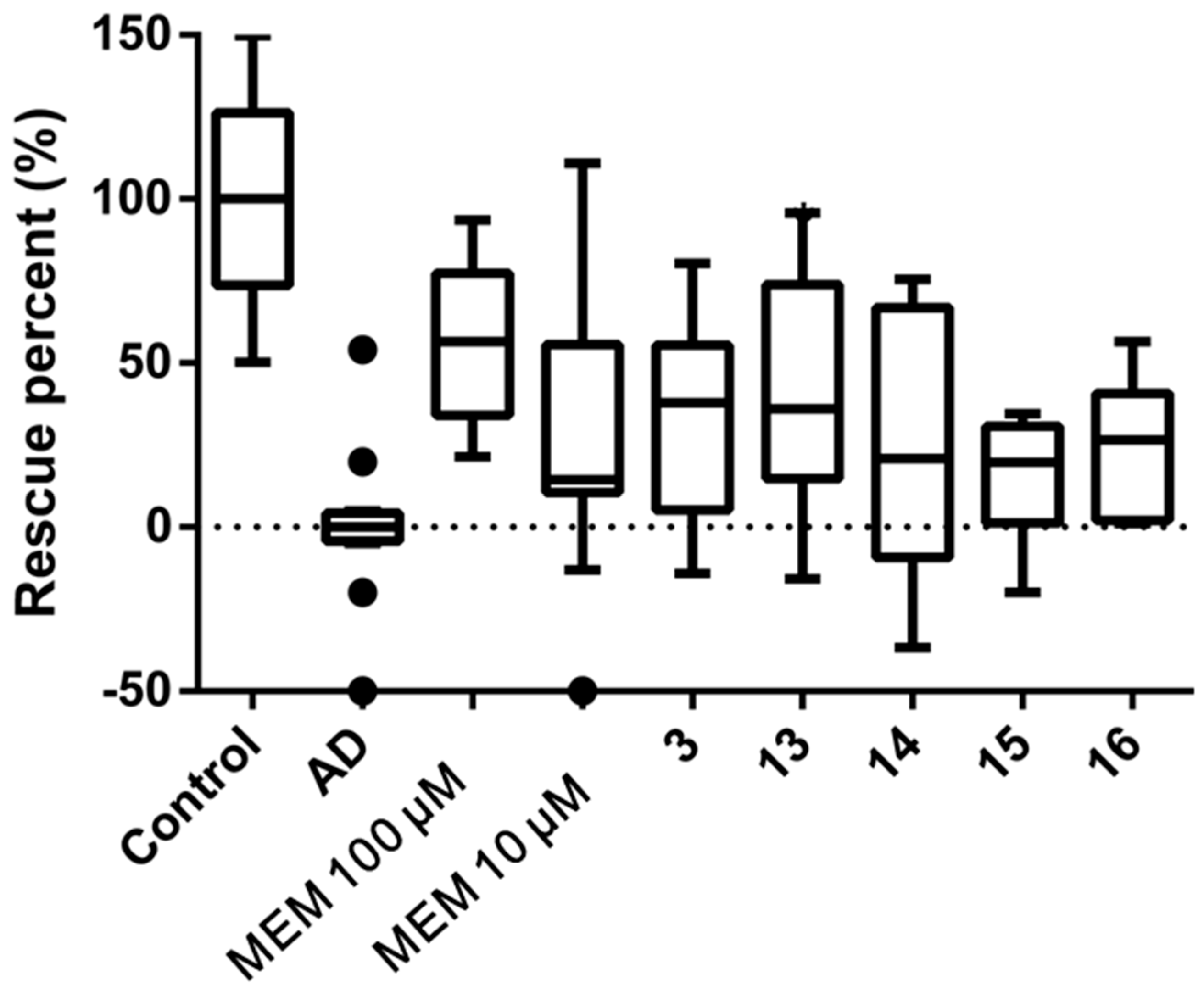
2.2.3. Pavlovian Olfactory Aversive Immediate Memory Test
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
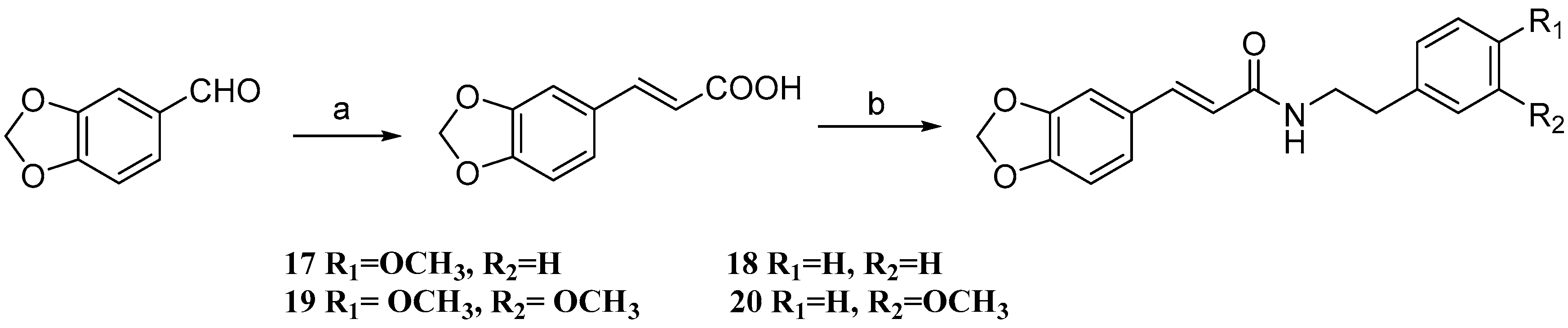
3.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of Compounds 1–20
3.2.1. Synthesis of Substituted Cinnamic Acids
3.2.2. Synthesis of Gx-50 Derivatives 1–20
3.2.3. Purity Check of Compounds 1–20 by HPLC/MS Analysis
3.3. Biological Assay
3.3.1. DPPH Assay
3.3.2. ThT Assay
3.4. Pavlov’s Olfactory Memory Test
3.4.1. Fly Stocks and Culture
3.4.2. Drug Intervention
3.4.3. Drosophila Olfactory Escape Behavior Test
4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz-Ruiz, P.; Rubio, L.; García-Palomero, E.; Dorronsoro, I.; del Monte-Millán, M.; Valenzuela, R.; Usán, P.; de Austria, C.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: new disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candeias, E.; Duarte, A.I.; Carvalho, C.; Correia, S.C.; Cardoso, S.; Santos, R.X.; Plácido, A.I.; Perry, G.; Moreir, P.I. The impairment of insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, T.; DeKosky, M.D. Pathology and pathways of Alzheimer’s disease with an update on new developments in treatment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, S314–S320. [Google Scholar]
- Blennow, K.; de Leon, M.J.D.; Zetterberg, H. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2006, 368, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, C.; Gauthier, S.; Corbett, A.; Brayne, C.; Aarsland, D.; Jones, E. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2011, 377, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsonego, A.; Zota, V.; Karni, A.; Krieger, J.I.; Bar-Or, A.; Bitan, G.; Budson, A.E.; Sperling, R.; Selkoe, D.J.; Weiner, H.L. Increased T cell reactivity to amyloid beta protein in older humans and patients with Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, D.S.; Bapat, A.M.; Ramteke, S.N.; Joshi, B.N.; Roussel, P.; Tomas, A.; Deschamps, P.; Kulkarni, P.P. Thiosemicarbazone modification of 3-acetyl coumarin inhibits Aβ peptide aggregation and protect against Aβ-induced cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benchekroun, M.; Romero, A.; Egea, J.; León, R.; Michalska, P.; Buendía, I.; Jimeno, M.L.; Jun, D.; Janockova, J.; Sepsova, V.; et al. The antioxidant additive approach for Alzheimer’s disease therapy: New ferulic (lipoic) acid plus melatonin modified tacrines as cholinesterases inhibitors, direct antioxidants, and nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 activators. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9967–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Samadi, A.; Unzeta, M.; Marco-Contelles, J. Analysis of the antioxidant properties of differently substituted 2- and 3-indolyl carbohydrazides and related derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.W.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Peng, I.F. Effects of Gardenia jasminoides extracts on cognition and innate immune response in an adult Drosophila model of Alzheimer’s disease. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.X.; Gu, H.; Xie, Z.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Arias, H.R.; Wei, D.Q.; Chou, K.C. Possible drug candidates for Alzheimer’s disease deduced from studying their binding interactions with α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Med. Chem. 2009, 5, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, S.; Tang, M.; Liang, D.; Xu, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Z. The suppressive effects of gx-50 on Aβ-induced chemotactic migration of microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Wei, D.; Qiao, Z. A novel drug candidate for Alzheimer’s disease treatment: Gx-50 derived from Zanthoxylum bungeanum. J. Alzheimer’s. Dis. 2013, 34, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.R.; Liu, J.; Li, J.Y.; Zheng, L.F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Q.J.; Wang, A.X.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, R.H.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of hydroxycinnamic acid hydrazide derivatives as inducer of caspase-3. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterenko, V.; Putt, K.S.; Hergenrother, P.J. Identification from a combinatorial library of a small molecule that selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14672–14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, A.P.; Kumar, S.; Varshney, V.; Singh, A.B.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sahu, D.P. Synthesis and antihyperglycemic activity of novel N-acyl-2-arylethylamines and N-acyl-3-coumarylamines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2301–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.C.; Chiu, H.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Chi, T.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Su, M.J. Antihyperglycemic effect of a caffeamide derivative, KS370G, in normal and diabetic mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10033–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, N.T.; Jin, S.Y.; Cho, D.J.; Kim, N.S.; Bae, E.H.; Han, D.; Han, B.H.; Kang, Y.H. Synthesis of substituted cinnamoyl-tyramine derivatives and their platelet anti-aggregatory activities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1997, 20, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W. A New Amide from the Stem Bark of Illicium difengpi and Its Anti-inflammatory Activity. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2015, 9, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Suh, J.H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Ho, C.T. Identification and Quantification of Potential Anti-inflammatory Hydroxycinnamic Acid Amides from Wolfberry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakami, S.; Shibuya, M.; Tseng, C.F.; Hanaoka, F.; Sankawa, U. Inhibition of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase by phenolic compounds. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 3960–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, M.H.V.; Criton, M. Phenylethylamide and Phenylmethylamide Derivatives as New Tyrosinase Inhibitors. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 301–303. [Google Scholar]
- Okombi, S.; Rival, D.; Bonnet, S.; Mariotte, A.M.; Perrier, E.; Boumendjel, A. Analogues of n-hydroxycinnamoylphenalkylamides as inhibitors of human melanocyte-tyrosinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2252–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarojini, B.K.; Vidyagayatri, M.; Darshanraj, C.G.; Bharath, B.R.; Manjunatha, H. DPPH scavenging assay of novel 1,3-disubstituted-1h-pyrazol-5-ols and their in silico studies on some proteins involved in alzheimers disease signaling cascade. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2010, 7, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ciau, D.; Cuevas-Glory, L.; Quijano, L.; Sauri-Duch, E. Chemical composition and antioxidant dpph activity of the floral and leaves essential oils of Cmontanoa speciosa DC. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, G.C.; Duh, P.D. Scavenging effect of methanolic extracts of peanut hulls on free-radical and active-oxygen species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizio, B.; Roberta, B.; Isabella, C.; Patrizia, G.; Annalisa, R. Synthesis and DPPH radical scavenging activity of novel compounds obtained from tyrosol and cinnamic acid derivatives. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 809–816. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, Y.; Picciano, M.; La Francois, J.; Duff, K. Fibrillar beta-amyloid evokes oxidative damage in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2001, 104, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.K.; Blancas-Mejia, L.M.; Weber, B.; Buchner, J.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Naiki, H.; Otzen, D. ThT 101: A primer on the use of thioflavin T to investigate amyloid formation. Amyloid 2017, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lv, P.C.; Guo, F.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, G.H.; Qian, S.S.; Zhu, H.L. Aromatic diacylhydrazine derivatives as a new class of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Tan, Y.; Xie, W.H.; Lei, H.; Cheung, H.Y.; Sun, H. A FRET-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for nitroxyl detection in living cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5438–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of orally available clioquinol-moracin m hybrids as multitarget-directed ligands for cognitive improvement in a rat model of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8616–8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, K.; Liu, H.P.; Chiang, A.S.; Hearn, S.A.; Konsolaki, M.; Zhong, Y. Dissecting the pathological effects of human β40 and β42 in Drosophila: A potential model for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6623–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Tully, T.; White, K. Human amyloid precursor protein ameliorates behavioral deficit of flies deleted for Appl gene. Neuron 1992, 9, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, K.; Chiang, H.C.; Hearn, S.A.; Hakker, I.; Gatt, A.; Shenton, C.; Granger, L.; Leung, A.; Iijima-Ando, K.; Zhong, Y. β42 mutants with different aggregation profiles induce distinct pathologies in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tully, T.; Quinn, W.G. Classical conditioning and retention in normal and mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1985, 157, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tully, T.; Preat, T.; Boynton, S.C.; Del Vecchio, M. Genetic dissection of consolidated memory in Drosophila. Cell 1994, 79, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.C.P.; Wallach, J.S.; Del Vecchio, M.; Wilder, E.L.; Zhou, H.; Quinn, W.G.; Tully, T. Induction of a dominant negative CREB transgene specifically blocks long-term memory in Drosophila. Cell 1994, 79, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–20 are not available from the authors. |
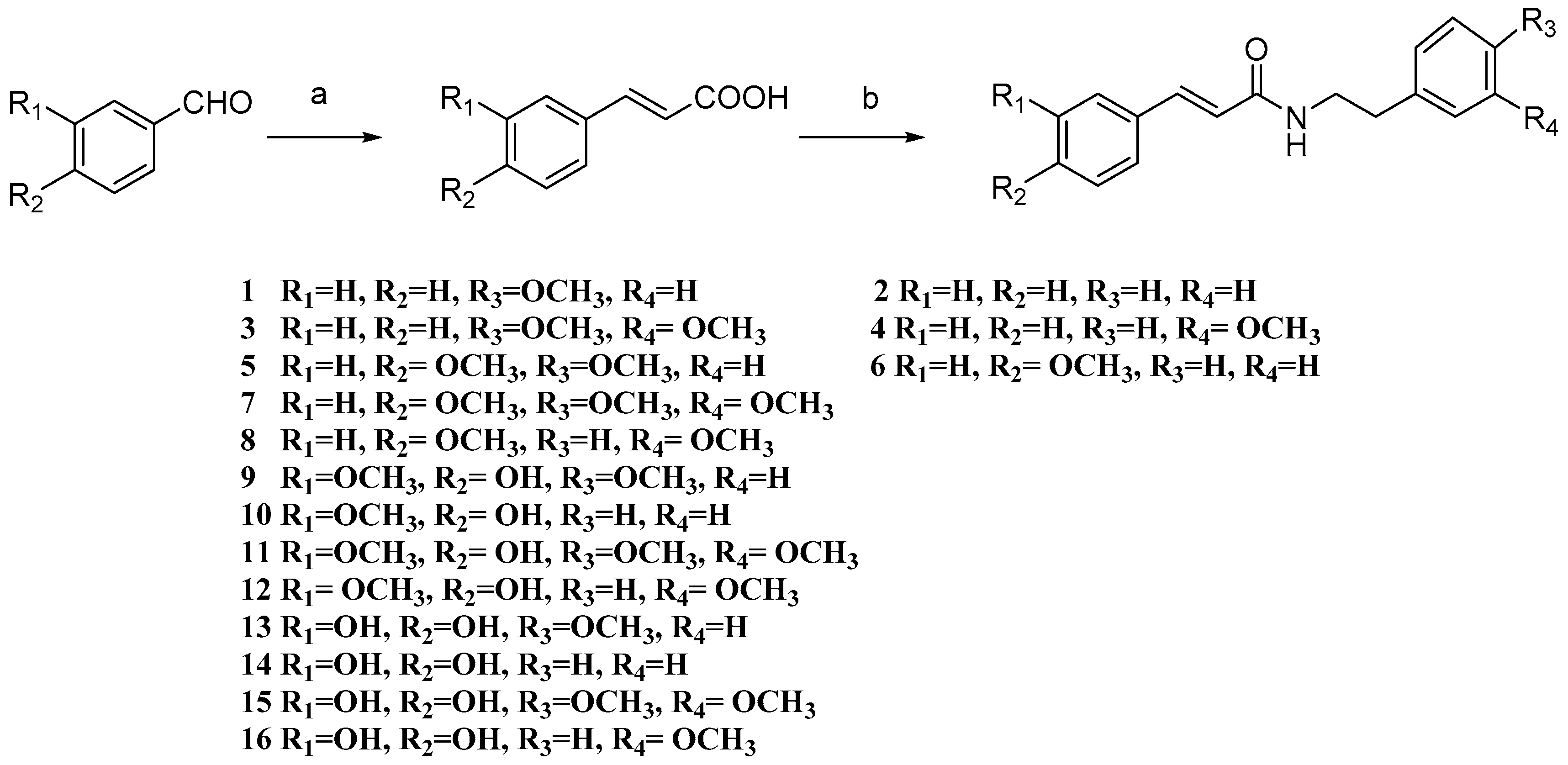
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Inhibition Ratio (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μM | 100 μM | 200 μM | |||||
| 1 | H | H | OCH3 | H | 2.97 ± 1.67 | 4.35 ± 2.29 | 4.93 ± 2.13 |
| 2 | H | H | H | H | 3.1 ± 0.30 | 6.69 ± 0.37 | 9.20 ± 0.67 |
| 3 | H | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | 2.92 ± 1.7 | 5.03 ± 2.01 | 6.18 ± 0.65 |
| 4 | H | H | H | OCH3 | 0.99 ± 0.55 | 2.91 ± 1.24 | 3.13 ± 0.59 |
| 5 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | 4.78 ± 2.8 | 9.78 ± 0.61 | 11.22 ± 0.43 |
| 6 | H | OCH3 | H | H | 1.08 ± 0.70 | 5.11 ± 2.06 | 12.91 ± 1.57 |
| 7 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | 3.61 ± 0.89 | 5.58 ± 0.78 | 9.58 ± 1.39 |
| 8 | H | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | 0.06 ± 2.63 | 2.81 ± 2.78 | 3.42 ± 0.78 |
| 9 | OCH3 | OH | OCH3 | H | 30.21 ± 1.52 | 36.28 ± 3.43 | 46.57 ± 0.86 |
| 10 | OCH3 | OH | H | H | 16.69 ± 0.46 | 34.06 ± 2.57 | 44.07 ± 2.20 |
| 11 | OCH3 | OH | OCH3 | OCH3 | 17.43 ± 0.46 | 40.28 ± 0.21 | 50.19 ± 1.90 |
| 12 | OCH3 | OH | H | OCH3 | 28.74 ± 0.78 | 46.93 ± 0.42 | 51.83 ± 1.42 |
| 13 | OH | OH | OCH3 | H | 54.34 ± 1.44 | 56.16 ± 1.78 | 56.37 ± 2.86 |
| 14 | OH | OH | H | H | 54.21 ± 1.21 | 55.01 ± 0.35 | 54.17 ± 2.62 |
| 15 | OH | OH | OCH3 | OCH3 | 57.85 ±0.15 | 59.96 ± 0.79 | 58.33 ± 2.71 |
| 16 | OH | OH | H | OCH3 | 58.86 ±0.43 | 60.85 ± 0.37 | 57.68 ± 0.54 |
| 17 | OCH3 | H | - | - | 2.13 ± 0.32 | 4.60 ± 0.33 | 4.82 ± 0.36 |
| 18 | H | H | - | - | 0.63 ± 0.27 | 1.99 ± 1.50 | 2.27 ± 1.52 |
| 19 | OCH3 | OCH3 | - | - | 1.44 ± 1.68 | 1.39 ± 0.85 | 2.02 ± 0.52 |
| 20 | H | OCH3 | - | - | 1.57 ± 0.13 | 4.09 ± 0.31 | 4.53 ± 0.83 |
| Vc | 41.42 ± 2.83 | 72.00 ± 1.15 | 78.88 ± 0.80 | ||||
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Aβ Aggregation (inhib. %) a | Disaggregation (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | H | OCH3 | H | 4.83 ± 8.10 | 4.40 ± 2.11 |
| 2 | H | H | H | H | 0.14 ± 1.49 | 0.27 ± 0.94 |
| 3 | H | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | 1.73 ± 2.15 | 2.39 ± 1.35 |
| 4 | H | H | H | OCH3 | 2.28 ± 3.24 | 3.85 ± 2.22 |
| 5 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | 14.47 ± 4.15 | 11.92 ± 2.32 |
| 6 | H | OCH3 | H | H | 12.26 ± 7.37 | 11.19 ± 1.70 |
| 7 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | 7.87 ± 2.90 | 9.04 ± 1.99 |
| 8 | H | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | 3.33 ± 1.26 | 4.49 ± 0.49 |
| 9 | OCH3 | OH | OCH3 | H | 2.72 ± 3.65 | 1.05 ± 1.04 |
| 10 | OCH3 | OH | H | H | 5.94 ± 3.13 | 4.16 ± 1.65 |
| 11 | OCH3 | OH | OCH3 | OCH3 | 4.37 ± 3.20 | 2.04 ± 0.71 |
| 12 | OCH3 | OH | H | OCH3 | 2.78 ± 4.27 | 0.33 ± 0.45 |
| 13 | OH | OH | OCH3 | H | 56.43 ± 1.72 | 52.76 ± 0.33 |
| 14 | OH | OH | H | H | 60.68 ± 1.76 | 57.28 ± 3.61 |
| 15 | OH | OH | OCH3 | OCH3 | 61.85 ± 1.70 | 64.44 ± 0.76 |
| 16 | OH | OH | H | OCH3 | 38.47 ± 2.37 | 51.51 ± 1.42 |
| 17 | OCH3 | H | − | − | 14.34 ± 2.37 | 15.50 ± 0.07 |
| 18 | H | H | − | − | 3.47 ± 7.57 | 7.74 ± 2.00 |
| 19 | OCH3 | OCH3 | − | − | 13.06 ± 4.58 | 18.68 ± 1.17 |
| 20 | H | OCH3 | − | − | 12.93 ± 3.66 | 0.61 ± 0.38 |
| curcumin | 48.85 ± 1.20 | 43.83 ± 1.22 | ||||
| resveratrol | 60.49 ± 2.71 | 51.27 ± 3.31 | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, T.; Zhao, X.-B.; Wang, W.-F.; Qiang, Y.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Yang, J.-L. Design, Synthesis of N-phenethyl Cinnamide Derivatives and Their Biological Activities for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Antioxidant, Beta-amyloid Disaggregating and Rescue Effects on Memory Loss. Molecules 2018, 23, 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102663
Chai T, Zhao X-B, Wang W-F, Qiang Y, Zhang X-Y, Yang J-L. Design, Synthesis of N-phenethyl Cinnamide Derivatives and Their Biological Activities for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Antioxidant, Beta-amyloid Disaggregating and Rescue Effects on Memory Loss. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102663
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Tian, Xiao-Bo Zhao, Wei-Feng Wang, Yin Qiang, Xiao-Yun Zhang, and Jun-Li Yang. 2018. "Design, Synthesis of N-phenethyl Cinnamide Derivatives and Their Biological Activities for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Antioxidant, Beta-amyloid Disaggregating and Rescue Effects on Memory Loss" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102663
APA StyleChai, T., Zhao, X.-B., Wang, W.-F., Qiang, Y., Zhang, X.-Y., & Yang, J.-L. (2018). Design, Synthesis of N-phenethyl Cinnamide Derivatives and Their Biological Activities for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: Antioxidant, Beta-amyloid Disaggregating and Rescue Effects on Memory Loss. Molecules, 23(10), 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102663




