The Process and Strategy for Developing Selective Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HDAC Subtypes
2.2. The Promise of Selective HDAC3 Inhibition
2.3. Available HDAC3 Selective Inhibitors
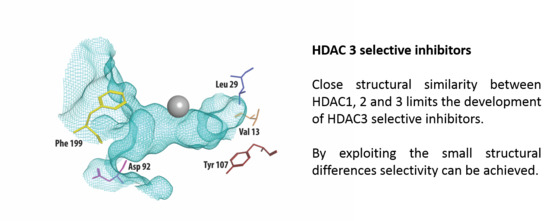
2.4. Strategies for Developing Selective HDAC3 Inhibitors
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roche, J.; Bertrand, P. Inside HDACs with more selective HDAC inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapenaar, H.; van den Bosch, T.; Leus, N.G.J.; van der Wouden, P.E.; Eleftheriadis, N.; Hermans, J.; Hailu, G.S.; Rotili, D.; Mai, A.; Dömling, A.; et al. The relevance of Kicalculation for bi-substrate enzymes illustrated by kinetic evaluation of a novel lysine (K) acetyltransferase 8 inhibitor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, E.E.; Montgomery, M.R.; Leyva, K.J. HDAC Inhibitors as Epigenetic Regulators of the Immune System: Impacts on Cancer Therapy and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.A.; Dai, Z.; Locasale, J.W. The impact of cellular metabolism on chromatin dynamics and epigenetics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, A.L.; Hazzalin, C.A.; Mahadevan, L.C. Enhanced Histone Acetylation and Transcription: A Dynamic Perspective. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.J.; Seto, E. The Rpd3/Hda1 family of lysine deacetylases: From bacteria and yeast to mice and men. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: Implications for disease and therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.-T.; Li, H.-Q.; Liu, F. Selective histone deacetylase small molecule inhibitors: Recent progress and perspectives. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 27, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of histone acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigushin, D.M.; Ali, S.; Pace, P.E.; Mirsaidi, N.; Ito, K.; Adcock, I.; Coombes, R.C. Trichostatin A is a histone deacetylase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against breast cancer in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournel, M.; Bonfils, C.; Hou, Y.; Yan, P.T.; Trachy-Bourget, M.-C.; Kalita, A.; Liu, J.; Lu, A.-H.; Zhou, N.Z.; Robert, M.-F.; et al. MGCD0103, a novel isotype-selective histone deacetylase inhibitor, has broad spectrum antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Ohta, T.; Kitagawa, H.; Kayahara, M.; Ninomiya, I.; Fushida, S.; Fujimura, T.; Nishimura, G.I.; Shimizu, K.; Miwa, K. FR901228, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, induces cell cycle arrest and subsequent apoptosis in refractory human pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 24, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Owa, T.; Hassig, C.A.; Shimada, J.; Schreiber, S.L. Depudecin induces morphological reversion of transformed fibroblasts via the inhibition of histone deacetylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3356–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyrenne, B.M.; Lewis, J.; Weed, J.; Carlson, K.; Mirza, F.N.; Foss, F.; Girardi, M. Synergy of BCL2 and histone deacetylase inhibition against leukemic cells from cutaneous T-cell lymphoma patients. Blood 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symanowski, J.; Vogelzang, N.; Zawel, L.; Atadja, P.; Pass, H.; Sharma, S. A histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 downregulates XIAP in mesothelioma cell lines which is likely responsible for increased apoptosis with TRAIL. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.S.; Quan, Y.; Zhang, D.X.; Liu, D.W.; Zhang, X.Z. Synergistic Inhibition of Breast Cancer Cell Growth by an Epigenome-Targeting Drug and a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Huang, J.S.; Wang, T.H.; Kuo, C.H.; Wang, C.J.; Wang, S.H.; Leu, Y.L. Dihydrocoumarin, an HDAC inhibitor, increases DNA damage sensitivity by inhibiting Rad52. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, J.; Suzuki, R.; Mazitschek, R.; Gorgun, G.; Ghosh, B.; Cirstea, D.; Hu, Y.; Mimura, N.; Ohguchi, H.; Cottini, F.; et al. Histone deacetylase 3 as a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leus, N.G.J.; van den Bosch, T.; van der Wouden, P.E.; Krist, K.; Ourailidou, M.E.; Eleftheriadis, N.; Kistemaker, L.E.M.; Bos, S.; Gjaltema, R.A.F.; Mekonnen, S.A.; et al. HDAC1-3 inhibitor MS-275 enhances IL10 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages and reduces cigarette smoke-induced airway inflammation in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazantsev, A.G.; Thompson, L.M. Therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors for central nervous system disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maolanon, A.R.; Madsen, A.S.; Olsen, C.A. Innovative Strategies for Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, F.F.; Lundh, M.; Kaya, T.; McCarren, P.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Gale, J.P.; Galbo, T.; Fisher, S.L.; Meier, B.C.; et al. An Isochemogenic Set of Inhibitors to Define the Therapeutic Potential of Histone Deacetylases in β-Cell Protection. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, C.J.; Watson, P.J.; Fairall, L.; Schwabe, J.W.R. Targeting Class I Histone Deacetylases in a “Complex” Environment. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Methot, J.L.; Chakravarty, P.K.; Chenard, M.; Close, J.; Cruz, J.C.; Dahlberg, W.K.; Fleming, J.; Hamblett, C.L.; Hamill, J.E.; Harrington, P.; et al. Exploration of the internal cavity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) with selective HDAC1/HDAC2 inhibitors (SHI-1:2). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, F.F.; Weïwer, M.; Steinbacher, S.; Schomburg, A.; Reinemer, P.; Gale, J.P.; Campbell, A.J.; Fisher, S.L.; Zhao, W.-N.; Reis, S.A.; et al. Kinetic and structural insights into the binding of histone deacetylase 1 and 2 (HDAC1, 2) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressi, J.C.; Jennings, A.J.; Skene, R.; Wu, Y.; Melkus, R.; De Jong, R.; O’Connell, S.; Grimshaw, C.E.; Navre, M.; Gangloff, A.R. Exploration of the HDAC2 foot pocket: Synthesis and SAR of substituted N-(2-aminophenyl)benzamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3142–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Oda, Y.; Eguchi, T.; Aishima, S.-I.; Yao, T.; Hosoi, F.; Basaki, Y.; Ono, M.; Kuwano, M.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Expression profile of class I histone deacetylases in human cancer tissues. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, S.; Shekari Khaniani, M.; Choupani, J.; Alivand, M.R.; Mansoori Derakhshan, S. HDACis (class I), cancer stem cell, and phytochemicals: Cancer therapy and prevention implications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.-Y.; Qu, Y.; Ni, A.-R.; Wang, G.-X.; Huang, W.-B.; Chen, Z.-P.; Lv, Z.-F.; Zhang, S.; Lindsay, H.; Zhao, S.; et al. Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor N25 exerts anti-tumor effects and induces autophagy in human glioma cells by inhibiting HDAC3. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 75232–75242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yin, Y.; Dorfman, R.G.; Zou, T.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, L.; Kong, B.; et al. Down-regulation of HDAC3 inhibits growth of cholangiocarcinoma by inducing apoptosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Jin, J.; Ye, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y. HDAC3 negatively regulates spatial memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganai, S.A.; Ramadoss, M.; Mahadevan, V. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors—Emerging Roles in Neuronal Memory, Learning, Synaptic Plasticity and Neural Regeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suelves, N.; Kirkham-McCarthy, L.; Lahue, R.S.; Ginés, S. A selective inhibitor of histone deacetylase 3 prevents cognitive deficits and suppresses striatal CAG repeat expansions in Huntington’s disease mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Morris, C.D.; Jacques, V.; Gottesfeld, J.M.; Rusche, J.R.; Thomas, E.A. The effects of pharmacological inhibition of histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) in Huntington’s disease mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, M.; Morinobu, A.; Chin, T.; Sakai, Y.; Kurosaka, M.; Kumagai, S. Expression and function of histone deacetylases in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisht Gopal, Y.N.; Van Dyke, M.W. Depletion of histone deacetylase protein: A common consequence of inflammatory cytokine signaling? Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 2738–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leus, N.G.J.; Zwinderman, M.R.H.; Dekker, F.J. Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC 3) as emerging drug target in NF-κB-mediated inflammation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2016, 33, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, F.J.; Van Den Bosch, T.; Martin, N.I. Small molecule inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases are potential drugs for inflammatory diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbein, G.; Wendling, D. Histone deacetylases in viral infections. Clin. Epigenet. 2010, 1, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, K.M.; Archin, N.M.; Keedy, K.S.; Espeseth, A.S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Gale, J.; Wagner, F.F.; Holson, E.B.; Margolis, D.M. Selective HDAC inhibition for the disruption of latent HIV-1 infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, B.; Kamali Jamil, R.; Hamidi-Fard, M.; Rahimi, P.; Momen, S.B.; Aghasadeghi, M.R.; Allahbakhshi, E. HIV-1 Vpr reactivates latent HIV-1 provirus by inducing depletion of class i HDACs on chromatin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuse, S.; Calao, M.; Kabeya, K.; Guiguen, A.; Gatot, J.S.; Quivy, V.; Vanhulle, C.; Lamine, A.; Vaira, D.; Demonte, D.; et al. Synergistic activation of HIV-1 expression by deacetylase inhibitors and prostratin: Implications for treatment of latent infection. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirice, E.; Ng, R.W.S.; Martinez, R.; Hu, J.; Wagner, F.F.; Holson, E.B.; Wagner, B.K.; Kulkarni, R.N. Isoform-selective inhibitor of histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) limits pancreatic islet infiltration and protects female nonobese diabetic mice from diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17598–17608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, B.C.; Wagner, B.K. Inhibition of HDAC3 as a strategy for developing novel diabetes therapeutics. Epigenomics 2014, 6, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundh, M.; Galbo, T.; Poulsen, S.S.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Histone deacetylase 3 inhibition improves glycaemia and insulin secretion in obese diabetic rats. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaLumiere, R.T. Opening the genome to reduce cocaine-seeking behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2442–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaghband, Y.; Kwapis, J.L.; López, A.J.; White, A.O.; Aimiuwu, O.V.; Al-Kachak, A.; Bodinayake, K.K.; Oparaugo, N.C.; Dang, R.; Astarabadi, M.; et al. Distinct roles for the deacetylase domain of HDAC3 in the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex in the formation and extinction of memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 145, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leus, N.G.J.; Van Der Wouden, P.E.; Van Den Bosch, T.; Hooghiemstra, W.T.R.; Ourailidou, M.E.; Kistemaker, L.E.M.; Bischoff, R.; Gosens, R.; Haisma, H.J.; Dekker, F.J. HDAC 3-selective inhibitor RGFP966 demonstrates anti-inflammatory properties in RAW 264.7 macrophages and mouse precision-cut lung slices by attenuating NF-κB p65 transcriptional activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 108, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Kasuya, Y.; Itoh, Y.; Ota, Y.; Zhan, P.; Asamitsu, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Okamoto, T.; Miyata, N. Identification of Highly Selective and Potent Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors Using Click Chemistry-Based Combinatorial Fragment Assembly. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, B.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Cohen, M.H.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA approval summary: Vorinostat for treatment of advanced primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Oncologist 2007, 12, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Z.; Kwitkowski, V.E.; Del Valle, P.L.; Ricci, M.S.; Saber, H.; Habtemariam, B.A.; Bullock, J.; Bloomquist, E.; Li Shen, Y.; Chen, X.-H.; et al. FDA Approval: Belinostat for the Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raedler, B.L.A.; Writer, M. Farydak (Panobinostat): First HDAC Inhibitor Approved for Patients with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Am. Heal. Drug Benefits 2016, 9, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dolskiy, A.A.; Pustylnyak, V.O.; Yarushkin, A.A.; Lemskaya, N.A.; Yudkin, D.V. Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases Are Weak Activators of the FMR1 Gene in Fragile X Syndrome Cell Lines. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3582601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvaez, M.; McQuown, S.C.; Rogge, G.A.; Astarabadi, M.; Jacques, V.; Carreiro, S.; Rusche, J.R.; Wood, M.A. HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.J.; Herman, D.; Gottesfeld, J.M. Pimelic diphenylamide 106 is a slow, tight-binding inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35402–35409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soragni, E.; Xu, C.; Plasterer, H.L.; Jacques, V.; Rusche, J.R.; Gottesfeld, J.M. Rationale for the development of 2-aminobenzamide histone deacetylase inhibitors as therapeutics for Friedreich ataxia. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Soragni, E.; Chou, C.J.; Barnes, G.; Jones, S.; Rusche, J.R.; Gottesfeld, J.M.; Pandolfo, M. Two new pimelic diphenylamide HDAC inhibitors induce sustained frataxin upregulation in cells from Friedreich’s ataxia patients and in a mouse model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Chou, C.J.; Gottesfeld, J.M. Design and synthesis of novel hybrid benzamide–peptide histone deacetylase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3928–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; He, R.; Chen, Y.; D’Annibale, M.A.; Langley, B.; Kozikowski, A.P. Studies of benzamide- and thiol-based histone deacetylase inhibitors in models of oxidative-stress-induced neuronal death: Identification of some HDAC3-selective inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marson, C.M.; Matthews, C.J.; Yiannaki, E.; Atkinson, S.J.; Soden, P.E.; Shukla, L.; Lamadema, N.; Thomas, N.S.B. Discovery of potent, isoform-selective inhibitors of histone deacetylase containing chiral heterocyclic capping groups and a N-(2-aminophenyl)benzamide binding unit. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6156–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.-Y.; Chuang, H.-C.; Shen, F.-H.; Detroja, K.; Hsin, L.-W.; Chen, C.-S. Targeting breast cancer stem cells by novel HDAC3-selective inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, J.J.; Inks, E.S.; Zhang, C.; Peterson, Y.K.; Li, J.; Chundru, K.; Lee, B.; Buchanan, A.; Miao, S.; Chou, C.J. Comparison of the Deacylase and Deacetylase Activity of Zinc-Dependent HDACs. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, M.E.; Xia, B.; Carreiro, S.; Ressler, K.J. The Class I HDAC inhibitor RGFP963 enhances consolidation of cued fear extinction. Learn. Mem. 2015, 22, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ourailidou, M.E.; Leus, N.G.J.; Krist, K.; Lenoci, A.; Mai, A.; Dekker, F.J. Chemical epigenetics to assess the role of HDAC1-3 inhibition in macrophage pro-inflammatory gene expression. Medchemcomm 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Fuller, J.H.; West, N.; Martinez, N.M.; Morse, E.M.; Weïwer, M.; Schreiber, S.L.; Bradner, J.E.; Koehler, A.N. A novel HDAC inhibitor with a hydroxy-pyrimidine scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4164–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, L.; Dobler, M.R.; Radetich, B.; Zhu, Y.; Atadja, P.W.; Claiborne, T.; Grob, J.E.; McRiner, A.; Pancost, M.R.; Patnaik, A.; et al. Human HDAC isoform selectivity achieved via exploitation of the acetate release channel with structurally unique small molecule inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4626–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.; Sodji, Q.H.; Kornacki, J.R.; Mrksich, M.; Oyelere, A.K. 3-Hydroxypyridin-2-thione as Novel Zinc Binding Group for Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3492–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.E.; Lim, S.-J. A structure-based virtual screening approach toward the discovery of histone deacetylase inhibitors: Identification of promising zinc-chelating groups. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| 13 | 29 | 92 | 107 | 199 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC3 | Val | Leu | Asp | Tyr | Phe |
| HDAC2 | Val | Ile | Glu | Ser | Tyr |
| HDAC1 | Ile | Ile | Glu | Ser | Tyr |
| Inhibitor | Structure | HDAC1 | HDAC2 | HDAC3 | HDAC4 | HDAC5 | HDAC6 | HDAC7 | HDAC8 | HDAC10 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entinostat (MS-275) |  | 0.19 | 0.41 | 0.95 | _ | _ | _ | _ | 76.5 | _ | [19] |
| RGFP966 |  | 28 | 17 | 0.08 | _ | _ | _ | _ | >100 | _ | [63] |
| PD-106 |  | 0.14 * | _ | 0.014 * | _ | _ | _ | _ | 5 * | _ | [55] |
| RGFP109 (RG2833) |  | 0.032 * | _ | 0.005 * | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | [57] |
| BRD3308 |  | 1.08 | 1.15 | 0.064 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | [22] |
| Inhibitor | Structure | HDAC1 | HDAC2 | HDAC3 | HDAC4 | HDAC5 | HDAC6 | HDAC7 | HDAC8 | HDAC10 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 84 | _ | 4 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | [58] |
| 2 |  | >30 | >30 | 0.12 | _ | _ | >30 | _ | >30 | >30 | [59] |
| 3 |  | >100 | 19 | 0.24 | >100 | _ | >100 | _ | >100 | _ | [49] |
| 4 |  | >100 | >100 | 0.26 | >100 | _ | >100 | _ | >100 | _ | [49] |
| 5 |  | 0.93 | 0.085 | 0.012 | _ | _ | >20 | _ | 4 | _ | [60] |
| 6 |  | >10 | >10 | 0.35 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | _ | [61] |
| 7 |  | >10 | >10 | 0.2 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >5 | _ | [61] |
| 8 |  | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.08 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | [62] |
| 9 |  | 5.8 | 7.9 | 0.17 | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | _ | [62] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, F.; Zwinderman, M.R.H.; Dekker, F.J. The Process and Strategy for Developing Selective Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030551
Cao F, Zwinderman MRH, Dekker FJ. The Process and Strategy for Developing Selective Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors. Molecules. 2018; 23(3):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030551
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Fangyuan, Martijn R. H. Zwinderman, and Frank J. Dekker. 2018. "The Process and Strategy for Developing Selective Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors" Molecules 23, no. 3: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030551
APA StyleCao, F., Zwinderman, M. R. H., & Dekker, F. J. (2018). The Process and Strategy for Developing Selective Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitors. Molecules, 23(3), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23030551