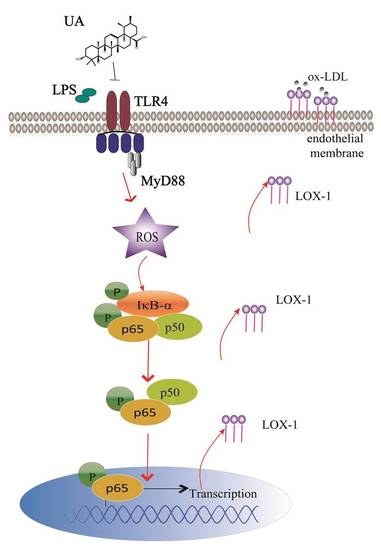
Ursolic Acid Attenuates Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− Mice: Role of LOX-1 Mediated by ROS/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. UA Decreased LPS-Induced LOX-1 Expression in HUVECs
2.2. UA Inhibited LPS-Induced LOX-1 Expression via TLR4/MyD88 Pathway
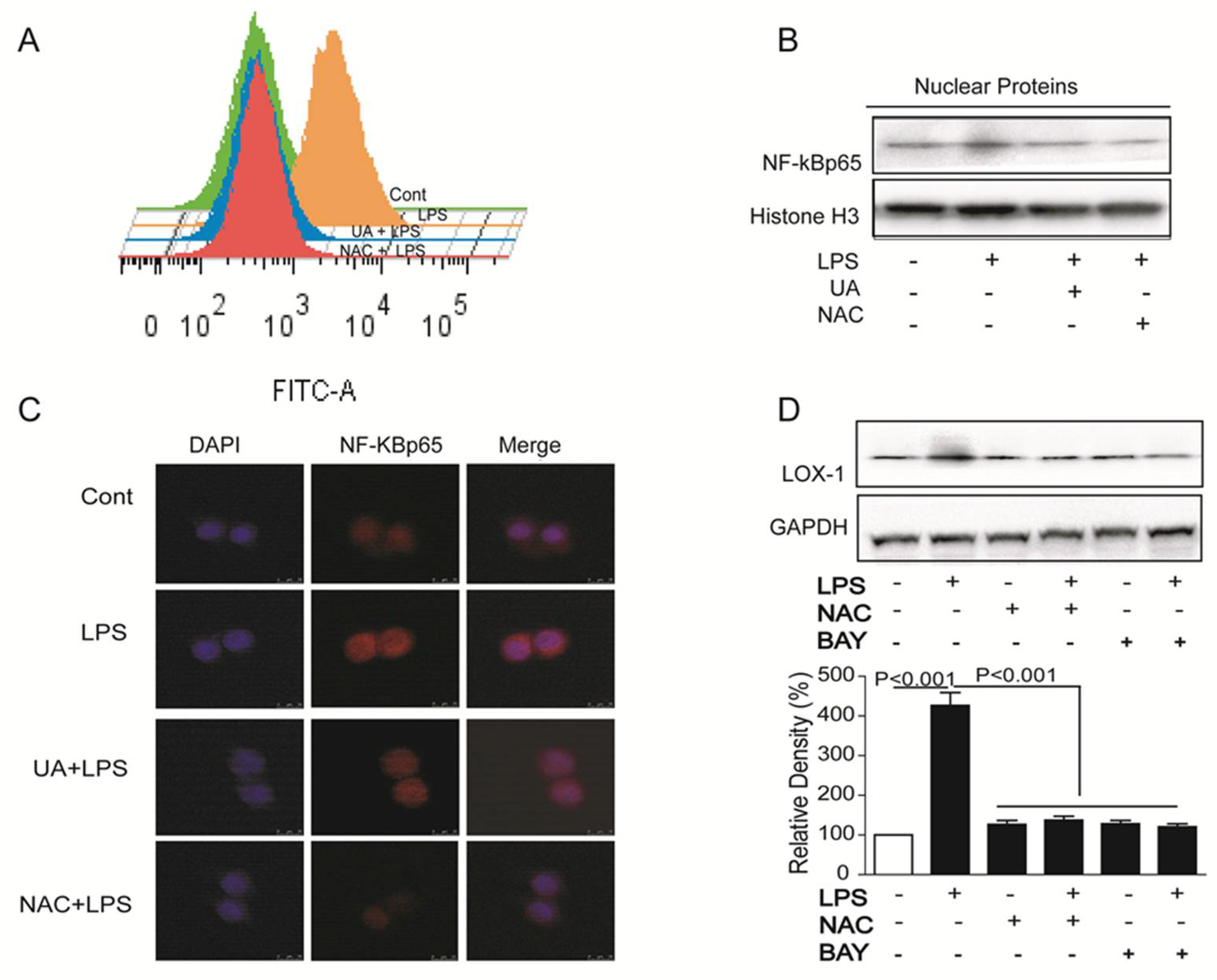
2.3. UA Reduced ROS Generation and Decreased NF-κB Activity to Block LOX-1 Expression
2.4. UA Reduced Atherosclerotic Plaque Development in ApoE−/− Mice
2.5. UA Inhibited LOX-1 Expression in Thoracic Aorta of ApoE−/− Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Animal Experiment
4.4. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. SiRNA Transfection
4.7. Real-Time RT-PCR
4.8. Aorta Collection and Lesion Size Evaluation
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaziano, T.A.; Bitton, A.; Anand, S.; Abrahams-Gessel, S.; Murphy, A. Growing epidemic of coronary heart disease in low- and middle-income countries. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2010, 35, 72–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, N.; Formoso, G.; Pandolfi, A. Physiology and pathophysiology of oxLDL uptake by vascular wall cells in atherosclerosis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 84, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.C.; Glass, C.K. The macrophage foam cell as a target for therapeutic intervention. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Masaki, T.; Sawamura, T. LOX-1, the receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein identified from endothelial cells: Implications in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 95, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Mehta, J.L. LOX-1: A critical player in the genesis and progression of myocardial ischemia. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2011, 25, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Ogura, S.; Chen, J.; Little, P.J.; Moss, J.; Liu, P. LOX-1 in atherosclerosis: Biological functions and pharmacological modifiers. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2859–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, G.; Messina, K.E.; Yan, J.; Messina, J.A.; Messina, L.M. Hypercholesterolemia induces oxidant stress that accelerates the ageing of hematopoietic stem cells. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baradaran, A.; Nasri, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Oxidative stress and hypertension: Possibility of hypertension therapy with antioxidants. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 358–367. [Google Scholar]
- Tangvarasittichai, S. Oxidative stress, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 456–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, B.; Sagan, A.; Ludew, D.; Mrowiecki, W.; Chwala, M.; Bujak-Gizycka, B.; Filip, G.; Grudzien, G.; Kapelak, B.; Zmudka, K.; et al. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in human aortic aneurysms–association with clinical risk factors for atherosclerosis and disease severity. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokce, G.; Ozsarlak-Sozer, G.; Oran, I.; Oktay, G.; Ozkal, S.; Kerry, Z. Taurine suppresses oxidative stress-potentiated expression of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor and restenosis in balloon-injured rabbit iliac artery. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odegaard, A.O.; Jacobs, D.R.; Sanchez, O.A.; Goff, D.C.; Reiner, A.P.; Gross, M.D. Oxidative stress, inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and incidence of type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siti, H.N.; Kamisah, Y.; Kamsiah, J. The role of oxidative stress, antioxidants and vascular inflammation in cardiovascular disease (a review). Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Micaelo, N.; Gonzalez-Abuin, N.; Terra, X.; Richart, C.; Ardevol, A.; Pinent, M.; Blay, M. Omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid and procyanidins inhibit cyclo-oxygenase activity and attenuate NF-kappaB activation through a p105/p50 regulatory mechanism in macrophage inflammation. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Qiao, C.; Ma, N.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W. Pycnogenol attenuates atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism through the TLR4-NF-kappaB pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, S.; Sudhakaran, P.R.; Helen, A. Quercetin attenuates atherosclerotic inflammation and adhesion molecule expression by modulating TLR-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell Immunol. 2016, 310, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, E.Q.; Wang, B.W.; Xu, X.R.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y.; Li, H.B. Microwave-assisted extraction of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5319–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Moon, H.; Kim, C.J. Effects of hydroxy pentacyclic triterpene acids from Forsythia viridissima on asthmatic responses to ovalbumin challenge in conscious guinea pigs. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Wu, R.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, D.; Yang, Y.; Androulakis, I.P.; Kong, A.-N. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of the Triterpenoid Ursolic Acid in Regulating the Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, and Epigenetic Gene Responses in Rat Leukocytes. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, B.A.; Lone, A.M.; Shah, W.A.; Qurishi, M.A. Synthesis and screening of ursolic acid-benzylidine derivatives as potential anti-cancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 111, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Nascimento, P.G.; Lemos, T.L.; Bizerra, A.; Arriaga, Â.; Ferreira, D.A.; Santiago, G.M.; Braz-Filho, R.; Costa, J.G.M. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of ursolic acid and derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, G.; Chen, X. Lipopolysaccharide induced LOX-1 expression via TLR4/MyD88/ROS activated p38MAPK-NF-kappaB pathway. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 63, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, M.A.; Royo, V.A.; Ferreira, D.S.; Crotti, A.E.; Andrade e Silva, M.L.; Carvalho, J.C.; Bastos, J.K.; Cunha, W.R. In vivo analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of ursolic acid and oleanoic acid from Miconia albicans (Melastomataceae). Z. Naturforsch. C 2006, 61, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurek, A.; Grudniak, A.M.; Szwed, M.; Klicka, A.; Samluk, L.; Wolska, K.I.; Janiszowska, W.; Popowska, M. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid affect peptidoglycan metabolism in Listeria monocytogenes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2010, 97, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, J.L.; Chen, J.; Hermonat, P.L.; Romeo, F.; Novelli, G. Lectin-like, oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1): A critical player in the development of atherosclerosis and related disorders. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, D.N.; Giddens, D.P.; Zarins, C.K.; Glagov, S. Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 1985, 5, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Ferguson, M.S.; Kerwin, W.S.; Saam, T.; Chu, B.; Takaya, N.; Polissar, N.L.; Yuan, C. In vivo quantitative measurement of intact fibrous cap and lipid-rich necrotic core size in atherosclerotic carotid plaque: Comparison of high-resolution, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and histology. Circulation 2005, 112, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Su, J.; Wang, K.; Zhu, T.; Li, X. Ursolic acid reduces oxidative stress to alleviate early brain injury following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 579, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.; Jialal, I. Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. Pathophysiology 2006, 13, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubackova, S.; Kucerova, A.; Michlits, G.; Kyjacova, L.; Reinis, M.; Korolov, O.; Bartek, J.; Hodny, Z. IFNgamma induces oxidative stress, DNA damage and tumor cell senescence via TGFbeta/SMAD signaling-dependent induction of Nox4 and suppression of ANT2. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checker, R.; Sandur, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Patwardhan, R.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Kohli, V.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Sainis, K.B. Potent anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-kappaB, AP-1 and NF-AT. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paigen, B.; Holmes, P.A.; Mitchell, D.; Albee, D. Comparison of atherosclerotic lesions and HDL-lipid levels in male, female, and testosterone-treated female mice from strains C57BL/6, BALB/c, and C3H. Atherosclerosis 1987, 64, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, X.; Hao, Z. Ursolic Acid Attenuates Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− Mice: Role of LOX-1 Mediated by ROS/NF-κB Pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051101
Li Q, Zhao W, Zeng X, Hao Z. Ursolic Acid Attenuates Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− Mice: Role of LOX-1 Mediated by ROS/NF-κB Pathway. Molecules. 2018; 23(5):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051101
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiu, Wenwen Zhao, Xi Zeng, and Zhihui Hao. 2018. "Ursolic Acid Attenuates Atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− Mice: Role of LOX-1 Mediated by ROS/NF-κB Pathway" Molecules 23, no. 5: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051101