A Gelatin Hydrogel-Containing Nano-Organic PEI–Ppy with a Photothermal Responsive Effect for Tissue Engineering Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
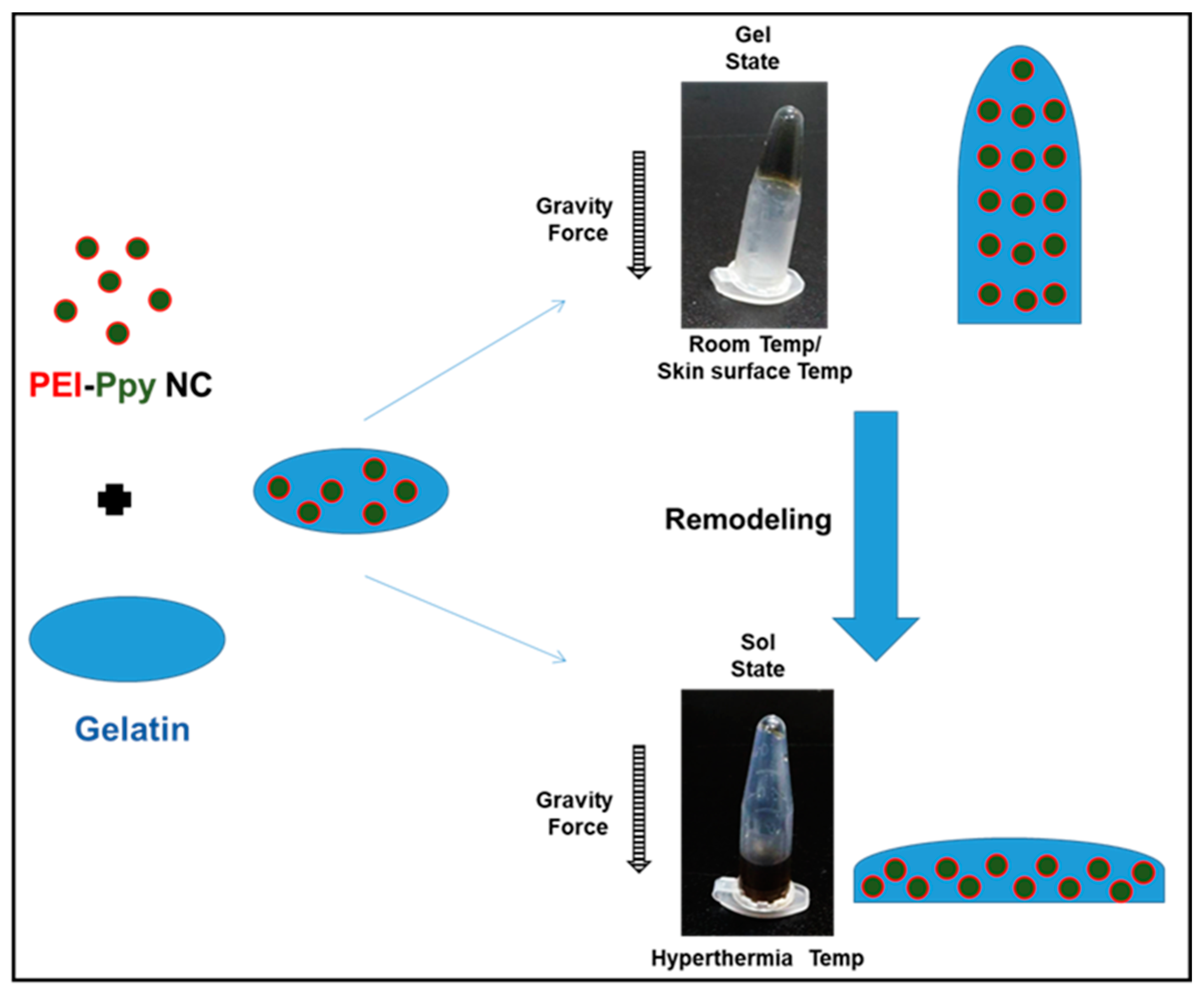
2.1. Preparation of the Test Gelatin Hydrogel Containing the PEI–Ppy NC
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of the Test Photothermal Hydrogel
2.3. Size and Zeta Potential (ZP) of the Test Sample
2.4. TEM Analysis of PEI–Ppy Nanoparticles
2.5. Structural Morphology of the Test Photothermal Hydrogel
2.6. Photothermal Properties of the Test Hydrogel
2.7. In Vitro MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. Cellular Interactions with the Test Photothermal Hydrogel
2.9. In Vivo Study Report
2.9.1. Wound Size Contraction
2.9.2. Wound Site Histology
2.9.3. Body Weight Change and Organ Toxicity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of the Test Gelatin Hydrogel Containing PEI–Ppy‒NC
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of the Test Photothermal Hydrogel
3.3. Cellular Interactions with Test Photothermal Hydrogel in In Vitro Study
3.3.1. MTT Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
3.3.2. Live/Dead Assay
3.4. In Vivo Study
3.4.1. Ethics
3.4.2. Full Thickness Excision Wounds
3.4.3. Wound Area Observation and Percentage of Wound Contraction (Healing) Measurement
3.4.4. Skin and Internal Organ Collection
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.; Silva, E.A.; Mooney, D.J. Growth factor delivery-based tissue engineering: General approaches and a review of recent developments. J. R. Soc. Interface 2011, 8, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronakis, I.S.; Grapenson, S.; Jakob, A. Conductive polypyrrole nanofibers via electrospinning: Electrical and morphological properties. Polymer 2006, 47, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlgren, A.; Bratengeier, C.; Gelmi, A.; Semeins, C.M.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Jager, E.W.; Bakker, A.D. Biocompatibility of polypyrrole with human primary osteoblasts and the effect of dopants. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brédas, J.-L.; Street, G.; Themans, B.; André, J. Organic polymers based on aromatic rings (polyparaphenylene, polypyrrole, polythiophene): Evolution of the electronic properties as a function of the torsion angle between adjacent rings. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Jiang, J. Facile synthesis and characterization of polypyrrole/Co3O4 nanocomposites with adjustable intrinsic electroconductivity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harraz, F.A. Electrochemical polymerization of pyrrole into nanostructured p-type porous silicon. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, C349–C356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Langer, R.; Jia, X. Nanostructured materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjaminsen, R.V.; Mattebjerg, M.A.; Henriksen, J.R.; Moghimi, S.M.; Andresen, T.L. The possible “proton sponge” effect of polyethylenimine (PEI) does not include change in lysosomal pH. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parhamifar, L.; Larsen, A.K.; Hunter, A.C.; Andresen, T.L.; Moghimi, S.M. Polycation cytotoxicity: A delicate matter for nucleic acid therapy—Focus on polyethylenimine. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4001–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, P.Y.; Yang, C.; Hedrick, J.L.; Engler, A.C.; Coady, D.J.; Ghaem-Maghami, S.; George, A.J.; Yang, Y.Y. Hydrophobic modification of low molecular weight polyethylenimine for improved gene transfection. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7971–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Xiong, W.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Zhu, Q. Gene transfection of hyperbranched PEI grafted by hydrophobic amino acid segment PBLG. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Xu, H.; Cheng, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. In vitro and in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer using polypyrrole organic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5586–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.-H.; Liu, B.-S.; Chang, C.-J.; Hsu, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-S. Preparation of networks of gelatin and genipin as degradable biomaterials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 83, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, A.P.; Tien, J. Fabrication of microfluidic hydrogels using molded gelatin as a sacrificial element. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koepff, P. Thermoplastic properties of gelatin. J. Photogr. Sci. 1992, 40, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S. Polymeric Hydrogels as Smart Biomaterials; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Firoozmand, H.; Murray, B.S.; Dickinson, E. Fractal-type particle gel formed from gelatin+ starch solution. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4646–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Chantre, C.O.; Gannon, A.R.; Lind, J.U.; Campbell, P.H.; Grevesse, T.; O’Connor, B.B.; Parker, K.K. Soy Protein/Cellulose Nanofiber Scaffolds Mimicking Skin Extracellular Matrix for Enhanced Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisani, M.; Pezzoli, D.; Chassande, O.; Mantovani, D. Cellularizing hydrogel-based scaffolds to repair bone tissue: How to create a physiologically relevant micro-environment? J. Tissue Eng. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Takai, K.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikada, Y. Challenges in tissue engineering. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, F.L.; Burnouf, T.; Lu, S.Y.; Lu, Y.J.; Lu, K.Y.; Ho, Y.C.; Kuo, C.Y.; Chuang, E.Y. Self-Targeting, Immune Transparent Plasma Protein Coated Nanocomplex for Noninvasive Photothermal Anticancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruel-Gariepy, E.; Leroux, J.-C. In situ-forming hydrogels—Review of temperature-sensitive systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol-gelatin hydrogel membranes for biomedical applications. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, E142–E146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebnesajjad, S. Handbook of Biopolymers and Biodegradable Plastics: Properties, Processing and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh Auddy, R.; Abdullah, M.F.; Das, S.; Roy, P.; Datta, S.; Mukherjee, A. New guar biopolymer silver nanocomposites for wound healing applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 912458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Khattab, A.; Islam, M.A.; Hweij, K.A.; Zeitouny, J.; Waters, R.; Sayegh, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Paul, A. Injectable hydrogels for cardiac tissue repair after myocardial infarction. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deen, G.R.; Loh, X.J. Stimuli-Responsive Cationic Hydrogels in Drug Delivery Applications. Gels 2018, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F.; Oveisi, Z.; Samani, S.M.; Amoozgar, Z. Chitosan based hydrogels: Characteristics and pharmaceutical applications. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cole, B.J.; Malek, M.M. Articular Cartilage Lesions: A Practical Guide to Assessment and Treatment; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Baronzio, G.F.; Hager, E.D. Hyperthermia in Cancer Treatment: A Primer; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Giombini, A.; Giovannini, V.; Cesare, A.D.; Pacetti, P.; Ichinoseki-Sekine, N.; Shiraishi, M.; Naito, H.; Maffulli, N. Hyperthermia induced by microwave diathermy in the management of muscle and tendon injuries. Br. Med. Bull. 2007, 83, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.-Y.; Herman, C. Analysis of skin cooling for quantitative dynamic infrared imaging of near-surface lesions. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 86, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, B.; Bagavathiappan, S.; Jayakumar, T.; Philip, J. Medical applications of infrared thermography: A review. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2012, 55, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wust, P.; Hildebrandt, B.; Sreenivasa, G.; Rau, B.; Gellermann, J.; Riess, H.; Felix, R.; Schlag, P. Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Liu, P.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Cai, L. IR-780 dye loaded tumor targeting theranostic nanoparticles for NIR imaging and photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6853–6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnowski, M. Infrared thermal imaging in connective tissue diseases. Reumatologia 2017, 55, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Boyer, J.-C.; Habault, D.; Branda, N.R.; Zhao, Y. Near infrared light triggered release of biomacromolecules from hydrogels loaded with upconversion nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16558–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenshalo, D.R.; Holmes, C.E.; Wood, P.B. Warm and cool thresholds as a function of rate of stimulus temperature change. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 1968, 3, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhu, F.; Ding, M.; Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. “Click” chemistry in polymeric scaffolds: Bioactive materials for tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2018, 273, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.B. Targeted Delivery of Osteogenic Drugs for Bone Tissue Engineering. Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, G.B.; English, A.; Abraham, M.; Zaharias, R.; Stanford, C.; Keller, J. The effect of hydrogel charge density on cell attachment. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano–bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bañobre-López, M.; Pineiro-Redondo, Y.; Sandri, M.; Tampieri, A.; De Santis, R.; Dediu, V.A.; Rivas, J. Hyperthermia induced in magnetic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Yacoub, M.H. Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: Progress and challenges. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2013, 2013, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroz, A. Reduced Order Modelling of Bone Resorption and Formation. Ph.D. Thesis, De Montfort University, Leicester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Finke, B.; Luethen, F.; Schroeder, K.; Mueller, P.D.; Bergemann, C.; Frant, M.; Ohl, A.; Nebe, B.J. The effect of positively charged plasma polymerization on initial osteoblastic focal adhesion on titanium surfaces. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4521–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.F. A Paradigm for the Evaluation of Tissue-Engineering Biomaterials and Templates. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2017, 23, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annan, K.; Houghton, P.J. Antibacterial, antioxidant and fibroblast growth stimulation of aqueous extracts of Ficus asperifolia Miq. and Gossypium arboreum L., wound-healing plants of Ghana. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, A.F.; Liu, H.; Davidson, J.M.; Daugherty, C.C.; Degen, J.L. Wound-healing defects in mice lacking fibrinogen. Blood 2001, 97, 3691–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eming, S.A.; Krieg, T.; Davidson, J.M. Inflammation in wound repair: Molecular and cellular mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatini, D.; Tempesti, P.; Ridi, F.; Fratini, E.; Bonini, M.; Baglioni, P. Pluronic/gelatin composites for controlled release of actives. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsett-Martin, W.A. Rat models of skin wound healing: A review. Wound Repair Regen. 2004, 12, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fátima Pereira de Carvalho, M.; Pereira, C.S.B.; Fregnani, J.H.T.G.; Ribeiro, F. Comparative histological study on wound healing on rat’s skin treated with Mitomycin C or Clobetasol propionate. Acta Cir. Bras. 2015, 30, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, I.; Bardaa, S.; Mzid, M.; Sahnoun, Z.; Rebaii, T.; Attia, H.; Ennouri, M. Antioxidant, antibacterial and in vivo dermal wound healing effects of Opuntia flower extracts. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Satapathy, M.K.; Nyambat, B.; Chiang, C.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Wong, P.-C.; Ho, P.-H.; Jheng, P.-R.; Burnouf, T.; Tseng, C.-L.; Chuang, E.-Y. A Gelatin Hydrogel-Containing Nano-Organic PEI–Ppy with a Photothermal Responsive Effect for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061256
Satapathy MK, Nyambat B, Chiang C-W, Chen C-H, Wong P-C, Ho P-H, Jheng P-R, Burnouf T, Tseng C-L, Chuang E-Y. A Gelatin Hydrogel-Containing Nano-Organic PEI–Ppy with a Photothermal Responsive Effect for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061256
Chicago/Turabian StyleSatapathy, Mantosh Kumar, Batzaya Nyambat, Chih-Wei Chiang, Chih-Hwa Chen, Pei-Chun Wong, Po-Hsien Ho, Pei-Ru Jheng, Thierry Burnouf, Ching-Li Tseng, and Er-Yuan Chuang. 2018. "A Gelatin Hydrogel-Containing Nano-Organic PEI–Ppy with a Photothermal Responsive Effect for Tissue Engineering Applications" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061256
APA StyleSatapathy, M. K., Nyambat, B., Chiang, C.-W., Chen, C.-H., Wong, P.-C., Ho, P.-H., Jheng, P.-R., Burnouf, T., Tseng, C.-L., & Chuang, E.-Y. (2018). A Gelatin Hydrogel-Containing Nano-Organic PEI–Ppy with a Photothermal Responsive Effect for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules, 23(6), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061256






