Recent Reports of Solid-Phase Cyclohexapeptide Synthesis and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
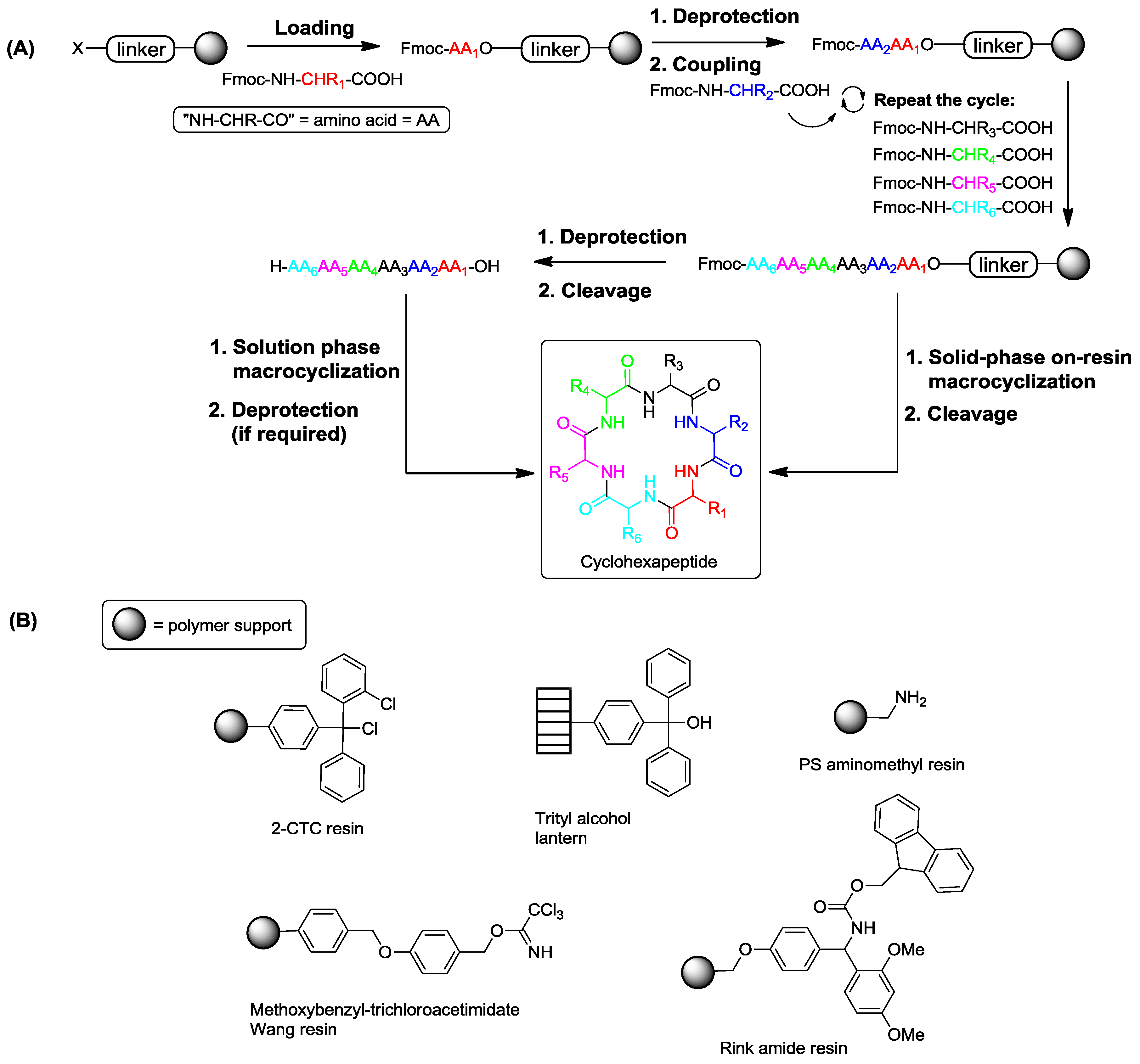
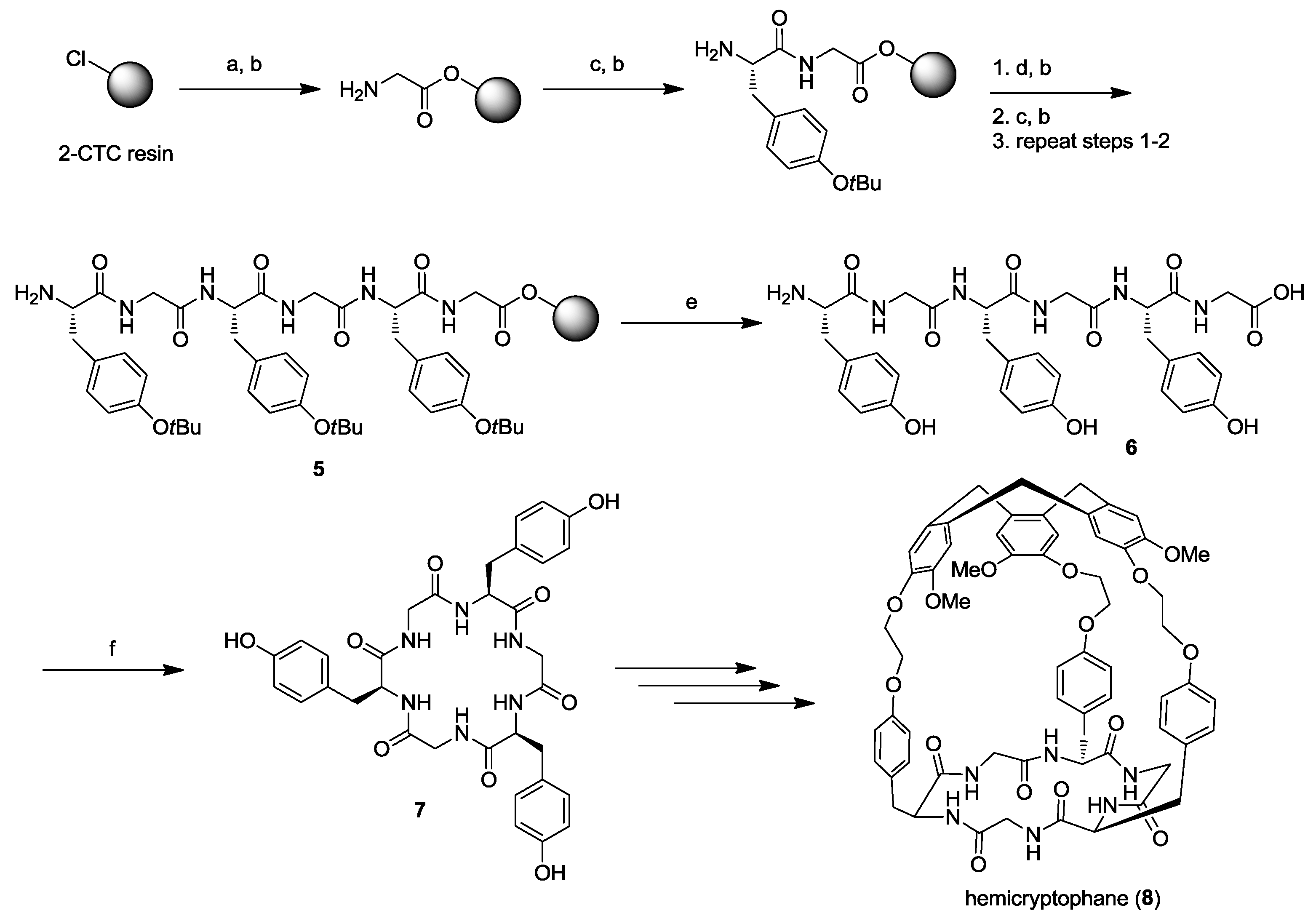
2. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Cyclohexapeptides Using Solution-Phase Cyclization
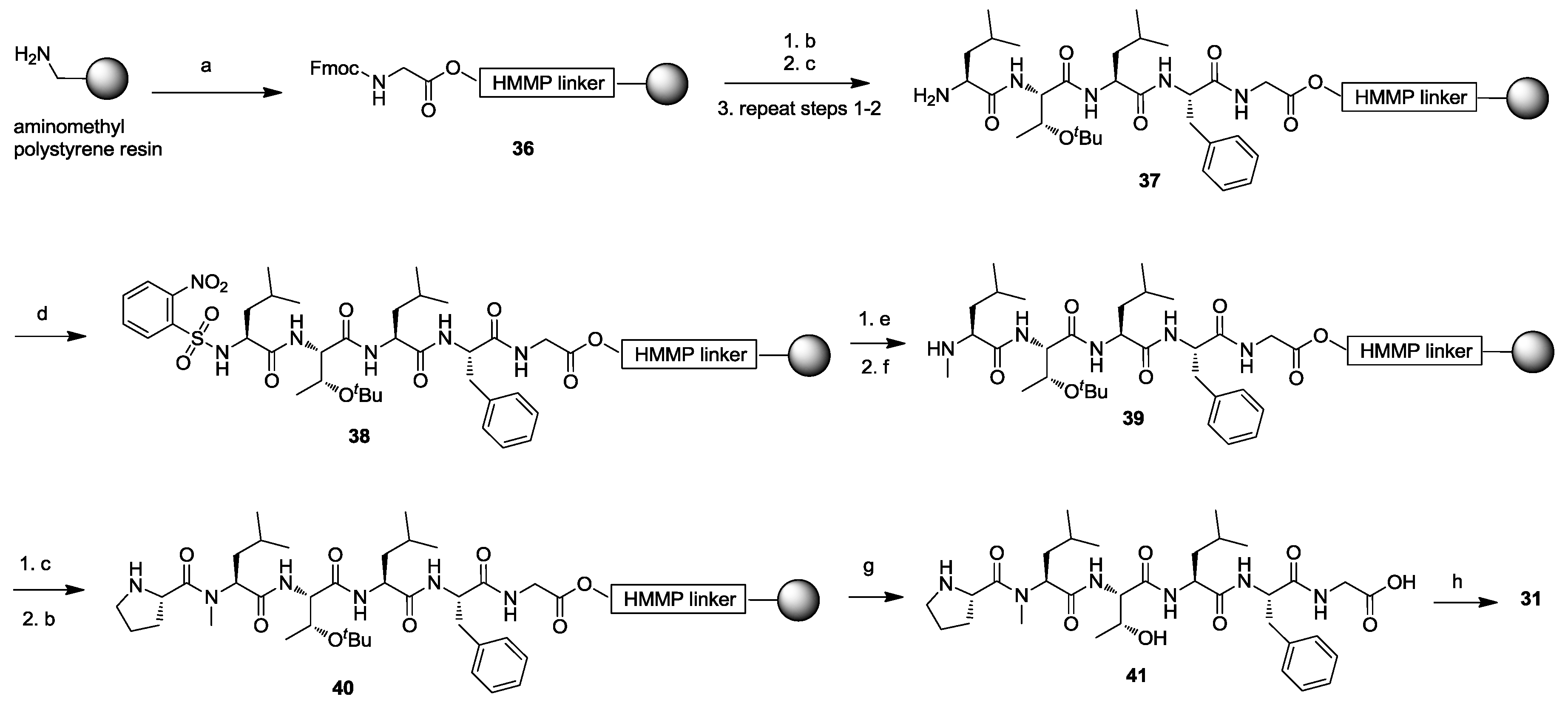
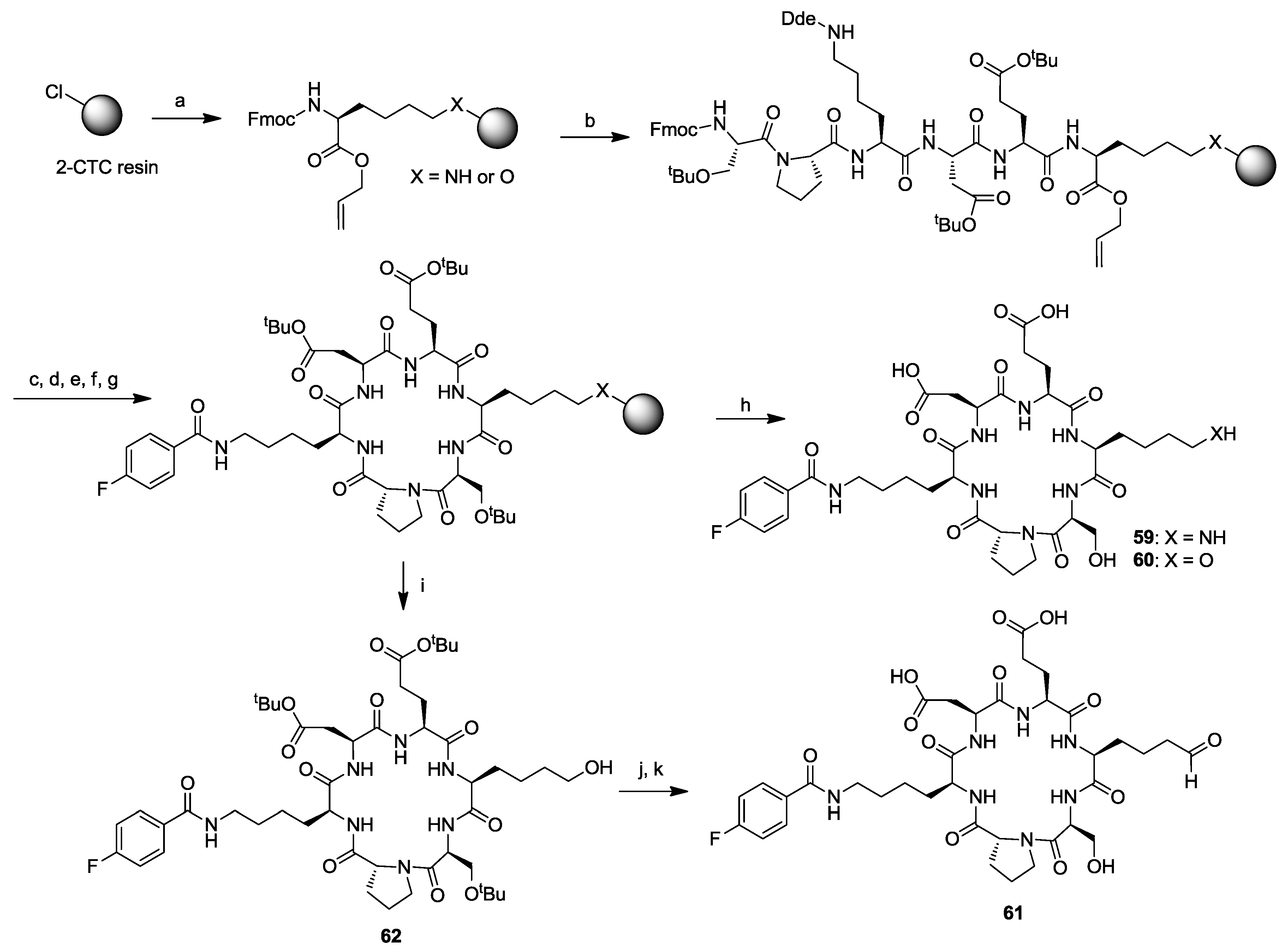
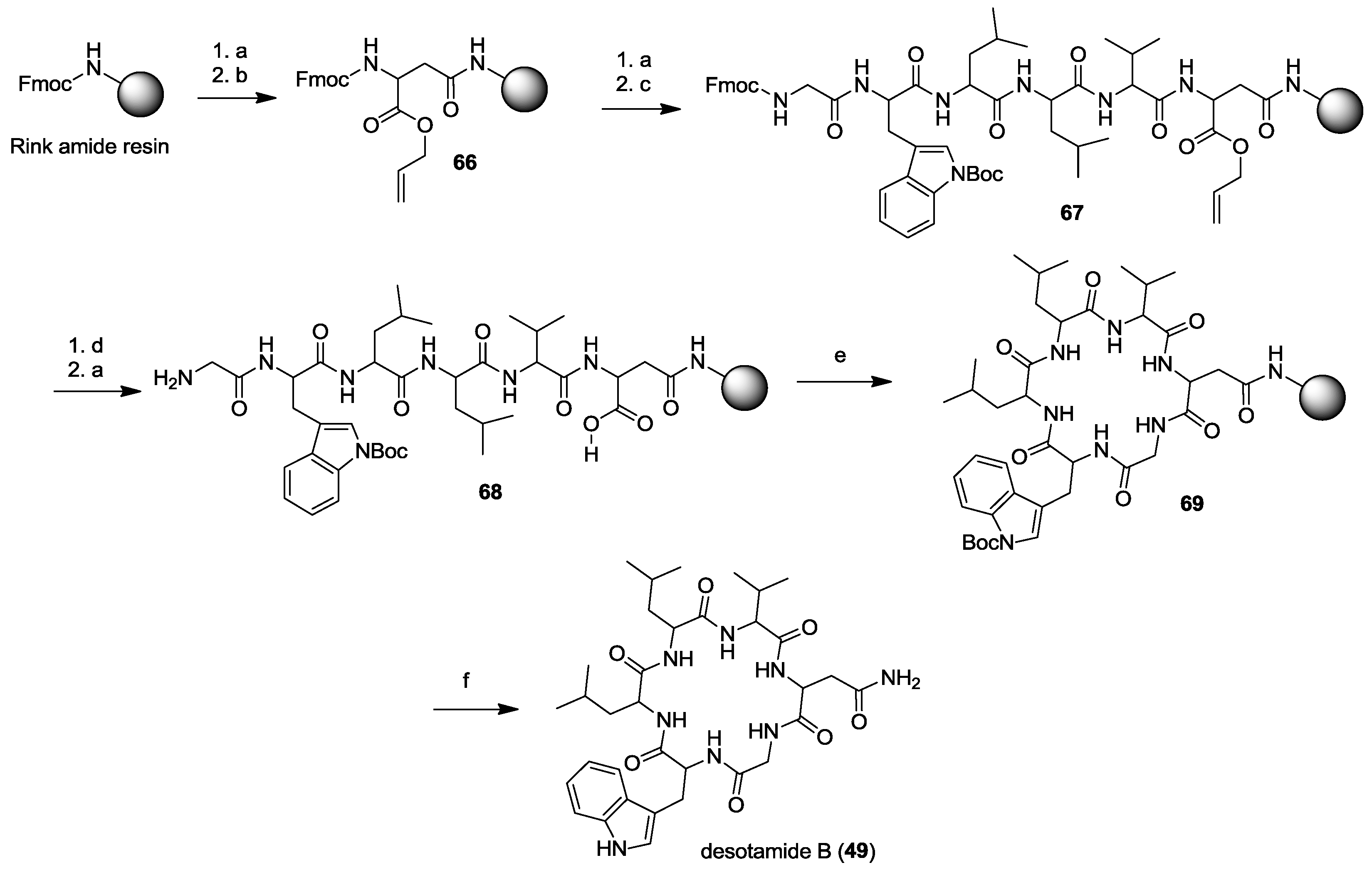
3. Solid-Phase Cyclohexapeptide Synthesis Using On-Resin Cyclization
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADME | Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion |
| BOP | (Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate |
| CsA | Cyclosporin A |
| 2-CTC | 2-Chlorotrityl chloride |
| DBU | 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| Dde | 1-(4,4-Dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohex-1-ylidene)-3-ethyl |
| DIC | N,N′-Diisopropylcarbodiimide |
| DIPEA | N,N-Diisopropylethylamine |
| DMAP | 4-Dimethylaminopyridine |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| DMTMM.BF4 | 4-(4,6-Dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium tetrafluoroborate |
| EC50 | 50% of Maximal effective concentration |
| Fmoc | 9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl |
| Fmoc-AA-OH | Fmoc protected amino acid |
| HATU | 1-[Bis(dimethylamino)methylene]-1H-1,2,3-triazolo[4,5-b]pyridinium 3-oxide hexafluorophosphate |
| HBTU | N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethyl-O-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)uronium hexafluorophosphate |
| HCTU | O-(1H-6-Chlorobenzotriazole-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate |
| HFIP | 1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-2-propanol |
| HMPP | 3-(4-Hydroxymethylphenoxy)propionic acid |
| HOAt | 3-Hydroxytriazolo[4,5-b]pyridine |
| HOBt | Hydroxybenzotriazole |
| IC50 | 50% of Maximal inhibitory concentration |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant S. aureus |
| NMM | N-Methylmorpholine |
| NMP | N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| PK | Pharmacokinetic |
| PyAOP | (7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yloxy)tripyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate |
| PyBOP | (Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)tripyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate |
| PyOxim | [Ethyl cyano(hydroxyimino)acetato-O2]tri-1-pyrrolidinylphosphonium hexafluorophosphate |
| RP-HPLC | Reverse phase-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| r.t. | Room temperature |
| SAR | Structure-activity relationship |
| SI | Selectivity index |
| SPPS | Solid-phase peptide synthesis |
| TES | Triethylsilane |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TFMSA | Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| TIPS | Triisopropylsilane |
| WA | Wollamide A |
| WB | Wollamide B |
References
- Giordanetto, F.; Kihlberg, J. Macrocyclic drugs and clinical candidates: What can medicinal chemists learn from their properties? J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 278–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walport, L.J.; Obexer, R.; Suga, H. Strategies for transitioning macrocyclic peptides to cell-permeable drug leads. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 48, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, A.; Bisang, C.; Obrecht, D. Advances in macrocyclic peptide-based antibiotics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2850–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, A.; Heyne, H.-U.; Winter, R.; Beyermann, M.; Haber, H.; Carpino, L.A.; Bienert, M. Cyclization of all-L-pentapeptides by means of 1-hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole-derived uronium and phosphonium reagents. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 8831–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopple Kenneth, D. Synthesis of cyclic peptides. J. Pharm. Sci. 1972, 61, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skropeta, D.; Jolliffe, K.A.; Turner, P. Pseudoprolines as removable turn inducers: Tools for the cyclization of small peptides. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 8804–8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayyadi, N.; Taleski, D.; Leesch, S.; Jolliffe, K.A. Investigating the scope of pseudoproline assisted peptide cyclization. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 7700–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.Y.; Taleski, D.; Jolliffe, K.A. Synthesis of dichotomin A: Use of a penicillamine-derived pseudoproline to furnish native valine residues. Aust. J. Chem. 2015, 68, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanathan, S.; Scherkenbeck, J. Cyclodepsipeptides: A rich source of biologically active compounds for drug research. Molecules 2014, 19, 12368–12420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lécaillon, J.; Gilles, P.; Subra, G.; Martinez, J.; Amblard, M. Synthesis of cyclic peptides via O–N-acyl migration. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 4674–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiya, T.; Kawashima, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Kimura, T.; Sohma, Y.; Kiso, Y. Epimerization-free synthesis of cyclic peptide by use of the O-acyl isopeptide method. J. Pept. Sci. 2010, 16, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, T.A.; Lohman, R.-J.; Hoang, H.N.; Nielsen, D.S.; Scully, C.C.G.; Kok, W.M.; Liu, L.; Lucke, A.J.; Stoermer, M.J.; Schroeder, C.I.; et al. Cyclic penta- and hexaleucine peptides without N-methylation are orally absorbed. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandadapu, S.R.; Weerawarna, P.M.; Prior, A.M.; Uy, R.A.Z.; Aravapalli, S.; Alliston, K.R.; Lushington, G.H.; Kim, Y.; Hua, D.H.; Chang, K.-O.; et al. Macrocyclic inhibitors of 3C and 3C-like proteases of picornavirus, norovirus, and coronavirus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3709–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.H. Cyclic peptides as therapeutic agents and biochemical tools. Biomol. Ther. 2012, 20, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyndall, J.D.A.; Nall, T.; Fairlie, D.P. Proteases universally recognize beta strands in their active sites. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 973–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madala, P.K.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; Nall, T.; Fairlie, D.P. Update 1 of: Proteases universally recognize beta strands in their active sites. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, PR1–PR31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.S.; Shepherd, N.E.; Xu, W.; Lucke, A.J.; Stoermer, M.J.; Fairlie, D.P. Orally absorbed cyclic peptides. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8094–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, M.R.; Bockus, A.T.; Blanco, M.-J.; Lokey, R.S. Cyclic peptide natural products chart the frontier of oral bioavailability in the pursuit of undruggable targets. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 38, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Sun, D. Macrocyclic drugs and synthetic methodologies toward macrocycles. Molecules 2013, 18, 6230–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driggers, E.M.; Hale, S.P.; Lee, J.; Terrett, N.K. The exploration of macrocycles for drug discovery—an underexploited structural class. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joel, D.A.T.; David, P.F. Macrocycles mimic the extended peptide conformation recognized by aspartic, serine, cysteine and metallo proteases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 893–907. [Google Scholar]
- Räder, A.F.B.; Reichart, F.; Weinmüller, M.; Kessler, H. Improving oral bioavailability of cyclic peptides by N-methylation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2766–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, I.; Schaefer, M.; Wagner, T.; Oberer, L.; Sager, E.; Wipfli, P.; Vorherr, T. A detailed investigation on conformation, permeability and PK properties of two related cyclohexapeptides. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2015, 21, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwochert, J.; Turner, R.; Thang, M.; Berkeley, R.F.; Ponkey, A.R.; Rodriguez, K.M.; Leung, S.S.F.; Khunte, B.; Goetz, G.; Limberakis, C.; et al. Peptide to peptoid substitutions increase cell permeability in cyclic hexapeptides. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2928–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, R.B. Solid phase peptide synthesis. I. The synthesis of a tetrapeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Doi, T. Conformation-based design and synthesis of apratoxin A mimetics modified at the α,β-unsaturated thiazoline moiety. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 6751–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese David, R.; Wenning, B.; Finlay John, A.; Callow Maureen, E.; Callow James, A.; Fischer, D.; Ober Christopher, K. Amphiphilic oligopeptides grafted to PDMS-based diblock copolymers for use in antifouling and fouling release coatings. Polym. Advan. Technol. 2015, 26, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.M. Solid-phase peptide synthesis: an overview focused on the preparation of biologically relevant peptides. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32658–32672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-C.; Li, S.; Nam, S.-J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C. Nocardiamides A and B, two cyclohexapeptides from the marine-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. CNX037. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, J.R.; Schmitt, A.; Wille, U.; Hutton, C.A. Synthesis of cyclic peptide hemicryptophanes: enantioselective recognition of a chiral zwitterionic guest. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8504–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Muthana, S.M.; Farnsworth, D.; Ludek, O.; Adams, K.; Barchi, J.J.; Gildersleeve, J.C. Enhanced epimerization of glycosylated amino acids during solid phase peptide synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6316–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, M.; Stueben, K.C. Amino acid active esters. III. Base-catalyzed racemization of peptide active esters1,2. J. Org. Chem. 1962, 27, 3409–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Kai, K.; Ganesan, A.; Doi, T. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of PF1171A, C, F, and G, cyclic hexapeptides with insecticidal activity. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 7844–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, Y.; Hanafusa, T.; Gohda, F.; Peterson, S.; Bills, G. Species-level assessment of secondary metabolite diversity among Hamigera species and a taxonomic note on the genus. Mycology 2014, 5, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liermann Johannes, C.; Thines, E.; Anke, H.; Opatz, T. Anthranicine, an unusual cyclic hexapeptide from Acremonium sp. A29-2004. Z. Naturforsch. B. 2009, 64, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-P.; Jung, H.J.; Han, J.M.; Jung, N.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Ko, S.-K.; Soung, N.-K.; Jang, J.-H.; Ahn, J.S. Two cyclic hexapeptides from Penicillium sp. FN070315 with antiangiogenic activities. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, S.; Fagundez, C.; Medeiros, A.; Comini, M.; Scarone, L.; Sellanes, D.; Manta, E.; Tulla-Puche, J.; Albericio, F.; Stewart, L.; et al. Synthesis of cyclohexapeptides as antimalarial and anti-trypanosomal agents. Med. Chem. Commun. 2014, 5, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portmann, C.; Blom, J.F.; Gademann, K.; Jüttner, F. Aerucyclamides A and B: isolation and synthesis of toxic ribosomal heterocyclic peptides from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, S.; Scarone, L.; Manta, E.; Stewart, L.; Yardley, V.; Croft, S.; Serra, G. Synthesis of a Microcystis aeruginosa predicted metabolite with antimalarial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 4994–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompanya, C.; Fernandes, C.; Cravo, S.; Pinto, M.; Dethoup, T.; Silva, A.; Kijjoa, A. A new cyclic hexapeptide and a new isocoumarin derivative from the marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus similanensis KUFA 0013. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1432–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Ganesan, A.; Doi, T. Structure revision of similanamide to PF1171C by total synthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amso, Z.; Kowalczyk, R.; Park, Y.-E.; Watson, M.; Lin, J.-M.; Musson, D.S.; Cornish, J.; Brimble, M.A. Synthesis and in vitro bone cell activity of analogues of the cyclohexapeptide dianthin G. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 6231–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Heapy, A.M.; Kowalczyk, R.; Amso, Z.; Watson, M.; Cornish, J.; Brimble, M.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of the osteoblast proliferating cyclic peptides dianthins G and H. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 7788–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, H.; Laqua, K.; Walkowska, A.M.; Cunningham, F.; Martinez-Martinez, M.S.; Cuevas-Zurita, J.C.; Ballell-Pages, L.; Imming, P. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship study of wollamide B; a new potential anti TB agent. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, L.S.; Tan, G.T.; Sun, D. Solid-phase synthesis of cyclic hexapeptides wollamides A, B and desotamide B. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 2675–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, L.S.; Elmore, J.M.; Dang, U.T.; Wallace, M.J.; Marreddy, R.; Lee, R.B.; Tan, G.T.; Hurdle, J.G.; Lee, R.E.; Sun, D. Solid-phase synthesis and antibacterial activity of cyclohexapeptide wollamide B analogs. ACS Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodtke, R.; Ruiz-Gomez, G.; Kuchar, M.; Pisabarro, M.T.; Novotna, P.; Urbanova, M.; Steinbach, J.; Pietzsch, J.; Loser, R. Cyclopeptides containing the DEKS motif as conformationally restricted collagen telopeptide analogues: synthesis and conformational analysis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 1878–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preference of Amino Acid Residues in the Synthesis of Cyclic Peptides. Available online: http://www.oyg.ac.jp/lib/wp/wp-content/uploads/86247540ee62dd20c98b9566a6a9d57c.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2018).
- Chen, Y.X.; Liu, C.; Liu, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Q.J.; Hu, H.G.; Li, X.; Zou, Y. Total synthesis and antibacterial study of cyclohexapeptides desotamide B, wollamide B and their analogs. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundez, C.; Sellanes, D.; Serra, G. Synthesis of cyclic peptides as potential anti-malarials. ACS Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






















© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prior, A.M.; Hori, T.; Fishman, A.; Sun, D. Recent Reports of Solid-Phase Cyclohexapeptide Synthesis and Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061475
Prior AM, Hori T, Fishman A, Sun D. Recent Reports of Solid-Phase Cyclohexapeptide Synthesis and Applications. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061475
Chicago/Turabian StylePrior, Allan M., Taylor Hori, Ashriel Fishman, and Dianqing Sun. 2018. "Recent Reports of Solid-Phase Cyclohexapeptide Synthesis and Applications" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061475
APA StylePrior, A. M., Hori, T., Fishman, A., & Sun, D. (2018). Recent Reports of Solid-Phase Cyclohexapeptide Synthesis and Applications. Molecules, 23(6), 1475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061475





