Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation of Novel Functionalized Sulfamidocarbonyloxyphosphonates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
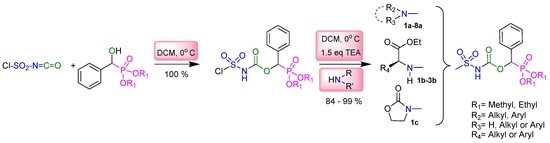
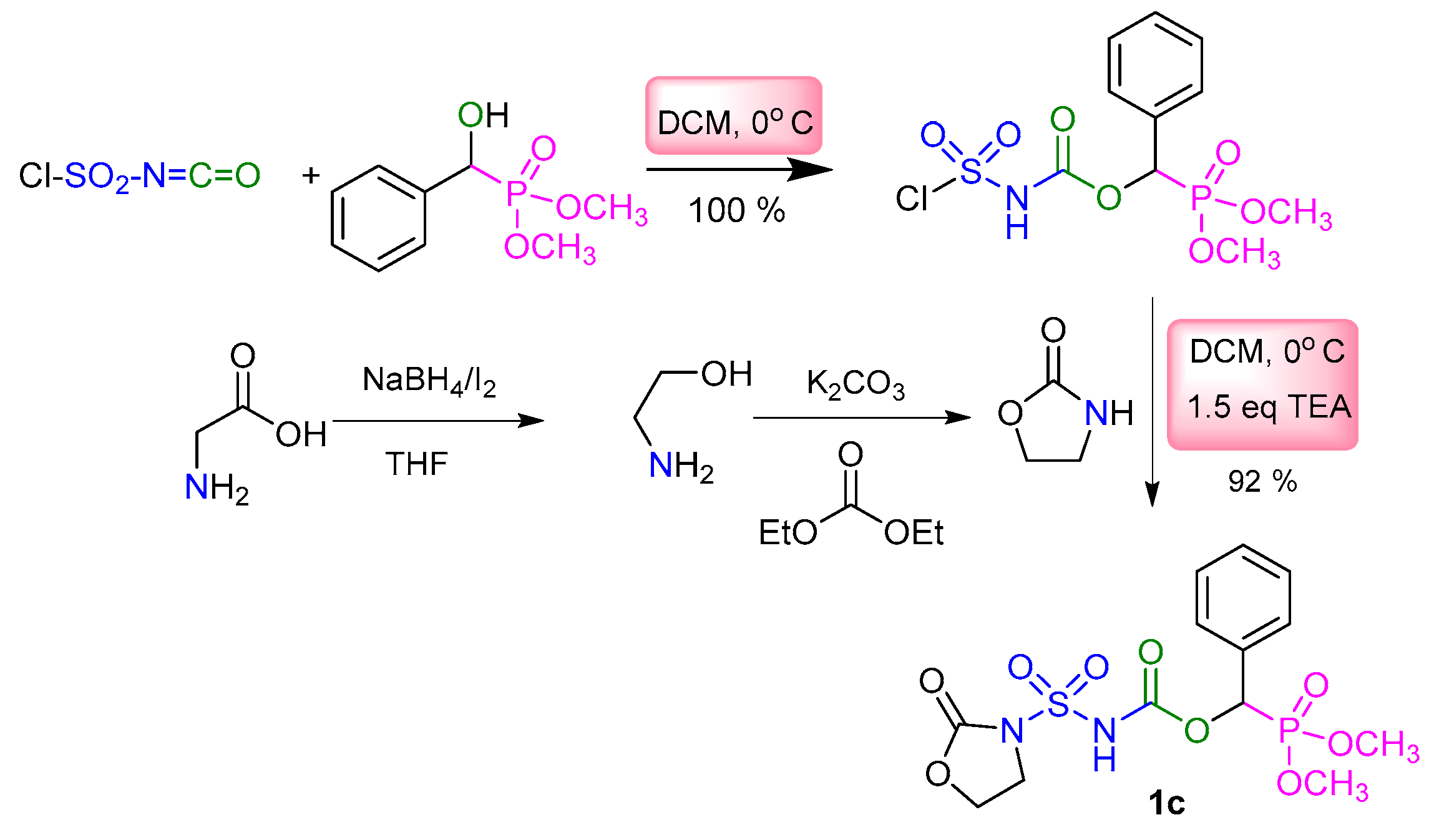
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation of Sulfamidocarbonyloxyphosphonates
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Typical Experimental Procedure for the Synthesis of Sulfamidocarbonyloxyphosphonates 1a–8a, 1b–3b, and 1c
3.3. Determination of In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spillane, W.; Malaubier, J.-B. Sulfamic acid and its N- and O-substituted derivatives. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 2507–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winum, J.Y.; Scozzafava, A.; Montero, J.L.; Supuran, C.T. Therapeutic potential of sulfamides as enzyme inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 767–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, A.B.; Smith, G.R.; Parker, M.H. The role of sulfamide derivatives in medicinal chemistry: A patent review (2006–2008). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2009, 19, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berredjem, H.; Reggami, Y.; Benlaifa, M.; Berredjem, M.; Bouzerna, N. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic potential of 3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-sulfonamide in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 11, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Suthagar, K.; Fairbanks, A.J. Synthesis and anti-mycobacterial activity of glycosyl sulfamides of arabinofuranose. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalba, M.L.; Enrique, A.V.; Higgs, J.; Castaño, R.A.; Goicoechea, S.; Taborda, F.D.; Gavernet, L.; Lick, I.D.; Marder, M.; Bruno Blanch, L.E. Novel sulfamides and sulfamates derived from amino esters: Synthetic studies and anticonvulsant activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 774, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becheker, I.; Berredjem, H.; Boufas, W.; Berredjem, M. The antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of four new sulfonamides against clinical Gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2016, 39, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Berrino, E.; Bua, S.; Mori, M.; Botta, M.; Murthy, V.S.; Vijayakumar, V.; Tamboli, Y.; Bartolucci, G.; Mugelli, A.; Cerbai, E.; et al. Novel sulfamide-containing compounds as selective carbonic anhydrase I inhibitors. Molecules 2017, 22, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juna, J.H.; Kumarb, V.; Dexheimerc, T.S.; Wedlichd, I.; Nicklausd, M.C.; Pommierc, Y.; Malhotra, S.V. Synthesis, anti-cancer screening and tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (Tdp1) inhibition activity of novel piperidinyl sulfamides. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.K.; Barton, D.H.; Ollis, R.; Jones, W.D. Sulfonic Acids and Their Derivatives in Comprehensive Organic Chemistry; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979; Volume 3, pp. 331–340. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, C.; Paez, J.A.; Goya, P.; Serrano, A.; Pavon, J.; Rodriguez de Fonseca, F.; Suardiaz, M.; Martin, M.I. Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of sulfamide-based analogues of anandamide. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4889–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Casini, A.; Mastrolorenzo, A.; Scozzafava, A. COX-2 selective inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase inhibition and anticancer properties of sulfonamides belonging to this class of pharmacological agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, F.; Casini, A.; Owa, T.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: E7070, a sulfonamide anticancer agent, potently inhibits cytosolic isozymes I and II, and transmembrane, tumor-associated isozyme IX. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, N.A.; Batchelor, D.; Beaudoin, S.; Bechle, B.M.; Bradley, P.A.; Brown, A.D.; Brown, B.; Butcher, K.J.; Butt, R.P.; Chapman, M.L.; et al. Discovery of clinical candidate 4-[2-(5-amino-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-4-chlorophenoxy]-5-chloro-2-fluoro-N-1,3-thiazol-4-ylbenzenesulfonamide (PF-05089771): Design and optimization of diaryl ether aryl sulfonamides as selective inhibitors of NaV1.7. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7029–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdoli, M.; Angeli, A.; Bozdag, M.; Carta, F.; Kakanejadifard, A.; Saeidian, H.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis and carbonic anhydrase I, II, VII, and IX inhibition studies with a series of benzo[d]thiazole-5- and 6-sulfonamides. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, S.A.; Salin, O.; Bastidas, R.J.; Sunduru, N.; Hedenström, M.; Andersson, C.D.; Otero, C.N.; Engström, P.; Valdivia, R.H.; Elofsson, M.; Gylfe, A. N-acylated derivatives of sulfamethoxazole block Chlamydia fatty acid synthesis and interact with FabF. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00716-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasone, A.; Tortorella, P.; Campestre, C.; Agamennone, M.; Preziuso, S.; Chiappini, M.; Nuti, E.; Carelli, P.; Rossello, A.; Mazza, F.; et al. α-Biphenylsulfonylamino 2-methylpropyl phosphonates: Enantioselective synthesis and selective inhibition of MMPs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Young, J.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Minh Thai, K. Synthesis and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitory activity of new sildenafil analogues containing a phosphonate group in the 5′-sulfonamide moiety of phenyl ring. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, C.P.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Xu, C.; Bhandari, A.; Moody, C.M.; Miguel, J.A.; Ferla, S.W.; De Francisco, M.N.; Frederick, B.T.; et al. Discovery and structure–activity relationships of novel sulfonamides as potent PTP1B inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4336–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, W.J.; Cho, A. Preparation of Phosphonate Derivatives of Mycophenolic Acid as Anticancer, Antiviral and Anti-Inflammatory Agents. WO2006047661, 4 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Timmler, H.; Wegler, R.; Unterstenhafer, G. Procédé de Fabrication de Dérivés Phosphorylés de Sulfonyle Urethanes. FR1,403,523A, 18 June 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Winum, J.Y.; Bouissiere, J.L.; Passagne, I.; Evrard, A.; Montero, V.; Cuq, P.; Montero, J.L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of fotemustine analogues on human melanoma cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzatt, R.; Cirillo, S.L.; Cirillo, J.D. Sulfonamide agents for treatment of Staphylococcus MRSA and MSSA infections of the central nervous system. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sköld, O. Sulfonamide resistance: Mechanisms and trends. Drug Resist. Updates 2000, 3, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huovinen, P. Resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karageorgopoulos, D.E.; Wang, R.; Yu, X.H.; Falagas, M.E. Fosfomycin: Evaluation of the published evidence on the emergence of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossolini, G.M.; Mantengoli, E. Antimicrobial resistance in Europe and its potential impact on empirical therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14 (Suppl. 6), 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheloufi, H.; Berredjem, M.; Boufas, W.; Bouchareb, F.; Aouf, N.E. Efficient synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of novel N-acylsulfonamides and sulfonylureas. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2014, 189, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Boufas, W.; Cheloufi, H.; Bouchareb, F.; Berredjem, M.; Aouf, N.E. Convenient synthesis of novel N-acylsulfonamides containing phosphonates moiety. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2015, 190, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchareb, F.; Berredjem, M.; Ait Kaki, S.; Bouaricha, A.; Bouzina, A.; Belhani, B.; Aouf, N.E. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of new chiral N-sulfamoyloxazolidin-2-ones. J. Chem. Sci. 2016, 128, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzina, A.; Grib, I.; Bechlem, K.; Belhani, B.; Aouf, N.E.; Berredjem, M. Efficient synthesis of novel N-acylsulfonamide oxazolidin-2-ones derivatives. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2016, 2, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 27th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Standards M02-M07; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhani, S.; Tashrifi, Z. Synthesis of α-functionalized phosphonates from α-hydroxyphosphonates. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzina, A.; Aouf, N.E.; Berredjem, M. Ultrasound assisted green synthesis of α-hydroxyphosphonates under solvent free conditions. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 5993–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboudin, B.; Afsharinezhad, M.B.; Yokomatsu, T. A convenient and general procedure for the synthesis of α-ureidophosphonates under catalyst-free conditions. Arkivoc 2012, 4, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Chen, W.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Silver-catalyzed, aldehyde-induced α-C−H functionalization of tetrahydroisoquinolines with concurrent C−P bond formation/N-alkylation. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the synthesized compounds are available from the corresponding authors. |





| Entry | -NR2R3 | Target Molecule | Yield % | m.p. °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 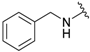 | 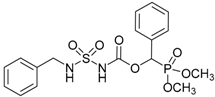 | 99 | 131–133 |
| 2a |  | 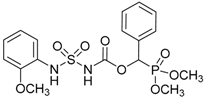 | 98 | 137–139 |
| 3a | 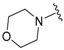 | 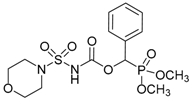 | 98 | 144–146 |
| 4a | 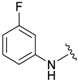 | 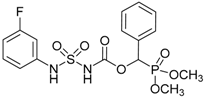 | 96 | 136–138 |
| 5a | 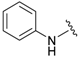 | 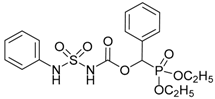 | 96 | 187–189 |
| 6a | 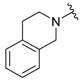 | 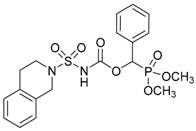 | 94 | 153–155 |
| 7a | 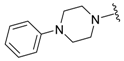 |  | 93 | 152–154 |
| 8a | 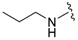 | 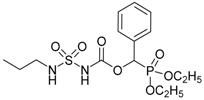 | 97 | 151–153 |
| Entry | R4 | Target Molecule | Yield | m.p. °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1b |  | 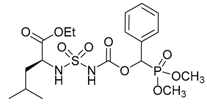 | 91 | 118–120 |
| 2b | 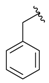 |  | 94 | 125–127 |
| 3b |  | 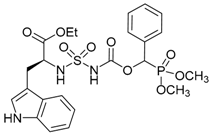 | 84 | 116–118 |
| Entry | Target Molecule | Yield % | m.p. °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1c | 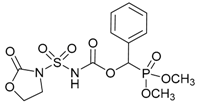 | 92 | 123–125 |
| Molecules | Diameters of Inhibition Zone (DIZ) in mm a | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Strains | 1a | 2a | 3a | 4a | 5a | 6a | 7a | 1b | SXT | |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 15 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 15 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 22 | |
| S. aureus 1 | 16 | 15 | 14 | R b | 18 | 13 | 14 | 12 | 20 | |
| S. aureus 2 | 16 | 15 | 16 | R | 16 | 15 | 12 | 13 | 18 | |
| S. aureus 3 | 17 | 14 | 15 | R | 17 | 14 | 13 | 15 | 18 | |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 24 | 23 | 25 | 25 | 23 | 21 | 23 | 18 | 20 | |
| E. coli 1 | 17 | 22 | 18 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 18 | |
| E. coli 2 | 22 | 19 | 24 | 24 | 22 | 18 | 23 | 20 | 18 | |
| E. coli 3 | 20 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 19 | 18 | 20 | 17 | 20 | |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 26 | 20 | 18 | 23 | 19 | 19 | 20 | 18 | 17 | |
| P. aeruginosa 1 | 24 | 20 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 20 | 18 | 20 | R | |
| P. aeruginosa 2 | 26 | 19 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 20 | |
| P. aeruginosa 3 | 25 | 21 | 21 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 19 | R | 18 | |
| K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603 | 22 | 19 | 13 | 20 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 19 | 22 | |
| K. pneumoniae 1 | 22 | 21 | 18 | 25 | 15 | 18 | 19 | 15 | R | |
| K. pneumoniae 2 | 20 | 21 | 17 | 25 | 20 | 18 | 16 | R | 17 | |
| K. pneumoniae 3 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 24 | 19 | 19 | 22 | 21 | R | |
| Molecules | MIC (µg/mL) a | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Strains | 1a | 2a | 3a | 4a | 5a | 6a | 7a | 1b | |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 128 | 128 | 256 | 512 | 256 | 128 | 256 | 15 | |
| S. aureus 1 | 128 | 256 | 256 | R b | 64 | 128 | 256 | 15 | |
| S. aureus 2 | 64 | 128 | 128 | R | 128 | 64 | 128 | 18 | |
| S. aureus 3 | 64 | 128 | 128 | R | 128 | 128 | 128 | 15 | |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0.5 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 18 | |
| E. coli 1 | 32 | 16 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 4 | 18 | |
| E. coli 2 | 4 | 16 | 2 | 0.5 | 4 | 16 | 8 | 20 | |
| E. coli 3 | 8 | 32 | 4 | 1 | 16 | 4 | 32 | 17 | |
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 0.5 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 18 | |
| P. aeruginosa 1 | 0.5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 20 | |
| P. aeruginosa 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 17 | |
| P. aeruginosa 3 | 0.5 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | R | |
| K. pneumoniae ATCC 700603 | 4 | 32 | 256 | 16 | 128 | 128 | 32 | 19 | |
| K. pneumoniae 1 | 4 | 64 | 32 | 2 | 128 | 64 | 128 | 15 | |
| K. pneumoniae 2 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 2 | 32 | 128 | 128 | R | |
| K. pneumoniae 3 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 4 | 128 | 64 | 64 | 21 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouzina, A.; Bechlem, K.; Berredjem, H.; Belhani, B.; Becheker, I.; Lebreton, J.; Le Borgne, M.; Bouaziz, Z.; Marminon, C.; Berredjem, M. Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation of Novel Functionalized Sulfamidocarbonyloxyphosphonates. Molecules 2018, 23, 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071682
Bouzina A, Bechlem K, Berredjem H, Belhani B, Becheker I, Lebreton J, Le Borgne M, Bouaziz Z, Marminon C, Berredjem M. Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation of Novel Functionalized Sulfamidocarbonyloxyphosphonates. Molecules. 2018; 23(7):1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071682
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouzina, Abdeslem, Khaoula Bechlem, Hajira Berredjem, Billel Belhani, Imène Becheker, Jacques Lebreton, Marc Le Borgne, Zouhair Bouaziz, Christelle Marminon, and Malika Berredjem. 2018. "Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation of Novel Functionalized Sulfamidocarbonyloxyphosphonates" Molecules 23, no. 7: 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071682
APA StyleBouzina, A., Bechlem, K., Berredjem, H., Belhani, B., Becheker, I., Lebreton, J., Le Borgne, M., Bouaziz, Z., Marminon, C., & Berredjem, M. (2018). Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, and In Vitro Antibacterial Evaluation of Novel Functionalized Sulfamidocarbonyloxyphosphonates. Molecules, 23(7), 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071682