Surface Hydrophobicity and Functional Properties of Citric Acid Cross-Linked Whey Protein Isolate: The Impact of pH and Concentration of Citric Acid
Abstract
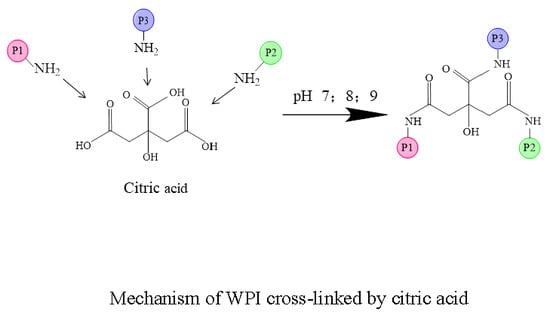
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.2. Zeta Potential
2.3. Protein Solubility
2.4. Emulsifying Properties
2.5. Foaming Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Citric Acid-Mediated Cross-Linking of WPI
3.3. Surface Hydrophobicity
3.4. Zeta Potential
3.5. Solubility
3.6. Emulsifying Activity and Emulsion Stability
3.7. Foaming Activity and Foam Stability
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Ning, J.; Clark, S. Changes in structure and functional properties of whey proteins induced by high hydrostatic pressure: A review. Front. Chem. Eng. China 2009, 3, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lópezfandiño, R. Functional improvement of milk whey proteins induced by high hydrostatic pressure. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Wicker, L. Laccase mediated conjugation of heat treated β-lactoglobulin and sugar beet pectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffensen, C.L.; Andersen, M.L.; Degn, P.E.; Nielsen, J.H. Cross-linking proteins by laccase-catalyzed oxidation: Importance relative to other modifications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 12002–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, T.; Sailakshmi, G.; Gnanamani, A.; Mandal, A.B. Studies on cross-linking of succinic acid with chitosan/collagen. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, J.E.; Scotchford, C.A.; Downes, S. Cytotoxicity of glutaraldehyde crosslinked collagen/poly(vinyl alcohol) films is by the mechanism of apoptosis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaee, A.; Madadlou, A.; Saboury, A.A. The formation of non-heat-treated whey protein cold-set hydrogels via non-toxic chemical cross-linking. Food Hydrocol. 2017, 63, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, T.; Madadlou, A.; Labbafi, M. Characteristics of the bulk hydrogels made of the citric acid cross-linked whey protein microgels. Food Hydrocol. 2015, 50, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shen, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y. Low-temperature crosslinking of proteins using non-toxic citric acid in neutral aqueous medium: Mechanism and kinetic study. Ind. Crop Prod. 2015, 74, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Alkali-catalyzed low temperature wet crosslinking of plant proteins using carboxylic acids. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 25, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, L.; Yarmand, M.; Madadlou, A.; Mousavi, M.E. Transglutaminase-induced or citric acid-mediated cross-linking of whey proteins to tune the characteristics of subsequently desolvated sub-micron and nano-scaled particles. J. Microencapsul. 2014, 31, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourbakhsh, H.; Emamdjomeh, Z.; Madadlou, A.; Mousavi, M.; Moosavimovahedi, A.A.; Gunasekaran, S. Antioxidant peptidic particles for delivery of gallic acid. J. Food Process Preserv. 2017, 41, e12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zand-Rajabi, H.; Madadlou, A. Citric acid cross-linking of heat-set whey protein hydrogel influences its textural attributes and caffeine uptake and release behaviour. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkis, J.; Villota, R. Effect of acylation on substructural properties of proteins: A study using fluorescence and circular dichroism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Qi, B.; Zhou, L. Relationship between secondary structure and surface hydrophobicity of soybean protein isolate subjected to heat treatment. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpashree, B.G.; Arora, S.; Chawla, P.; Tomar, S.K. Effect of succinylation on physicochemical and functional properties of milk protein concentrate. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, F.J.; German, J.B.; Kinsella, J.E. Effect of ph and temperature on protein unfolding and thiol/disulfide interchange reactions during heat-induced gelation of whey proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhg, P.; Gasparetto, C.A. Whey proteins solubility as function of temperature and pH. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 38, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Krasaechol, N.; Sanguandeekul, R.; Duangmal, K.; Owusuapenten, R.K. Structure and functional properties of modified threadfin bream sarcoplasmic protein. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S.; Adebowale, K.O.; Adebowale, Y.A. Functional properties of native and chemically modified protein concentrates from bambarra groundnut. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leila, M.; Mahdi, K.; Mohammad, S. Effects of succinylation and deamidation on functional properties of oat protein isolate. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, O.S. Functionality of native and succinylated lablab bean (lablab purpureus) protein concentrate. Food Hydrocol. 2005, 19, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgorzata, K.; Alexander, T.; Ulrich, K. Impact of pH on the interactions between whey and egg white proteins as assessed by the foamability of their mixtures. Food Hydrocol. 2009, 23, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Maria, S.D.; Ferrari, G.; Maresca, P. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on the conformational structure and the functional properties of bovine serum albumin. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, R.N.; Tolkach, A.; Kulozik, U.; Aguilera, J.M. Kinetics of formation and physicochemical characterization of thermally-induced beta-lactoglobulin aggregates. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, E261–E268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, F. Effects of high pressure processing on the structural and functional properties of bovine lactoferrin. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Wang, C.; Li, T.; Ma, L.; Sun, D.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Z. Surface Hydrophobicity and Functional Properties of Citric Acid Cross-Linked Whey Protein Isolate: The Impact of pH and Concentration of Citric Acid. Molecules 2018, 23, 2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092383
Li T, Wang C, Li T, Ma L, Sun D, Hou J, Jiang Z. Surface Hydrophobicity and Functional Properties of Citric Acid Cross-Linked Whey Protein Isolate: The Impact of pH and Concentration of Citric Acid. Molecules. 2018; 23(9):2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092383
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tong, Chunyan Wang, Tianqi Li, Ling Ma, Dongxue Sun, Juncai Hou, and Zhanmei Jiang. 2018. "Surface Hydrophobicity and Functional Properties of Citric Acid Cross-Linked Whey Protein Isolate: The Impact of pH and Concentration of Citric Acid" Molecules 23, no. 9: 2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092383
APA StyleLi, T., Wang, C., Li, T., Ma, L., Sun, D., Hou, J., & Jiang, Z. (2018). Surface Hydrophobicity and Functional Properties of Citric Acid Cross-Linked Whey Protein Isolate: The Impact of pH and Concentration of Citric Acid. Molecules, 23(9), 2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092383