Simultaneous Characterization and Quantification of Varied Ingredients from Sojae semen praeparatum in Fermentation Using UFLC–TripleTOF MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
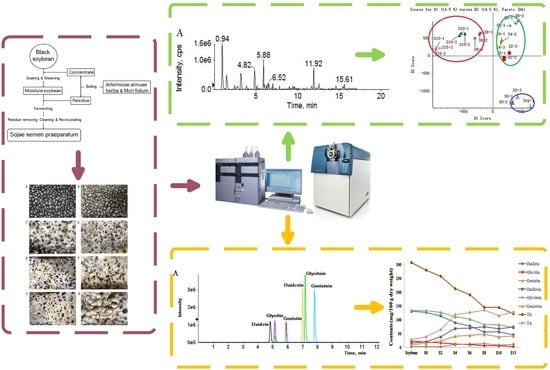
2.1. Morphologic Changes
2.2. Qualitative Analysis and Principle Component Analysis (PCA)
2.3. Relative Quantitative Analysis
2.4. Accurate Quantitative Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. SSP Fermentation
3.3. Sample Extraction
3.4. Standard Solutions Preparation
3.5. LC-MS Spectrometric Conditions
3.6. Method Validation
3.7. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, M.-Y.; Chai, C.; Park, J.H.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.; Kwon, S.W. Effects of storage period and heat treatment on phenolic compound composition in dried citrus peels (chenpi) and discrimination of chenpi with different storage periods through targeted metabolomic study using hplc-dad analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortera, P.; Zuljan, F.A.; Magni, C.; Bortolato, S.A.; Alarcon, S.H. Multivariate analysis of organic acids in fermented food from reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography data. Talanta 2018, 178, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Ju, H.K.; Kim, S.C.; Park, J.H.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, J. Determination of bioactive compounds in fermented soybean products using gc/ms and further investigation of correlation of their bioactivities. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 880, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bi, K.; Han, F.; Guan, J.; Zhang, X.; Mao, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Hou, X.; Yin, R. Identification of the absorbed components and metabolites of zhi-zi-da-huang decoction in rat plasma by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 111, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, P.; Xie, M.; An, F.; Qiu, B.; Wu, R. Metaproteomics of microbiota in naturally fermented soybean paste, da-jiang. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, B.; Park, H.; Ji, Y.; Holzapfel, W.; Kim, D.Y.; Hyun, C.K. Long-term fermented soybean paste improves metabolic parameters associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.W.; Shahzad, R.; Bilal, S.; Adhikari, B.; Kim, I.D.; Lee, J.D.; Lee, I.J.; Kim, B.O.; Shin, D.H. Comparison of antioxidants potential, metabolites, and nutritional profiles of korean fermented soybean (cheonggukjang) with bacillus subtilis kctc 13241. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2871–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Fan, G.; Peng, J.; Mi, H. Isolation of six isoflavones from semen sojae praeparatum by preparative HPLC. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Bai, Y.T.; Wen, H.M.; Song, L.H.; Tu, J.Y.; Shan, C.X. Determination of 3 kinds of isoflavone aglycones in semen sojae praeparatum by uplc. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2012, 12, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Chang, R.; Liu, Z.; Hao, H.; Huang, T.; Wen, J.; Zhou, T. A new strategy for statistical analysis-based fingerprint establishment: Application to quality assessment of semen sojae praeparatum. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Shi, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, M. Simultaneous high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and time-of-flight mass spectrometric confirmation of the ten bioactive compounds in semen sojae preparatum. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3360–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Tatsumi, E.; Ding, C.-H.; Li, L.-T. Angiotensin i-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in douchi, a chinese traditional fermented soybean product. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Kung, H.-F.; Chang, S.-C.; Lee, T.-M.; Wei, C.-I. Histamine formation by histamine-forming bacteria in douchi, a chinese traditional fermented soybean product. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Cui, X.; Shan, C.; Yu, S.; Wen, H. Contents variation analysis of free amino acids, nucleosides and nucleobases in semen sojae praeparatum fermentation using uflc-qtrap ms. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Yu, S.; Cui, X.B.; Zhang, A.H.; Zhu, D.; Shan, C.X.; Wen, H.M. Analysis of volatile components in semen sojae praepatum with automatic static headspace and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Res. Dev. 2013, 34, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, H.; Feng, X.; Zhu, K.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Kan, J. Shuidouchi (fermented soybean) fermented in different vessels attenuates hcl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury. Molecules 2015, 20, 19748–19763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Zhao, L.; Luo, X.; Zhang, C.; Hou, P.; Bi, K.; Chen, X. An LC-MS method for simultaneous determination of five iridoids from zhi-zi-chi decoction in rat brain microdialysates and tissue homogenates: Towards an in depth study for its antidepressive activity. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 965, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cheng, Y.-Q.; Yamaki, K.; Li, L.-T. Anti-α-glucosidase activity of chinese traditionally fermented soybean (douchi). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean, S.; Beggs, L.B.; Welch, R.W. Antimicrobial activity of antihypertensive food-derived peptides and selected alanine analogues. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.J.C.P. Screening and enzymatic activity analysis of dominant fermentive bacteria of sojae semen praeparatum from different production places. China Pharma. 2017, 28, 4359–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Long, K.; Su, M.S.; Liang, Y.H.; Yang, A.J.; Xie, X.M. Preliminary study on dynamic change of microbial flora in fermentation process to ‘yellow cladding’ of sojoe semen praeparatum. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2014, 20, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Blay, M.; Espinel, A.E.; Delgado, M.A.; Baiges, I.; Bladé, C.; Arola, L.; Salvadó, J. Isoflavone effect on gene expression profile and biomarkers of inflammation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.H.; Chen, B.H. Effects of different carriers on the production of isoflavone powder from soybean cake. Molecules 2007, 12, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Biswas, A.; Chhetri, A.; Sarkar, P.K. Response surface optimisation of antioxidant extraction from kinema, a bacillus-fermented soybean food. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, L.; Li, D.; Zou, L.; Saito, M.; Tatsumi, E.; Li, L. Influences of processing and nacl supplementation on isoflavone contents and composition during douchi manufacturing. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Fernández, E.; Gómez-Romero, M.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Application and potential of capillary electroseparation methods to determine antioxidant phenolic compounds from plant food material. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 1130–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, P.; Medina, M.; Sanchez-Jimenez, A.; Landete, J.M. Phytoestrogen metabolism by adult human gut microbiota. Molecules 2016, 21, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Seo, S.-H.; Ahn, J.-K.; Kim, S.-H. Effect of processing, fermentation, and aging treatment to content and profile of phenolic compounds in soybean seed, soy curd and soy paste. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L. Hydrolysis of soybean isoflavone glycosides by a thermostable β-glucosidase from paecilomyces thermophila. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Ito, J.; Kotaka, A.; Matsumura, K.; Bando, H.; Sahara, H.; Ogino, C.; Shibasaki, S.; Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M.; et al. Isoflavone aglycones production from isoflavone glycosides by display of beta-glucosidase from aspergillus oryzae on yeast cell surface. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Su, W.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Peng, W.; Yao, H. UFLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS-based screening and identification of flavonoids and derived metabolites in human urine after oral administration of exocarpium citri grandis extract. Molecules 2018, 23, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Pharmacopoeia Commission of the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China; Part I; Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ben, P.; Duan, Y.; Lu, M.; Li, Z.; Cui, Z. Characterization of a novel gh36 alpha-galactosidase from bacillus megaterium and its application in degradation of raffinose family oligosaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.W.; Wei, X.J. Fatty acid analysis of edible oils. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 962–965, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.M.; Doehlert, D.C.; Crawford, C.G. Sugar metabolism in germinating soybean seeds. Evidence for the sorbitol pathway in soyabean axes. Plant Physiol. 1990, 93, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Qiu, J. Study on chemical composition of folium mori. Food Drug 2007, 30, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Extraction and isolation of potential anti-stroke compounds from flowers of pueraria lobata guided by in vitro pc12 cell model. J. chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1048, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Yao, Y.S.; Qin, Y.C.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.G.; Li, J.; Gu, X. Investigation and analysis of main afn in soybean meal and fermented soybean meal. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2016, 49, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, N.; Lin-Jie, B.I.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.J. The condition optimization of bacterial combinations for fermentation of bean and determination of the content of stachyose and raffinose. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2015, 54, 4007–4011. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.; Qi, W.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Liang, X.; Yun, T.; Wang, Y. Effects of different bacteria on fermentative degradation of stachyose and raffinose in soybean meal and detection technology. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2014, 29, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.H.; Chou, C.C. Distribution profiles of isoflavone isomers in black bean kojis prepared with various filamentous fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |







| Ionization Mode | Compound No. | tR a (min) | Molecular Formula | Mass (Da) | Ion Species | Mean Measured Mass (Da) | Mass Accuracy (ppm) | Assigned Identity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 1 | 0.93 | C12H18N6O6 | 342.1288 | [M + K]+ | 381.0907 | −0.4 | / b | – c |
| 2 | 0.93 | C18H32O16 | 504.1690 | [M + K]+ | 543.1474 | −1.9 | Raffinose | [33] | |
| 3 | 0.95 | C24H42O21 | 666.2213 | [M + K]+ | 705.2045 | −1.2 | Stachyose | [33] | |
| 4 | 1.44 | C13H15N3O5 | 293.1012 | [M + NH4]+ | 311.1328 | −2.2 | / b | − c | |
| 5 | 3.86 | C14H14N2O5 | 290.0903 | [M + H]+ | 291.0955 | −4.6 | N−(3−Indolylacetyl)−dl−aspartic acid | − c | |
| 6 | 4.81 | C21H20O9 | 416.1107 | [M + H]+ | 417.1307 | 0.8 | Daidzin | [37] | |
| 7 | 5.14 | C22H22O10 | 446.1213 | [M + H]+ | 447.1429 | −0.3 | Glycitin | [37] | |
| 8 | 5.89 | C21H20O10 | 432.1057 | [M + H]+ | 433.1266 | 0.9 | Genistin | [37] | |
| 9 | 6.03 | C24H22O12 | 502.1111 | [M + H]+ | 503.1335 | −0.6 | 6″−O−malonyldaidzin | [37] | |
| 10 | 6.04 | C25H24O13 | 532.1217 | [M + H]+ | 533.1451 | −1.3 | 6″−O−malonylglycitin | [37] | |
| 11 | 6.44 | C23H22O10 | 458.1213 | [M + H]+ | 459.1435 | −0.2 | 6″−O−acetyldaidzin | [37] | |
| 12 | 6.51 | C24H24O11 | 488.1319 | [M + H]+ | 489.1535 | −1.0 | 6″−O−acetylglycitin | [37] | |
| 13 | 6.57 | C24H22O13 | 518.1060 | [M + H]+ | 519.1285 | −0.8 | 6″−O−malonylgenistin | [37] | |
| 14 | 7.00 | C15H10O4 | 254.0579 | [M + H]+ | 255.0726 | 0.9 | Daidzein | [37] | |
| 15 | 7.05 | C23H22O11 | 474.1162 | [M + H]+ | 475.1379 | −1.0 | 6″−O−acetylgenistin | [37] | |
| 16 | 7.17 | C16H12O5 | 284.0685 | [M + H]+ | 285.0840 | 0.3 | Glycitein | [37] | |
| 17 | 7.69 | C7H16N4O2 | 188.1268 | [M + H + H2O]+ | 207.1452 | −3.9 | Methylarginine | − c | |
| 18 | 7.80 | C15H10O5 | 270.0528 | [M + H]+ | 271.0680 | 1.0 | Genistein | [37] | |
| 19 | 11.94 | C21H45N9O6 | 519.3493 | [M + H]+ | 520.3534 | 1.0 | / b | − c | |
| 20 | 13.29 | C18H32O3 | 296.2710 | [M + H]+ | 297.2517 | −3.9 | Dimorphecolic acid | − c | |
| 21 | 13.77 | C23H44O2 | 352.3336 | [M + H]+ | 353.2797 | 0.1 | / b | − c | |
| 22 | 14.61 | C18H30O2 | 278.2246 | [M + H]+ | 279.2408 | −0.4 | α−Linolenic acid | [34] | |
| 23 | 14.76 | C23H46O2 | 354.3492 | [M + H] + | 355.2950 | 0.8 | / b | − c | |
| 24 | 15.62 | C18H32O2 | 280.2402 | [M + H]+ | 281.2567 | 0.7 | Linoleic acid | [34] | |
| 25 | 15.70 | C18H34O2 | 282.2559 | [M + H + CH3OH]+ | 315.2915 | 0.6 | Oleic acid | [34] | |
| 26 | 16.01 | C21H40O2 | 324.3023 | [M + H + CH3OH]+ | 357.3101 | 2.9 | / b | − c | |
| 27 | 16.67 | C16H32O2 | 256.2402 | [M + H]+ | 257.2565 | −0.3 | Palmitic acid | [34] | |
| 28 | 17.04 | C18H36O2 | 284.2715 | [M + H]+ | 285.3050 | −0.8 | Stearic acid | [34] | |
| Negative | 29 | 0.92 | C12H18N6O6 | 342.1288 | [M + HCOO]− | 387.1623 | 1.7 | / b | − c |
| 3 | 0.95 | C24H42O21 | 666.2213 | [M + HCOO]− | 711.3077 | 1.3 | Stachyose | [33] | |
| 30 | 1.05 | C30H32N6O9 | 620.2220 | [M – H − H2O]− | 601.2133 | −1.1 | / b | − c | |
| 31 | 3.12 | C16H18N6 | 294.1582 | [M − H]− | 293.1552 | −1.4 | / b | − c | |
| 32 | 3.21 | C6H14O6 | 182.0790 | [M + CH3COO]− | 241.0915 | 0.8 | Sorbitol | [35] | |
| 5 | 3.85 | C14H14N2O5 | 290.0903 | [M − H]− | 289.1078 | −1.3 | N−(3−Indolylacetyl)−dl−aspartic acid | − c | |
| 6 | 4.81 | C21H20O9 | 416.1107 | [M + HCOO]− | 461.1650 | 0.2 | Daidzin | [37] | |
| 33 | 5.64 | C18H10N2O6 | 350.0528 | [M − H]− | 349.0451 | −2 | / b | − c | |
| 8 | 5.89 | C21H20O10 | 432.1057 | [M + HCOO]− | 477.1629 | −2.5 | Genistin | [37] | |
| 34 | 6.15 | C18H4N6 | 304.0497 | [M + CH3COO]− | 363.0635 | −0.5 | / b | − c | |
| 11 | 6.42 | C23H22O10 | 458.1213 | [M + HCOO]− | 503.1805 | −2.3 | 6″−O−acetyldaidzin | [37] | |
| 35 | 6.47 | C13H10O6 | 262.0466 | [M − H]− | 261.0400 | 2.4 | / b | − c | |
| 36 | 6.68 | C19H6N6O3 | 366.0490 | [M − H]− | 365.0430 | −1.3 | / b | − c | |
| 15 | 7.04 | C23H22O11 | 474.1162 | [M + HCOO]− | 519.1784 | 2.3 | 6″−O−acetylgenistin | [37] | |
| 16 | 7.15 | C16H12O5 | 284.0685 | [M − H]− | 283.0969 | 2.1 | Glycitein | [37] | |
| 37 | 7.91 | C18H18O10 | 394.0895 | [M + HCOO]− | 439.0878 | −2.0 | / b | − c | |
| 38 | 10.83 | C31H50N2O9 | 594.3505 | [M − H]− | 593.3490 | −0.6 | / b | − c | |
| 39 | 11.29 | C19H36O3 | 312.2654 | [M – H − H2O]− | 293.2483 | 1.7 | / b | − c | |
| 40 | 11.66 | C32H48N6O5 | 596.3675 | [M − H]− | 595.3613 | 1.9 | / b | − c | |
| 41 | 12.06 | C17H36N8O5 | 432.2798 | [M − H]− | 431.2728 | 0.1 | / b | − c | |
| 42 | 12.54 | C34H68O2 | 508.3389 | [M − H]− | 507.3340 | 0.1 | Gheddic acid | [36] | |
| 43 | 12.58 | C19H38O2 | 298.2861 | [M − H]− | 297.2814 | 4.0 | Nonadecanoic acid | − c | |
| 44 | 13.57 | C18H42N10O | 414.3543 | [M + HCOO]− | 459.3520 | −1.3 | / b | − c | |
| 45 | 15.55 | C12H28N8O6 | 380.2121 | [M − H]− | 379.2049 | −2.6 | / b | − c |
| Compound No. | Assigned Identity (Ion Mode) | MS/MS Fragments Ions |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Raffinose (+) | 543.1474[M + K]+, 381.0905[M + K − glu + H2O]+, |
| 3 | Stachyose (+) | 705.2045[M + K]+, 543.1471[M+K − glu]+, |
| (−) | 711.3077[M + HCOO]−, 665.3014[M − H]−, 485.2130[M – H − glu]−, 341.1514[M − H − 2glu + 2H2O]−, | |
| 5 | N−(3−Indolylacetyl)−dl−aspartic acid (+) | 291.0955[M + H]+, 161.0645[C5H6O2N + H]+, 139.0428[M + H − C8H6N − 2H2O]+, |
| (−) | 289.1078[M − H]−, 271.0968[M − H − H2O]−, 245.1127[M − H − CO2]−, 227.1008[M − H − CO2 − H2O]−, | |
| 6 | Daidzin (+) | 439.1128[M + Na]+, 417.1307[M + H]+, 277.0551[M + Na − glu + H2O]+, 255.0728[M + H − glu + H2O]+, |
| (−) | 461.1650[M + HCOO]−, 415.1556[M − H]−, 253.0825[M − H − glu + H2O]−, | |
| 7 | Glycitin (+) | 469.1235[M + Na]+, 447.1429[M + H]+, 307.0662[M + Na − glu + H2O]+, 285.0839[M + H – glu + H2O]+, |
| 8 | Genistin (+) | 433.1266[M + H]+, 271.0674[M + H – glu + H2O]+, 243.0712[M + H – glu + H2O − CO]+, 215.0752[M + H – glu + H2O − 2CO]+, 153.0218[M + H − C13H12O7]+, |
| (−) | 477.1629[M + HCOO]−, 431.1529[M − H]−, 269.0795[M – H – glu + H2O]−, | |
| 9 | 6″−O−malonyldaidzin (+) | 525.1146[M + Na]+, 503.1335[M + H]+, 481.1244[M + Na − CO2]+, 439.1133[M + Na − malonyl − H2O]+, 277.0549[M + Na – malonyl − glu]+, 255.0728[M + H – malonyl − glu]+, |
| 10 | 6″−O−malonylglycitin (+) | 533.1451[M + H]+, 285.0845[M + H – malonyl − glu]+, |
| 11 | 6″−O−acetyldaidzin (+) | 459.1435[M + H]+, 255.0726[M + H – acetyl − glu]+, |
| (−) | 503.1805[M + HCOO]−, 457.1720[M − H]−, 253.0822[M − H − acetyl − glu]−, | |
| 12 | 6″−O−acetylglycitin (+) | 489.1535[M + H]+, 285.0839[M + H – acetyl − glu]+, |
| 13 | 6″−O−malonylgenistin (+) | 541.1093[M + Na]+, 523.0995[M + Na − H2O]+, 519.1285[M + H]+, 497.1167[M + Na − CO2]+, 455.1096[M + Na – malonyl − H2O]+, 293.0505[M + Na – malonyl − glu]+, 271.0678[M + H – malonyl − glu]+, |
| 14 | Daidzein (+) | 277.0550[M + Na]+, 255.0726[M + H]+, 237.0611[M + H − H2O]+, 227.0762[M + H − CO]+, 199.0806[M + H − 2CO]+, 181.0695[M + H − 2CO − H2O]+, 137.0273[M + H − C8H6O]+, 91.0582[M + H − H2O − C9H6O2]+, |
| 15 | 6″−O−acetylgenistin (+) | 475.1379[M + H] +, 271.0682[M + H − acetyl − glu]+, |
| (−) | 519.1784[M + HCOO]−, 473.1689[M − H]−, 269.0795[M − H – acetyl − glu]−, | |
| 16 | Glycitein (+) | 307.0672[M + Na]+, 285.0840[M + H]+, 270.0599[M + H − CH3]+, 242.0642[M + H − CH3 − CO]+, 169.0614[M + H − C8H4O]+, 141.0740[M + H − C9H4O2]+, |
| (−) | 283.0969[M − H]−, 268.0714[M − H − CH3]−, 240.0729[M − H − CH3 − CO]−, 196.0776[M − C2H3O − OH − OH]−, | |
| 17 | Methylarginine (+) | 207.1452[M + H + H2O]+, 189.1321[M + H]+, 161.1377[M + H − H2O]+, |
| 18 | Genistein (+) | 271.0680[M + H]+, 253.0565[M + H − H2O]+, 243.0716[M + H − CO]+, 215.0757[M + H − 2CO]+, 153.0223[M + H − C8H6O]+, |
| 20 | Dimorphecolic acid (+) | 297.2517[M + H]+, 279.2398[M + H − H2O]+, 261.2287[M + H − 2H2O]+, 233.2328[M + H − 2H2O − CO]+, 109.1051[M + H − C9H17COOH − CH4]+, 97.1051[M + H − C9H17COOH − C2H4]+, 81.0743[M + H − C9H17COOH − C3H8]+, 67.0590[M + H − C9H17COOH − C4H10]+ |
| 22 | α−Linolenic acid (+) | 297.2517[M + H + H2O]+, 279.2408[M + H]+, 149.0276[M + H − C6H3COOH]+, 135.1206[M + H − C7H15COOH]+, 125.1000[M + H − C8H13COOH]+, 123.1200[M + H − C8H15COOH]+, 109.1045[M + H − C9H17COOH]+, 95.0892[M + H − C10H19COOH]+, 81.0738[M + H − C11H21COOH]+, 67.0588[M + H − C12H23COOH]+, |
| 24 | Linoleic acid (+) | 313.2827[M + H + CH3OH]+, 281.2567[M + H]+, 263.2443[M + H − H2O]+, 239.2433[M + H + CH3OH − H2O − C4H8]+, 221.2318[M + H − CH3COOH]+, 147.1210[M + H + CH3OH − C12H22]+ 133.1051[M + H + CH3OH − C13H24]+, 109.1049[M + H − C9H19COOH]+, 95.0895[M + H − C10H21COOH]+, 71.0902[M + H − C12H21COOH]+, 57.0755[M + H − C13H23COOH]+, |
| 25 | Oleic acid (+) | 315.2915[M + H + CH3OH]+, 283.2461[M + H]+, 271.5449[M + H + CH3OH − CO2]+, 267.0220[M + H − CH4]+, 265.2757[M + H − H2O]+, 187.1151[M + H + CH3OH − C9H20]+, 171.0300[M + H − C8H16]+, 114.9656[M + H − C9H15COOH]+, 96.9540[M + H − C10H21COOH]+, 83.0875[M + H − C11H23COOH]+, 57.0750[M + H − C13H25COOH]+ |
| 27 | Palmitic acid (+) | 257.2565[M + H]+, 201.1894[M + H − C4H8]+, 97.1025[M + H − H2O − C10H22]+, 71.0902[M + H − C10H21COOH]+, 57.0753[M + H − C11H23COOH]+, |
| 28 | Stearic acid (+) | 285.3050[M + H]+, 267.2656[M + H − H2O]+, 126.9036[M + H − C8H17COOH]+, 83.0895[M + H − C10H21COOH − CH4]+, 69.0739[M + H − C11H23COOH − CH4]+, 57.0742[M + H − C13H27COOH]+, |
| 32 | Sorbitol (−) | 241.0915[M + CH3COO]−, 223.0801[M + CH3COO − H2O]−, 181.0622[M − H]−, 149.0803[M – H − CH3OH]−, |
| 42 | Gheddic acid (−) | 507.3340[M − H]−, 279.2671[M – H − C13H27COOH]−, 153.0148[M – H − C22H45COOH]−, |
| 43 | Nonadecanoic acid (−) | 297.2814[M − H]−, 279.2672[M – H − H2O]−, 183.1614[M − H − C5H9COOH]−, |
| Isoflavone | RT a (min) | Regression Equation b | Linear Range | r | LOD c | LOQ d | Precision (RSD % e) | Repeatability (RSD, %) | Recovery (Mean f ± RSD %) | Stability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µg/mL) | (ng/mL) | (ng/mL) | Intra Day | Inter Day | (RSD % a) | ||||||
| Daidzin | 4.81 | Y = 58544X + 384206 | 0.010−100.0 | 0.9979 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 1.14 | 4.24 | 3.98 | 103.83 ± 3.15 | 4.10 |
| Glycitin | 5.14 | Y = 49463X + 421236 | 0.010−100.0 | 0.9981 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 0.57 | 2.87 | 3.27 | 104.84 ± 2.58 | 1.84 |
| Genistin | 5.89 | Y = 60953X +286019 | 0.100−600.0 | 0.9980 | 10.0 | 50.0 | 0.48 | 4.48 | 4.41 | 97.76 ± 4.70 | 3.04 |
| Daidzein | 7.02 | Y = 76972 X + 705619 | 0.100−100.0 | 0.9840 | 0.1 | 3.0 | 1.61 | 3.50 | 2.53 | 97.61 ± 3.73 | 3.34 |
| Glycitein | 7.17 | Y = 52697 X + 643182 | 0.010−200.0 | 0.9973 | 0.1 | 2.0 | 1.42 | 2.61 | 4.19 | 103.71 ± 2.69 | 3.78 |
| Genistein | 7.80 | Y = 78899 X + 342189 | 0.50−200.0 | 0.9973 | 50.0 | 250.0 | 2.35 | 3.99 | 4.82 | 99.67 ± 3.16 | 2.39 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, C.; Cui, X.; Shan, C.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Wen, H. Simultaneous Characterization and Quantification of Varied Ingredients from Sojae semen praeparatum in Fermentation Using UFLC–TripleTOF MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101864
Chai C, Cui X, Shan C, Yu S, Wang X, Wen H. Simultaneous Characterization and Quantification of Varied Ingredients from Sojae semen praeparatum in Fermentation Using UFLC–TripleTOF MS. Molecules. 2019; 24(10):1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101864
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Chuan, Xiaobing Cui, Chenxiao Shan, Sheng Yu, Xinzhi Wang, and Hongmei Wen. 2019. "Simultaneous Characterization and Quantification of Varied Ingredients from Sojae semen praeparatum in Fermentation Using UFLC–TripleTOF MS" Molecules 24, no. 10: 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101864
APA StyleChai, C., Cui, X., Shan, C., Yu, S., Wang, X., & Wen, H. (2019). Simultaneous Characterization and Quantification of Varied Ingredients from Sojae semen praeparatum in Fermentation Using UFLC–TripleTOF MS. Molecules, 24(10), 1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101864