Screening of the Active Component Promoting Leydig Cell Proliferation from Lepidium meyenii Using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
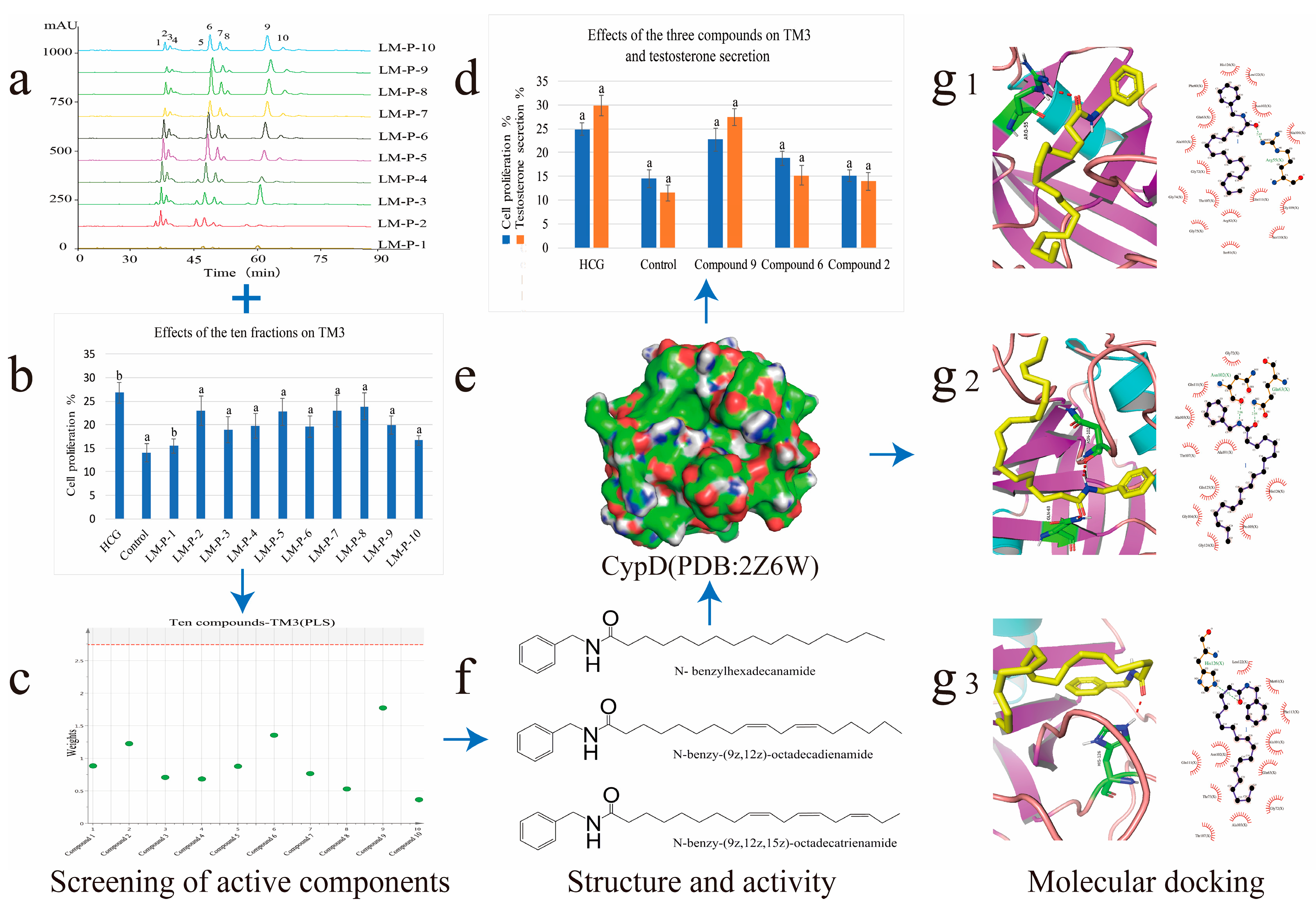
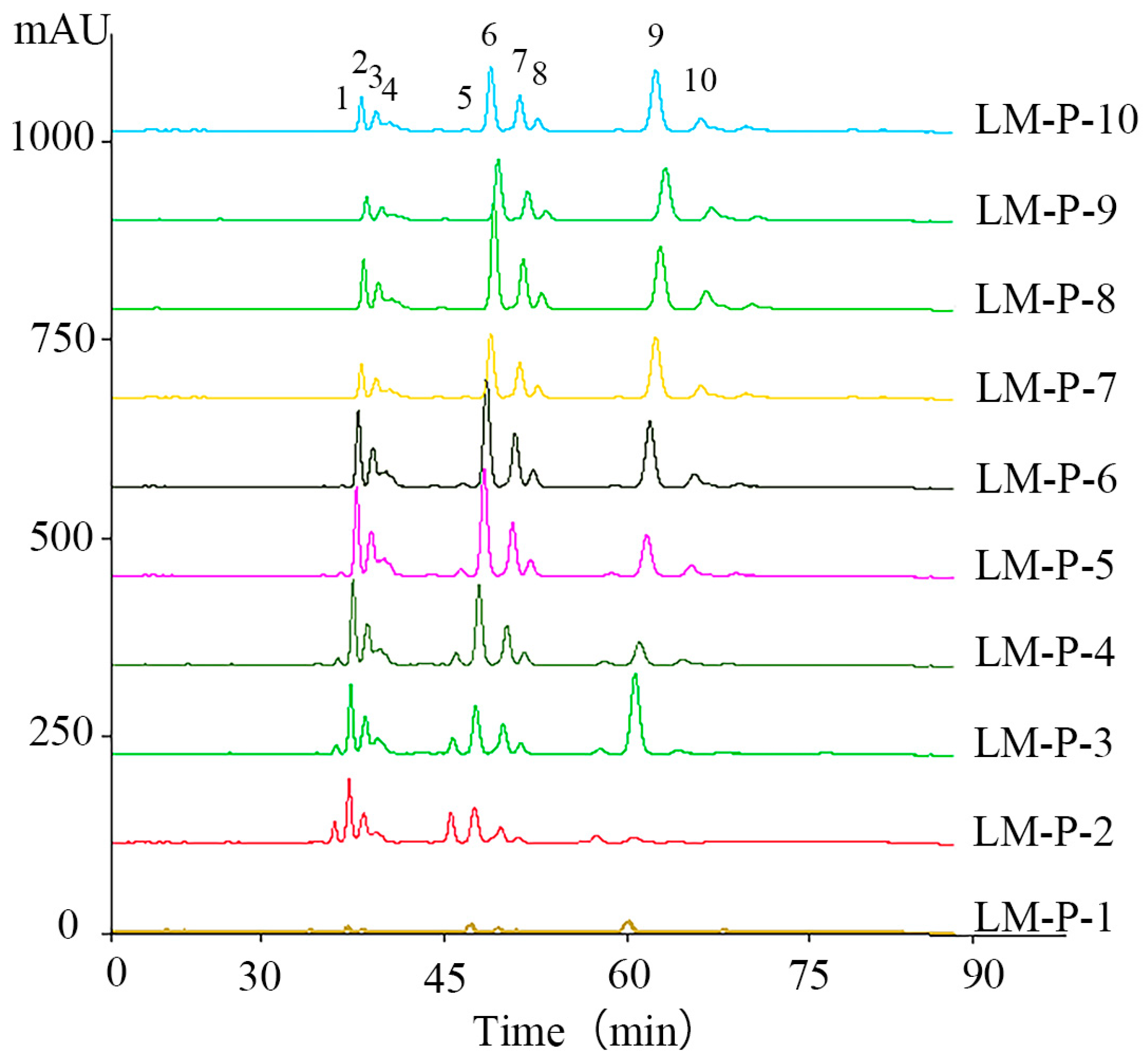
2.1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Photodiode Array Detector-Electrospray Ionization/Mass Spectrometry Method Analysis of Ten Common Peeks
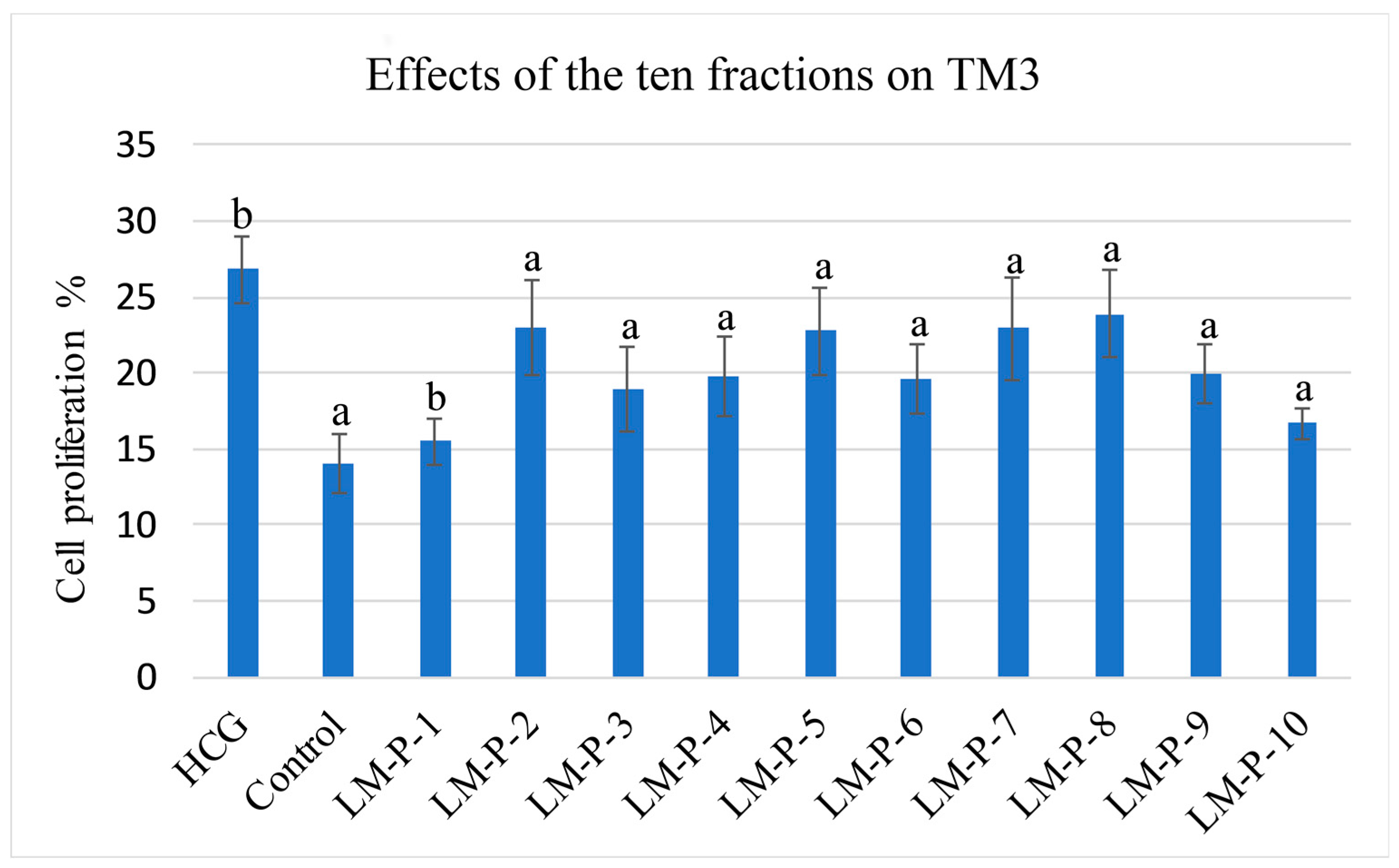
2.2. Mouse Leydig Cells Proliferation Activity of Ten Fractions
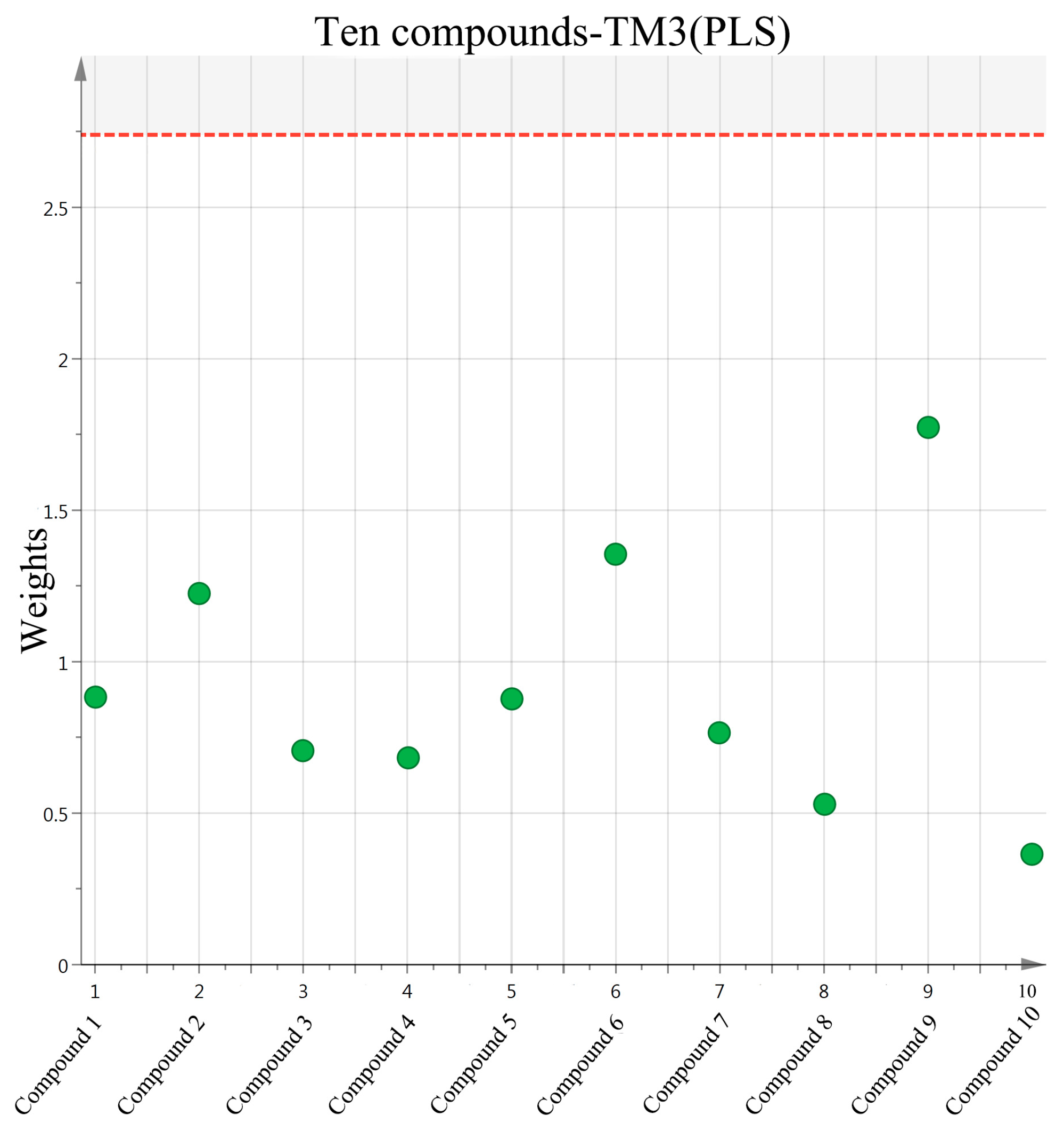
2.3. Screening of Active Compounds by Using Partial Least Squares
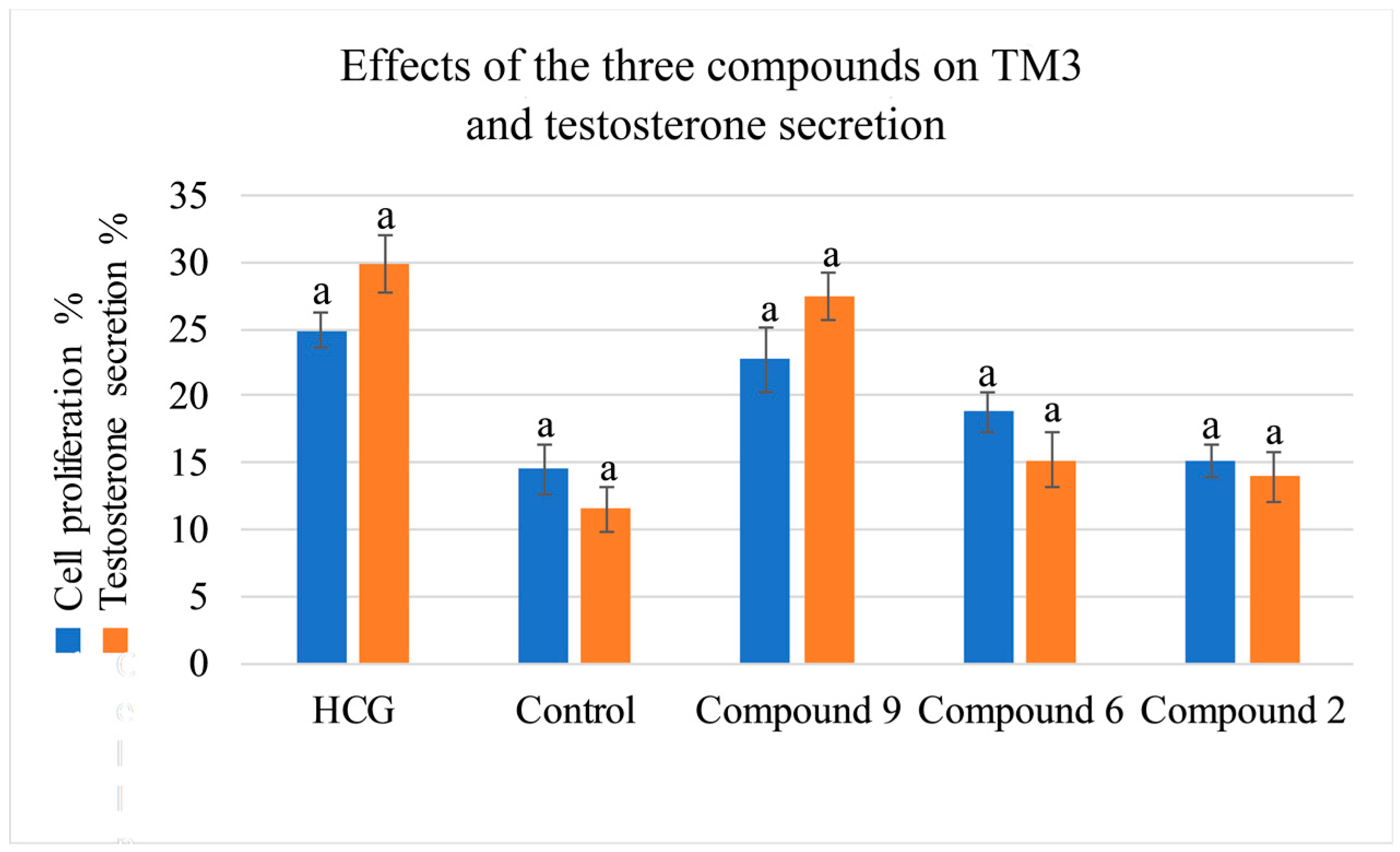
2.4. Activity Evaluation of Active Components
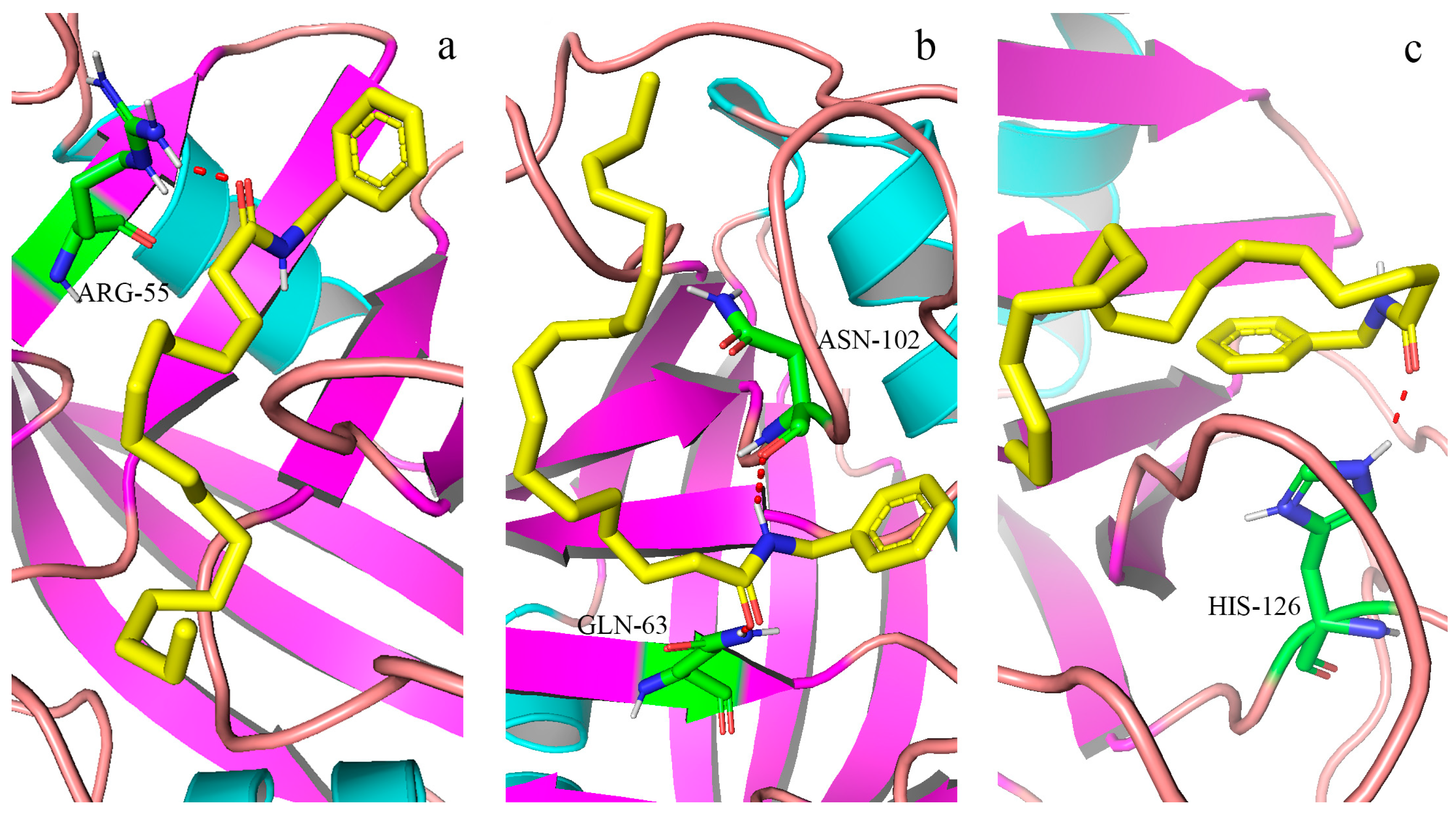
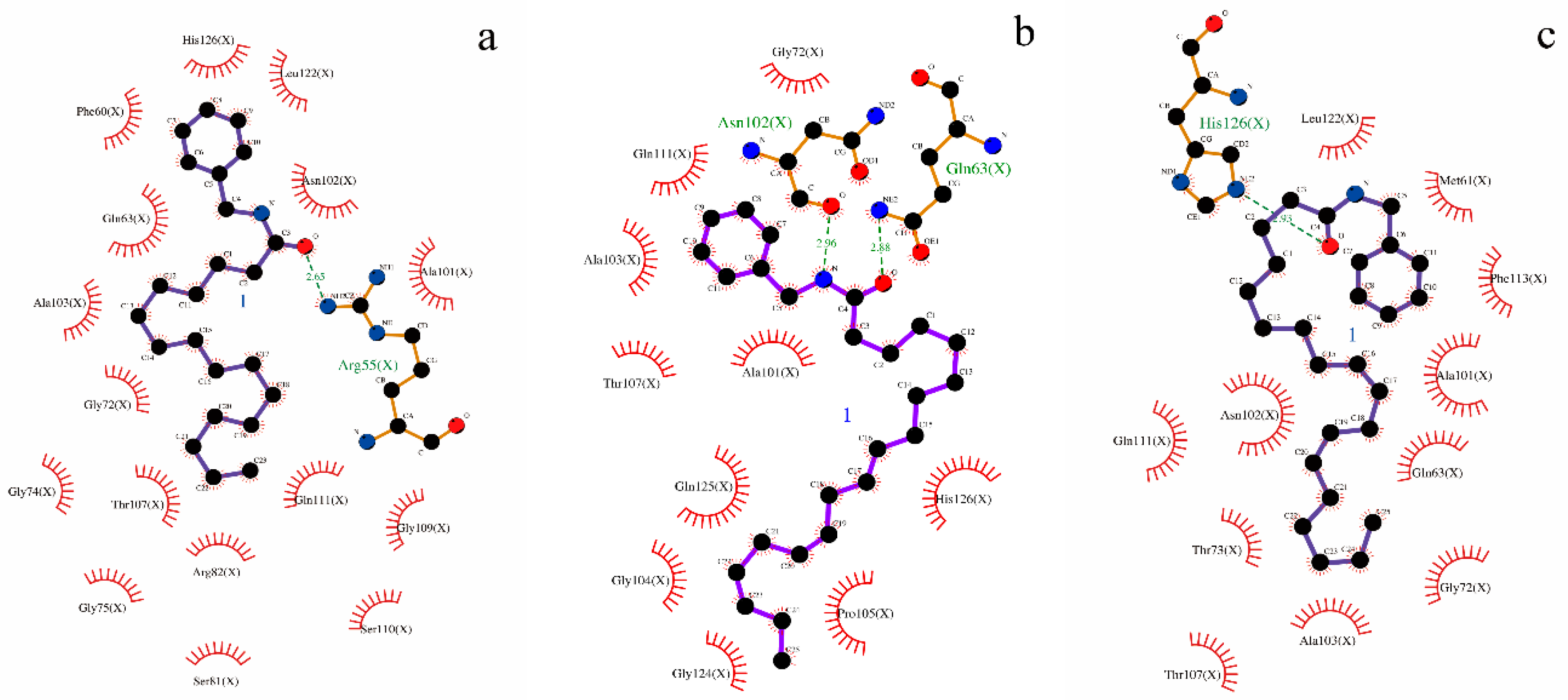
2.5. Analysis of Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Photodiode Array Detector-Electrospray Ionization/Mass Spectrometry Method
3.4. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
3.5. Partial Least Squares Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3.6. Molecular Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toledo, J.; Dehal, P.; Jarrin, F.; Hu, J.; Hermann, M.; Al-Shehbaz, I.; Quiros, C.F. Genetic Variability ofLepidium meyeniiand other AndeanLepidiumSpecies (Brassicaceae) Assessed by Molecular Markers. Ann. Bot. 1998, 82, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.Z.; Li, W.Y. Simultaneous Analysis of Macamides in Maca (Lepidium meyenii) with Different Drying Process by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Chemical composition and health effects of maca (Lepidium meyenii). Food Chem. 2019, 288, 422–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Brantner, A.; Wang, H.; Shu, X.; Yang, J.; Si, N.; Han, L.; Zhao, H.; Bian, B. Chemical profiling analysis of Maca using UHPLC-ESI-Orbitrap MS coupled with UHPLC-ESI-QqQ MS and the neuroprotective study on its active ingredients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccollom, M.M.; Villinski, J.R.; Mcphail, K.L.; Craker, L.E.; Gafner, S. Analysis of macamides in samples of Maca (Lepidium meyenii) by HPLC-UV-MS/MS. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2010, 16, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.C.; Lee, M.S.; Yang, E.J.; Lim, H.S.; Ernst, E. Maca (L. meyenii) for improving sexual function: A systematic review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Luna, A.C.; Salazar, S.; Aspajo, N.J.; Rubio, J.; Gasco, M.; Gonzales, G.F. Lepidium meyenii (Maca) increases litter size in normal adult female mice. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2005, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rubio, J.; Caldas, M.; Dávila, S.; Gasco, M.; Gonzales, G.F. Effect of three different cultivars of Lepidium meyenii (Maca) on learning and depression in ovariectomized mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2006, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.H.; Youngblood, G.L. Regulation of expression of steroidogenic enzymes in Leydig cells. Biol. Reprod. 1995, 52, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Gao, C.C.; Ma, X.F.; Bai, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X. The isolation of 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-beta-d-glucose from Acer truncatum Bunge by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 850, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, P. Mitochondrial transport of cations: Channels, exchangers, and permeability transition. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1127–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.; Londhe, A.M.; Lim, J.W.; Park, B.G.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, S.M.; No, K.T.; Lee, J.; Pae, A.N. Discovery of non-peptidic small molecule inhibitors of cyclophilin D as neuroprotective agents in Aβ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2017, 31, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valasani, K.R.; Vangavaragu, J.R.; Day, V.W.; Yan, S.S. Structure based design, synthesis, pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, and molecular docking studies for identification of novel cyclophilin D inhibitors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, E.R.; Awais, M.; Kershaw, N.M.; Gibson, R.R.; Pandalaneni, S.; Latawiec, D.; Wen, L.; Javed, M.A.; Criddle, D.N.; Berry, N. Small molecule inhibitors of cyclophilin D to protect mitochondrial function as a potential treatment for acute pancreatitis. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2596–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Lee, J.; Park, B.G.; Park, I.; Pae, A.N.; Roh, E.J. Novel quinazoline-urea analogues as modulators for Aβ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: Design, synthesis, and molecular docking study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 84, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; He, D.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Zheng, L.; Li, J. Emodin targets mitochondrial cyclophilin D to induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Sun, X. Exploring on the bioactive markers of Codonopsis Radix by correlation analysis between chemical constituents and pharmacological effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 236, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Cheng, P.; Wang, W.; Yan, S.; Tang, Q.; Liu, D.; Xie, H. Rapid investigation and screening of bioactive components in simo decoction via LC-Q-TOF-MS and UF-HPLC-MD methods. Molecules 2018, 23, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Xingliang, L.I.; Wei, Q. Study and application of partial least squares regression on relationship between soil nutrient and fruit quality. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 17, 362–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, C.; Fang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhenkun, L.; Lian, Q.; Ge, R.S. Stem Leydig cell regeneration in the adult rat testis is inhibited after a short-term triphenyltin exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 306, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.X.; Wang, F.; Yu, K.Q.; Chen, J.; Bai, D.L.; Chen, K.X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H.L. Novel cyclophilin D inhibitors derived from quinoxaline exhibit highly inhibitory activity against rat mitochondrial swelling and Ca2+ uptake/release. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helekar, S.A.; Patrick, J. Peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity of cyclophilin A in functional homo-oligomeric receptor expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5432–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, M. Mitochondrial intermembrane junctional complexes and their role in cell death. J. Physiol. 2000, 529, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, M.; Virji, S.; Ward, J.M. Cyclophilin-D binds strongly to complexes of the voltage-dependent anion channel and the adenine nucleotide translocase to form the permeability transition pore. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 258, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.M.; Yue, G.L.; Li, P.; Wong, C.W.; Lee, K.M.; Kennelly, E.J.; Lau, B.S. Screening and analysis of potential anti-tumor components from the stipe of Ganoderma sinense using high-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry with multivariate statistical tool. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1487, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, X.; Jin, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Screening and determination for potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitory constituents from ginseng stem–leaf saponins using ultrafiltration (UF)-LC-ESI-MS2. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Chen, H.; Shen, S.; Huang, T.; Huang, B.; Hu, G.; Li, L.; Xu, Y. Proteasome activator REGγ promotes inflammation in Leydig cells via IkBε signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shi, J.; Zou, L.; Liu, X.; Tang, R.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Tan, M.; Chen, J. Quality Evaluation of Wild and Cultivated Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus Based on Simultaneous Determination of Multiple Bioactive Constituents Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, G.W.A. Software Review of ChemBioDraw 12.0. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Gr. Model. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mura, C.; Mccrimmon, C.M.; Vertrees, J.; Sawaya, M.R. An introduction to biomolecular graphics. Plos Comput. Biol. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No. | Retention Time (min) | UV Absorption Characteristics λmax (nm) | Observed m/z | Fragment Ion | Compound Structure | Component Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35.3 | 210 | 398 | 138,261 | 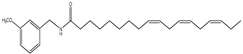 | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-(9zN,12zN,15z)- octadecatrienamide |
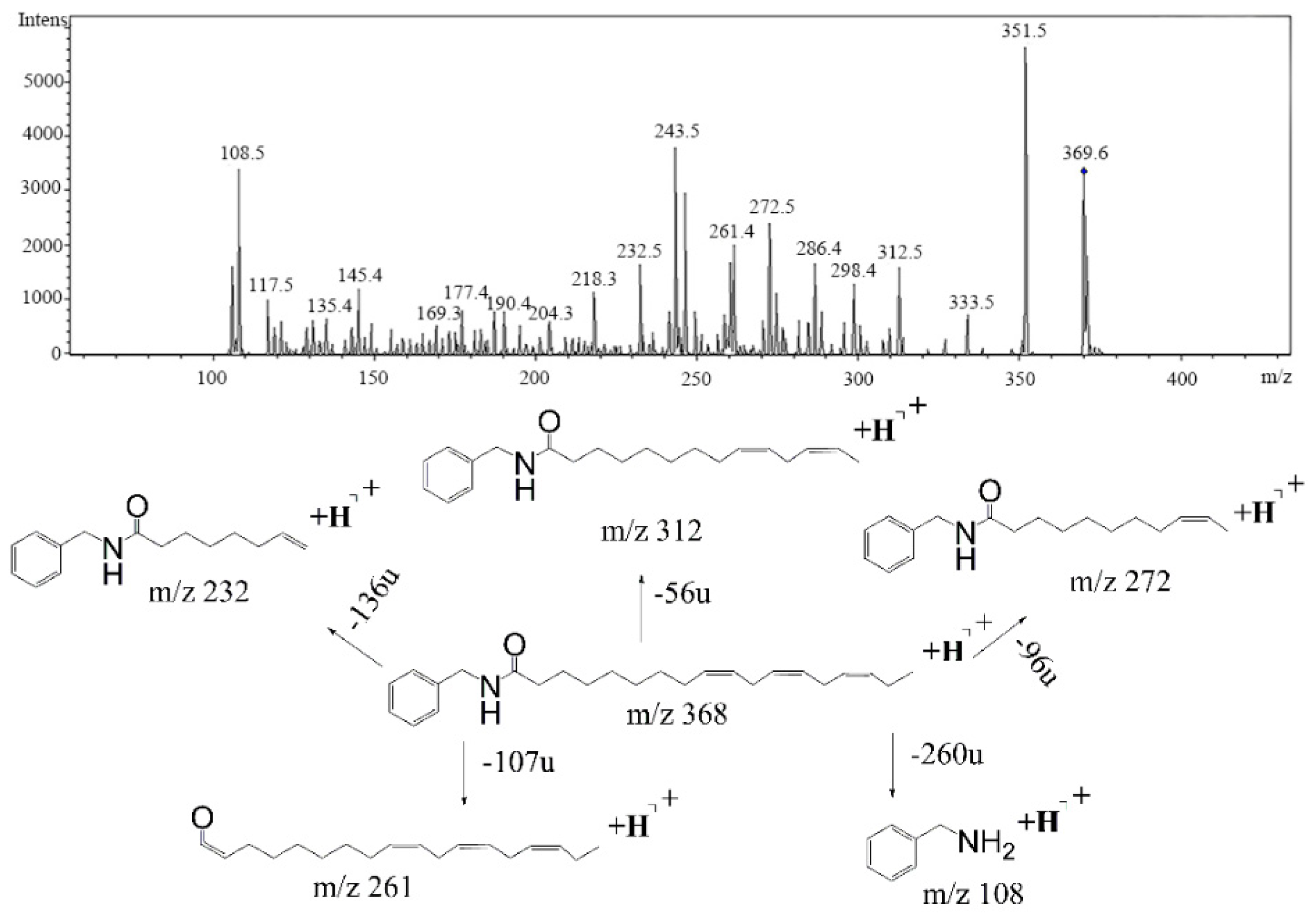
| 2 | 36.4 | 210 | 368 | 108,232, 261,272 | 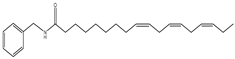 | N-benzyl-(9z,12z,15z)-octadecatrienamide |
| 3 | 37.7 | 210 | 368 | 108,261, 285 | 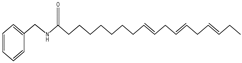 | N-benzyl-(9E,12E,15E)- octadecatrienamide |
| 4 | 38.7 | 210 | 368 | 108,261 | Unknown | Unknown |
| 5 | 44.8 | 210 | 400 | 138,263, 302 |  | N-(3-methoxybenzyl)-(9Z,12Z)-octadecadienamide |
| 6 | 46.6 | 210 | 370 | 108,232, 263,272 |  | N-benzyl-(9z,12z)-octadecadienamide |
| 7 | 48.9 | 210 | 370 | 108,263 | Unknown | Unknown |
| 8 | 50.3 | 210 | 370 | 108,263, 285 | 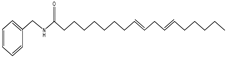 | N-benzyl-(9E,12E)-octadecadienamide |
| 9 | 59.6 | 210 | 346 | 108,239, 268,268 | 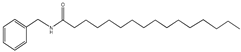 | N- benzyl- hexadecanamide |
| 10 | 63.0 | 210 | 372 | 108,165 | 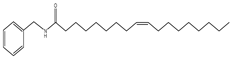 | N-benzyl-9Z-octadecenamide |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.-c.; Lv, J.-w.; Li, C.-n.; Zhang, N.-x.; Tian, L.-l.; Han, X.-y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.-m. Screening of the Active Component Promoting Leydig Cell Proliferation from Lepidium meyenii Using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112101
Gao X-c, Lv J-w, Li C-n, Zhang N-x, Tian L-l, Han X-y, Zhang H, Sun J-m. Screening of the Active Component Promoting Leydig Cell Proliferation from Lepidium meyenii Using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112101
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiao-chen, Jing-wei Lv, Chun-nan Li, Nan-xi Zhang, Lin-lin Tian, Xi-ying Han, Hui Zhang, and Jia-ming Sun. 2019. "Screening of the Active Component Promoting Leydig Cell Proliferation from Lepidium meyenii Using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112101
APA StyleGao, X.-c., Lv, J.-w., Li, C.-n., Zhang, N.-x., Tian, L.-l., Han, X.-y., Zhang, H., & Sun, J.-m. (2019). Screening of the Active Component Promoting Leydig Cell Proliferation from Lepidium meyenii Using HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Molecules, 24(11), 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112101




