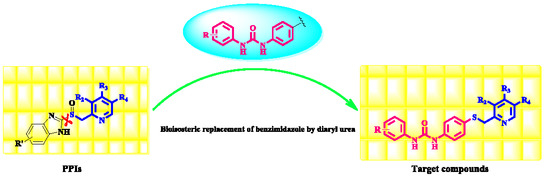
Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a New Series of 1-Aryl-3-{4-[(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)thio]phenyl}urea Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
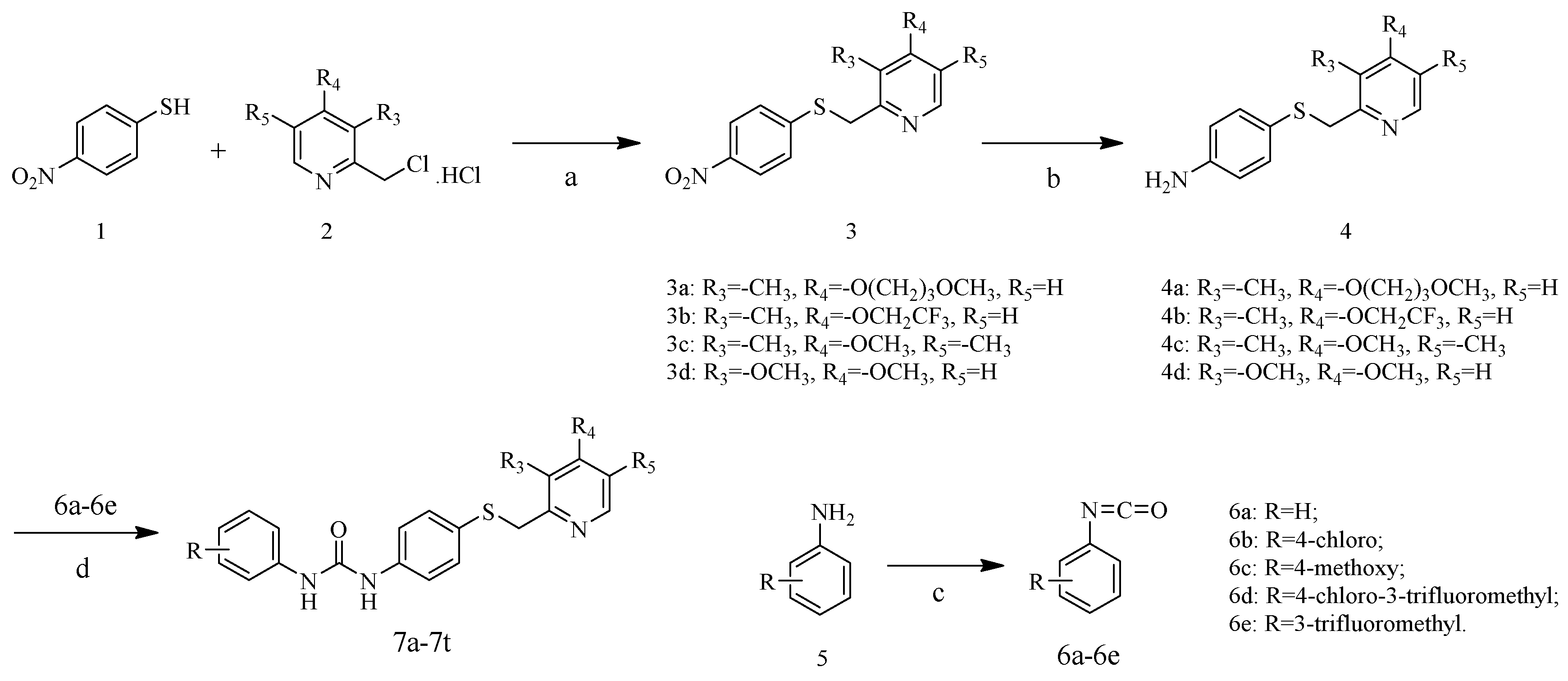
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. Antiproliferative Activity
2.2.2. Cell Apoptosis Assay
2.2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Preparation of 2-{[(4-nitrophenyl)thio]methyl}pyridine Derivatives (3a–3d)
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Preparation of 4-{[(pyridin-2-yl)methyl]thio}aniline Derivatives (4a–4d)
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Preparation of the Target Compounds (7a–7t)




















3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. Antiproliferative Activity Assays
3.2.2. Cell Apoptosis Assay
3.2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, D.M.; Bateman, E.H. Tumor control versus adverse events with targeted anticancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 9, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; Park, J.H.; Miyamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Hisada, S.; Alachkar, H.; Nakamura, Y. TOPK inhibitor induces complete tumor regression in xenograft models of human cancer through inhibition of cytokinesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.Y.; Lin, L.; Zheng, M.Z.; Sun, H.M.; Xiao, J.J.; Lu, T.; Huang, G.Q.; Chen, P.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhu, F.; et al. Pantoprazole, an FDA-approved proton-pump inhibitor, suppresses colorectal cancer growth by targeting T-cell-originated protein kinase. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22460–22473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.Z.; Luan, S.S.; Gao, S.Y.; Cheng, L.; Hao, B.; Li, J.C.; Chen, Y.; Hou, X.M.; Chen, L.X.; Li, H. Proton pump inhibitor ilaprazole suppresses cancer growth by targeting T-cell-originated protein kinase. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39143–39153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abe, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Kito, K.; Ueda, N. Cloning and Expression of a Novel MAPKK-like Protein Kinase, Lymphokine-activated Killer T-cell-originated Protein Kinase, Specifically Expressed in the Testis and Activated Lymphoid Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21525–21531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lin, M.L.; Nishidate, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Katagiri, T. PDZ-binding kinase/T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase, a putative cancer/testis antigen with anoncogenic activity in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9186–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons-Evelyn, M.; Bailey-Dell, K.; Toretsky, J.A.; Ross, D.D.; Fenton, R.; Kalvakolanu, D.; Rapoport, A.P. PBK/TOPK is a novel mitotic kinase which is upregulated in Burkitt’s lymphoma and other highly proliferative malignant cells. Blood Cells, Mol., Dis. 2001, 27, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.; Tidwell, M.; Karp, J.; Rapoport, A.P. Protein expression of PDZ-binding kinase is up-regulated in hematologic malignancies and strongly downregulated during terminal differentiation of HL-60 leukemic cells. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2004, 32, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, T.A.; Zhu, F.; Lu, C.; Higgins, L.; Tatsumi, Y.; Abe, Y.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Lymphokine-activated killer T-cell-originated protein kinase phosphorylation of histone H2AX prevents arsenite-induced apoptosis in RPMI7951 melanoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6884–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Hung, J.J.; Chou, T.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Lu, P.J.; Cheng, H.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Kuo, Y.L.; Chen, K.Y.; et al. Overexpression of T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase predicts poor prognosis in patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, M.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Jan, Y.H.; Yang, B.M.; Lu, P.J.; Cheng, H.C.; Huang, M.S.; Yang, C.J.; Hsiao, M.; et al. TOPK/PBK promotes cell migration via modulation of the PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway and is associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2389–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Lei, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Sheng, W.; Lin, P.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.; Shen, H. Expression of PBK/TOPK in cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 8059–8064. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Wei, J.; Sun, A.; Shao, G.; Childress, C.; Yang, W.; Lin, Q. PBK/TOPK mediates geranylgeranylation signaling for breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.X.; Wang, T.C.; Ruel, R.; Thibeault, C.; L’Heureux, A.; Schumacher, W.A.; Spronk, S.A.; Hiebert, S.; Bouthillier, G.; Lloyd, J.; et al. Conformationally constrained orthoanilino diaryl ureas, discovery of 1-(2-(1′-neopentylspiro[indoline-3,4′-piperidine]-1-yl)phenyl)-3-(4-(trifluoro-methoxy) phenyl)urea, a potent, selective, and bioavailable P2Y1 antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9275–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.W.; Sarantakis, D.; Terpinski, J.; Kumar, T.R.; Tsai, H.C.; Kuo, M.; Ager, A.L.; Jacobs, W.R., Jr.; Schiehser, G.A.; Ekins, S.; et al. Novel diaryl ureas with efficacy in a mouse model of malaria. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keche, A.P.; Hatnapure, G.D.; Tale, R.H.; Rodge, A.H.; Kamble, V.M. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial evaluation of novel 1-acetyl-3,5-diaryl-4,5-dihydro (1H) pyrazole derivatives bearing urea, thiourea and sulfonamide moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6611–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keche, A.P.; Hatnapure, G.D.; Tale, R.H.; Rodge, A.H.; Birajdar, S.S.; Kamble, V.M. A novel pyrimidine derivatives with aryl urea, thiourea and sulfonamide moieties, synthesis, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3445–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R.G.; Laufer, S.; Mangannavar, C.; Garlapati, A. Design, synthesis and characterization of N’, N”-diaryl ureas as p38 kinase inhibitors. Med. Chem. 2013, 9, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Ding, W.; Hui, H.X. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of diaryl urea derivatives with a 4-methylpiperazinylcarbonyl moiety. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 3857–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tang, K.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Lin, Z.; Yin, D.; Chen, X.; Huang, H. Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel diaryl urea derivative as potent antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 77, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, H.; El-Gamal, M.I.; Oh, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Sim, T.; Hah, J.M.; Yoo, K.H. New diarylureas and diarylamides possessing acet(benz)amidophenyl scaffold, design, synthesis, and antiproliferative activity against melanoma cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3269–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudio, V.J.; Amanda, D.; Vanderlan da Silva, B.; Eliezer, J.B.; Carlos alberto manssour, F. Molecular hybridization: a useful tool in the design of new drug prototypes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, M.; Miyamoto, N.; Aikawa, K.; Aramaki, Y.; Kanzaki, N.; Iizawa, Y.; Babab, M.; Shiraishia, M. Orally active CCR5 antagonists as anti-HIV-1 agents. Part 3: Synthesis and biological activities of 1-benzazepine derivatives containing a sulfoxide moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Yang, T.M.; Go, M.L. Functionalized acridin-9-yl phenylamines protected neuronal HT22 cells from glutamate-induced cell death by reducing intracellular levels of free radical species. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.Z.; Tian, Z.; Yan, Z.H.; Wu, L.X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H.G.; Yang, C. Design, synthesis and evaluation of 1,2-benzisothiazol-3-one derivatives as potent caspase-3 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2960–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immun. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, S.B.; Yang, S.M.; Zhang, A.; Yin, L.J.; Swarts, S.; Vidyasagar, S.; Zhang, L.R.; et al. Synthesis and anticancer potential of novel xanthone derivatives with 3,6-substituted chains. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4263–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Deng, X.S.; Zhang, C.; Meng, G.P.; Wu, J.F.; Li, X.S.; Zhao, Q.C.; Hu, C. Design, synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation of a novel series of benzo[d]thiazole-2-carboxamide derivatives as potential EGFR inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 2180–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Jin, Z.; Zhan, X.; Hu, J.; Wan, D.C.; Hu, C. Discovery of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2 ′,3′:2,3]thiepino [4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxamide Derivatives as the Potential Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, R.X.; Xin, A.Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, J.X.; Li, W.G.; Di, D.L. Design, synthesis, and anticancer properties of isocorydine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 6542–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.M.; Jing, D.W.; Chen, R.; Rashid, U.H.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.S.; Xie, P. Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel sophoridinic imine derivatives containing conjugated planar structure as potent anticancer agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4136–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of all the target compounds are available from the authors. |








| Compound | R | R3 | R4 | R5 | IC50 (μM) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | HCT-116 | PC-3 | |||||
| 7a | H | -CH3 | -O(CH2)3OCH3 | H | 12.31 ± 1.90 | 29.26 ± 4.53 | 27.22 ± 3.36 |
| 7b | 4-chloro | -CH3 | -O(CH2)3OCH3 | H | 3.03 ± 2.79 | 4.80 ± 1.57 | 6.00 ± 0.22 |
| 7c | 4-methoxy | -CH3 | -O(CH2)3OCH3 | H | 6.35 ± 0.51 | 5.29 ± 0.22 | 6.95 ± 1.24 |
| 7d | 4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl | -CH3 | -O(CH2)3OCH3 | H | 2.02 ± 2.20 | 1.94 ± 3.45 | 3.97 ± 1.02 |
| 7e | 3-trifluoromethyl | -CH3 | -O(CH2)3OCH3 | H | 2.90 ± 0.36 | 3.78 ± 1.41 | 11.48 ± 0.98 |
| 7f | H | -CH3 | -OCH2CF3 | H | 14.29 ± 1.77 | 19.31 ± 3.64 | 20.40 ± 2.89 |
| 7g | 4-chloro | -CH3 | -OCH2CF3 | H | 2.23 ± 1.27 | 3.04 ± 0.37 | 6.78 ± 0.23 |
| 7h | 4-methoxy | -CH3 | -OCH2CF3 | H | 4.71 ± 0.11 | 12.09 ± 1.46 | 15.65 ± 0.69 |
| 7i | 4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl | -CH3 | -OCH2CF3 | H | 1.53 ± 0.46 | 1.11 ± 0.34 | 1.98 ± 1.27 |
| 7j | 3-trifluoromethyl | -CH3 | -OCH2CF3 | H | 4.22 ± 0.99 | 10.69 ± 0.87 | 14.33 ± 3.24 |
| 7k | H | -CH3 | -OCH3 | -CH3 | 13.37 ± 0.81 | >100 | >100 |
| 7l | 4-chloro | -CH3 | -OCH3 | -CH3 | 2.23 ± 1.38 | 3.20 ± 2.75 | 5.97 ± 0.55 |
| 7m | 4-methoxy | -CH3 | -OCH3 | -CH3 | 5.27 ± 1.01 | 3.49 ± 0.78 | 6.95 ± 0.35 |
| 7n | 4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl | -CH3 | -OCH3 | -CH3 | 2.63 ± 1.25 | 2.51 ± 0.15 | 6.32 ± 1.68 |
| 7o | 3-trifluoromethyl | -CH3 | -OCH3 | -CH3 | 4.88 ± 1.02 | 3.50 ± 0.13 | 7.18 ± 1.58 |
| 7p | H | -OCH3 | -OCH3 | H | 26.98 ± 4.12 | 45.93 ± 6.65 | 30.95 ± 5.41 |
| 7q | 4-chloro | -OCH3 | -OCH3 | H | 14.52 ± 2.67 | 5.15 ± 1.01 | 18.57 ± 2.34 |
| 7r | 4-methoxy | -OCH3 | -OCH3 | H | 16.47 ± 4.51 | 33.10 ± 2.90 | 22.51 ± 3.07 |
| 7s | 4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl | -OCH3 | -OCH3 | H | 6.23 ± 0.60 | 5.61 ± 0.66 | 10.05 ± 2.23 |
| 7t | 3-trifluoromethyl | -OCH3 | -OCH3 | H | 14.13 ± 1.82 | 17.37 ± 1.69 | 19.77 ± 0.74 |
| sorafenib | 2.12 ± 0.18 | 2.25 ± 0.71 | 3.60 ± 1.08 | ||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Tan, X.; Feng, J.; Ding, N.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Meng, Q.; Liu, X.; Hu, C. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a New Series of 1-Aryl-3-{4-[(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)thio]phenyl}urea Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules 2019, 24, 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112108
Zhang C, Tan X, Feng J, Ding N, Li Y, Jin Z, Meng Q, Liu X, Hu C. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a New Series of 1-Aryl-3-{4-[(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)thio]phenyl}urea Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112108
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chuanming, Xiaoyu Tan, Jian Feng, Ning Ding, Yongpeng Li, Zhe Jin, Qingguo Meng, Xiaoping Liu, and Chun Hu. 2019. "Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a New Series of 1-Aryl-3-{4-[(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)thio]phenyl}urea Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112108
APA StyleZhang, C., Tan, X., Feng, J., Ding, N., Li, Y., Jin, Z., Meng, Q., Liu, X., & Hu, C. (2019). Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a New Series of 1-Aryl-3-{4-[(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)thio]phenyl}urea Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents. Molecules, 24(11), 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112108