Metal-Organic Frameworks of MIL-100(Fe, Cr) and MIL-101(Cr) for Aromatic Amines Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
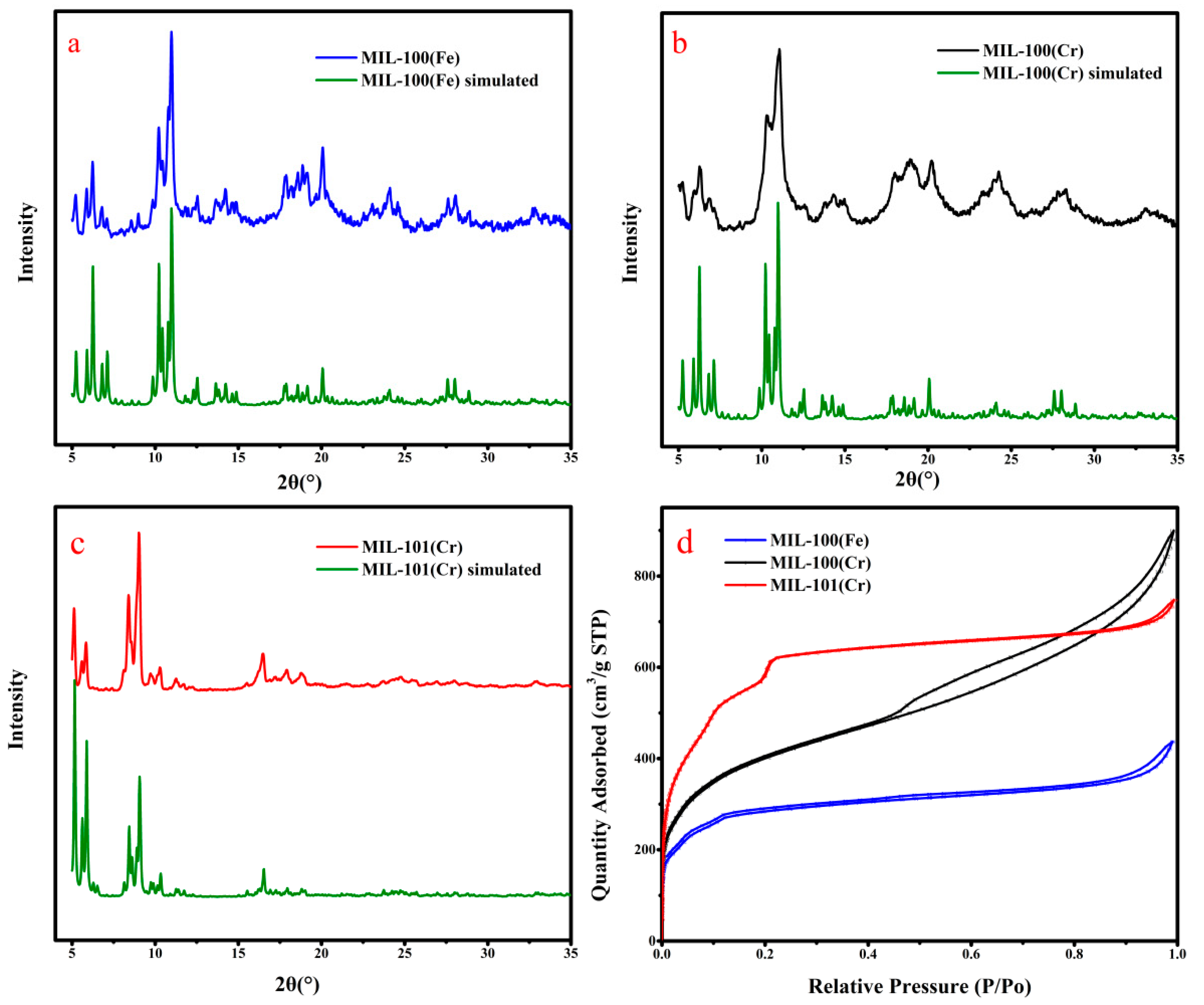
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Results
2.3. Adsorption Performance
2.4. Discussion on Adsorption Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the MOFs
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jagadeesh, R.V.; Surkus, A.-E.; Junge, H.; Pohl, M.-M.; Radnik, J.; Rabeah, J.; Huan, H.; Schuenemann, V.; Brueckner, A.; Beller, M. Nanoscale Fe2O3-Based Catalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes to Anilines. Science 2013, 342, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacic, P.; Somanathan, R. Novel, unifying mechanism for aromatic primary-amines (therapeutics, carcinogens and toxins): Electron transfer, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and metabolites. Med. Chem. Commun. 2011, 2, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielesz, A.; Baranowska, I.; Rybakt, A.; Włochowicz, A. Detection and determination of aromatic amines as products of reductive splitting from selected azo dyes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2002, 53, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, H.M.; Touraud, E.; Thomas, O. Aromatic amines from azo dye reduction: Status review with emphasis on direct UV spectrophotometric detection in textile industry wastewaters. Dye. Pigment. 2004, 61, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Heinze, T.M.; Paine, D.D.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Chen, H. Sudan azo dyes and Para Red degradation by prevalent bacteria of the human gastrointestinal tract. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Jian, Y.; Meng, M.; Wan, Y.P.; Feng, C.W.; Wang, S.L.; Xiao, L.; Xi, R. Preparation of anti-Sudan red monoclonal antibody and development of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Sudan red in chilli jam and chilli oil. Analyst 2010, 135, 2566. [Google Scholar]
- Aeenehvand, S.; Toudehrousta, Z.; Kamankesh, M.; Mashayekh, M.; Tavakoli, H.R.; Mohammadi, A. Evaluation and application of microwave-assisted extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of polar heterocyclic aromatic amines in hamburger patties. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 190, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.; Catto, J.W.; Dalbagni, G.; Grossman, H.B.; Herr, H.; Karakiewicz, P.; Kassouf, W.; Kiemeney, L.A.; La, V.C.; Shariat, S. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.S. Tobacco Smoke Carcinogens and Lung Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011, 91, 1194–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeltz, I.; Hoffmann, D. Nitrogen-containing compounds in tobacco and tobacco smoke. Chem. Rev. 1977, 77, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.J.; Perman, J.A.; Zaworotko, M.J. Design and synthesis of metal-organic frameworks using metal-organic polyhedra as supermolecular building blocks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1400–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, S.; Quartapelleprocopio, E.; Carmona, F.J.; Romero, M.A.; Navarro, J.a.R.; Barea, E. Biophysical characterisation, antitumor activity and MOF encapsulation of a half-sandwich ruthenium(II) mitoxantronato system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2473–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, W.; Li, H.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Metal-organic frameworks as advanced sorbents in sample preparation for small organic analytes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 397, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M.; Foroughi, M.M.; Ebrahimpoor, N.; Jahani, S.; Omidi, A.; Khatami, M. A review on metal-organic frameworks: Synthesis and applications. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 117, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbert, S.; Shyam, B. Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Routes to various MOF topologies, morphologies, and composites. Chem. Rev. 2012, 43, 933–969. [Google Scholar]
- Hiroyasu, F.; Cordova, K.E.; Michael, O.K.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2013, 341, 1230444. [Google Scholar]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Moler, D.B.; Li, H.; Chen, B.; Reineke, T.M.; O’keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Modular Chemistry: SecondaryBuilding Units as a Basis forthe Design of Highly Porous andRobust Metal−OrganicCarboxylate Frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Metal-organic framework membranes: Production, modification, and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 100, 21–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Fu, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions by novel-nanomaterials: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.-S.; Bu, X.; Feng, P. Metal-Organic Frameworks for Separation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Wang, L.J.; Xu, G.J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.S. Highly Stable Zr(IV)-Based Porphyrinic Metal−Organic Frameworks as an Adsorbent for the Effective Removal of Gatifloxacin from Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2018, 23, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue-Xue, L.; Nan, W.; You-Le, Q.; Li-Ye, Y.; Yang-Guang, W.; Xiao-Kun, O. Facile Preparation of Metal-Organic Framework (MIL-125)/Chitosan Beads for Adsorption of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Molecules 2018, 23, 1524. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jeremias, F.; Khutia, A.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. MIL-100(Al, Fe) as water adsorbents for heat transformation purposes—a promising application. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10148–10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, P.; Surblé, S.; Serre, C.; Hong, D.Y.; Seo, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; Grenèche, J.M.; Margiolaki, I.; Férey, G. Synthesis and catalytic properties of MIL-100(Fe), an iron(III) carboxylate with large pores. Chem. Commun. 2007, 27, 2820–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimchuk, N.V.; Kholdeeva, O.A. Metal–organic frameworks of the MIL-101 family as heterogeneous single-site catalysts. Proc. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Endineering Sci. 2012, 43, 2017–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan-Alcaniz, J.; Goesten, M.G.; Ramos-Fernandez, E.V.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Towards efficient polyoxometalate encapsulation in MIL-100(Cr): Influence of synthesis conditions. N. J. Chem. 2012, 36, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Dutour, J.; Surblé, S.; Margiolaki, I. A Chromium Terephthalate-Based Solid with Unusually Large Pore Volumes and Surface Area. Science 2005, 309, 2040–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholdeeva, O.A.; Skobelev, I.Y.; Ivanchikova, I.D.; Kovalenko, K.A.; Fedin, V.P.; Sorokin, A.B. Hydrocarbon oxidation over Fe- and Cr-containing metal-organic frameworks MIL-100 and MIL-101-a comparative study. Catal. Today 2014, 238, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Mechanistic insight into the adsorption of diclofenac by MIL-100: Experiments and theoretical calculations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.H.; Yan, X.P. Metal–organic framework MIL-100(Fe) for the adsorption of malachite green from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7449–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Trekels, M.; Boulhout, M.; Schouteden, S.; Vermoortele, F.; Alaerts, L.; Heurtaux, D.; Seo, Y.-K.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S.; et al. Selective removal of N-heterocyclic aromatic contaminants from fuels by lewis acidic metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2011, 50, 4210–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Sun, Q.; Xue, F.; Lin, D. Adsorption of volatile organic compounds by metal–organic frameworks MIL-101: Influence of molecular size and shape. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, G.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. Applications of Porous Metal–Organic Framework MIL-100(M = Cr,Fe,Sc,Al,V). Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 7730–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, C.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, C. Selective adsorption of arsenate and the reversible structure transformation of the mesoporous metal-organic framework MIL-100(Fe). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Yan, J.; Ying, T.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Pan, L.; Liu, Y. Hydroxyalkylation of Phenol with Formaldehyde to Bisphenol F Catalyzed by Keggin Phosphotungstic Acid Encapsulated in Metal–Organic Frameworks MIL-100(Fe or Cr) and MIL-101(Fe or Cr). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 11804–11813. [Google Scholar]
- Bahnemann, D.; Dillert, R.; Kandiel, T.A. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Nanostructures. Curr. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2, 94–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bezverkhyy, I.; Weber, G.; Bellat, J.P. Degradation of fluoride-free MIL-100(Fe) and MIL-53(Fe) in water: Effect of temperature and pH. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 219, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi-Kui, L.; Jian-Ping, M.; Yu-Bin, D. Adsorption and separation of reactive aromatic isomers and generation and stabilization of their radicals within cadmium(II)-triazole metal-organic confined space in a single-crystal-to-single-crystal fashion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7005–7017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, S.; Rong, C.; Mi, K.; Wang, J. Kinetic and equilibrium of U(VI) adsorption onto magnetic amidoxime-functionalized chitosan beads. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Removal of various pollutants from water and wastewater by modified chitosan adsorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Cheng, R.; Wang, J. Adsorption of diclofenac from aqueous solution using UiO-66-type metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Liang, N.; Hou, X. Core-Shell Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) Magnetic Nanoparticle for Effective Removal of Meloxicam and Naproxen in Aqueous Solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 2997–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, F.; Christian, S.; Caroline, M.D.; Franck, M.; Suzy, S.; Julien, D.; Irène, M. A hybrid solid with giant pores prepared by a combination of targeted chemistry, simulation, and powder diffraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2010, 116, 6456–6461. [Google Scholar]
- Grissom, T.G.; Sharp, C.H.; Usov, P.M.; Troya, D.; Morris, J.R. Benzene, Toluene, and Xylene Transport through UiO-66: Diffusion Rates, Energetics, and the Role of Hydrogen Bonding. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 16060–16069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokolov, D.I.; Maryasov, A.G.; Ollivier, J.; Freude, D.; Haase, J.; Stepanov, A.G.; Jobic, H. Uncovering the Rotation and Translational Mobility of Benzene Confined in UiO-66 (Zr) Metal-Organic Framework by 2H NMR – QENS Experimental Toolbox. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2844–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Seo, Y.K.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; Leclerc, H.; Wuttke, S.; Bazin, P.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Bloch, E. Controlled reducibility of a metal-organic framework with coordinatively unsaturated sites for preferential gas sorption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2010, 49, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.K.; Hong, D.Y.; Chang, J.S.; Jhung, S.H.; Seo, Y.K.; Kim, J.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Serre, C.; Férey, G. Amine Grafting on Coordinatively Unsaturated Metal Centers of MOFs: Consequences for Catalysis and Metal Encapsulation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2008, 47, 4144–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Some samples of the compounds MIL-100(Fe, Cr) and MIL-101(Cr) are available from the authors. |







| Adsorbents | Aromatic Amine | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | R2 | K2 | R2 | ||
| MIL-100(Fe) | aniline | 4.29 × 10−2 | 0.783 | 6.37 × 10−3 | 0.997 |
| o-toluidine | 3.04 × 10−2 | 0.766 | 8.44 × 10−3 | 0.998 | |
| 1-naphthylamine | 1.35 × 10−2 | 0.335 | 5.23 × 10−3 | 0.963 | |
| MIL-101(Cr) | 2-nitroaniline | 5.11 × 10−2 | 0.96 | 3.86 × 10−3 | 0.997 |
| 2-amino-4-nitrotoluene | 9.21 × 10−2 | 0.81 | 5.96 × 10−3 | 0.997 | |
| Adsorbents | Aromatic Amine | Temperature (°C) | Freundlich Model | Langmuir Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KF | n | R2 | qm | KL | R2 | |||
| MIL-100(Fe) | aniline | 25 | 5.16 | 1.58 | 0.93 | 84.74 | 0.0374 | 0.95 |
| o-toluidine | 25 | 5.14 | 1.60 | 0.94 | 79.68 | 0.0369 | 0.96 | |
| 1-naphthylamine | 25 | 7.09 | 1.85 | 0.93 | 72.25 | 0.0572 | 0.94 | |
| MIL-101(Cr) | 2-nitroaniline | 25 | 1.86 | 1.04 | 0.93 | 65.79 | 0.006 | 0.76 |
| 2-amino-4-nitrotoluene | 25 | 0.469 | 1.08 | 0.97 | 147.2 | 0.014 | 0.43 | |
| Aromatic amines | MIL-100(Fe) | MIL-100(Cr) | MIL-101(Cr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| aniline | 52.0 mg/g | 22.7 mg/g | 19.6 mg/g |
| 1-naphthylamine | 53.4 mg/g | 25.8 mg/g | 37.3 mg/g |
| o-toluidine | 49.6 mg/g | 13.7 mg/g | 44.0 mg/g |
| 2-amino-4-nitrotoluene | 3.0 mg/g | 9.7 mg/g | 25.0 mg/g |
| 2-nitroaniline | 3.7 mg/g | 7.4 mg/g | 54.3 mg/g |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.-L.; Zhou, S.-Y.; Xu, Z.; Ding, L.; Cheng, Y.-H. Metal-Organic Frameworks of MIL-100(Fe, Cr) and MIL-101(Cr) for Aromatic Amines Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. Molecules 2019, 24, 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203718
Chen M-L, Zhou S-Y, Xu Z, Ding L, Cheng Y-H. Metal-Organic Frameworks of MIL-100(Fe, Cr) and MIL-101(Cr) for Aromatic Amines Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. Molecules. 2019; 24(20):3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203718
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Mao-Long, Shu-Yang Zhou, Zhou Xu, Li Ding, and Yun-Hui Cheng. 2019. "Metal-Organic Frameworks of MIL-100(Fe, Cr) and MIL-101(Cr) for Aromatic Amines Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions" Molecules 24, no. 20: 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203718
APA StyleChen, M.-L., Zhou, S.-Y., Xu, Z., Ding, L., & Cheng, Y.-H. (2019). Metal-Organic Frameworks of MIL-100(Fe, Cr) and MIL-101(Cr) for Aromatic Amines Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. Molecules, 24(20), 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203718







