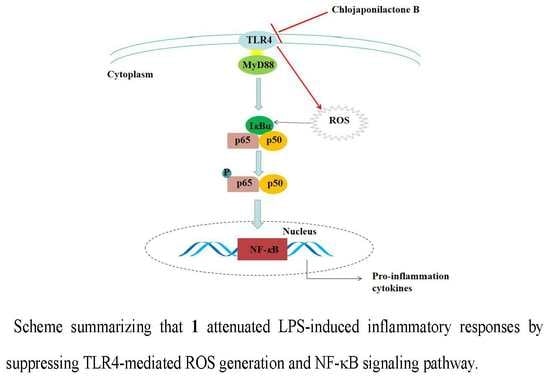
Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated ROS Generation and NF-?B Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Distinct Transcriptome Profile upon Treating LPS-induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages with 1, as Determined by RNA-seq
2.2. Effects of 1 on the mRNA Expression of TLR4, MyD88 and Pro-Inflammatory Mediators in LPS- Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages
2.3. Effects of 1 on the Protein Expression of TLR4 and MyD88 in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages
2.4. Affected TLR4 Signaling by Inhibiting TLR4 Protein
2.5. Effects of 1 on NO Production and ROS Generation in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages
2.6. Effects of 1 on NF-κB Phosphorylation, and the Expression of iNOS, COX-2, IL-6 and TNF-α in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. NO Production
4.6. ROS Measurement
4.7. RNA-seq Analysis
4.8. Molecular Docking Study
4.9. RT-PCR
4.10. Determination of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Levels
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, J.J.; Guo, Y.Q.; Yang, D.P.; Xue, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.P.; Yin, S.; Zhao, Z.M. Chlojaponilactone B from chloranthus japonicus: Suppression of inflammatory responses via inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2257–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Seon, M.R.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, S.G.; Park, J.H. 3,3′-Diindolylmethane suppresses the inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide in murine macrophages. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofseth, L.J.; Ying, L. Identifying and defusing weapons of mass inflammation in carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1765, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.U. An overview of inflammation: Mechanism and consequences. Front. Biol. 2011, 6, 274–281. [Google Scholar]
- Tabas, I.; Glass, C.K. Anti-inflammatory therapy in chronic disease: Challenges and opportunities. Science 2013, 339, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Nie, S.P.; Wang, J.Q.; Huang, D.F.; Li, W.J.; Xie, M.Y. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates the antitumor host response induced by Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.T.; Bian, C.; Yuan, J.C.; Chu, W.H.; Xiang, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, C.S.; Feng, H.; Lin, J.K. Curcumin attenuates acute inflammatory injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in experimental traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.L.; Wang, T.; Tong, D.D.; Kang, W.Y.; Liang, Q.Y.; Ge, S.H. Prolyl hydroxylases positively regulated LPS-induced inflammation in human gingival fibroblasts via TLR4/MyD88-mediated AKT/NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Cell Proliferat. 2018, 51, e12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, D.; Gruber, M.; Piskaty, C.; Woehs, F.; Renner, A.; Nagy, Z.; Kaltenboeck, A.; Wasserscheid, T.; Bazylko, A.; Kiss, A.K.; et al. Inhibition of NF-κB-dependent cytokine and inducible nitric oxide synthesis by the macrocyclic ellagitannin oenothein B in TLR-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Lee, L.Y.; Lin, T.W.; Kuo, C.F. N6-(2-Hydroxyethyl) adenosine in the medicinal mushroom Cordyceps cicadae attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated pro-inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.; Mira, J.P.; Frees, K.L.; Schwartz, D.A. Relevance of mutations in the TLR4 receptor in patients with Gram-negative septic shock. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Ma, Y.Y.; Adebayo, A.; Pope, R.M. Increased macrophage activation mediated through toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukkapalli, S.S.; Velsko, I.M.; Rivera-Kweh, M.F.; Larjava, H.; Lucas, A.R.; Kesavalu, L. Global TLR2 and 4 deficiency in mice impacts bone resorption, inflammatory markers and atherosclerosis to polymicrobial infection. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2017, 32, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrchen, J.M.; Sunderkötter, C.; Foell, D.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J. The endogenous Toll-like receptor 4 agonist S100A8/S100A9 (calprotectin) as innate amplifier of infection, autoimmunity, and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiangsu New Medical College. Dictionary of Chinese Traditional Medicine (Zhong Yao Da Ci Dian); Shanghai Science & Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 2169–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, B.S.; Shin, M.K. Encyclopedia of Illustrated Korean Natural Drugs; Young Lim Sa: Seoul, Korea, 1998; pp. 813–814. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto, T.; Ii, M.; Kitazaki, T.; Iizawa, Y.; Kimura, H. TAK-242 selectively suppresses Toll-like receptor 4 signaling mediated by the intracellular domain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 584, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feghali, C.A.; Wright, T.M. Cytokines in acute and chronic inflammation. Front. Biosci. 1997, 2, d12–d26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Dong, Z.Y.; Lan, X.Z.; Liao, Z.H.; Chen, M. Sweroside alleviated LPS-induced inflammation via SIRT1 mediating NF-κB and FOXO1 signaling pathways in RAW264.7 cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S.; McPherson, J.D.; McCombie, W.R. Coming of age: Ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nature 2016, 17, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledergerber, C.; Dessimoz, C. Base-calling for next-generation sequencing platforms. Brief. Bioinform. 2011, 12, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.R.; Levine, J.E.; Hakonarson, H.; Keating, B.J. Making the genomic leap in HCT: Application of second-generation sequencing to clinical advances in hematopoietic cell transplantation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aerle, R.; Santos, E.M. Advances in the application of high-throughput sequencing in invertebrate virology. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 147, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, J.M.; Levy, R.M.; Yang, R.K.; Mollen, K.P.; Fink, M.P.; Vodovotz, Y.; Billiar, T.R. Toll-like receptor-4 signaling mediates hepatic injury and systemic inflammation in hemorrhagic shock. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2006, 202, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nardo, D. Toll-like receptors: Activation, signalling and transcriptional modulation. Cytokine 2015, 74, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.L.; Azuma, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Ohura, K. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated signal pathway induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide in human gingival fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, X.H.; Zheng, X.F.; Sun, C.L.; Liu, H.Y. Chlojaponilactones B–E, four new lindenane sesquiterpenoid lactones from Chloranthus japonicus. Helv. Chim. Acta 2013, 96, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, N.; Tsuchimori, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Ii, M. TAK-242 (Resatorvid), a small-molecule inhibitor of toll-Like receptor (TLR) 4 signaling, binds selectively to TLR4 and interferes with interactions between TLR4 and its adaptor molecules. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.T.; Cheng, K.; Wang, X.H.; Yin, H. Selection, synthesis, and anti-inflammatory evaluation of the arylidene malonate derivatives as TLR4 signaling inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6073–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baatar, D.; Siddiqi, M.Z.; Im, W.T.; Khaliq, N.U.; Hwang, S.G. Anti-inflammatory effect of ginsenoside Rh2-mix on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Su, M.; Song, S.J.; Hong, J.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, J.H. An anti-inflammatory PPAR-γ agonist from the Jellyfish-derived fungus Penicillium chrysogenum J08NF-4. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.; Maes, M. Role of the toll like receptor (TLR) radical cycle in chronic inflammation: Possible treatments targeting the TLR4 pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.Y.; Ju, J.M.; Mo, L.H.; Ma, L.; Hu, W.H.; You, R.R.; Chen, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Qiu, S.Q.; et al. Anti-inflammation action of xanthones from Swertia chirayita by regulating COX-2/NF-κB/MAPKs/Akt signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.P.; Brodsky, I.E.; Rahner, C.; Woo, D.K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Walsh, M.C.; Choi, Y.; Shadel, G.S.; Ghosh, S. TLR signalling augments macrophage bactericidal activity through mitochondrial ROS. Nature 2011, 472, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajakumar, D.; Senguttuvan, S.; Alexander, M.; Oommen, A. Involvement of oxidative stress, nuclear factor kappaB and the Ubiquitin proteasomal pathway in dysferlinopathy. Life Sci. 2014, 108, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.P.; Xu, T.Q.; Liu, B.L.; Lei, X.P.; Hambrook, J.R.; Zhang, D.M.; Zhou, G.X. Sasanquasaponin III from Schima crenata Korth induces autophagy through Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway and promotes apoptosis in human melanoma A375 cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1 is available from the authors. |







| Serial Number | Anti-Inflammatory Pathways |
|---|---|
| [1] | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway |
| [2] | MAPK signaling pathway |
| [3] | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) |
| [4] | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway |
| [5] | NF-κB signaling pathway |
| [6] | PPAR signaling pathway |
| [7] | AMPK signaling pathway |
| [8] | Jak-STAT signaling pathway |
| [9] | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway |
| [10] | Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels |
| [11] | TNF signaling pathway |
| [12] | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Gene Symbol | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GADPH | GGTGAAGGTCGGTGTGAACG | CTCGCTCCTGGAAGATGGTG |
| TLR4 | AAATGCACTGAGCTTTAGTGGT | TGGCACTCATAATGATGGCAC |
| MyD88 | ATCGCTGTTCTTGAACCCTCG | CTCACGGTCTAACAAGGCCAG |
| iNOS | GGAGTGACGGCAAACATGACT | TCGATGCACAACTGGGTGAAC |
| COX-2 | ATCCCAACAAACGACCTAAA | CAGAACGACTCGGTTATCAA |
| IL-6 | AGTCACAGAAGGAGTGGCTAA | GGCATAACGCACTAGGTTT |
| TNF-α | ACAGCCAGGCTTCGTTTAGG | GCCAATTTCGGACTCAGCATC |
| NF-κB | ATGGCAGACGATGATCCCTAC | TGTTGACAGTGGTATTTCTGGTG |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, B.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Z. Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated ROS Generation and NF-?B Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 3731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203731
Ye S, Zheng Q, Zhou Y, Bai B, Yang D, Zhao Z. Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated ROS Generation and NF-?B Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2019; 24(20):3731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203731
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Shaoxia, Qiyao Zheng, Yang Zhou, Bai Bai, Depo Yang, and Zhimin Zhao. 2019. "Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated ROS Generation and NF-?B Signaling Pathway" Molecules 24, no. 20: 3731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203731
APA StyleYe, S., Zheng, Q., Zhou, Y., Bai, B., Yang, D., & Zhao, Z. (2019). Chlojaponilactone B Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4-Mediated ROS Generation and NF-?B Signaling Pathway. Molecules, 24(20), 3731. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203731