Control of Crystalline-Amorphous Structures of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes Containing Two Types of Ammonium Side-Chain Groups and Their Properties as Protic Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of POSSs Containing One Type of Ammonium Side-Chain Group (Am-POSS(x))
2.2. Evaluation of Crystalline-Amorphous Structures of Am-POSS(x)
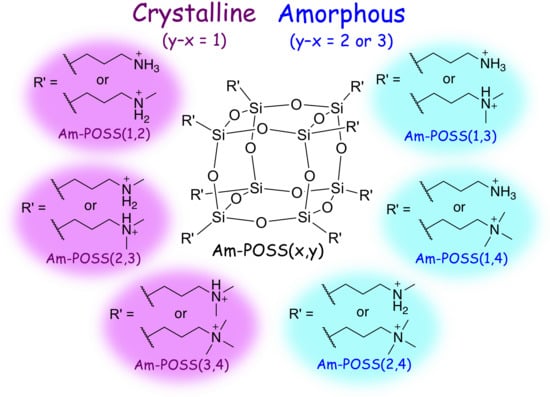
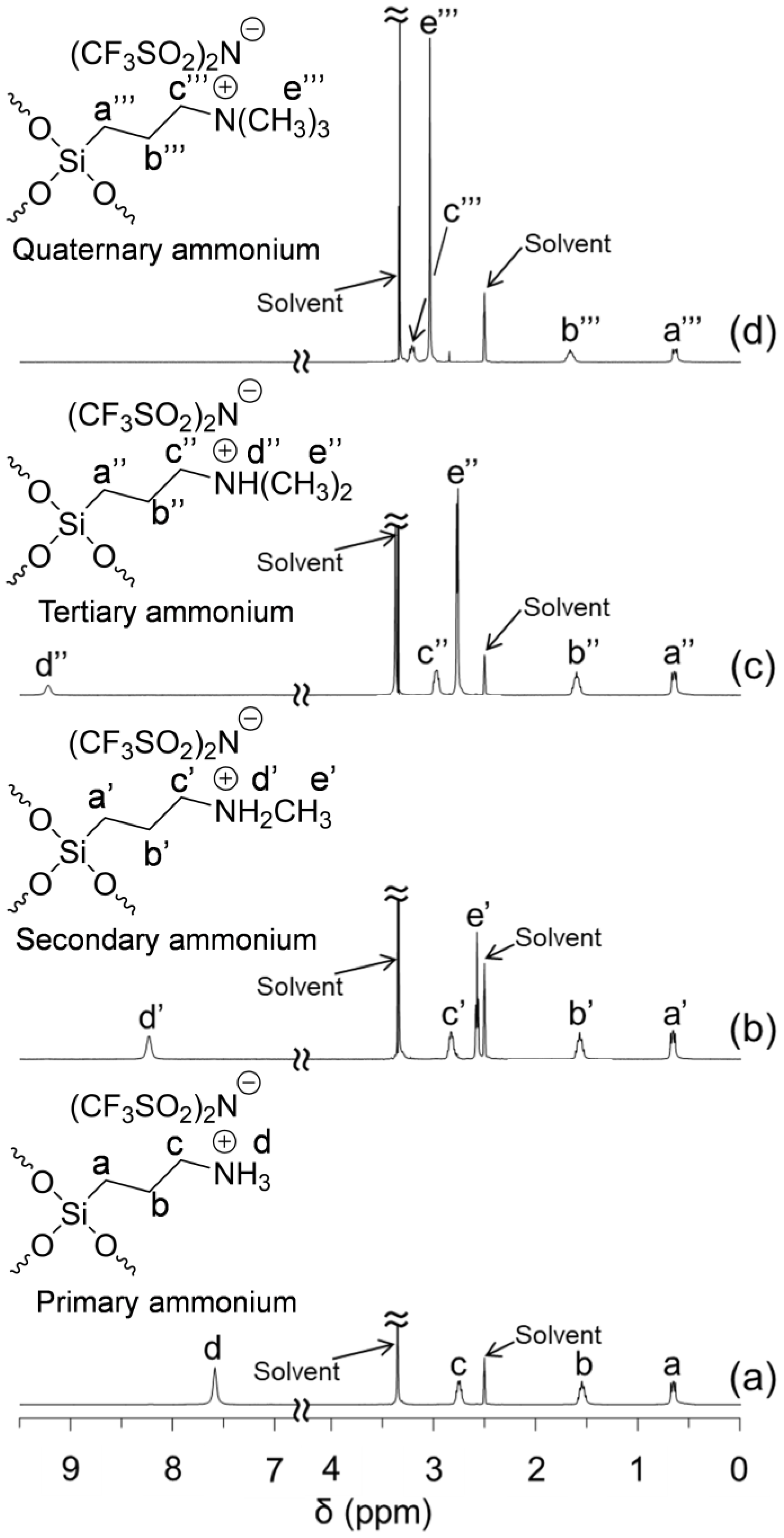
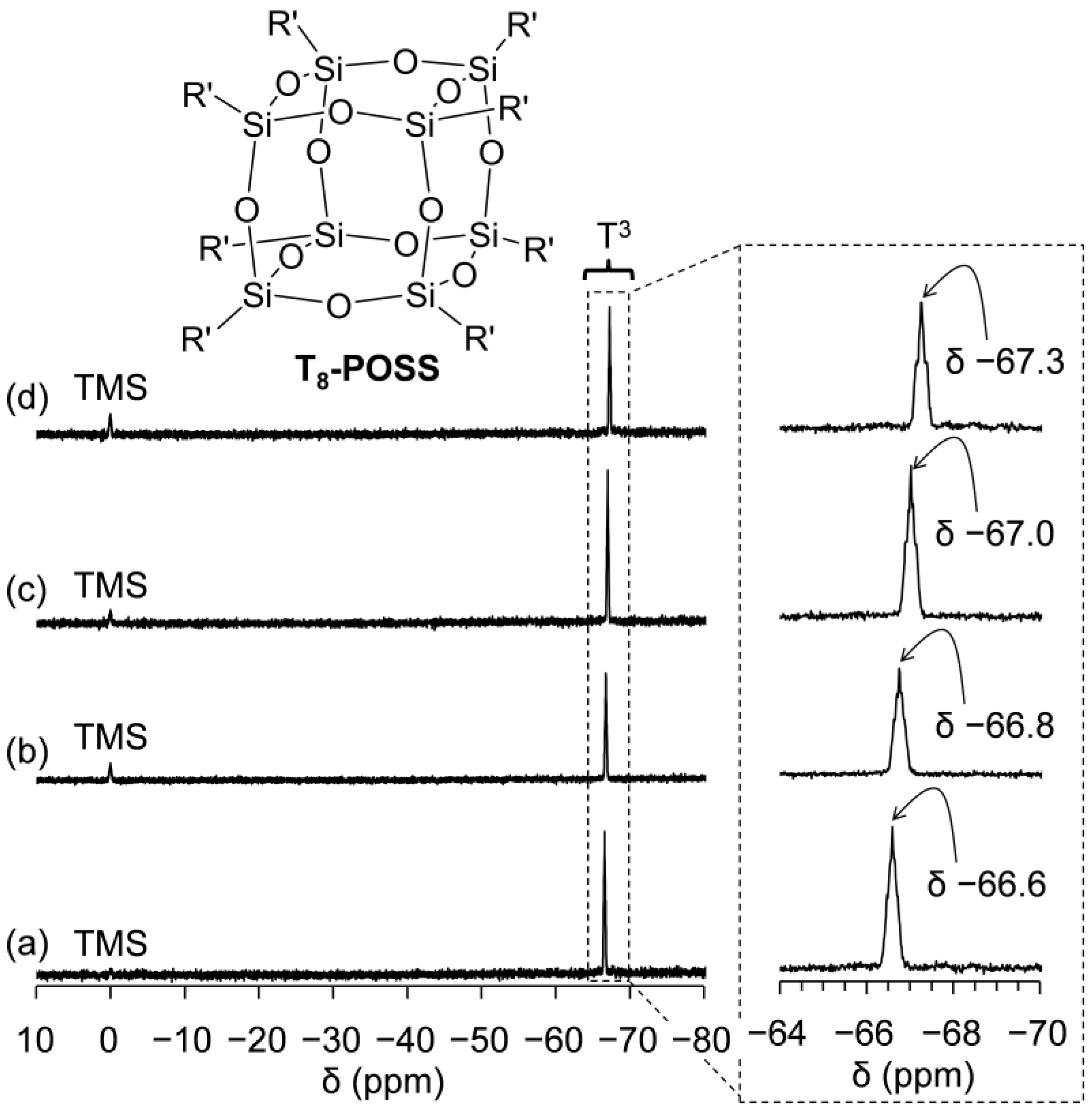
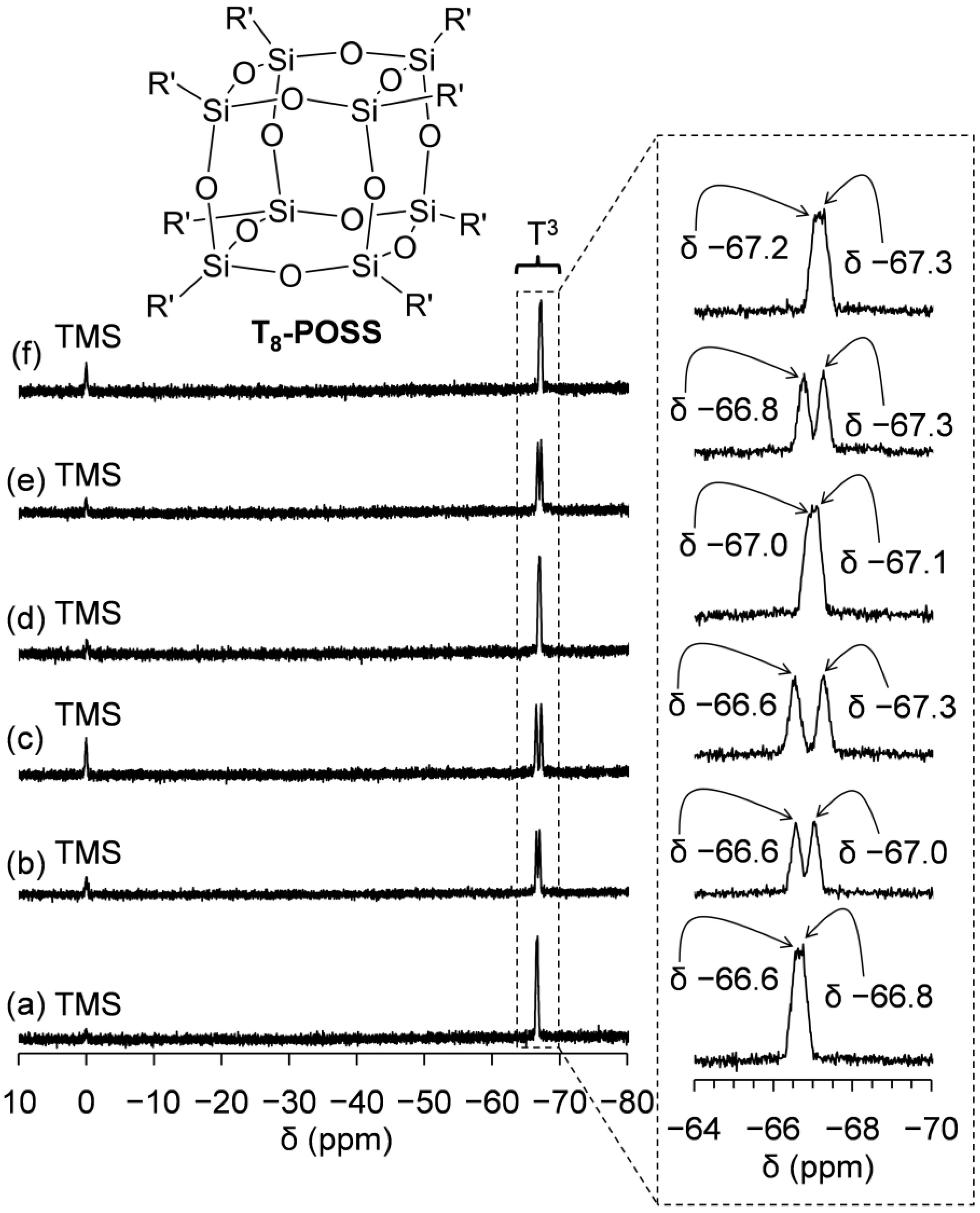
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of POSSs Containing Two Types of Ammonium Side-Chain Groups (Am-POSS(x,y))
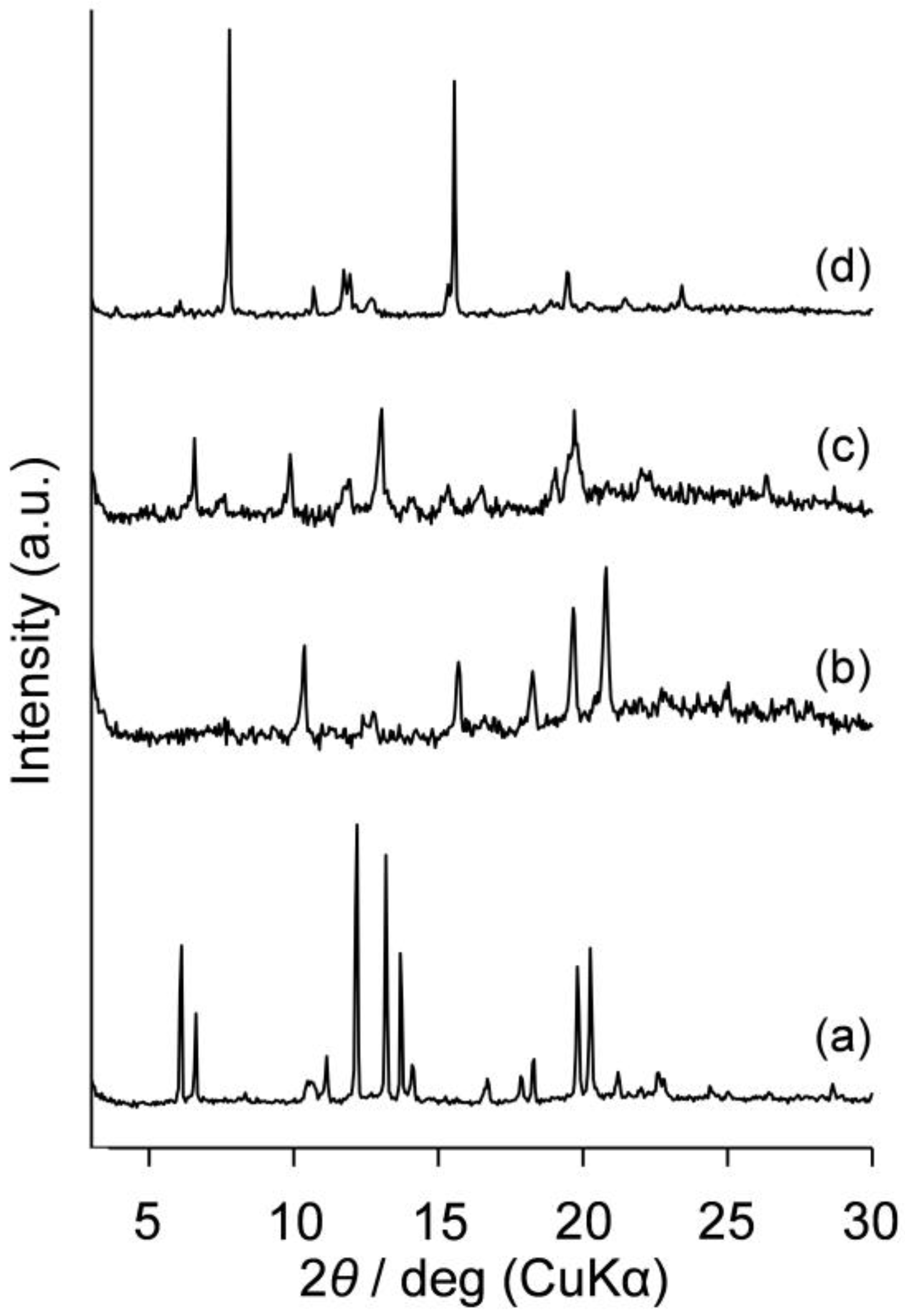
2.4. Evaluation of Crystalline-Amorphous Structures of Am-POSS(x,y)
2.5. Evaluation of Am-POSS(x,y) as ILs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Am-POSS(1)
3.3. Preparation of Am-POSS(2)
3.4. Preparation of Am-POSS(3)
3.5. Preparation of Am-POSS(4)
3.6. Preparation of Am-POSS(1,2)
3.7. Preparation of Am-POSS(1,3)
3.8. Preparation of Am-POSS(1,4)
3.9. Preparation of Am-POSS(2,3)
3.10. Preparation of Am-POSS(2,4)
3.11. Preparation of Am-POSS(3,4)
3.12. Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baney, R.H.; Itoh, M.; Sakakibara, A.; Suzuki, T. Silsesquioxanes. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1409–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, D.A.; Baugher, B.M.; Baugher, C.R.; Schneider, D.A.; Rahimian, K. Substituent effects on the sol−gel chemistry of organotrialkoxysilanes. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 3624–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, D.B.; Lickiss, P.D.; Rataboul, F. Recent developments in the chemistry of cubic polyhedral oligosilsesquioxanes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2081–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Chujo, Y. Advanced functional materials based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS). J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, F.J.; Wyndham, K.D. Amine and ester-substituted silsesquioxanes: Synthesis, characterization and use as a core for starburst dendrimers. Chem. Commun. 1998, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, K.; Sato, M.; Chujo, Y. Stabilized spherical aggregate of palladium nanoparticles prepared by reduction of palladium acetate in octa(3-aminopropyl)octasilsesquioxane as a rigid template. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2719–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, R.M.; Roll, M.F. Polyhedral phenylsilsesquioxanes. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 1073–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. POSS related polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1649–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samthong, C.; Laine, R.M.; Somwangthanaroj, A. Synthesis and characterization of organic/inorganic epoxy nanocomposites from poly(aminopropyl/phenyl)silsesquioxanes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 3601–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sloan, R.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Nazarenko, S.I.; Wiggins, J.S. Structure-property relationships in epoxy hybrid networks based on high mass fraction pendant POSS incorporated at molecular level. Polymer 2018, 139, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Naka, K. Syntheses of dumbbell-shaped trifluoropropyl-substituted POSS derivatives linked by simple aliphatic chains and their optical transparent thermoplastic films. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6039–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Naka, K. Syntheses and properties of star-and dumbbell-shaped POSS derivatives containing isobutyl groups. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maegawa, T.; Irie, Y.; Fueno, H.; Tanaka, K.; Naka, K. Synthesis and polymerization of a para-disubstituted T8-caged hexaisobutyl-POSS monomer. Chem. Lett. 2014, 43, 1532–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, T.; Koge, S.; Mizumo, T.; Ohshita, J.; Kaneko, Y. Facile preparation of a soluble polymer containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane units in its main chain. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3039–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimjarn, S.; Kunthom, R.; Chancharone, P.; Sodkhomkhum, R.; Sangtrirutnugul, P.; Ervithayasuporn, V. Synthesis of aromatic functionalized cage-rearranged silsesquioxanes (T8, T10, and T12) via nucleophilic substitution reactions. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Kaneko, Y. Preparation of ammonium-functionalized polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes with high proportions of cagelike decamer and their facile separation. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 4133–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, S.; Sato, Y.; Imoto, H.; Naka, K. Thermal properties of open-cage silsesquioxanes: The effect of substituents at the corners and opening moieties. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 92, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, T.; Shoiriki, M.; Mizumo, T.; Kaneko, Y. Preparation of low-crystalline POSS containing two types of alkylammonium groups and its optically transparent film. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 2496–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Koge, S.; Ohshita, J.; Kaneko, Y. Preparation of a thermally stable room temperature ionic liquid containing cage-like oligosilsesquioxane with two types of side-chain groups. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 89, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Shoiriki, M.; Mizumo, T. Preparation of cage-like octa(3-aminopropyl)silsesquioxane trifluoromethanesulfonate in higher yield with a shorter reaction time. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14475–14478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Kaneko, Y. Selective and high-yielding preparation of ammonium-functionalized cage-like octasilsesquioxanes using superacid catalyst in dimethyl sulfoxide. Chem. Lett. 2018, 47, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, A.; Kulikov, D.V.; Verevkin, S.P. Thermodynamic properties of mixtures containing ionic liquids. 1. Activity coefficients at infinite dilution of alkanes, alkenes, and alkylbenzenes in 4-methyl-n-butylpyridinium tetrafluoroborate using gas−liquid chromatography. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2001, 46, 1526–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, A.; Kulikov, D.V.; Verevkin, S.P. Thermodynamic properties of mixtures containing ionic liquids. Activity coefficients at infinite dilution of polar solutes in 4-methyl-N-butyl-pyridinium tetrafluoroborate using gas–liquid chromatography. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2002, 34, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emel’yanenko, V.N.; Verevkin, S.P.; Heintz, A. The gaseous enthalpy of formation of the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide from combustion calorimetry, vapor pressure measurements, and ab initio calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3930–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids. Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: Solvents for synthesis and catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Willauer, H.D.; Swatloski, R.P.; Visser, A.E.; Rogers, R.D. Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for ‘clean’ liquid–liquid extraction. Chem. Commun. 1998, 1765–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyuba, S.V.; Bartsch, R.A. Recent advances in applications of room-temperature ionic liquid/supercritical CO2 systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapatibhotla, L.V.N.R.; Zheng, J.; Roy, D.; Krishnan, S. PEGylated imidazolium ionic liquid electrolytes: Thermophysical and electrochemical properties. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6347–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurumaki, A.; Kagimoto, J.; Ohno, H. Properties of polymer electrolytes composed of poly(ethylene oxide) and ionic liquids according to hard and soft acids and bases theory. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Evolving structure–property relationships and expanding applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11379–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Ishiguro, F.; Chujo, Y. POSS ionic liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17649–17651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Ma, D.; Sun, X.; Feng, S.; Zhang, C. Synthesis and characterization of an octaimidazolium-based polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes ionic liquid by an ion-exchange reaction. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 4337–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Mizumo, T.; Kaneko, Y. Facile preparation of ionic liquid containing silsesquioxane framework. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 87, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Enoki, T.; Mizumo, T.; Ohshita, J.; Kaneko, Y. Preparation of imidazolium-type ionic liquids containing silsesquioxane frameworks and their thermal and ion-conductive properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 15226–15232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohara, T.; Kai, T.; Ohshita, J.; Kaneko, Y. Preparation of protic ionic liquids containing cyclic oligosiloxane frameworks. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10575–10582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds may be available from the authors. |








| Am-POSS(x) | Water | DMSO | DMF | Methanol | Acetone | Acetonitrile | Chloroform | Toluene | n-Hexane |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Am-POSS(1) | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(2) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(3) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(4) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(x,y) | Water | DMSO | DMF | Methanol | Acetone | Acetonitrile | Chloroform | Toluene | n-Hexane |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Am-POSS(1,2) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(1,3) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(1,4) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(2,3) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(2,4) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Am-POSS(3,4) | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| Run | Am-POSS(x,y) | Tg/°C (a) | Tm/°C (a) | Flow Temp./°C (b) | Td5/°C (c) | Td10/°C (c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Am-POSS(1,2) | ND (d) | 154 | 140 | 384 | 397 |
| 2 | Am-POSS(1,3) | −6 | ND (d) | 45 | 374 | 395 |
| 3 | Am-POSS(1,4) | 15 | ND (d) | 60 | 380 | 401 |
| 4 | Am-POSS(2,3) | ND (d) | 104 | 95 | 371 | 387 |
| 5 | Am-POSS(2,4) | 1 | ND (d) | 45 | 378 | 395 |
| 6 | Am-POSS(3,4) | −2 | 86,118 | 95 | 383 | 400 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasebe, R.; Kaneko, Y. Control of Crystalline-Amorphous Structures of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes Containing Two Types of Ammonium Side-Chain Groups and Their Properties as Protic Ionic Liquids. Molecules 2019, 24, 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244553
Hasebe R, Kaneko Y. Control of Crystalline-Amorphous Structures of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes Containing Two Types of Ammonium Side-Chain Groups and Their Properties as Protic Ionic Liquids. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244553
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasebe, Ryoya, and Yoshiro Kaneko. 2019. "Control of Crystalline-Amorphous Structures of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes Containing Two Types of Ammonium Side-Chain Groups and Their Properties as Protic Ionic Liquids" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244553
APA StyleHasebe, R., & Kaneko, Y. (2019). Control of Crystalline-Amorphous Structures of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes Containing Two Types of Ammonium Side-Chain Groups and Their Properties as Protic Ionic Liquids. Molecules, 24(24), 4553. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244553