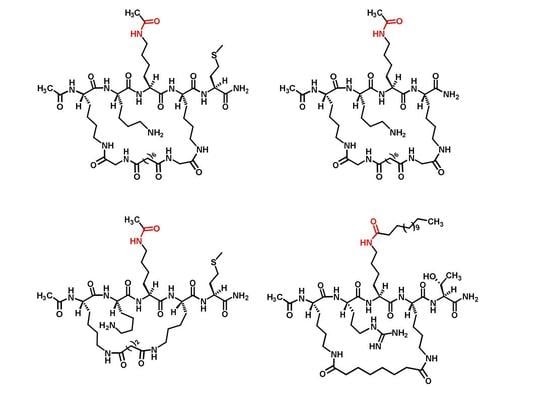
Cyclic Peptide-Based Sirtuin Substrates
Abstract
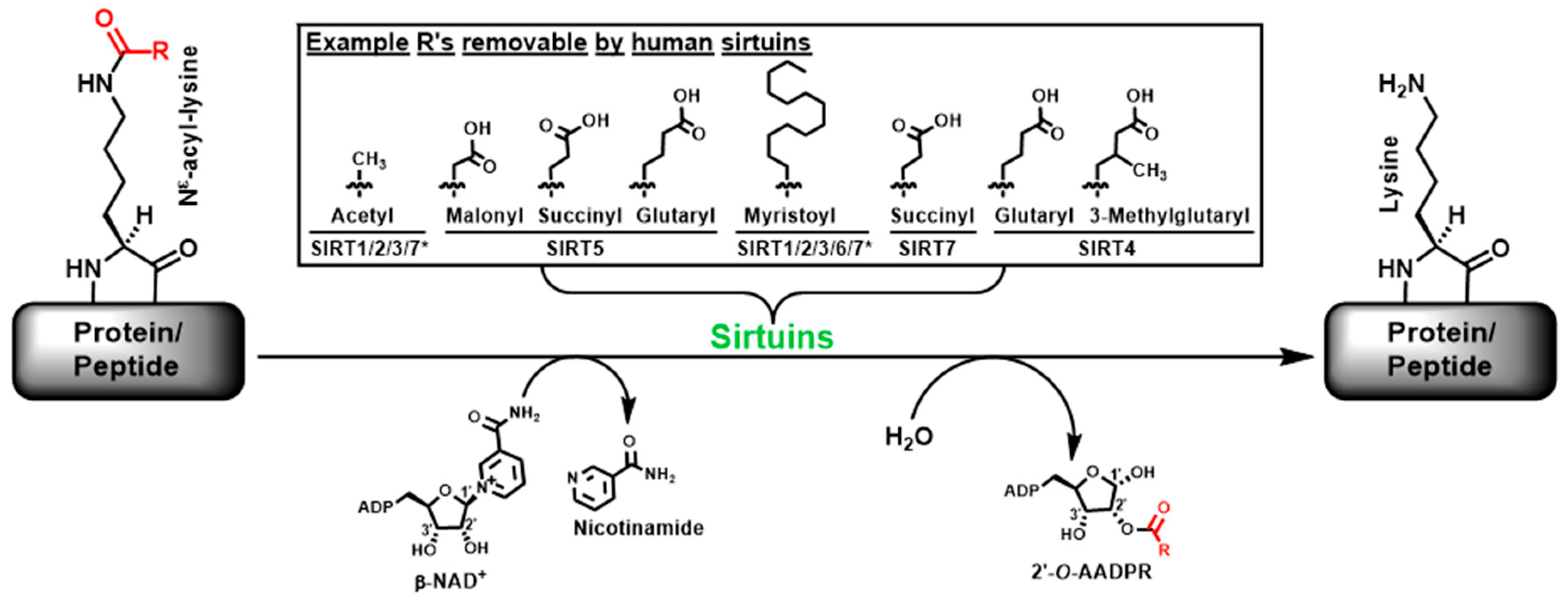
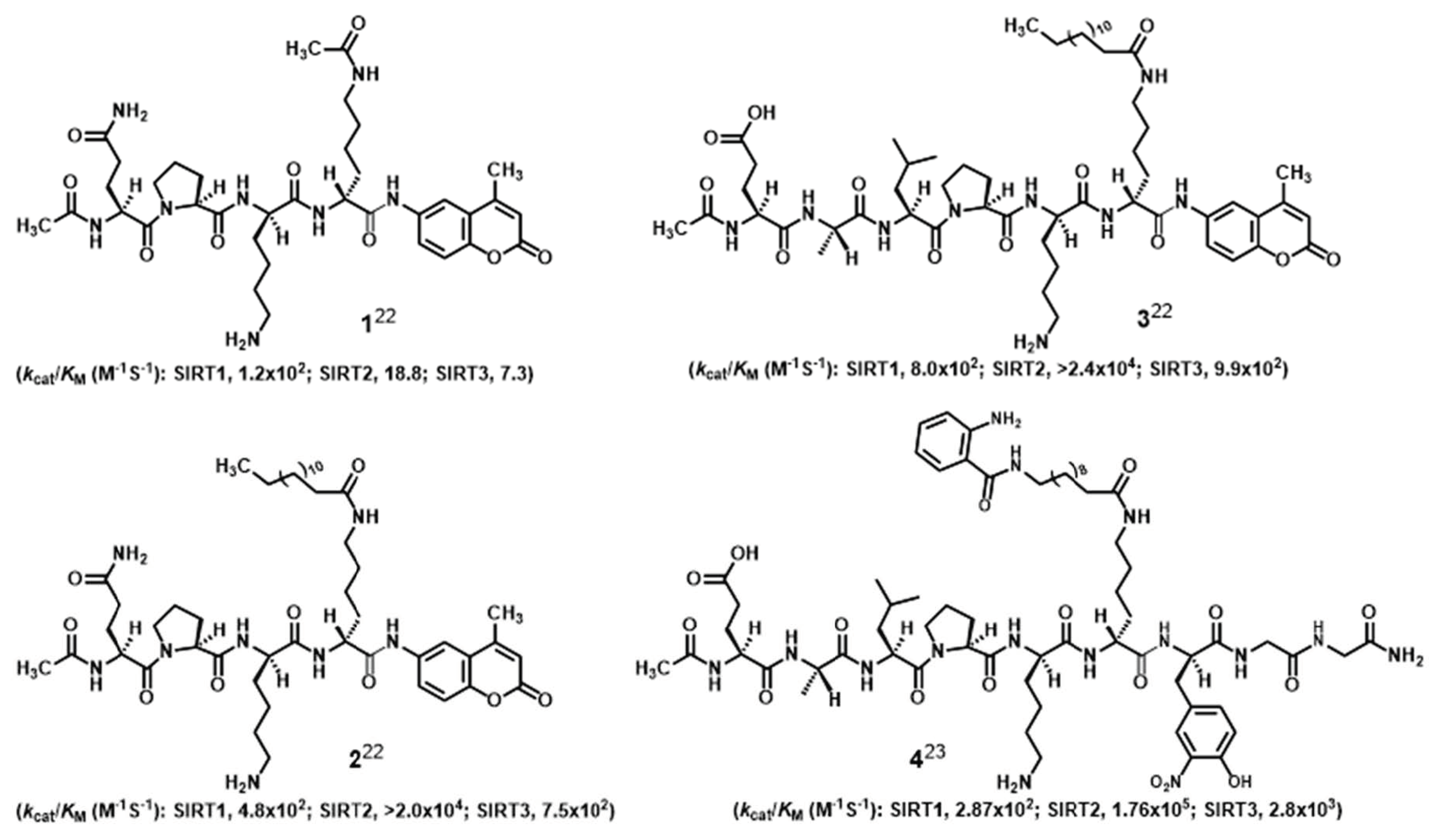
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
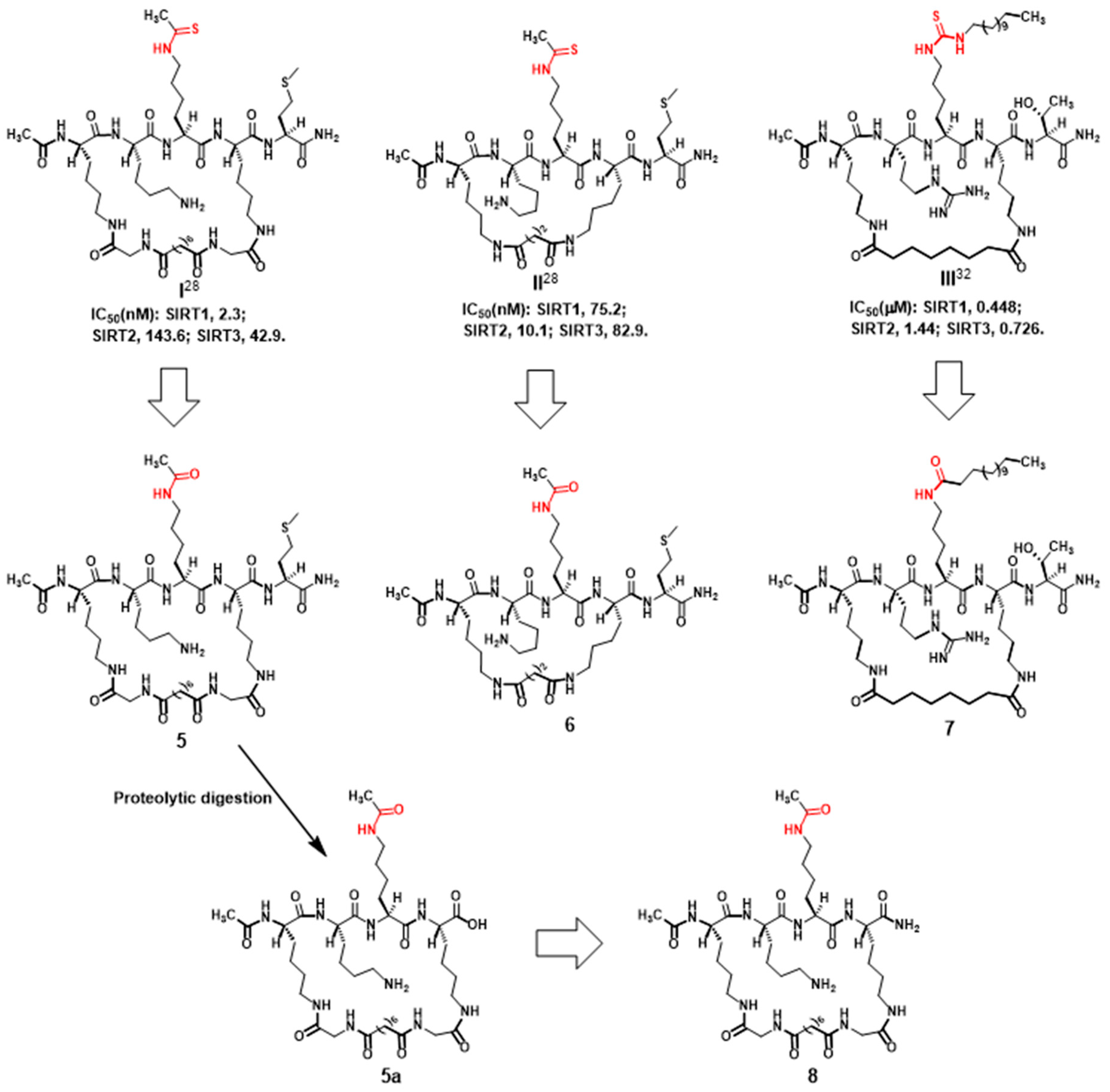
2.1. Compound Design
2.2. Compound Preparation
2.3. Compound Evaluation with Pronase Digestion Assay
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
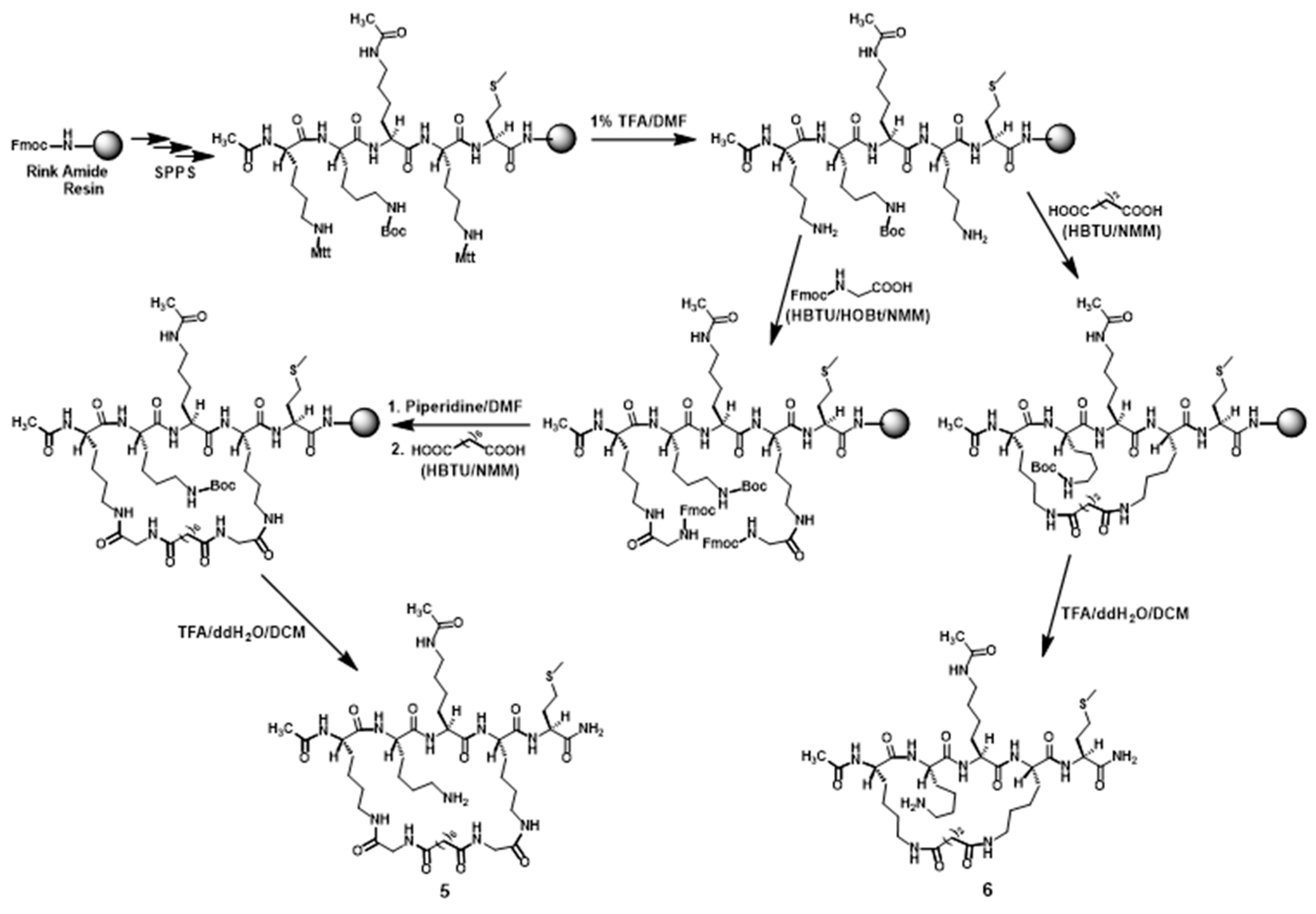
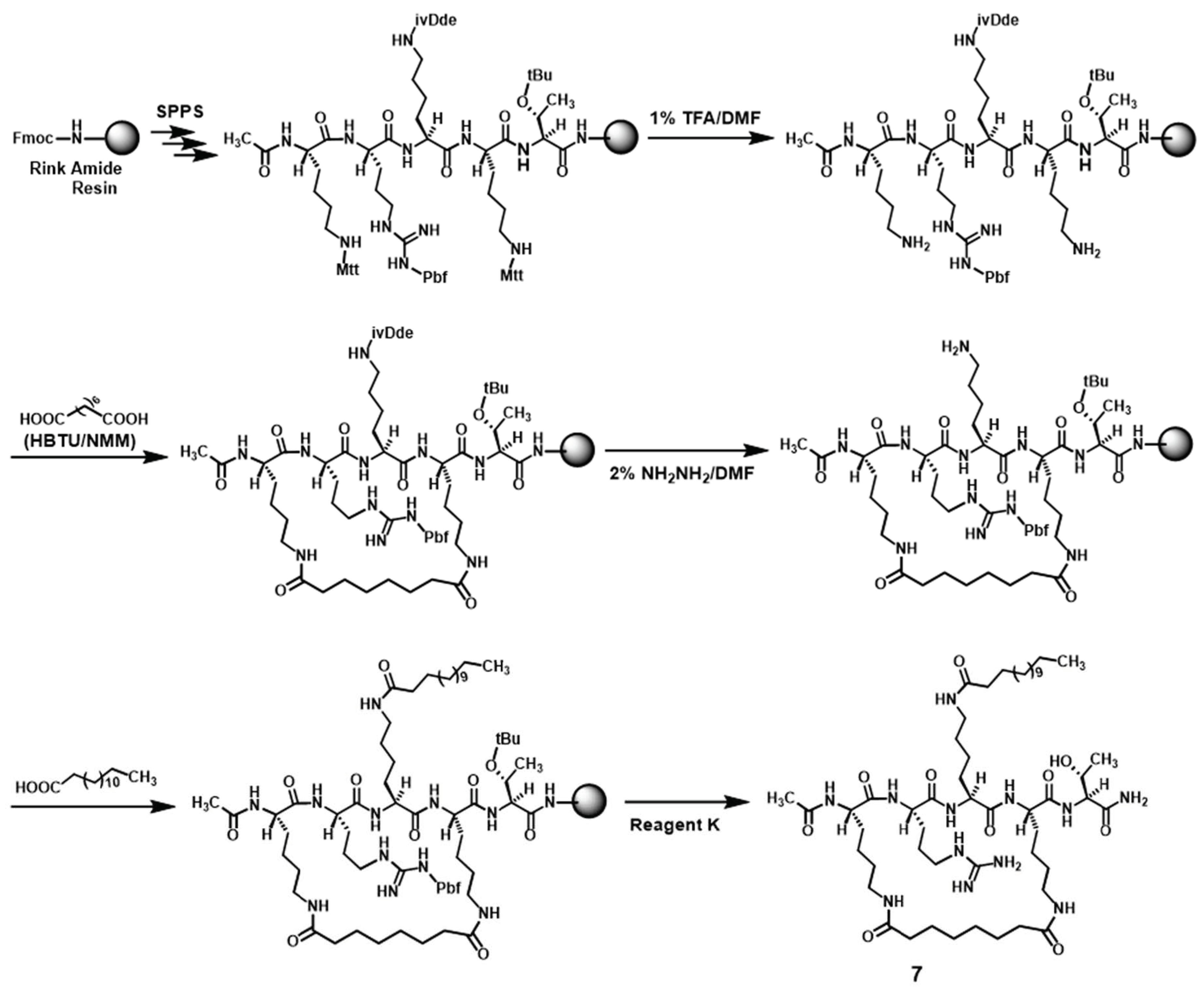
3.2. Compound Preparation
3.2.1. Preparation of Compounds 5 and 6 (Scheme 1)
3.2.2. Preparation of Compound 7 (Scheme 2)
3.2.3. Preparation of Compound 8 (Scheme 3)
3.3. Kinetic Parameter Determination for 5–8’s Substrate Activities with SIRT1/2/3
3.4. Pronase Digestion Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greiss, S.; Gartner, A. Sirtuin/Sir2 phylogeny, evolutionary considerations and structural conservation. Mol. Cells 2009, 28, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; He, B. SIRT4 is the last puzzle of mitochondrial sirtuins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3861–3865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zheng, W. Chemical probes in sirtuin research. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. Sirtuins in Health and Disease, 1st ed.; Zheng, W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 154, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabi, N.; Galleano, I.; Madsen, A.S.; Olsen, C.A. Targeting sirtuins: Substrate specificity and inhibitor design. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. Sirtuins in Health and Disease, 1st ed.; Zheng, W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 154, pp. 25–69. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zheng, W. Mammalian sirtuins SIRT4 and SIRT7. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. Sirtuins in Health and Disease, 1st ed.; Zheng, W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 154, pp. 147–168. [Google Scholar]
- Bheda, P.; Jing, H.; Wolberger, C.; Lin, H. The substrate specificity of sirtuins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zang, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; He, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, W. The chemical biology of sirtuins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5246–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Redondo, P.; Vaquero, A. The diversity of histone versus nonhistone sirtuin substrates. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Lombard, D.B. Functions of the sirtuin deacylase SIRT5 in normal physiology and pathobiology. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhwanky, M.S.; Hakkola, J. Extranuclear sirtuins and metabolic stress. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2018, 28, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringman-Rodenbarger, L.R.; Guo, A.H.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Lombard, D.B. Emerging roles for SIRT5 in metabolism and cancer. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2018, 28, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastián, C.; Mostoslavsky, R. The role of mammalian sirtuins in cancer metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 43, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Mostoslavsky, R. Sirtuins, metabolism, and DNA repair. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2014, 26, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Faller, D.V. Transcription regulation by class III histone deacetylases (HDACs)-sirtuins. Transl. Oncogenomics 2008, 3, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, J.; Liao, M.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, X.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, L. An overview of sirtuins as potential therapeutic target: Structure, function and modulators. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 48–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neo, S.H.; Tang, B.L. Sirtuins as modifiers of huntington’s disease (HD) pathology. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. Sirtuins in Health and Disease, 1st ed.; Zheng, W., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 154, pp. 105–145. [Google Scholar]
- Schiedel, M.; Robaa, D.; Rumpf, T.; Sippl, W.; Jung, M. The current state of NAD+-dependent histone deacetylases (sirtuins) as novel therapeutic targets. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 147–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Yan, L.; Zheng, W. Sirtuin inhibition: Strategies, inhibitors, and therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Sinclair, D.A.; Ellis, J.L.; Steegborn, C. Sirtuin activators and inhibitors: Promises, achievements, and challenges. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 188, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H. HPLC-based enzyme assays for sirtuins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1813, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galleano, I.; Schiedel, M.; Jung, M.; Madsen, A.S.; Olsen, C.A. A continuous, fluorogenic sirtuin 2 deacylase assay: Substrate screening and inhibitor evaluation. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.L.; Lin, H. An improved fluorogenic assay for SIRT1, SIRT2, and SIRT3. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 2186–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.; Roessler, C.; Meleshin, M.; Zimmermann, P.; Simic, Z.; Kambach, C.; Schiene-Fischer, C.; Steegborn, C.; Hottiger, M.O.; Schutkowski, M. A continuous sirtuin activity assay without any coupling to enzymatic or chemical reactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Liao, S.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; He, B. A mini-review on sirtuin activity assays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, C.; Tüting, C.; Meleshin, M.; Steegborn, C.; Schutkowski, M. A novel continuous assay for the deacylase sirtuin 5 and other deacetylases. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7217–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.B.; Jing, H.; Aramsangtienchai, P.; He, B.; Khan, S.; Hu, J.; Lin, H.; Hao, Q. Efficient demyristoylase activity of SIRT2 revealed by kinetic and structural studies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, M.; Ro, S. Peptidomimetics for drug design. In Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery. Principles and Practice, 5th ed.; Wolff, M.E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 1, pp. 803–861. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yan, L.; Zheng, W. Simple Nε-thioacetyl-lysine-containing cyclic peptides exhibiting highly potent sirtuin inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatkins, D.G.; Monnot, A.D.; Zheng, W. Nε-thioacetyl-lysine: A multi-facet functional probe for enzymatic protein lysine Nε-deacetylation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 3651–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.C.; Denu, J.M. Mechanism-based inhibition of Sir2 deacetylases by thioacetyl-lysine peptide. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 14478–14486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, J.L.; Baeza, J.; Denu, J.M. Activation of the protein deacetylase SIRT6 by long-chain fatty acids and widespread deacylation by mammalian sirtuins. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31350–31356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, W. Cyclic peptide-based potent human SIRT6 inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 5928–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, B.M.; Hao, Y.; Li, X.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, W. A mechanism-based potent sirtuin inhibitor containing Nε-thiocarbamoyl-lysine (TuAcK). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4753–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche Applied Science. Pronase: Product Description. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/roche/pronro?lang=en®ion=SX (accessed on 19 January 2019).
- Hirsch, B.M.; Gallo, C.A.; Du, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, W. Discovery of potent, proteolytically stable, and cell permeable human sirtuin peptidomimetic inhibitors containing Nε-thioacetyl-lysine. Med. Chem. Comm. 2010, 1, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | Ionic Formula | Calculated m/z | Observed m/z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | [C45H81N12O11S]+ | 997.5863 | 997.5856 |
| 6 | [C37H67N10O9S]+ | 827.4808 | 827.4778 |
| 7 | [C52H97N12O10]+ | 1049.7445 | 1049.7449 |
| 8 | [C40H71N11O10Na]+ | 888.5278 | 888.5282 |
| Compound | 5 | 6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sirtuin | KM (μM) | kcat (10−3, s−1) | kcat/KM (M−1·s−1) | KM (μM) | kcat (10−3, s−1) | kcat/KM (M−1·s−1) |
| SIRT1 | 22.2 ± 1.8 | 35.6 ± 5.1 | (1.6 ± 0.1) × 103 | 41.3 ± 1.83 | 25.9 ± 2.3 | (0.63 ± 0.03) × 103 |
| SIRT2 | 11.6 ± 2.2 | 36.0 ± 4.9 | (3.2 ± 1.0) × 103 | 49.7 ± 7.78 | 138.9 ± 26.7 | (2.79 ± 0.1) × 103 |
| SIRT3 | 4.5 ± 0.9 | 15.8 ± 1.4 | (3.6 ± 0.4) × 103 | 34.9 ± 4.04 | 155.3 ± 16.6 | (4.51 ± 1.0) × 103 |
| Compound | 7 | 8 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sirtuin | KM (μM) | kcat (10−3, s−1) | kcat/KM (M−1·s−1) | KM (μM) | kcat (10−3, s−1) | kcat/KM (M−1·s−1) |
| SIRT1 | 2.85 ± 0.13 | 5.8 ± 0.1 | (2.04 ± 0.06) × 103 | 42.2 ± 17.5 | 90.2 ± 39.4 | (2.2 ± 0.05) × 103 |
| SIRT2 | 37.6 ± 14.4 | 90.9 ± 2.62 | (2.6 ± 0.93) × 103 | 43.1 ± 16.0 | 414.0 ± 25.0 | (10.4 ± 4.4) × 103 |
| SIRT3 | 4.2 ± 0.38 | 60.0 ± 2.8 | (14.3 ± 0.66) × 103 | 99.9 ± 48.7 | 221.0 ± 32.0 | (2.4 ± 0.9) × 103 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, D.; Yan, L.; Zheng, W. Cyclic Peptide-Based Sirtuin Substrates. Molecules 2019, 24, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030424
Chen D, Yan L, Zheng W. Cyclic Peptide-Based Sirtuin Substrates. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030424
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Di, Lingling Yan, and Weiping Zheng. 2019. "Cyclic Peptide-Based Sirtuin Substrates" Molecules 24, no. 3: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030424
APA StyleChen, D., Yan, L., & Zheng, W. (2019). Cyclic Peptide-Based Sirtuin Substrates. Molecules, 24(3), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030424