Geochemical Significance of Biomarkers in the Methane Hydrate-Bearing Sediments from the Shenhu Area, the South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results
3.2. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Extraction and Separation
4.2. GC-MS and GC×GC-TOFMS Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sloan, E.D. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1990; p. 641. [Google Scholar]
- Max, M.D.; Johnson, A.H.; Dillon, W.P. Economic Geology of Natural Gas Hydrate; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–341. [Google Scholar]
- Makogon, Y.F. Natural gas hydrates—A promising source of energy. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2010, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.R.; Yang, S.H.B.; Babu, P.; Linga, P.; Li, X.S. Review of natural gas hydrates as an energy resource: Prospects and challenges. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 1633–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, B.; Parkes, R.; Fry, J.; Weightman, A.; Rochelle, P.; Maxwell, J. Bacterial populations and processes in sediments containing gas hydrates (ODP Leg 146: Cascadia Margin). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1996, 139, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, F.; Nunoura, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Teske, A.; Lever, M.; Lauer, A.; Suzuki, M.; Takai, K.; Delwiche, M.; Colwell, F.S.; et al. Biogeographical distribution and diversity of microbes in methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments on the Pacific Ocean Margin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanoil, B.D.; Sassen, R.; La Duc, M.T.; Sweet, S.T.; Nealson, K.H. Bacteria and Archaea physically associated with Gulf of Mexico gas hydrates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5143–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Chung, K.H.; Jin, Y.K.; Shin, K.H. Characterizing lipid biomarkers in methanotrophic communities of gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the Sea of Okhotsk. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2011, 28, 1884–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F. Microbial diversity in the hydrate-containing and-free surface sediments in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. Geosci. Front. 2015, 6, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Sun, X.; Xu, L.; Lu, H. Contribution of thermogenic organic matter to the formation of biogenic gas hydrate: Evidence from geochemical and microbial characteristics of hydrate-containing sediments in the Taixinan Basin, South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 80, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidle, K.A.; Kastner, M.; Bartlett, D.H. A phylogenetic analysis of microbial communities associated with methane hydrate containing marine fluids and sediments in the Cascadia margin (ODP site 892B). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 177, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Su, X.; Fu, S.; Sha, Z.; Yang, T. Variations of pore water sulfate gradients in sediments as indicator for underlying gas hydrate in Shenhu Area, the South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.X.; Ni, Y.Y.; Huang, S.P.; Peng, W.L.; Han, W.X.; Gong, D.Y.; Wei, W. Genetic types of gas hydrates in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Lu, J.A. The characteristics and origin of gas hydrate in Shenhu area, South China Sea. Mar. Geol. Lett. 2010, 26, 6–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Meng, Q.; He, X.; Li, C.; Ye, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, J. Comparison of the characteristics for natural gas hydrate recovered from marine and terrestrial areas in China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 152, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, J.F.; Lipp, J.S.; Lever, M.A.; Lloyd, K.G.; Sørensen, K.B.; Anderson, R.; Fredricks, H.F.; Elvert, M.; Kelly, T.J.; Schrag, D.P.; et al. Heterotrophic Archaea dominate sedimentary subsurface ecosystems off Peru. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3846–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipp, J.S.; Hinrichs, K.U. Structural diversity and fate of intact polar lipids in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 6816–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Sakata, S.; Fujii, T. Archaeal polar lipids in subseafloor sediments from the Nankai Trough: Implications for the distribution of methanogens in the deep marine subsurface. Org. Geochem. 2015, 78, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orphan, V.J.; Jahnke, L.L.; Embaye, T.; Turk, K.A.; Pernthaler, A.; Summons, R.E.; Marais, D.J. Characterization and spatial distribution of methanogens and methanogenic biosignatures in hypersaline microbial mats of Baja California. Geobiology 2008, 6, 376–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.E.; Walters, C.C.; Moldowan, J.M. The Biomarker Guide; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.B. (Ed.) Formation and Evolution of Marginal Seas in China and Their Effect on Resources; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 377–384. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.Y.; Yang, S.X.; Wang, H.B.; Liang, J.Q.; Gong, Y.H.; Lu, Z.Q.; Wu, D.D.; Guan, H.X. Gas-bearing fluid influx subsystem for gas hydrate geological system in Shenhu Area, northern South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2009, 52, 1641–1650. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Chen, C.M.; Peng, D.J.; Zhou, D.; Chen, H.H. The Pearl River Deep-Water Fan System and Petroleum in South China Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Su, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, H.F.; Liu, G.H.; Zhen, Z.X.; Chen, C.Y. Variations in biogenic components of late Miocene-Holocene sediments from Shenhu area in the northern South China Sea and their geological implication. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2009, 29, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, S.L.; Max, M.D.; Cherkis, N.Z.; Czarnecki, M.F. Tectono-sedimentary controls on the likelihood of gas hydrate occurrence near Taiwan. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2000, 17, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Yang, S.X.; Wu, N.Y.; Su, X.; Holland, M. Successful and Surprising Results for China’s First Gas Hydrate Drilling Expedition; Fire in the Ice: Methane Hydrate Newsletter; National Energy Technology Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Knittel, K.; Boetius, A. Anaerobic oxidation of methane: Progress with an unknown process. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiticar, M.J.; Faber, E.; Schoell, M. Biogenic methane formation in marine and freshwater environments: CO2 reduction vs. acetate fermentation-isotope evidence. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 693–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papendick, S.L.; Downs, K.R.; Vo, K.D.; Hamilton, S.K.; Dawson, G.K.; Golding, S.D.; Gilcrease, P.C. Biogenic methane potential for Surat Basin, Queensland coal seams. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 88, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meslé, M.; Dromart, G.; Oger, P. Microbial methanogenesis in subsurface oil and coal. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocks, J.J.; Pearson, A. Building the biomarker tree of life. In Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry; Banfield, J., Nealson, K., Cervini-Silva, J., Eds.; The Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2005; Volume 59, pp. 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, T.C.; Logan, G.A.; Grosjean, E.; Ryan, D.; Marriott, P.J. Use of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the characterization of biodegradation and unresolved complex mixtures in petroleum. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6468–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, G.T.; Kenig, F.; Reddy, C.M.; Frysinger, G.S.; Nelson, R.K.; Mooy, B.V.; Gaines, R.B. Analysis of unresolved complex mixtures of hydrocarbons extracted from Late Archean sediments by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC × GC). Org. Geochem. 2008, 39, 846–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, G.T.; Raghuraman, B.; Nelson, R.K.; Mullins, O.C.; Reddy, C.M. Compound class oil fingerprinting techniques using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC × GC). Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiserbeck, C.; Nelson, R.K.; Grice, K.; Curiale, J.; Reddy, C.M. Comparison of GC–MS, GC–MRM-MS, and GC × GC to characterise higher plant biomarkers in Tertiary oils and rock extracts. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 87, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cao, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, D.; Fan, R. Analysis of terpanes in biodegraded oils from China using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Fuel 2014, 133, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cao, J.; Hu, S. Analyzing hydrocarbon fractions in crude oils by two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry under reversed-phase column system. Fuel 2015, 158, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cao, J.; Hu, S.; Luo, G. Characterization of compounds in unresolved complex mixtures (UCM) of a Mesoproterzoic shale by using GC× GC-TOFMS. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 66, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.Z.; Li, S.F.; Wang, J.H.; Cao, J. Origin of unresolved complex mixtures (UCMs) in biodegraded oils: Insights from artificial biodegradation experiments. Fuel 2018, 231, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.A.; Lewis, C.A.; Rowland, S.J. Isolated of individual hydrocarbons from the unresolved complex hydrocarbon mixture of a biodegraded crude oil using preparative capillary gas chromatography. Org. Geochem. 2005, 36, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinson, D.S.; Blair, N.E.; Martini, A.M.; Larter, S.; Orem, W.H.; McIntosh, J.C. Microbial methane from in situ biodegradation of coal and shale: A review and reevaluation of hydrogen and carbon isotope signatures. Chem. Geol. 2017, 453, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Su, X.; Lu, H.F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, C. Relations between biogenic component (foraminifera) and highly saturated gas hydrates distribution from Shenhu area, northern South China Sea. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2013, 38, 907–915. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Stefanova, M. Head-to-head linked isoprenoids in Miocene coal lithotypes. Fuel 2000, 79, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, P.F.; Summons, R.E. GC–MS detection and significance of crocetane and pentamethylicosane in sediments and crude oils. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.M.; Freeman, K.H.; Popp, B.N.; Hoham, C.H. Compound-specific isotopic analyses: A novel tool for reconstruction of ancient biogeochemical processes. Org. Geochem. 1990, 16, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsté, J.S.S.; Schouten, S. Is there evidence for a substantial contribution of prokaryotic biomass to organic carbon in Phanerozoic carbonaceous sediments? Org. Geochem. 1997, 26, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourisson, G.; Albrecht, P.; Rohmer, M. Predictive microbial biochemistry-from molecular fossils to procaryotic membranes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1982, 7, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Gong, Z.S.; Liang, D.G.; Wu, K.Q.; Wang, J.R.; Song, F.Q.; Wang, P.R.; Wang, H.T.; Zhong, H. Geochemistry of petroleum systems in the Eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin-1: Oil family classification, oil-source correlation and mixed oil analysis. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2004, 22, 15–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Pan, C.; Yu, S.; Li, E.; Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Qin, J.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, P.; Wang, L.; et al. Organic geochemistry of marine source rocks and pyrobitumen-containing reservoir rocks of the Sichuan Basin and neighbouring areas, SW China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 56, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Pang, X.; Xiao, S.; Peng, H.; Li, Q.; Song, S.; Wu, L.; Chen, D.; Hu, T. Secondary migration of hydrocarbons in the zhujiang formation in the huixi half-graben, Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 53, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Dong, D.; Yang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Liang, J.; Gong, Y.; Sun, Y. Genetic model of the hydrate system in the fine grain sediments in the northern continental slope of South China Sea. Chin. J. Geophys. 2009, 52, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Pang, X.; Shi, H.; Yu, Q.; Cao, Z.; Yu, R.; Chen, D.; Long, Z.; Jiang, F. Source rock characteristics and hydrocarbon expulsion potential of the Middle Eocene Wenchang formation in the Huizhou depression, Pearl River Mouth basin, South China sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 67, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Hou, D.; Zhang, P.; Harris, M.; Mi, J.; Chen, T.; Li, J. Reservoir characteristics in the LW3-1 structure in the deepwater area of the Baiyun sag, South China Sea. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Sha, Z.B. Gas hydrate and associated free gas in the Dongsha Area of northern South China Sea. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2013, 39, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Su, M.; Qiao, S.H.; Cong, X.R.; Su, Z.; Liang, J.Q.; Wu, N.Y. Migration of methane associated with gas hydrates of the Shenhu Area, northern slope of South China Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2015, 36, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

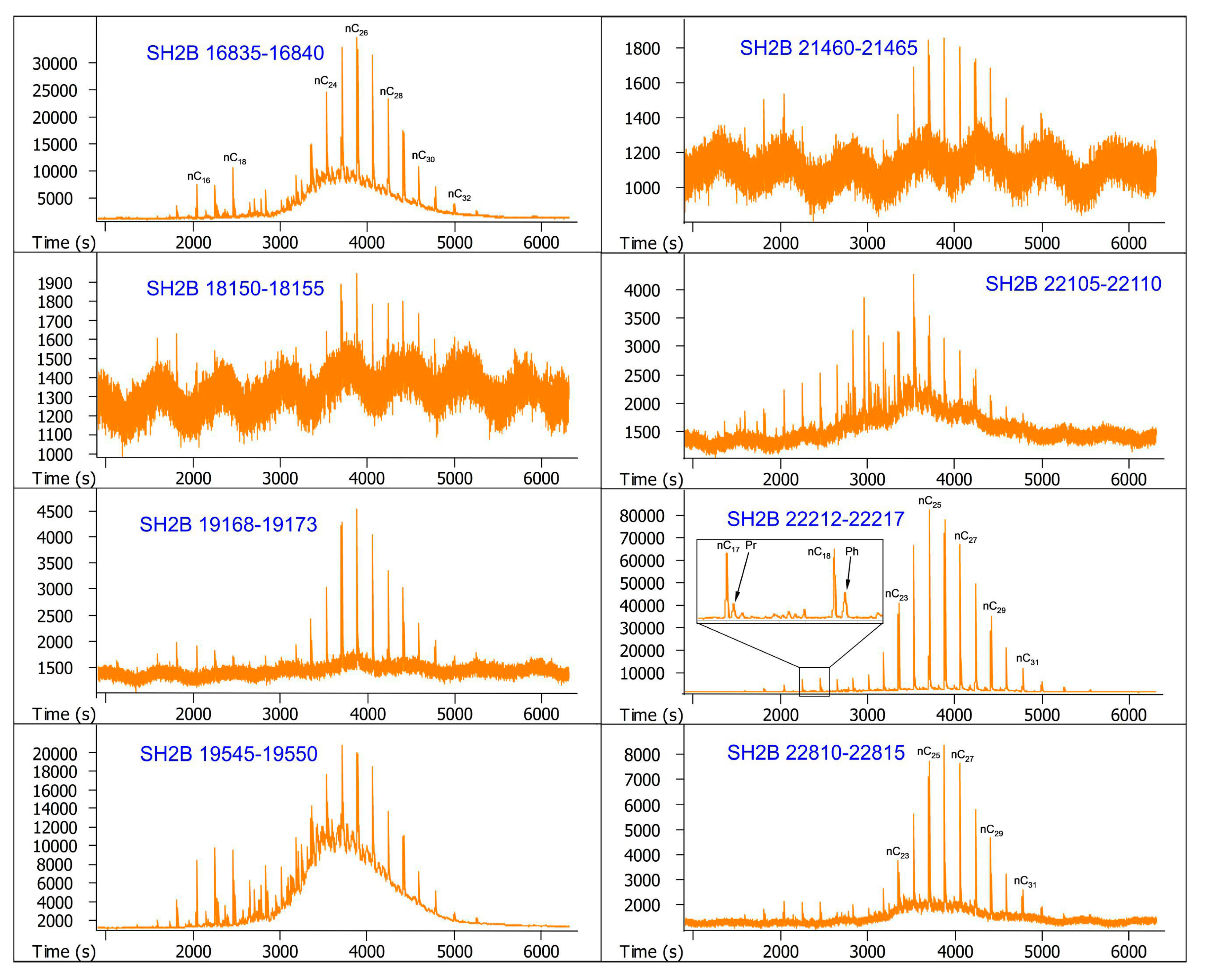
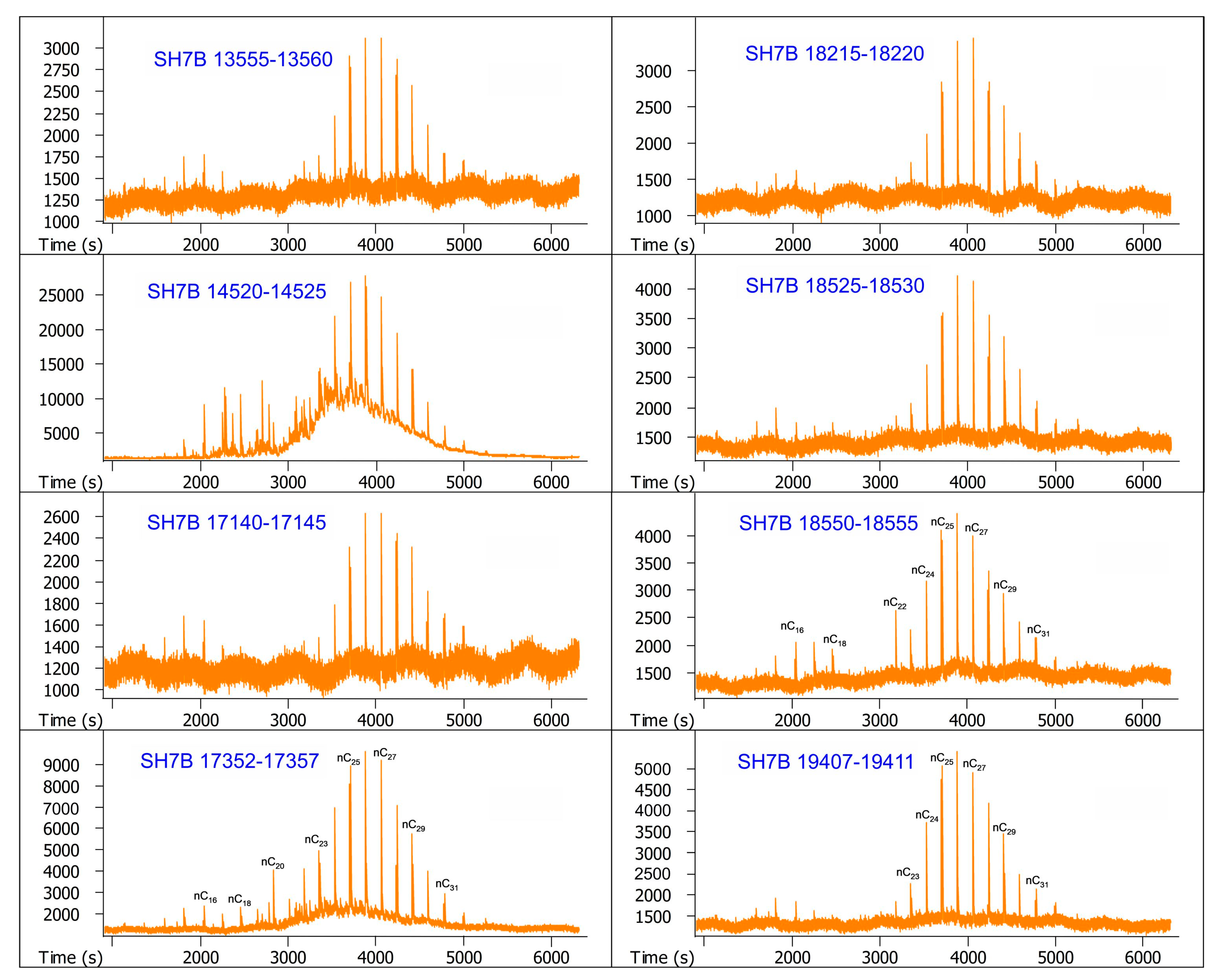
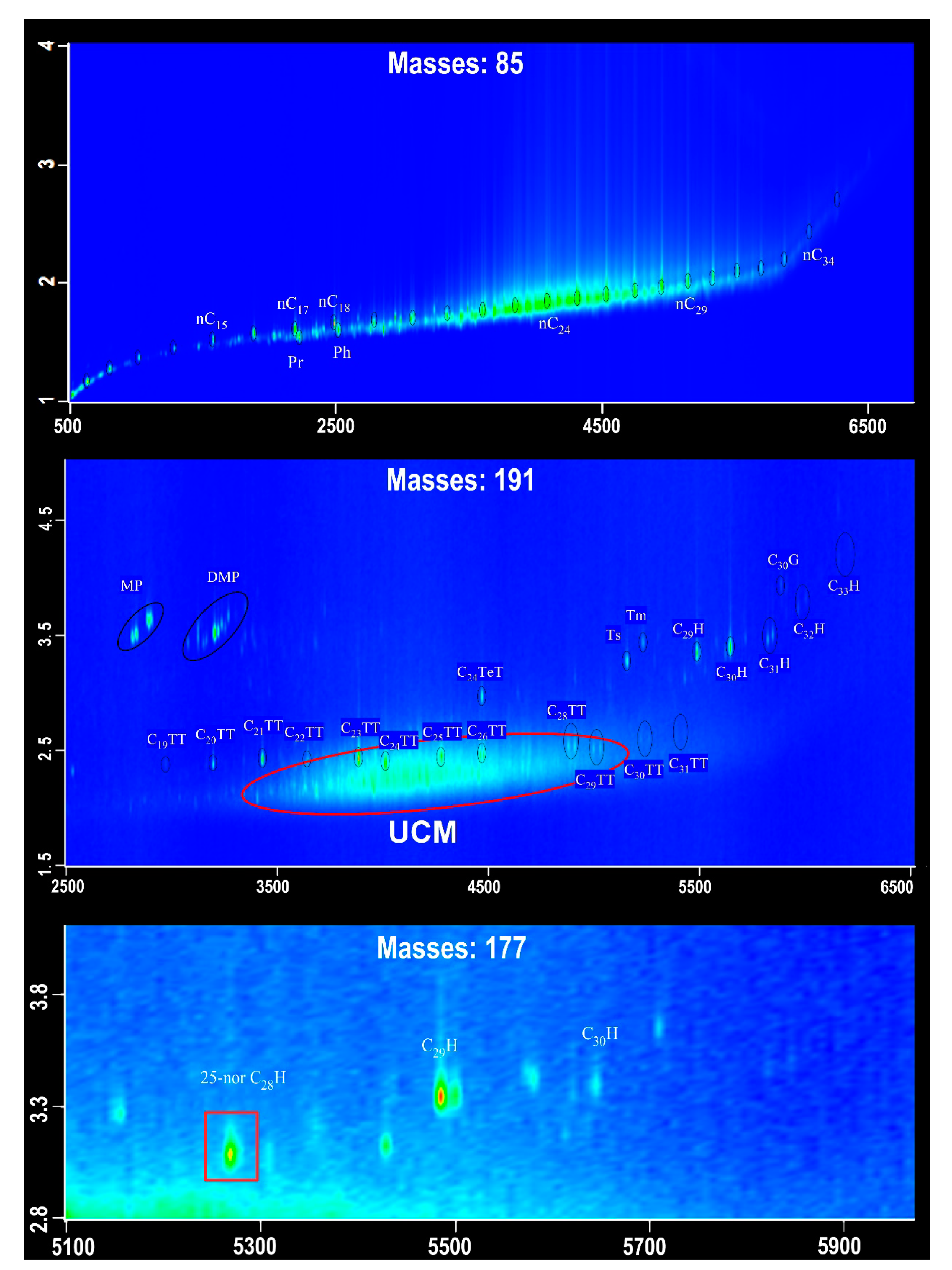
| Sample Number | Core Number | Depth Interval (cm) | Lithology | Layers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SH2B | 16,835–16,840 | Silty clay | Overlying layer |
| 2 | SH2B | 18,150–18,155 | Silty clay | Overlying layer |
| 3 | SH2B | 19,168–19,173 | Silty clay | Methane hydrate-bearing layer |
| 4 | SH2B | 19,545–19,550 | Silty clay | Methane hydrate-bearing layer |
| 5 | SH2B | 21,460–21,465 | Silty clay | Methane hydrate-bearing layer |
| 6 | SH2B | 22,105–22,110 | Silty clay | Methane hydrate-bearing layer |
| 7 | SH2B | 22,212–22,217 | Silty clay | Methane hydrate-bearing layer |
| 8 | SH2B | 22,810–22,815 | Silty clay | Underlying layer |
| 9 | SH7B | 13,555–13,560 | Sand | Overlying layer |
| 10 | SH7B | 14,520–14,525 | Sand | Overlying layer |
| 11 | SH7B | 17,140–17,145 | Silty clay | Methane hydrate-bearing layer |
| 12 | SH7B | 17,352–17,357 | Silty clay | Methane hydrate-bearing layer |
| 13 | SH7B | 18,215–18,220 | Silty clay | Underlying layer |
| 14 | SH7B | 18,525–18,530 | Silty clay | Underlying layer |
| 15 | SH7B | 18,550–18,555 | Silty clay | Underlying layer |
| 16 | SH7B | 19,407–19,411 | Silty clay | Underlying layer |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.-Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, S.-F.; Dong, S.-J.; Zhang, F.-L.; Xu, X.-M.; Wang, J.-H. Geochemical Significance of Biomarkers in the Methane Hydrate-Bearing Sediments from the Shenhu Area, the South China Sea. Molecules 2019, 24, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030456
Zhou Q-Z, Li Y, Chen F, Li S-F, Dong S-J, Zhang F-L, Xu X-M, Wang J-H. Geochemical Significance of Biomarkers in the Methane Hydrate-Bearing Sediments from the Shenhu Area, the South China Sea. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030456
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qian-Zhi, Yan Li, Fang Chen, Shui-Fu Li, Shu-Jun Dong, Feng-Lin Zhang, Xiao-Ming Xu, and Jiang-Hai Wang. 2019. "Geochemical Significance of Biomarkers in the Methane Hydrate-Bearing Sediments from the Shenhu Area, the South China Sea" Molecules 24, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030456
APA StyleZhou, Q.-Z., Li, Y., Chen, F., Li, S.-F., Dong, S.-J., Zhang, F.-L., Xu, X.-M., & Wang, J.-H. (2019). Geochemical Significance of Biomarkers in the Methane Hydrate-Bearing Sediments from the Shenhu Area, the South China Sea. Molecules, 24(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030456





