Profiling and Pharmacokinetic Studies of Alkaloids in Rats After Oral Administration of Zanthoxylum nitidum Decoction by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and HPLC-MS/MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
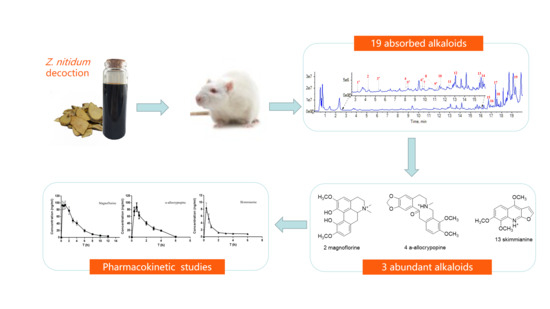
2.1. Identification of Absorbed Alkaloids of Z. nitidum Decocotion in Rat Plasma
2.2. Quantitative Method Validation
2.3. Pharmacokinetic Study
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemical, Reagents and Materials
3.2. Instrumentation and Analytical Conditions
3.2.1. Qualitative Analysis
3.2.2. Quantitative Analysis
3.3. Preparation of Samples
3.3.1. Preparation of Z. nitidum Decoction
3.3.2. Preparation of Plasma Samples
Qualitative Analysis
Quantitative Analysis
3.3.3. Calibration Samples and Quality Control Samples
3.4. Method Validation
3.5. Animal Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Commission, C.P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 169–170. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.X.; Qin, Z.H.; Zeng, D.; Han, Z.Z.; Zhan, R.T.; Tan, Y.; Chen, W.W. Comparative Study on Effects of Anti-contusion Injury, Analgesia and Anti-inflammation of Root and Stem of Zanthoxylum nitidum. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2015, 38, 2358–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.H.; Chen, W.X.; Li, R.L.; Han, Z.Z.; Yang, T.C.; Zhan, R.T.; Chen, W.W. Comparative study on effects of anti-gastritis, gastric mucosal protection and gastrointestinal movement promotion of root and stem of Zanthoxylum nitidum. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2016, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Imai, M.; Johji, S.; Tan, S.; Chen, I.-S.; Ishikawa, T. Studies on the Chemical Constituents of Xanthoxylum nitidum (ROXB.) D. C. (Fagara nitida ROXB.). II. Examination of the Chemical Constituents by Membrane Filtration: Identification of Magnoflorine, a Water-Soluble Quaternary Aporphine Alkaloid. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Akaike, M.; Tohjoh, T.; Toyoki, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Chen, I.S.; Lu, S.T. [Studies on the chemical constituents of rutaceous plants. LIX. The chemical constituents of Xanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) D.C. (Fagara nitida Roxb.) (1) Examination of the alkaloidal fraction of the bark]. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1984, 104, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyun, K.; Gray, A.I.; Hartley, T.G.; Waterman, P.G. Alkaloids from an Australian accession of Zanthoxylum nitidum (Rutaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1996, 24, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Min, Z. Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2004, 2, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, M.; Ding, L. Chemical constituents of Zanthoxylum nitidum. Chin. Pharm. J. 2008, 43, 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Hu, W.; Li, H. Isolation, identification and activity determination on the anti-inflammatory components of roots of Zanthoxylum nitidum. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2013, 30, 100–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyasu, M.; Ichimaru, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Kato, A. (R)-(+)-isotembetarine, a quaternary alkaloid from Zanthoxylum nitidium. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, Z. Studies on the antitumor constituents of Zanthoxylum nitidum (ROXB.) DC. Acta Chim. Sin. 1980, 6, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, W.D.; Shen, Y.H.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Liu, R.H.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.K. Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2007, 35, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. A study on the chemical constituents of Zanthoxylum nitidum (Lam) DC. Isolation of potential anticancer alkaloids and studies on the structure of alkaloids C. J. Sun Yat-Sen Univ. Med. Sci. 1980, 1, 341–349, 402. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.D.; Wang, L.K.; Hecht, S.M. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerase-I Isolated from Zanthoxylun nitidum. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 5025–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, W.D.; Liu, R.H.; Zhang, C.; Shen, Y.H.; Li, H.L.; Liang, M.J.; Xu, X.K. Benzophenanthridine alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum (ROXB.) DC, and their analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2006, 3, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Mu, S.; Wang, Q.; Xie, X.; Deng, L. Isolation and identification of chemical constituents from the roots of Zanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC. in Yunan province. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2016, 33, 275–279, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.-N.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Tan, N.-H. Chemical and cytotoxic constituents of Zanthoxylum nitidum. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Chen, D. Alkaloids from the roots of Zanthoxylum nitidum and their antiviral and antifungal effects. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 1718–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.G.; Zhao, Q.J.; Chen, Q.L.; Xu, L.; Song, Y.; Jin, Y.S.; Xu, D.F. Two new benzophenanthridine alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Cheng, M.J.; Chiang, M.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, C.J.; Chen, I.S. Dihydrobenzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids from stem bark of Zanthoxylum nitidum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, F. Analysis of alkaloids in Zanthoxylum nitidum by HPLC-DAD/ESI-Q-TOF-MS. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Qing, Z.; Xiang, F.; Mo, C.; Tang, Q. Identification of alkaloids in Zanthoxylum nitidum and Zanthoxylum dissitum by HPLC-Q-TOF /MS. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2017, 39, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Dai, Y.; Yao, Z.; He, L.; Wang, Q.; Geng, J.; Chen, H.; Yao, X. Study on chemical profiles and metabolites of Allii Macrostemonis Bulbus as well as its representative steroidal saponins in rats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Qin, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, H.; Yao, X. Metabolites profile of Gualou Xiebai Baijiu decoction (a classical traditional Chinese medicine prescription) in rats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1085, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, Z.X.; Cheng, P.; Liu, X.B.; Liu, Y.S.; Zeng, J.G.; Wang, W. Structural speculation and identification of alkaloids in Macleaya cordata fruits by high-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with a screening procedure. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.X.; Li, M.; Yao, Z.H.; Li, C.; Qiao, L.R.; Shen, X.Y.; Yu, K.T.; Dai, Y.; Yao, X.S. A target and nontarget strategy for identification or characterization of the chemical ingredients in Chinese herb preparation Shuang-Huang-Lian oral liquid by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Xu, H.; Zhan, R.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Chi, Y.; Chen, D.; Ji, X.; Luo, C. Metabolic Profile of Skimmianine in Rats Determined by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2017, 22, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevigny, C.; Jiwan, J.L.; Rozenberg, R.; de Hoffmann, E.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. Key fragmentation patterns of aporphine alkaloids by electrospray ionization with multistage mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, P.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z.; Lin, Y.; Pan, G.; Huang, C. Systematic and comprehensive strategy for metabolite profiling in bioanalysis using software-assisted HPLC-Q-TOF: Magnoflorine as an example. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 2239–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zeng, J. Research progress on mass spectral fragmentation behaviour of alkaloids in Macleaya cordata. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2013, 2929–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z.; Cheng, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J. Systematic identification of alkaloids in Macleaya microcarpa fruits by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry combined with the isoquinoline alkaloids biosynthetic pathway. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 103, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Li, S. Mass Spectrometry of Natural Products; China Medicine Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2003; p. 191. [Google Scholar]
- Atta ur, R.; Khalid, A.; Sultana, N.; Ghayur, M.N.; Mesaik, M.A.; Khan, M.R.; Gilani, A.H.; Choudhary, M.I. New natural cholinesterase inhibiting and calcium channel blocking quinoline alkaloids. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006, 21, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P. The Role of Organic Cation Transportes and CYPs in the Transportation and Toxicity of Nitidine Chloride. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.H.; Liu, Y.P.; Wang, X.; Di, X. A sensitive and selective liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of five isoquinoline alkaloids from Chelidonium majus L. in rat plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Feng, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, K.; Sun, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, C.-H.; Lu, W.W.; Chiu, K.-Y. Magnoflorine with hyaluronic acid gel promotes subchondral bone regeneration and attenuates cartilage degeneration in early osteoarthritis. Bone 2018, 116, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Jiang, K.; Wu, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, G.; Deng, G. Magnoflorine Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing NF-kappa B and MAPK Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Jantan, I.; Harikrishnan, H.; Abdul Wahab, S.M. Magnoflorine Enhances LPS-Activated Pro-Inflammatory Responses via MyD88-Dependent Pathways in U937 Macrophages. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, M.-H. Potential Biological Activities of Magnoflorine: A Compound from Aristolochia debilis Sieb. et Zucc. Korean J. Plant Resour. 2014, 27, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, L.-Y.; Li, N.; Chen, X.; Cai, Z.-Q.; Zhu, C.; Li, Y. Effects of allocryptopine on outward potassium current and slow delayed rectifier potassium current in rabbit myocardium. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Fu, Y.; Liu, L.; Lin, K.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. Effect of alpha-Allocryptopine on Delayed Afterdepolarizations and Triggered Activities in Mice Cardiomyocytes Treated with Isoproterenol. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 634172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, B.; Wen, Y.; Xiang, G.; Wei, G.; Zhu, C.; Xing, Y.; Li, Y. Electrophysiological and trafficking defects of the SCN5A T353I mutation in Brugada syndrome are rescued by alpha-allocryptopine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 746, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratheesh, M.; Sindhu, G.; Helen, A. Anti-inflammatory effect of quinoline alkaloid skimmianine isolated from Ruta graveolens L. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Hao, C.Y.; Liu, F.; Bian, C.F.; Chen, J.M. Analgesic, antispastic and sedative effects of skimmianine. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 1982, 3, 163–165. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.D.; Zhang, D.B.; Ren, J.; Yang, M.J. Skimmianine, a furoquinoline alkaloid from Zanthoxylum nitidum as a potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |







| NO. | RT (min) | Mass Found | Error (ppm) | Selected ion | Formula | MS2 Ions | Identification | Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.2 * | 518.2016 | 0.3 | [M + H]+ | C26H32NO10 | 356.1491, 338.1389, 188.0704 | glucothalictrisine/glucohunnemannine | protopine |
| 2 | 4.2 | 342.1702 | −1 | [M]+ | C20H24NO4 | 297.1111, 282.0876, 265.0848, 237.0900 | magnoflorine | aporphine |
| 3 | 5.3 * | 356.1494 | −1.2 | [M + H]+ | C20H22NO5 | 338.1389, 275.0698, 206.0809, 188.0809 | thalictrisine/hunnemannine | protopine |
| 4 | 8.1 | 370.1664 | 0.8 | [M + H]+ | C21H23NO5 | 352.1555, 206.0813 189.0773, 188.0704 | α-allocryptopine | protopine |
| 5 | 8.4 * | 260.1284 | 1.1 | [M + H]+ | C15H17NO3 | 242.1180, 188.0709, 176.0706, 134.0609 | 2.2,6-trimethy-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2H-pyrano[3,2-c]quinoline | quinoline |
| 6 | 9.8 * | 246.0761 | 0.2 | [M + H]+ | C13H12NO4 | 231.0526, 213.0419, 185.0471 | 4-hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxy-furanquinoline | quinoline |
| 7 | 9.9 | 334.1072 | −2 | [M]+ | C20H16NO4 | 319.0831, 291.0886, 276.0663 | isofagaridine | benzophenanthrine |
| 8 | 11.3 | 348.1239 | 0.7 | [M]+ | C21H18NO4 | 332.0934, 304.0985, 290.0806 | nitidine | benzophenanthrine |
| 9 | 11.4 * | 260.1283 | 0.9 | [M + H]+ | C15H17NO3 | 242.1174, 188.0709, 176.0706, 134.0609 | ribalinine | quinoline |
| 10 | 11.6 | 348.1231 | 0.5 | [M]+ | C21H18NO4 | 332.0923, 304.0975, 290.0817 | chelerythrine | benzophenanthrine |
| 11 | 12.2 | 276.0656 | 0.5 | [M + H]+ | C17H9NO3 | 248.0698, 218.0594 190.0636 | liriodenine | aporphine |
| 12 | 13.1 | 246.0759 | −0.5 | [M + H]+ | C13H12NO4 | 231.0526, 216.0286, 188.0346 | haplopine | quinoline |
| 13 | 15.5 | 260.0916 | 0.9 | [M + H]+ | C14H13NO4 | 245.0682, 227.0575, 199.0627 | skimmianine | quinoline |
| 14 | 15.8 | 230.0809 | −0.9 | [M + H]+ | C13H11NO3 | 230.0809, 215.0809, 186.0539, 172.0573 | γ-fagarine | quinoline |
| 15 | 16.6 | 200.0703 | −1.5 | [M + H]+ | C12H9NO2 | 185.0471,129.0579 | dictamine | quinoline |
| 16 | 16.8 | 382.1287 | 0.4 | [M + H]+ | C21H19NO6 | 364.1177, 354.1321, 349.0947, 323.0913, 292.0724 | isoarnottianamide | benzophenanthrine |
| 17 | 17.4 | 366.1340 | 1 | [M + H]+ | C21H19NO5 | 348.1232, 333.0983, 320.0920, 305.0700, 292.0739, 275.0700 | O-demethyl-becconoline | benzophenanthrine |
| 18 | 17.5 | 382.1288 | 0.7 | [M + H]+ | C21H19NO6 | 364.1179, 354.1334, 339.1098, 336.1225, 292.0718 | arnottianamide | benzophenanthrine |
| 19 | 19.1 | 334.1076 | 0.8 | [M + H]+ | C20H16NO4 | 319.0848, 318.0760, 290.0840 | Norchelerythrine | benzophenanthrine |
| Analyte | Linear Regression Equation | r | Linear Range (ng/mL) | LLOQ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (ng/mL) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | ||||
| magnoflorine | y = 0.011x + 0.018 | 0.9990 | 2–200 | 2 | 8.72 | −6.88 |
| α-allocryptopine | y =0.012x + 0.010 | 0.9995 | 2–200 | 2 | 13.04 | −7.25 |
| skimmianine | y = 0.014x − 0.010 | 0.9996 | 0.5–50 | 0.5 | 14.81 | 5.63 |
| Analyte | Concentration (ng/mL) | Intraday | Interday | Extraction Recovery (Mean ± SD, %) | Matrix Effect (Mean ± SD, %) | Related Matrix Effect (RSD, %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | |||||
| magnoflorine | 5 | 4.22 | −8.05 | 10.0 | 11.03 | 89.87 ± 7.75 | 108.46 ± 9.4 | 6.51 |
| 50 | 2.89 | 5.62 | 8.12 | −3.45 | 90.52 ± 3.16 | 98.91 ± 5.59 | 4.76 | |
| 160 | 6.78 | 3.16 | 5.26 | 6.64 | 95.57 ± 3.82 | 94.47 ± 7.18 | 5.43 | |
| α-allocryptopine | 5 | 1.83 | 9.33 | 3.96 | 7.56 | 92.68 ± 5.38 | 102.38 ± 8.43 | 8.37 |
| 50 | 3.75 | −3.87 | 5.77 | −1.57 | 96.08 ± 6.77 | 99.32 ± 4.35 | 7.12 | |
| 160 | 2.23 | 1.82 | 7.02 | −8.02 | 94.30 ± 4.16 | 93.82 ± 5.63 | 5.56 | |
| skimmianine | 1 | 2.62 | 4.41 | 4.01 | 6.33 | 93.41 ± 4.41 | 101.10 ± 6.42 | 6.39 |
| 10 | 2.84 | 6.51 | 11.23 | −7.75 | 98.32 ± 6.47 | 99.39 ± 5.84 | 8.41 | |
| 32 | 3.56 | 4.97 | 2.65 | 4.39 | 94.06 ± 3.56 | 92.73 ± 5.52 | 5.17 | |
| Analyte | Concentration (ng/mL) | Three Freeze-Thaw Cycle | 8 h at Room Temperature | 24 h at 4 °C | 40 Days at = −80 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | RSD (%) | RE (%) | ||
| magnoflorine | 5 | 7.53 | −10.00 | 8.25 | −5.14 | 4.46 | −5.59 | 6.43 | 10.17 |
| 50 | 4.58 | 11.03 | 3.26 | 6.87 | 3.81 | 9.24 | 3.68 | −8.92 | |
| 160 | 5.54 | 9.16 | 1.53 | 5.74 | 9.95 | 4.61 | 4.15 | 5.74 | |
| α-allocryptopine | 5 | 8.61 | 8.97 | 6.55 | 12.53 | 2.07 | 2.99 | 5.88 | 8.59 |
| 50 | 6.62 | −5.58 | 3.68 | −7.13 | 6.14 | −6.21 | 3.71 | −4.82 | |
| 160 | 1.19 | 4.24 | 1.59 | 3.27 | 1.26 | 7.75 | 2.73 | −6.91 | |
| skimmianine | 1 | 9.22 | 10.43 | 11.06 | −9.41 | 8.18 | 9.47 | 8.57 | 9.69 |
| 10 | 8.51 | −5.95 | 10.44 | 6.62 | 11.32 | −4.39 | 9.92 | −6.48 | |
| 32 | 7.13 | −9.01 | 8.43 | 9.51 | 4.31 | −1.09 | 8.01 | −4.07 | |
| Parameters | Analytes (Mean ± SD, n = 6) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnoflorine | α-ALlocryptopine | Skimmianine | |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 112.69 ± 18.79 | 100.28 ± 49.91 | 8.91 ± 1.89 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.05 ± 0.71 | 0.47 ± 0.13 | 0.38 ± 0.12 |
| T1/2 (h) | 3.24 ± 1.31 | 0.78 ± 0.17 | 5.99 ± 1.62 |
| AUC0-t (h*ng/mL) | 408.13 ± 91.34 | 180.361 ± 96.32 | 11.08 ± 2.02 |
| AUC0-∞ (h*ng/mL) | 437.99 ± 106.29 | 186.41 ± 98.68 | 17.05 ± 6.32 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, A.; Chi, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Qin, J.; Ou, L.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhan, R.; Xu, H. Profiling and Pharmacokinetic Studies of Alkaloids in Rats After Oral Administration of Zanthoxylum nitidum Decoction by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and HPLC-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030585
Huang A, Chi Y, Liu J, Wang M, Qin J, Ou L, Chen W, Zhao Z, Zhan R, Xu H. Profiling and Pharmacokinetic Studies of Alkaloids in Rats After Oral Administration of Zanthoxylum nitidum Decoction by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and HPLC-MS/MS. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030585
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Aihua, Yuguang Chi, Jiawei Liu, Mincun Wang, Jialiang Qin, Lijuan Ou, Weiwen Chen, Zhongxiang Zhao, Ruoting Zhan, and Hui Xu. 2019. "Profiling and Pharmacokinetic Studies of Alkaloids in Rats After Oral Administration of Zanthoxylum nitidum Decoction by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and HPLC-MS/MS" Molecules 24, no. 3: 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030585
APA StyleHuang, A., Chi, Y., Liu, J., Wang, M., Qin, J., Ou, L., Chen, W., Zhao, Z., Zhan, R., & Xu, H. (2019). Profiling and Pharmacokinetic Studies of Alkaloids in Rats After Oral Administration of Zanthoxylum nitidum Decoction by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and HPLC-MS/MS. Molecules, 24(3), 585. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030585