An Organic Chemist’s Guide to Electrospray Mass Spectrometric Structure Elucidation
Abstract
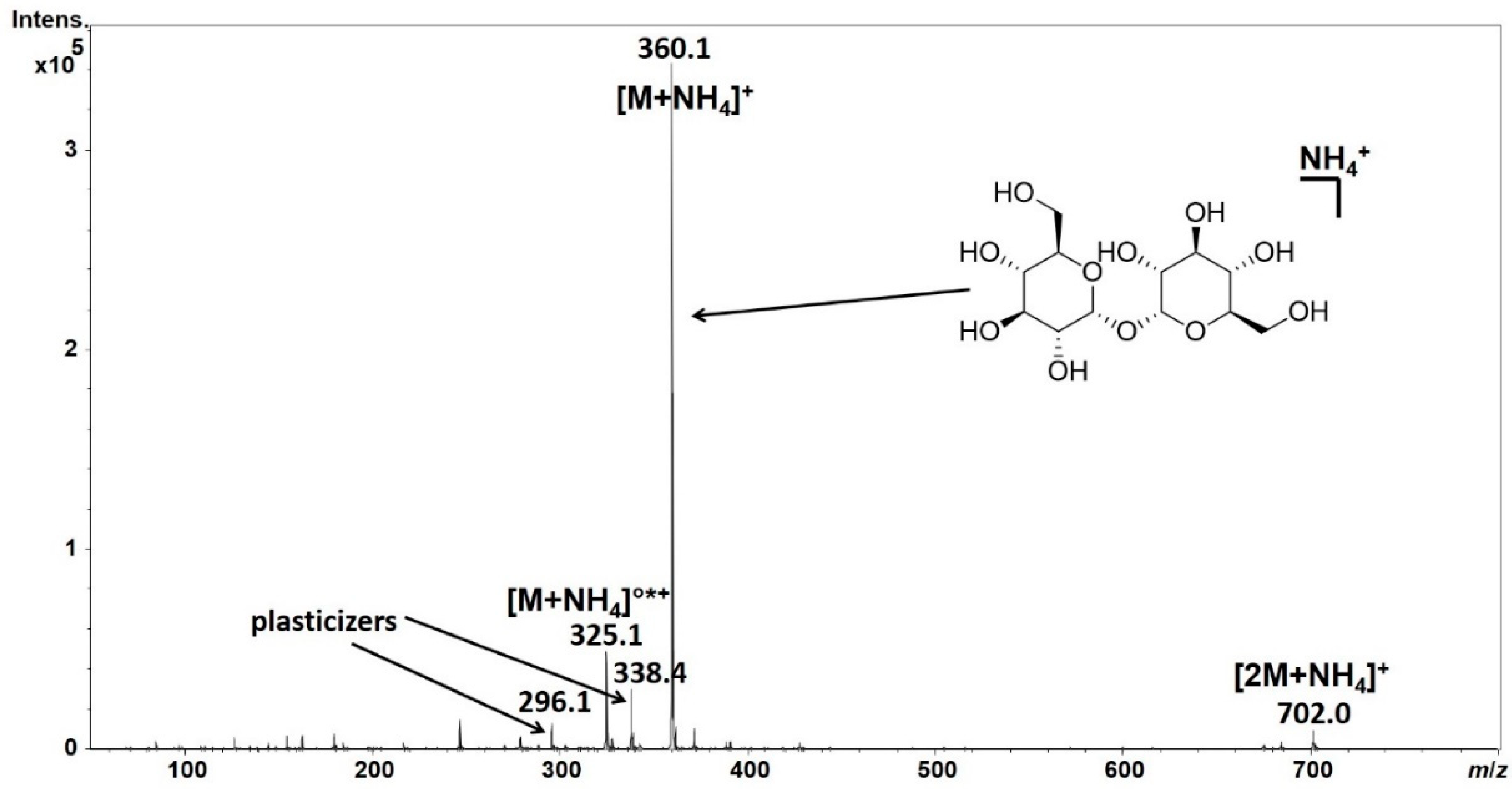
1. Introduction
2. Choosing the Precursor Ion for Fragmentation
3. Performing MS/MS Experiments
4. General Fragmentation Characteristics of Protonated Molecules
Types of Cleavages and Reaction Routes
5. Software-Aided Structural Analyses
6. Summary
- selection of ionization mode is based on the basicity of the compound of interest
- analytes are ionised to yield even-electron ions in most cases
- the fragmentation processes of even-electron ions are much closer to the concepts laid down in organic chemistry as opposed to the ones observed in electron ionization
- the resulting fragments are generally even-electron ions
- elimination of small neutral molecules from precursors are preferable
- most fragment ions are a result of inductive cleavages, acyclic hydrogen rearrangements as well as some (a)cyclic special rearrangements
- the identity of a previously described compound in an unknown sample could be determined by using (U)HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and software-based annotation
7. Notes
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLafferty, F.W.; Tureček, F. Interpretation of Mass Spectra, 4th ed.; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, K.K.; Boyd, R.K.; Eberlin, M.N.; Langley, G.J.; Li, L.; Naito, Y. Definitions of terms relating to mass spectrometry (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1515–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, W.M.A.; Correa, R.A. Fragmentation of even-electron ions. In Interpretation of MS-MS Mass Spectra of Drugs and Pesticides, 1st ed.; Desiderio, M., Loo, J.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 71–128. [Google Scholar]
- Levsen, K.; Schiebel, H.M.; Terlouw, J.K.; Jobst, K.J.; Elend, M.; Preiß, A.; Thiele, H.; Ingendoh, H. Even-electron ions: A systematic study of the neutral species lost in the dissociation of quasi-molecular ions. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 1024–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissberg, A.; Dagan, S. Interpretation of ESI (+)-MS-MS spectra—Towards the identification of “unknowns”. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 299, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarque, D.P.; Crotti, A.E.M.; Vessecchi, R.; Lopes, J.L.C.; Lopes, L.P. Fragmentation reactions using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: An important tool for the structural elucidation and characterization of synthetic and natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 432–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holčapek, M.; Jirásko, R.; Lísa, M. Basic rules for the interpretation of atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectra of small molecules. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 3908–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenn, J.B.; Mann, M.; Meng, C.K.; Wong, S.F.; Whitehouse, C.M. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science 1989, 246, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, E.P.L.; Lias, S.G. Evaluated Gas Phase Basicities and Proton Affinities of Molecules: An Update. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1998, 27, 413–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.-F.; Turk, J. Structural characterization of triacylglycerols as lithiated adducts by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using low-energy collisionally activated dissociation on a triple stage quadrupole instrument. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 10, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, E.; Gförer, P.; Rentel, C. Coordination-Ion Spray-MS (CIS-MS), a Universal Detection and Characterization Method for Direct Coupling with Separation Techniques. Angew. Chem. 1999, 38, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Safi, N.-E.; Kerhoas, L.; Ducrot, P.-H. Fragmentation study of iridoid glucosides through positive and negative electrospray ionization, collision-induced dissociation and tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.-L.; Liu, P.; Wang, Q.-J.; Cai, W.-J.; Yuan, B.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q. Derivatization for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2014, 59, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrdwell, W.C. Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Analysis of Lipids. Lipids 2001, 36, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffaelli, A.; Saba, A. Atmospheric Pressure Photoionization Mass Spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2003, 22, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Breemen, R.B.; Huang, C.-R.; Tan, Y.; Sander, L.C.; Schilling, A.B. Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry of Carotenoids Using Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization. J. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 31, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleno, L.; Volmer, D.A. Ion activation methods for tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 1091–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.P.; Garg, A.; Putlur, S.P.; Wagh, S.; Kumar, V.; Rao, V.; Sing, S.; Mandlekar, S.; Desikan, S. Practical and Economical Implementation of Online H/D Exchange in LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10904–10912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturiale, L.; Palmigiano, A.; Silipo, A.; Knirel, Y.A.; Anisimov, A.P.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Molinaro, A.; Garozzo, D. Reflectron MALDI TOF and MALDI TOF/TOF mass spectrometry reveal novel structural details of native lipooligosaccharides. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 46, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenauer, E.; Allmaier, G. The Renaissance of High-Energy CID for Structural Elucidation of Complex Lipids: MALDI-TOF/RTOF-MS of Alkali Cationized Triacylglycerols. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanucara, F.; Holman, S.W.; Gray, C.J.; Eyers, C.E. The power of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for structural characterization and the study of conformational dynamics. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaia, J. Mass spectrometry of oligosaccharides. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2004, 23, 161–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, W.J. Tandem mass spectrometry in the study of fatty acids, bile acids, and steroids. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2003, 22, 81–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, R.C.; Axelsen, P.H. Mass spectrometric analysis of long-chain lipids. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2011, 30, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Lissemore, L.; Nguyen, B.; Kleywegt, S.; Yang, P.; Solomon, K. Determination of pharmaceuticals in environmental waters by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 384, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordhoff, E.; Kirpekar, F.; Roepstorff, P. Mass spectrometry of nucleic acids. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1996, 15, 67–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, J.H.; Brinkworth, C.S.; Dua, S. Collision-induced fragmentations of the (M − H)− parent anions of underivatized peptides: An aid to structure determination and some unusual negative ion cleavages. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2002, 21, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, T.; Fiehn, O. Seven Golden Rules for heuristic filtering of molecular formulas obtained by accurate mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinf. 2007, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubarev, R.A.; Horn, D.M.; Fridriksson, E.K.; Kelleher, N.L.; Kruger, N.A.; Lewis, N.A.; Carpenter, B.K.; McLafferty, F.W. Electron Capture Dissociation for Structural Characterization of Multiply Charged Protein Cations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 72, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syka, J.E.P.; Coon, J.J.; Schroeder, M.J.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D.F. Peptide and protein sequence analysis by electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9528–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, V.H.; Tsaprailis, G.; Smith, L.L.; Breci, L.A. Mobile and localized protons: A framework for understanding peptide dissociation. J. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 35, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.; Alex, A.; Pullen, F. Predicting collision-induced dissociation mass spectra: Understanding the role of the mobile proton in small molecule fragmentation. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, R.R.; Ly, T.; Finaldi, A.M.; Morton, T.H. Dissociation of a protonated secondary amine in the gas phase via an ion–neutral complex. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 265, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, M.S.B.; Field, F.H. Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. I. General Introduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 2621–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, W.M.A. Fragmentation of toxicologically relevant drugs in positive-ion liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2011, 30, 626–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karni, M.; Mendelbaum, A. The ‘even-electron rule’. Org. Mass Spectrom. 1980, 15, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, E.M.; Ferrer, I.; Pozo, O.J.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernandez, F. The even-electron rule in electrospray mass spectra of pesticides. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 3855–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Dai, W.; Liu, D.Q. Fragmentation of aromatic sulfonamides in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: Elimination of SO2 via rearrangement. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rijke, E.; Out, P.; Niessen, W.M.A.; Ariese, F.; Gooijer, C.; Brinkman, U.A.T. Analytical separation and detection methods for flavonoids. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1112, 31–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, G.C.; Borges, C.M.; Florêncio, M.H. Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry fragmentation of protonated flavone and flavonol aglycones: A re-examination. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F.; Greiner, R.; Wishart, D. Competitive fragmentation modeling of ESI-MS/MS spectra for putative metabolite identification. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Odd Electron Precursor (OE) | Even-Electron Precursor (EE) | |
|---|---|---|
| Ionization | EI | ESI, MALDI, APCI, (APPI) 1 |
| Type of precursor | M+ | [M + zH]z+, [M + C]+, [M − H]−, [M + A]− |
| Nitrogen rule | ✓ | ✓ |
| RDBE 2 | integer | half-integer |
| Type of fragments | OE | EE |
| Prediction of fragment abundance | Stevenson’s rule | Field’s rule |
| Preferred cleavage type | homolytic | heterolytic |
| Odd m/z | Even m/z | |
|---|---|---|
| OE 1 | odd #N | even #N |
| EE 2 | even #N | odd #N |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steckel, A.; Schlosser, G. An Organic Chemist’s Guide to Electrospray Mass Spectrometric Structure Elucidation. Molecules 2019, 24, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030611
Steckel A, Schlosser G. An Organic Chemist’s Guide to Electrospray Mass Spectrometric Structure Elucidation. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030611
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteckel, Arnold, and Gitta Schlosser. 2019. "An Organic Chemist’s Guide to Electrospray Mass Spectrometric Structure Elucidation" Molecules 24, no. 3: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030611
APA StyleSteckel, A., & Schlosser, G. (2019). An Organic Chemist’s Guide to Electrospray Mass Spectrometric Structure Elucidation. Molecules, 24(3), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030611





