Dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 after Mannitol Infusion and Glutamate Tablet Administration: Preliminary Results of EUDRACT/RSO 2016-002732-32 IRST Protocol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients and Treatment Characteristics
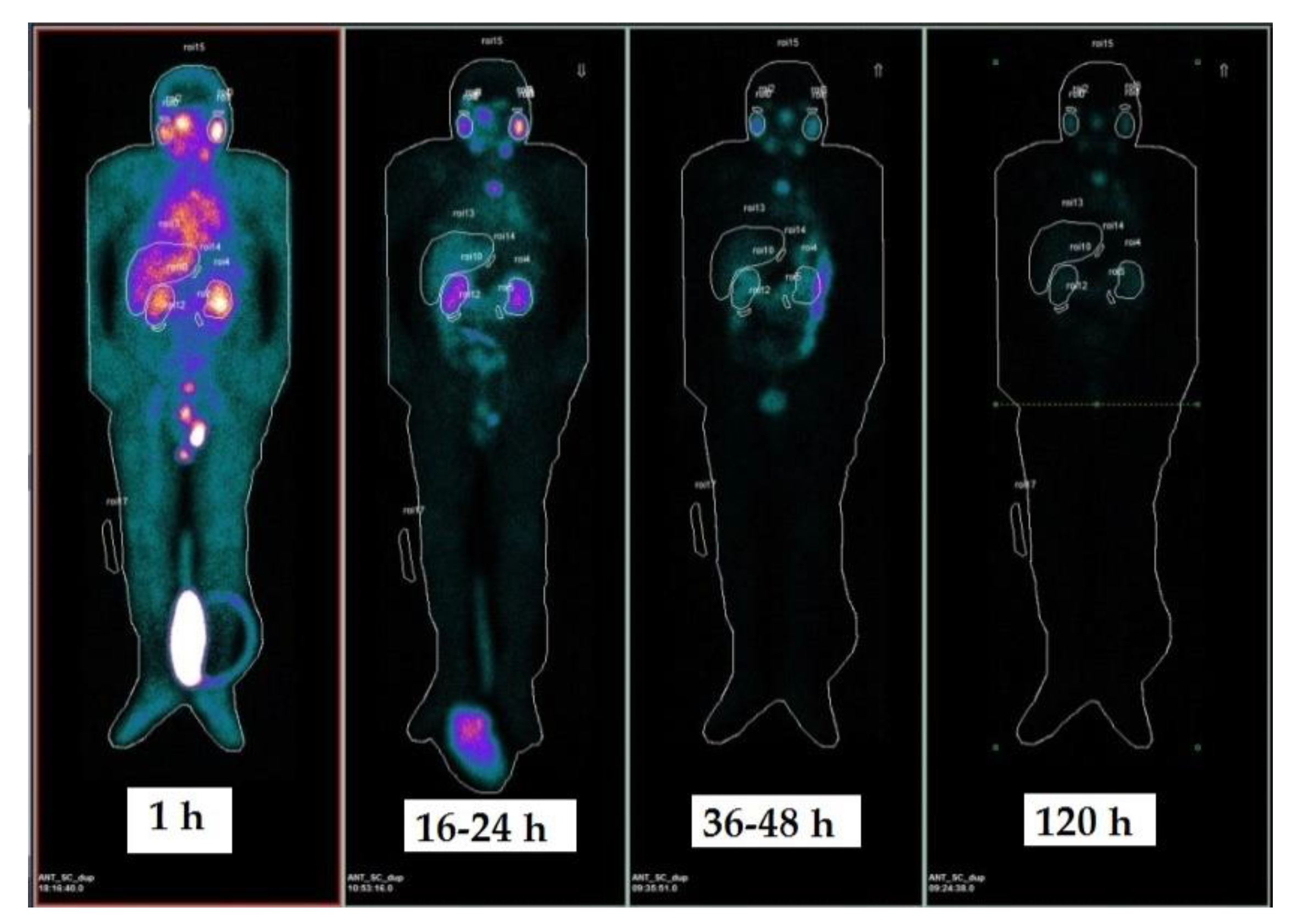
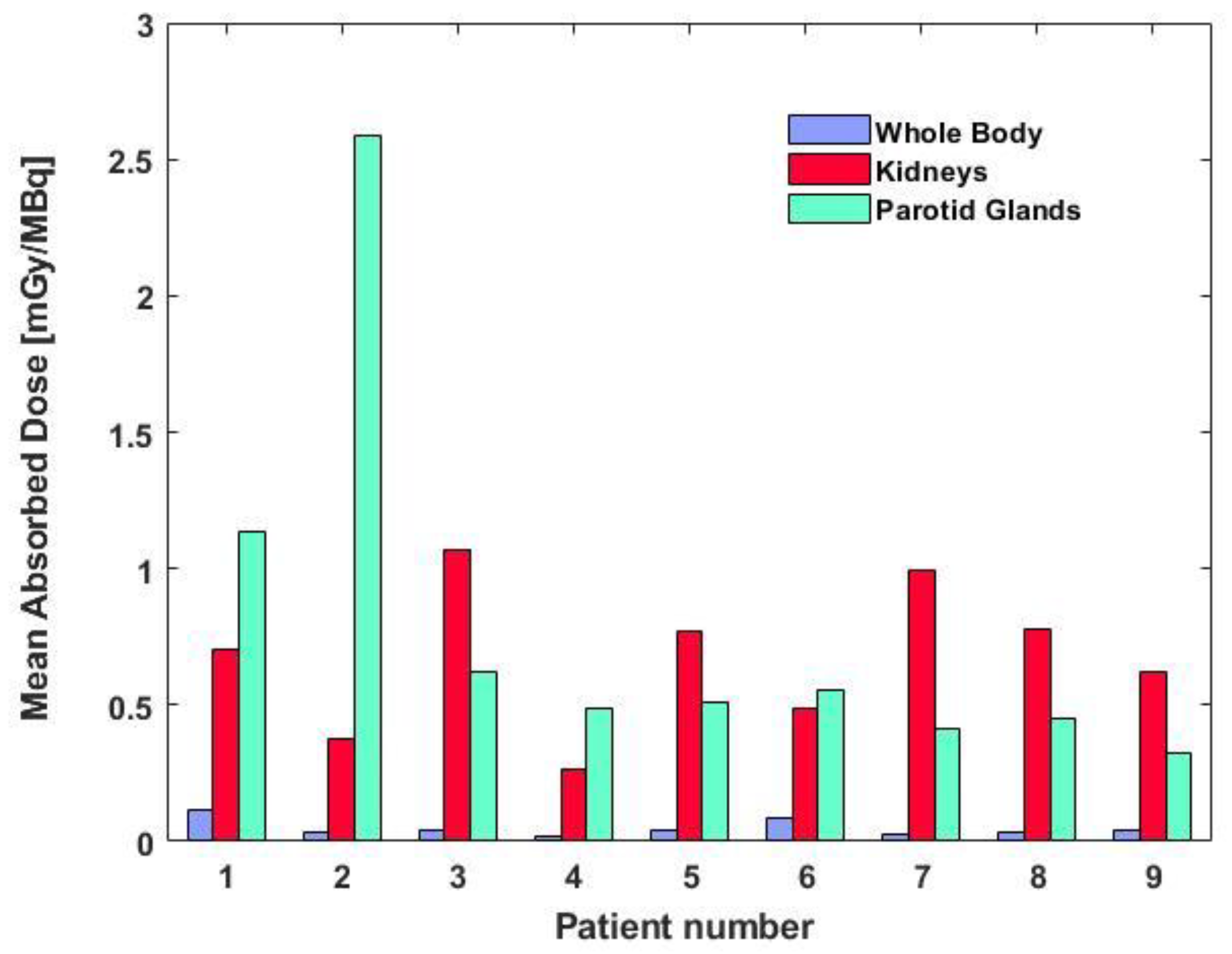
2.2. Dosimetry Results
2.3. Comparison with Previous Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Enrolment
4.2. Radiopharmaceutical Production
4.3. Treatment Procedure
4.4. Renal and Salivary Gland Protection
4.5. Image Acquisition and Analysis
4.6. Blood Sample Acquisition and Analysis
4.7. Dosimetric Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Dose Calibrator Response Verification: Prior to each production, the background and instrument response are measured using a certified source of 137Cs (NuklearMedizin, Dresden, Germany) with known activity; the percentage of deviation between the measured value and the expected value is measured and recorded. The deviation must never be greater than 5%.
- Measure of the incoming 177Lu activity: the arrival vial of 177LuCl3 is measured in the dose calibrator, after which a mixture is prepared containing a sufficient quantity of DOTA-PSMA-617 (calculated with a ratio of 0.9 μg/mCi) and a sufficient volume of the buffer solution to maintain the reaction pH at 5.0.
- Complexation Reaction 177Lu-DOTA-PSMA-617: the reaction mixture is heated to 100 degrees for 8 min.
- Transfer and dilution: the radiopharmaceutical is then transferred into a 30 mL bottle (Drytec, GE Healthcare Buchler, 38110, Braunschweig, Germany), through a sterile line equipped with 0.22-μm ventilated sterilizing filter (Millex-GV Syringe Filter Unit, 25 mm PVDF (low protein binding membrane)). This solution is then diluted with physiological solution until a final volume of 17-22 mL is obtained.
- Measurement of the final activity and concentration calculation: the final vial is measured in a dose calibrator with the appropriate geometry to evaluate the yield and the final activity available for the patient-specific doses.
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 3, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; Bellmunt, J. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of advanced, relapsing and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, A.; Porres, D. Prostate cancer: Treatment sequencing for CRPC—What do we know? Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Kuratsukuri, K. Expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen in normal and malignant humantissues. World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L. PSMA-targeted radionuclide therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with 177Lu-Labeled PSMA-617. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, M.; Fenlder, W.P. Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) ligands for diagnosis and therapy of prostate cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 11, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, R.P.; Kulkarni, H.R. 177Lu-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen radioligand therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Safety and efficacy. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delker, A.; Fendler, W.P. Dosimetry for 177Lu-DKFZ-PSMA-617: A new radiopharmaceutical for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabasakal, L.; AbuQbeitah, M. Pre-therapeutic dosimetry of normal organs and tissues if 177Lu-PSMA-617 prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) inhibitor in patients with castration resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kalmthout, L.W.M.; Lam, M.G.E.H. Impact of external cooling with icepacks on 68Ga-PSMA uptake in salivary glands. EJNMMI Res. 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.; Krenning, E. New advances in peptide receptor radionuclide therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2002, 43, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barone, R.; Pauwels, S. Metabolic effects of amino acid solutions infused for renal protection during therapy with radiolabelled somatostatin analogues. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jamar, F.; Barone, R. 86Y-DOTA0-d-Phe1-Tyr3-octreotide (SMT487)—A phase 1 clinical study: Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and renal protective effect of different regimens of amino acid co-infusion. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegt, E.; de Jong, M. Renal toxicity of radiolabeled peptides and antibody fragments: Mechanisms, impact on radionuclide therapy and strategies for prevention. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, H.R.; Singh, A. PSMA-based radioligand therapy for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: The bad berka experience since 2013. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 97S–104S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccala, A.; Sercia, L. Expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen in tumor-associated neovasculature of renal neoplasms. Urology 2007, 70, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, K.M.; Mei, T.-S. Substrate specificity of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 6678–6686. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Matteucci, F.; Mezzenga, E. Reduction of 68Ga-PSMA renal uptake with mannitol infusion: Preliminary results. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, Q. The evolving Gleason grading system. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 28, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Rahbar, K.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. German multicenter study investigating 177Lu-PSMA-617 radioligand therapy in advanced prostate cancer patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violet, J.A.; Jackson, P. Dosimetry of Lu-177 PSMA-617 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: Correlations between pre-therapeutic imaging and “whole body” tumor dosimetry with treatment outcomes. J. Nucl. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochwil, C.; Bruchertseifer, F. Targeted alpha therapy of mCRPC with 225Actinium-PSMA-617: Swimmer-plot analysis suggests efficacy regarding duration of tumor-control. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taïeb, D.; Foletti, J.-M. PSMA-Targeted Radionuclide Therapy and salivary gland toxicity: Why does it matter? J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochwil, C.; Bruchertseifer, F. Targeted alpha therapy of mCRPC with 225Actinium-PSMA-617: Dosimetry estimate and empirical dose finding. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkema, R.; Pauwels, S.A. Long-term follow-up of renal function after peptide receptor radiation therapy with 90Y-DOTA0, Tyr3-Octreotide and 177Lu-DOTA0, Tyr3-Octreotate. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Nedelcovych, M.T.; Dash, R.P. JHU-2545 selectively shields salivary glands and kidneys during PSMA-Targeted radiotherapy. bioRxiv 2018, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Scher, H.I.; Morris, M.J. Trial design and objectives for castration-resistant prostate cancer: Updated recommendations from the prostate cancer clinical trials working group 3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1402–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, M.; Creech, R. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, G.; De Giorgi, U. Radiometabolic Therapy (RMT) with 177Lu PSMA 617 in advanced castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC): Efficacy and toxicity evaluation. IRST Protoc. 2017, 1, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Salvo, D.; Bui, F. Norme di buona preparazione dei radiofarmaci in medicina nucleare. AIMN Notiziario di Medicina Nucleare ed Imaging Molecolare 2006, 1, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, A.D.; Davis, W.L. Immunohistochemical and pharmacokinetic characterization of the site-specific immunoconjugate CYT-356 derived from antiprostate monoclonal antibody 7E11-C5. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 6423–6429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stabin, M.G. Foundamentals of Nuclear Medicine Dosimetry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, J.; Thomas, S.R. MIRD pamphlet no. 16: Techniques for quantitative radiopharmaceutical biodistribution data acquisition and analysis for use in human radiation dose estimates. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 40, 37S–61S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snyder, W.S.; Ford, M.R. “S” Absorbed Dose Per Unt Cumulate Activity for Selected Radionuclides and Organs. MIRD Pamphlet No. 11. 1975. Available online: http://snmmi.files.cms-plus.com/docs/hpra/MIRD Pamphlet 11.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2018).
- Bolch, W.E.; Bouchet, L.G. MIRD Pamphlet No. 17: The dosimetry of nonuniform activity distributions-radionuclide S values at the voxel level. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 40, 11s–36s. [Google Scholar]
- Stabin, M.G.; Sparks, R.B. OLINDA/EXM: The second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stabin, M.G.; Konijnenberg, M.W. Re-evaluation of absorbed fractions for photons and electrons in spheres of various sizes. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 41, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sgouros, G. Bone marrow dosimetry for radioimmunotherapy: Theoretical considerations. J. Nucl. Med. 1993, 34, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neyrinck, M.M.; Vrielink, H. Calculations in apheresis. J. Clin. Apher. 2013, 28, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient | Age [y] | Gleason Score [19] | Injected Activity [GBq] | Bone Marrow Dosimetry | Main Lesion Sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 64 | NA | 5.5 | No | Bone |
| 2 | 85 | NA | 4.4 | No | Bone/tissue |
| 3 | 71 | 8 | 4.4 | Yes | Bone/tissue |
| 4 | 66 | 9 | 4.4 | Yes | Bone/tissue |
| 5 | 68 | 7 | 5.5 | Yes | Bone/tissue |
| 6 | 53 | 10 | 4.4 | Yes | Bone |
| 7 | 62 | 9 | 5.5 | Yes | Bone/tissue |
| 8 | 76 | 8 | 5.5 | No | Bone |
| 9 | 70 | 8 | 5.5 | Yes | Bone |
| Patient | Parotid Glands [h] | Kidneys [h] | Liver [h] | Red Marrow [h] | Whole Body [h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35.4 | 50.7 | 62.9 | - | 78.0 |
| 2 | 41.5 | 12.2 | 18.1 | - | 31.9 |
| 3 | 34.6 | 28.8 | 30.0 | 8.7 | 66.2 |
| 4 | 25.6 | 21.8 | 12.5 | 7.7 | 31.6 |
| 5 | 30.3 | 31.4 | 16.2 | 3.1 | 40.1 |
| 6 | 60.7 | 57.9 | 59.9 | 2.5 | 77.4 |
| 7 | 28.1 | 39.8 | 21.6 | 14.7 | 33.6 |
| 8 | 29.7 | 29.4 | 25.4 | - | 33.5 |
| 9 | 33.0 | 80.6 | 54.9 | 11.4 | 79.7 |
| Median (range) | 33.0 (25.6–60.7) | 31.4 (12.2–80.6) | 25.4 (12.5–62.9) | 8.2 (2.5–14.7) | 40.1 (31.6–79.7) |
| Mean (SD) | 35.4 (10.6) | 39.2 (20.9) | 33.5 (20.0) | 8.0 (4.7) | 52.4 (22.2) |
| Patient | Parotid Glands [mGy/MBq] | Kidneys [mGy/MBq] | Liver [mGy/MBq] | Red Marrow [mGy/MBq] | Whole Body [mGy/MBq] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.23 | 0.70 | 0.11 | - | 0.113 |
| 2 | 2.63 | 0.38 | 0.10 | 0.044 | 0.035 |
| 3 | 0.79 | 1.07 | 0.15 | - | 0.044 |
| 4 | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.023 | 0.018 |
| 5 | 0.48 | 0.77 | 0.14 | 0.061 | 0.038 |
| 6 | 0.65 | 0.50 | 0.05 | 0.067 | 0.088 |
| 7 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 0.036 | 0.027 |
| 8 | 0.41 | 0.78 | 0.19 | - | 0.033 |
| 9 | 0.33 | 0.63 | 0.53 | 0.033 | 0.043 |
| Median (range) | 0.48 (0.33–2.63) | 0.70 (0.26–1.07) | 0.13 (0.05–0.53) | 0.044 (0.023–0.067) | 0.038 (0.018–0.113) |
| Mean (SD) | 0.81 (0.74) | 0.67 (0.27) | 0.16 (0.15) | 0.044 (0.017) | 0.049 (0.031) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarnelli, A.; Belli, M.L.; Di Iorio, V.; Mezzenga, E.; Celli, M.; Severi, S.; Tardelli, E.; Nicolini, S.; Oboldi, D.; Uccelli, L.; et al. Dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 after Mannitol Infusion and Glutamate Tablet Administration: Preliminary Results of EUDRACT/RSO 2016-002732-32 IRST Protocol. Molecules 2019, 24, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030621
Sarnelli A, Belli ML, Di Iorio V, Mezzenga E, Celli M, Severi S, Tardelli E, Nicolini S, Oboldi D, Uccelli L, et al. Dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 after Mannitol Infusion and Glutamate Tablet Administration: Preliminary Results of EUDRACT/RSO 2016-002732-32 IRST Protocol. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030621
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarnelli, Anna, Maria Luisa Belli, Valentina Di Iorio, Emilio Mezzenga, Monica Celli, Stefano Severi, Elisa Tardelli, Silvia Nicolini, Devil Oboldi, Licia Uccelli, and et al. 2019. "Dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 after Mannitol Infusion and Glutamate Tablet Administration: Preliminary Results of EUDRACT/RSO 2016-002732-32 IRST Protocol" Molecules 24, no. 3: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030621
APA StyleSarnelli, A., Belli, M. L., Di Iorio, V., Mezzenga, E., Celli, M., Severi, S., Tardelli, E., Nicolini, S., Oboldi, D., Uccelli, L., Cittanti, C., Monti, M., Ferrari, M., & Paganelli, G. (2019). Dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 after Mannitol Infusion and Glutamate Tablet Administration: Preliminary Results of EUDRACT/RSO 2016-002732-32 IRST Protocol. Molecules, 24(3), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030621






