The Antidepressant-like Effect of Flavonoids from Trigonella Foenum-Graecum Seeds in Chronic Restraint Stress Mice via Modulation of Monoamine Regulatory Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Results of Screening for MAO-A Inhibitors in Vitro
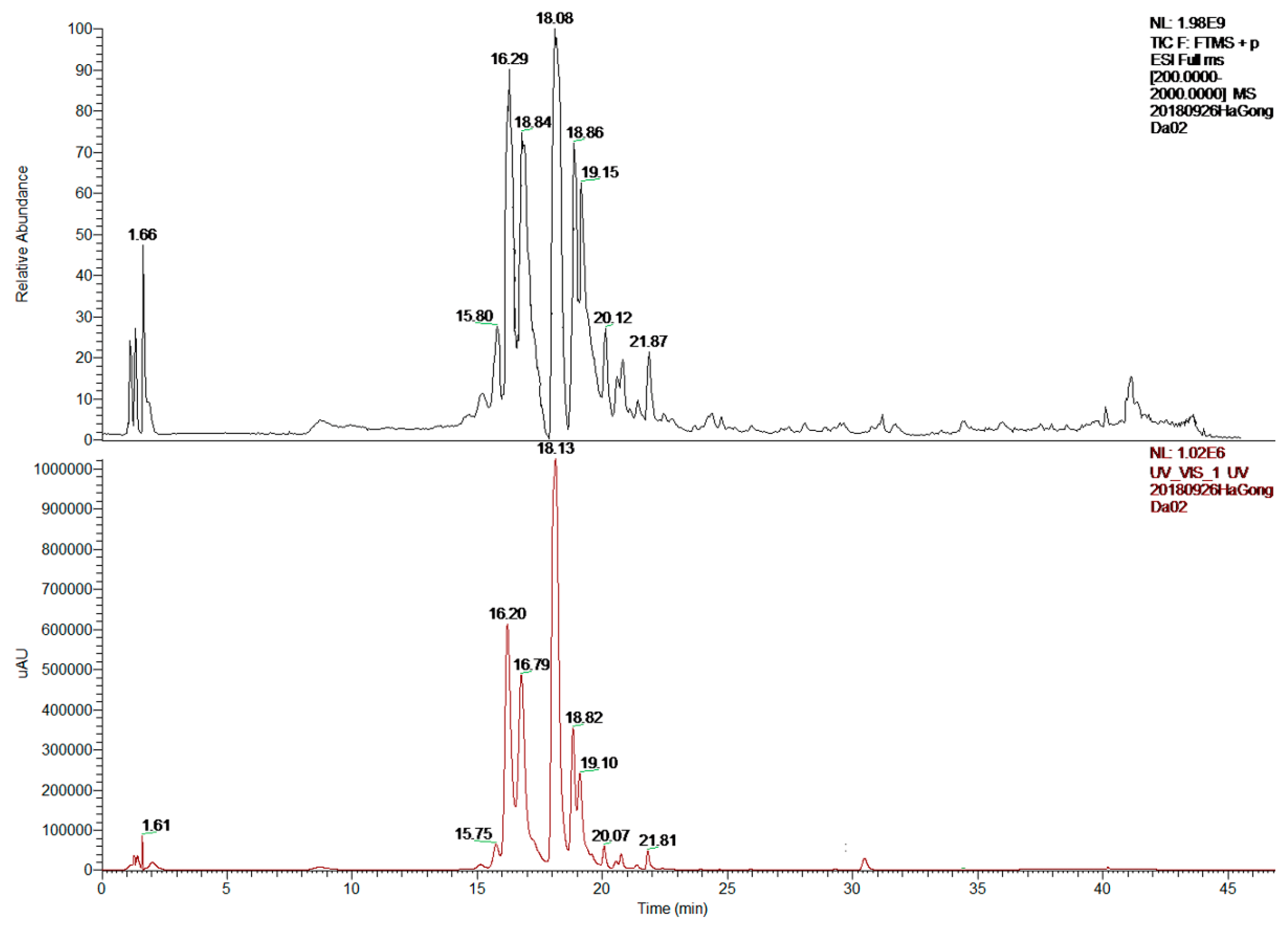
2.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.3. Body Weight
2.4. Effects of FSF on Behavioral Tests
2.5. Effects of FSF on Organ Index
2.6. Effects of FSF on Serum CORT Level
2.7. Effects of FSF on NE Level in Different Brain Regions of Mice
2.8. Effects of FSF on 5-HT and 5-HIAA Levels in Different Brain Regions of Mice
2.9. Effects of FSF on DA, DOPAC, and HVA Levels in Different Brain Regions of Mice
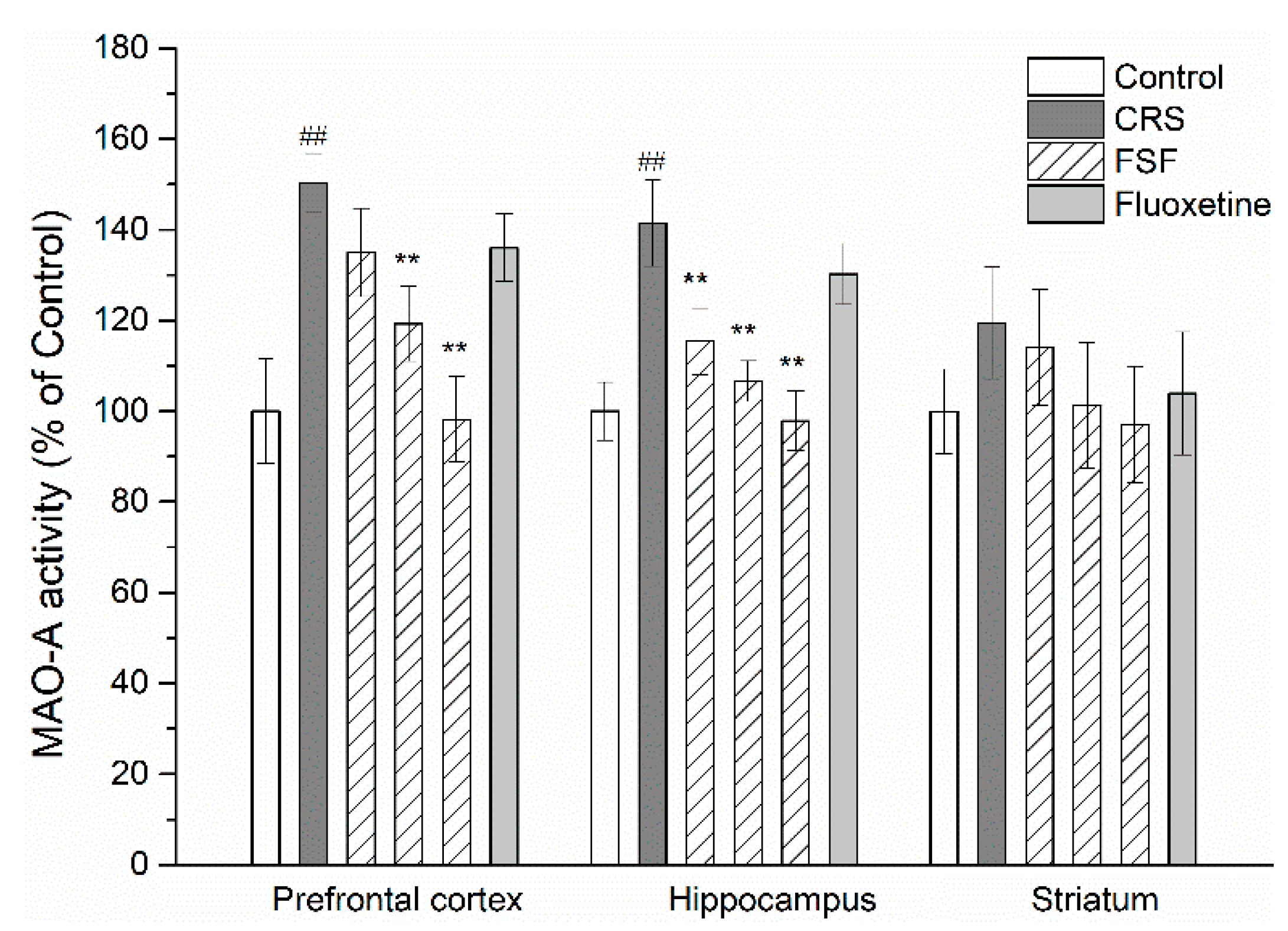
2.10. Effects of FSF on MAO-A Activity in Different Brain Regions of Mice
2.11. Effects of FSF on KLF11, SIRT1 and MAO-A Protein Level in Different Brain Regions of Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Drugs
4.2. Extraction and Isolation
4.3. Screening for MAO-A Inhibitors In Vitro
4.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
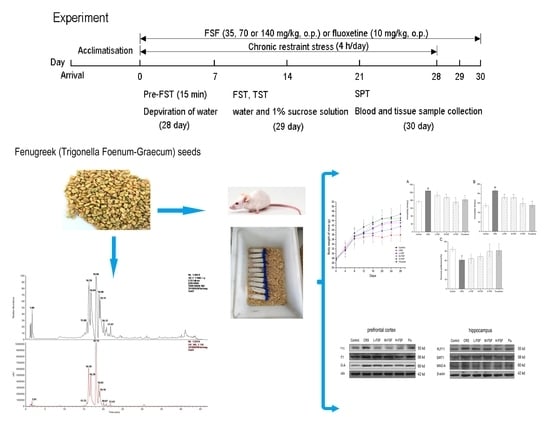
4.5. Animals and Experimental Design
4.6. Chronic Restraint Stress Protocol
4.7. Behavioral Tests
4.7.1. Forced Swimming Test
4.7.2. Tail Suspension Test
4.7.3. Sucrose Preference Test
4.8. Blood and Tissue Sample Collection
4.9. Determination of CORT, Monoamines and Its Metabolites
4.10. Measurements of MAO-A Activity
4.11. Western Blot Analysis
4.12. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lépine, J.P.; Briley, M. The increasing burden of depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2011, 2011, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Thakare, V.N.; Dhakane, V.D.; Patel, B.M. Potential antidepressant-like activity of silymarin in the acute restraint stress in mice: Modulation of corticosterone and oxidative stress response in cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, E.; Prien, R.F.; Jarrett, R.B.; Keller, M.B.; Kupfer, D.J.; Lavori, P.W.; Rush, A.J.; Weissman, M.M. Conceptualization and rationale for consensus definitions of terms in major depressive disorder. Remission, recovery, relapse, and recurrence. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1991, 48, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, G.; Lin, M.; Yu, Y.; Pan, J. Piperine potentiates the effects of trans -resveratrol on stress-induced depressive-like behavior: involvement of monoaminergic system and cAMP-dependent pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W.; Shamoto-Nagai, M. Type A monoamine oxidase and serotonin are coordinately involved in depressive disorders: from neurotransmitter imbalance to impaired neurogenesis. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Pu, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, C.; Xie, P. The identification of metabolic disturbances in the prefrontal cortex of the chronic restraint stress rat model of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 305, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Soga, T.; Parhar, I.S. Regulatory Pathways of Monoamine Oxidase A during Social Stress. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowska, K.J.A.; Hamann, T.M. Marine indole alkaloids: potential new drug leads for the control of depression and anxiety. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Ooi, J.; Bardile, C.F.; Liang, J.T.; George, M.; Drum, C.L.; Lin, R.Y.; Hayden, M.R.; Pouladi, M.A. Treatment with the MAO-A inhibitor clorgyline elevates monoamine neurotransmitter levels and improves affective phenotypes in a mouse model of Huntington disease. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 278, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinelo, U.; Shakevia, J.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Jia, L.; Albert, P.R.; Junming, W.; May, W.L.; Grazyna, R.; Sharonda, H.; Sittman, D.B. The expression of KLF11 (TIEG2), a monoamine oxidase B transcriptional activator in the prefrontal cortex of human alcohol dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Matthew, G.; Shakevia, J.; Deyin, L.; Zhe, W.; Gwen, L.; Albert, P.R.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Meyer, J.H.; Raul, U.; Miczek, K.A. Mechanistic role for a novel glucocorticoid-KLF11 (TIEG2) protein pathway in stress-induced monoamine oxidase A expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24195–24206. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Johnson, S.; Harris, S.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Rajkowska, G.; Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J.; Sittman, D. Chronic Social Stress and Ethanol Increase Expression of KLF11, a Cell Death Mediator, in Rat Brain. Neurotox. Res. 2015, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libert, S.; Pointer, K.; Bell, E.; Das, A.; Cohen, D.; Asara, J.; Kapur, K.; Bergmann, S.; Preisig, M.; Otowa, T. SIRT1 Activates MAO-A in the Brain to Mediate Anxiety and Exploratory Drive. Cell 2011, 147, 1459–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Kretzschmar, W.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Song, L.; Hu, J.; Li, Q.; Jin, W.; Hu, Z. Sparse whole-genome sequencing identifies two loci for major depressive disorder. Nature 2015, 523, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karson, A.; Demirtaş, T.; Bayramgürler, D.; Balci, F.; Utkan, T. Chronic Administration of Infliximab (TNF-Alpha Inhibitor) Decreases Depression and Anxiety-like Behaviour in Rat Model of Chronic Mild Stress. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 112, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P.; Muscat, R.; Papp, M. Chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia: A realistic animal model of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1992, 16, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y.; Jin, F. Administration of Lactobacillus helveticus NS8 improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused by chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.E.; Lin, S.H.; Chen, W.C.; Ho, C.T.; Lai, Y.S.; Panyod, S.; Sheen, L.Y. Antidepressant-like effects of water extract of Gastrodia elata Blume in rats exposed to unpredictable chronic mild stress via modulation of monoamine regulatory pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 187, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Sasaki, H.; Uddin, K.R.; Ikeda, Y.; Miyakawa, H.; Shibata, S. Anxiolytic effects of gamma-oryzanol in chronically- stressed mice are related to monoamine levels in the brain. Life Sci. 2019, 216, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Perviz, S.; Sureda, A.; Nabavi, S.M.; Tejada, S. Current standing of plant derived flavonoids as an antidepressant. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.E. Potential of Natural Products of Herbal Origin as Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Gidaro, M.C.; Petzer, A.; Costa, G.; Guglielmi, P.; Chimenti, P.; Alcaro, S.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase: Biological and Molecular Modeling Studies on Selected Natural Flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 64, 9004–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushouk, A.I.; Negida, A.; Ahmed, H.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Neuroprotective mechanisms of plant extracts against MPTP induced neurotoxicity: Future applications in Parkinson’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiger, A.K.; Bente, G.; Jacob, A.; Anne, A.; Lene, G. Screening of plants used in Danish folk medicine to treat depression and anxiety for affinity to the serotonin transporter and inhibition of MAO-A. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Ming, L.; Ping, L.; Dai-Hong, G.; Ri-Bao, W.; Khalid, R. Possible mechanism of the antidepressant effect of 3,6′-disinapoyl sucrose from Polygala tenuifolia Willd. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 869–874. [Google Scholar]
- Sloley, B.; Urichuk P, L.; Durkin, J.; Shan, J.; Pang, P.; Coutts, R. Identification of kaempferol as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor and potential Neuroprotectant in extracts of Ginkgo biloba leaves. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 52, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsnafi, A. Detoxification capacity and protective effects of medicinal plants (part 2): plant based review. IOSR J. Pharm. 2016, 6, 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S. Antidepressant-like effect of the ethanolic extract from Suanzaorenhehuan Formula in mice models of depression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Duan, H.; Jin, M.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, J.; Qi, Y.; Qiao, W. Antidepressant-like effect of the saponins part of ethanol extract from SHF. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrisab, J.; Schweitzer, I.; Stough, C.; Scholey, A. Herbal medicine for depression, anxiety and insomnia: A review of psychopharmacology and clinical evidence. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 21, 841–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Dai, W.; Lu, M.; Xie, D.; Tan, J.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Metabolomic analysis reveals the composition differences in 13 Chinese tea cultivars of different manufacturing suitabilities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A. Alliuocide G, a new flavonoid with potent alpha-amylase inhibitory activity from Allium cepa L. Arkivoc 2008, 2008, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Stobiecki, M.; Kachlicki, P.; Wojakowska, A.; Marczak, Ł. Application of LC/MS systems to structural characterization of flavonoid glycoconjugates ☆. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 11, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.K.; Ji, H.S.; Jo, D.S.; Dong, W.S.; Choi, D.H.; Kim, W.J.; Park, K.; Jin, K.K.; Joo, C.G.; Lee, J.S. Anti-melanogenic activity of schaftoside in Rhizoma Arisaematis by increasing autophagy in B16F1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, D.S.; Ming, Z.H.; Chun Qi, B.; Fang, W.C.; Zhi, L.Q.; Long, L.Z.; Yan, W.Y.; Wei, D.Z. Nematocidal flavone-C-glycosides against the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) from Arisaema erubescens tubers. Molecules 2011, 16, 5079–5086. [Google Scholar]
- Laitonjam, W. Study on Isolation and Comparison of the Chemical Compositions of Cissus adnata Roxb. leaves and Smilax lanceaefolia Roxb. Roots and Their Free Radical Scavenging Activities. Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioukia, F.N.; Antoniou, K.; Bekris, S.; Liapi, C.; Christofidis, I.; Papadopoulou-Daifoti, Z. The effects of stress exposure on the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, thymus, thyroid hormones and glucose levels. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 26, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, K.; Lu, C.; Dong, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, X. Effects of the chronic restraint stress induced depression on reward-related learning in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 321, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregus, A.; Wintink, A.J.; Davis, A.C.; Kalynchuk, L.E. Effect of repeated corticosterone injections and restraint stress on anxiety and depression-like behavior in male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2005, 156, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogaça, M.V.; Campos, A.C.; Coelho, L.D.; Duman, R.S.; Guimarães, F.S. The anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol in chronically stressed mice are mediated by the endocannabinoid system: Role of neurogenesis and dendritic remodeling. Neuropharmacology 2018, 135, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Byung-Hak, K.; Sang-Kyu, Y.; Myoung-Hwan, K. Chronic non-social stress affects depressive behaviors but not anxiety in mice. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. 2014, 18, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Yingcong, Y.; Rui, W.; Chunbai, C.; Xia, D.; Lina, R.; Jiao, S.; Jianxin, L.; Lu, Z.; O’Donnell, J.M.; Jianchun, P. Antidepressant-like effect of trans-resveratrol in chronic stress model: behavioral and neurochemical evidences. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y. Pre-gestational stress reduces the ratio of 5-HIAA to 5-HT and the expression of 5-HT1A receptor and serotonin transporter in the brain of foetal rat. Bmc Neurosci. 2012, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Ku, B.S.; Yao, H.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Xing, M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, X.J. Antidepressant effects of curcumin in the forced swim test and olfactory bulbectomy models of depression in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 82, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Mineur, Y.S.; Adetokunbo, O.; Wigestrand, M.B.; Fote, G.M.; Calarco, C.A.; Li, A.M.; Picciotto, M.R. Cholinergic signaling in the hippocampus regulates social stress resilience and anxiety- and depression-like behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2013, 110, 3573–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Johnson, S.; Harris, S.; Udemgba, C.; Ou, X.M.; Youdim, M.B.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Wang, J.M. Binge ethanol exposure increases the Krüppel-like factor 11-monoamine oxidase (MAO) pathway in rats: Examining the use ofMAO inhibitors to prevent ethanol-induced brain injury. Neuropharmacology 2016, 105, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Hesterman, J.; Call, T.; Magazu, S.; Keeley, E.; Armenta, K.; Kronman, H.; Neve, R.L.; Nestler, E.J.; Ferguson, D. SIRT1 Mediates Depression-Like Behaviors in the Nucleus Accumbens. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8441–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, A.; Sharman, D.F.; Baker, G.B.; Palcic, M.M. A Continuous Spectrophotometric Assay for Monoamine Oxidase and Related Enzymes in Tissue Homogenates. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 244, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, K.K.; Yang, Z.D.; Shi, D.F.; Yao, X.J.; Wang, M.G. Desmodeleganine, a new alkaloid from the leaves of Desmodium elegans as a potential monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Fitoterapia 2014, 98, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuichi, C.; Tadahiro, N.; Midori, N.; Richards, M.C.; Chisato, W.; Hiroshi, K. Chronic restraint stress causes anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, downregulates glucocorticoid receptor expression, and attenuates glutamate release induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the prefrontal cortex. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 39, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto, K.; Toki, H.; Iijima, M.; Hashihayata, T.; Yamaguchi, J.I.; Hashimoto, K.; Chaki, S. Antidepressant Potential of (R)-Ketamine in Rodent Models: Comparison with (S)-Ketamine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 361, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, F.; Turco, F.; Iannotta, M.; De, G.D.; Palumbo, I.; Sarnelli, G.; Furiano, A.; Napolitano, F.; Boccella, S.; Luongo, L. Antibiotic-induced microbiota perturbation causes gut endocannabinoidome changes, hippocampal neuroglial reorganization and depression in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 67, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, M.A.; Parrott, J.M.; Mccusker, R.H.; Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W.; O’Connor, J.C. Intracerebroventricular administration of lipopolysaccharide induces indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-dependent depression-like behaviors. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsman, J.P. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Paxinos, G., Franklin, K.B.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 28, ISBN 0-12-547637-X. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |








| Ethanol Extracts/Purified Fractions | MAO-A Inhibition IC50 (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Gynostemma pentaphyllum | 3.322 |
| Ginkgo biloba leaves | 16.445 |
| Polygala tenuifolia | 4.470 |
| Trigonella foenum-graecum seeds | 2.968 |
| Astragalus membranaceus | 7.682 |
| Radix paeoniae alba | 12.568 |
| Suanzaorenhehuan Formula | 27.827 |
| Fr 1 | 21.022 |
| Fr 2 | 7.152 |
| Fr 3 | 0.947 |
| Fr 4 | 8.240 |
| Fr 5 | 2.377 |
| Fr 6 | 2.862 |
| Fr 3-1 | 0.985 |
| Fr 3-2 | 1.878 |
| Fr 3-3 | 0.191 |
| Clorgiline | 0.016 |
| Peak | RT (min) | MW | [M + H]+ (m/z) | MS2 (m/z) | Molecular Formula | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.80 | 594 | 595 | 431, 147 | C30H26O13 | Kaempferol 3-(p-coumaryl) glucoside |
| 2 | 16.29 | 464 | 465 | 303 | C21H20O12 | Quercetin 4′-O-β-d-glucopyranoside |
| 3 | 16.84 | 594 | 595 | 433, 271 | C27H30O15 | Apigenin 4′,7-O-diglucoside |
| 4 | 18.08 | 564 | 565 | 529, 499, 391 | C26H28O14 | Schaftoside |
| 5 | 18.86 | 564 | 565 | 547, 511, 427 | C26H28O14 | Isoschaftoside |
| 6 | 21.87 | 432 | 433 | 415, 397, 313, 283 | C21H20O10 | Apigenin 8-C-α-d-glucopyranoside |
| Group | Liver Index (mg/g) | Spleen Index (mg/g) | Thymus Index (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 56.33 ± 4.39 | 2.70 ± 0.63 | 2.66 ± 0.82 |
| CRS | 50.84 ± 2.48 # | 2.38 ± 0.37 # | 2.07 ± 0.76 ## |
| L-FSF | 51.51 ± 4.32 | 2.50 ± 0.25 | 2.41 ± 0.85 * |
| M-FSF | 56.33 ± 4.39 * | 2.79 ± 0.37 * | 2.40 ± 0.79 * |
| H-FSF | 56.73 ± 6.40 * | 2.79 ± 0.25 * | 2.66 ± 0.82 ** |
| Fluoxetine | 56.27 ± 7.33 * | 2.87 ± 0.61 * | 2.50 ± 0.73 * |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Cheng, C.; Xin, C.; Wang, Z. The Antidepressant-like Effect of Flavonoids from Trigonella Foenum-Graecum Seeds in Chronic Restraint Stress Mice via Modulation of Monoamine Regulatory Pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061105
Wang J, Cheng C, Xin C, Wang Z. The Antidepressant-like Effect of Flavonoids from Trigonella Foenum-Graecum Seeds in Chronic Restraint Stress Mice via Modulation of Monoamine Regulatory Pathways. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061105
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiancheng, Cuilin Cheng, Chao Xin, and Zhenyu Wang. 2019. "The Antidepressant-like Effect of Flavonoids from Trigonella Foenum-Graecum Seeds in Chronic Restraint Stress Mice via Modulation of Monoamine Regulatory Pathways" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061105
APA StyleWang, J., Cheng, C., Xin, C., & Wang, Z. (2019). The Antidepressant-like Effect of Flavonoids from Trigonella Foenum-Graecum Seeds in Chronic Restraint Stress Mice via Modulation of Monoamine Regulatory Pathways. Molecules, 24(6), 1105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061105