Synthesis, In Silico, and In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Leishmanial Activity of Oxadiazoles and Indolizine Containing Compounds Flagged against Anti-Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
2.1.1. Synthesis of 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles
2.1.2. Synthesis of Indolizines
2.2. Virtual Screening
2.2.1. EIIP Filtering
2.2.2. 3D QSAR Filtering
2.2.3. Arginase Docking
2.2.4. Anti-Target Interaction Matrix
2.2.5. In vitro Evaluation of Anti-Leishmanial Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry and Physico-Chemical Analyses
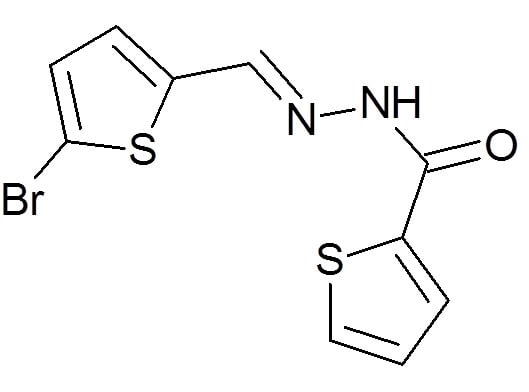
4.1.1. General Procedure for the Automated Synthesis of Compounds 1–5:

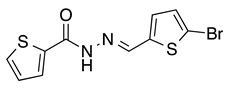

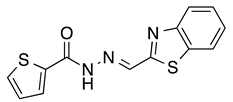

4.1.2. General Procedure for the Automated Synthesis of Compounds 6 and 7:


4.1.3. Procedure for the Synthesis of Compound 8:

4.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 11–13:
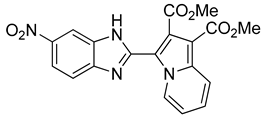


4.2. Ligands
4.3. Virtual Screening
4.3.1. EIIP/AQVN
4.3.2. 3D QSAR
4.4. Arginase
4.5. Anti-Targets
4.6. Biological Evaluation
4.6.1. Cultures for Parasites and Cells
4.6.2. Macrophage
4.6.3. In Vitro Anti-Leishmanial Compound Testing on Axenic and Intramacrophage Amastigotes:
4.6.4. Cytotoxicity Tests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO, Leishmaniasis: Situation and Trends. World Health Organization, 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/neglected_diseases/leishmaniasis/en/ (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- WHO Fact Sheet. 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Chappuis, F.; Sundar, S.; Hailu, A.; Ghalib, H.; Rijal, S.; Peeling, R.W.; Alvar, J.; Boelaert, M. Visceral leishmaniasis: What are the needs for diagnosis, treatment and control? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Silva, A.; Guimarães, P.P.; Tavares, C.A.; Sinisterra, R.D. New perspectives for leishmaniasis chemotherapy over current anti-leishmanial drugs: A patent landscape. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, R.; Chen, Y.P. Potential therapeutic targets and the role of technology in developing novel antileishmanial drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Menezes, J.; Guedes, C.; Petersen, A.; Fraga, D.; Veras, P. Advances in development of new treatment for Leishmaniasis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 815023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponte-Sucre, A.; Gamarro, F.; Dujardin, J.C.; Barrett, M.P.; López-Vélez, R.; García-Hernández, R.; Pountain, A.W.; Mwenechanya, R.; Papadopoulou, B. Drug resistance and treatment failure in leishmaniasis: A 21st century challenge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 14, e0006052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.; Goyal, V.; Haque, R.; Jamil, K.; Faiz, A.; Samad, R.; Ellis, S.; Balasegaram, M.; Boer, M.D.; Rijal, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of short course combination regimens with AmBisome, miltefosine and paromomycin for the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis (VL) in Bangladesh. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.; Kropf, P.; Choi, B.S.; Dillon, R.; Podinovskaia, M.; Bates, P.; Müller, I. Proteophosophoglycans regurgitated by Leishmania-infected sand flies target the L-arginine metabolism of host macrophages to promote parasite survival. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilari, A.; Fiorillo, A.; Genovese, I.; Colotti, G. Polyamine-trypanothione pathway: An update. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.R.; Castilho, T.M.; Pioker, F.C.; Tomich de Paula Silva, C.H.; Floeter-Winter, L.M. Genomic organisation and transcription characterisation of the gene encoding Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis arginase and its protein structure prediction. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocedi, A.; Dawood, K.F.; Fabrini, R.; Federici, G.; Gradoni, L.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Ricci, G. Trypanothione efficiently intercepts nitric oxide as a harmless iron complex in trypanosomatid parasites. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colotti, G.; Ilari, A. Polyamine metabolism in Leishmania: From arginine to trypanothione. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, R.M.; Balaña-Fouce, R.; Showalter, M.; Hickerson, S.; Beverley, S.M. Leishmania major lacking arginase (ARG) are auxotrophic for polyamines but retain infectivity to susceptible BALB/c mice. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 165, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, B.; Madhubala, R. Drug targets in Leishmania. J. Parasit. Dis. 2010, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepesheva, G.I.; Hargrove, T.Y.; Rachakonda, G.; Wawrzak, Z.; Pomel, S.; Cojean, S.; Nde, P.N.; Nes, W.D.; Locuson, C.W.; Calcutt, M.W.; et al. VFV as a New Effective CYP51 Structure-Derived Drug Candidate for Chagas Disease and Visceral Leishmaniasis. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottrell, D.M.; Capers, J.; Salem, M.M.; DeLuca-Fradley, K.; Croft, S.L.; Werbovetz, K.A. Antikinetoplastid activity of 3-aryl-5-thiocyanatomethyl-1,2,4-oxadiazoles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 2815–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, V. Indolizine: A biologically active moiety. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 3593–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaisankar, P.; Pal, B.; Manna, R.K.; Pradhan, P.K.; Medda, S.; Basu, M.K.; Giri, V.S. Synthesis of antileishmanial(5R)-(-)-5-carbomethoxy-3-formyl-5, 6-dihydroindolo-[2, 3-a]-indolizine. ARKIVOC 2003, ix, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Glisic, S.; Sencanski, M.; Perovic, V.; Stevanovic, S.; García-Sosa, A.T. Arginase Flavonoid Anti-Leishmanial in Silico Inhibitors Flagged against Anti-Targets. Molecules 2016, 21, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekanth Thota, S.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Murteira Pinheiro, P.S.; Lima, L.M.; Fraga, C.A.M.; Barreiro, E.J. N-Acylhydrazones as drugs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2797–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.M.; Barros, M.T. Fast synthesis of N-acylhydrazones employing a microwave assisted neat protocol. J. Comb. Chem. 2010, 12, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, P.F.M.; Guidetti, B.; Chamayou, A.; André-Barrès, C.; Madacki, J.; Korduláková, J.; Mori, G.; Orena, B.S.; Chiarelli, L.R.; Pasca, M.R.; et al. Mechanochemical synthesis and biological C. evaluation of novel isoniazid derivatives with potent antitubercular activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, R.O.; Dar, B.; Pradhan, V.; Farooqui, M. 1,2,4-Oxadiazoles: Synthesis and Biological applications. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, C.J.P.; Rufino de Freitas, J.J.; De Oliveira, R.N.; De Freitas Filho, J.R. Synthesis of amidoximes using an efficient and rapid ultrasound method. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2011, 56, 721–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, A.J.; Harington, J.S. The anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of some benzimidazoles, and their ability to protect erythrocytes from hemolysis by silica powder. Carbohydr. Res. 1975, 43, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde, E.; Pérez-García, L.; Miravitlles, C.; Rius, J.; Valentí, E. Heterocyclic Betaines. 13. Synthesis, Electronic and Molecular Structures of Methylenepyridinium and Methylenimidazolium Azolate Inner Salts. J. Organ. Chem. 1992, 57, 4829–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Lizzi, F.; Perozzo, R.; Brun, R.; Cavalli, A. Synthesis of a small library of 2-phenoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone and 2-phenoxy-1,4-anthraquinone derivatives bearing anti-trypanosomal and anti-leishmanial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2272–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veljkovic, V. A Theoretical Approach to Preselection of Carcinogens and Chemical Carcinogenesis; Gordon & Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Veljkovic, V.; Slavic, I. Simple general-model pseudopotential. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1972, 29, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtual Screening Workflow; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- García-Sosa, A.T.; Sild, S.; Maran, U. Docking and virtual screening using distributed grid technology. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2009, 28, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sosa, A.T.; Maran, U. Improving the use of ranking in virtual screening against HIV-1 integrase with triangular numbers and including ligand profiling with Antitargets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3172–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaraman, K.; Vieira, N.C.; Moussa, F.; Vacus, J.; Cojean, S.; Pomel, S.; Bories, C.; Figadère, B.; Kesavan, V.; Loiseau, P.M. In vitro and in vivo antileishmanial properties of a 2-n-propylquinoline hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin formulation and pharmacokinetics via intravenous route. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 76, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |
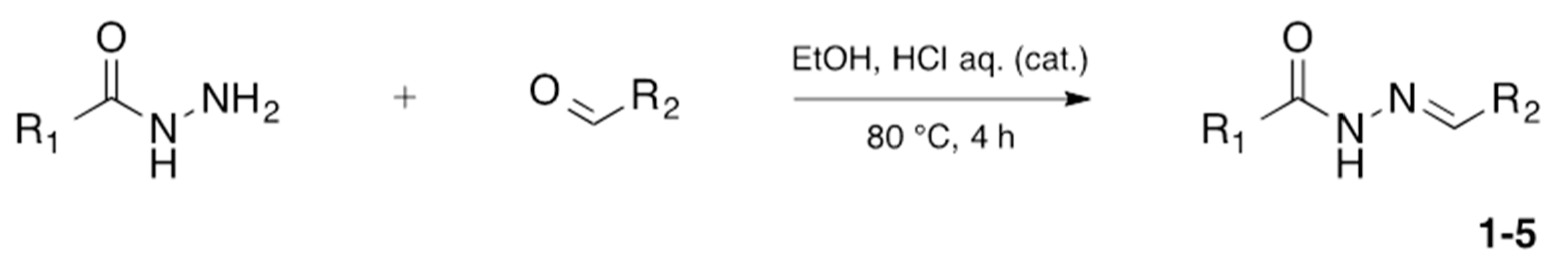






| Compound | Hydrazide | Aldehyde | Yield (%) | Purity 1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  | 61 | 92 |
| 2 |  |  | 72 | 99 |
| 3 | 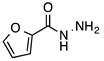 |  | 71 | 99 |
| 4 |  | 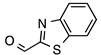 | quant. | 99 |
| 5 |  | 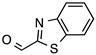 | 70 | 92 |
| No | Code | AQVN | EIIP | Structure | Pred. pIC50 | Autodock Score (kcal/mol) Leishmania Arginase | Autodock Score (kcal/mol) Human Arginase | Leishmania donovani LV9 axenic Amastigotes Forms IC50 ± SD (μM) | Leishmania donovani Intramacrophage Amastigotes Forms IC50 ± SD (μM) | Toxicity on RAW 264.7 Macrophages CC50 ± SD (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 1 | 3.28 | 0.125 | 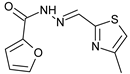 | 3.85 | −6 | −5.9 | 11.89 ± 1.87 | 6.25 ± 1.89 | 13.86 ± 2.11 |
| 21 | 2 | 3.304 | 0.129 |  | 3.77 | −5.8 | −5.0 | 1.09 ± 0.12 | 2.18 ± 0.01 | 4.87 ± 0.39 |
| 22 | 3 | 3.304 | 0.129 |  | 3.94 | −6.2 | −5.8 | > 100 | > 100 | > 100 |
| 23 | 4 | 3.357 | 0.134 |  | 3.55 | −6.3 | −6.2 | 12.50 ± 0.61 | 11.22 ± 0.62 | 16.34 ± 1.42 |
| 24 | 5 | 3.267 | 0.123 |  | 3.54 | −6.4 | −6.3 | 61.52 ± 5.99 | 55.22 ± 4.77 | >100 |
| 25 | 8 | 3.259 | 0.122 |  | 3.77 | −7.4 | −6.8 | 59.86 ± 6.45 | 51.26 ± 4.35 | >100 |
| 26 | 7 | 3.4 | 0.134 |  | 5.39 | −7.4 | −7.3 | 51.21 ± 4.98 | 47.24 ± 3.12 | >100 |
| 38 | 12 | 3.3 | 0.128 |  | 3.94 | −7.6 | −6.8 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| Compound | Leishmania donovani LV9 Axenic Amastigotes IC50 ± SD (μM) | Leishmania donovani LV9 Intramacrophage Amastigotes IC50 ± SD (μM) | Cytotoxicity on RAW 264.7 Macrophages CC50 ± SD (μM) | SI = CC50/IC50 Intramacro. Amas. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1.09 ± 0.12 | 2.18 ± 0.12 | 4.87 ± 0.39 | 2.2 |
| 3 | >100 | >100 | >100 | / |
| 4 | 12.50 ± 0.62 | 11.22 ± 0.62 | 16.34 ± 1.42 | 1.4 |
| 5 | 61.52 ± 5.99 | 55.22 ± 4.77 | > 100 | >1.8 |
| 1 | 11.89 ± 1.87 | 6.25 ± 1.89 | 13.86 ± 2.11 | 2.2 |
| 8 | 59.86 ± 6.45 | 51.26 ± 4.35 | >100 | >1.9 |
| 7 | 51.21 ± 4.98 | 47.24 ± 3.12 | >100 | >2.1 |
| 12 | >100 | >100 | >100 | / |
| AmB | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 0.11 ± 0.09 | 5.36 ± 0.52 | 48.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stevanovic, S.; Sencanski, M.; Danel, M.; Menendez, C.; Belguedj, R.; Bouraiou, A.; Nikolic, K.; Cojean, S.; Loiseau, P.M.; Glisic, S.; et al. Synthesis, In Silico, and In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Leishmanial Activity of Oxadiazoles and Indolizine Containing Compounds Flagged against Anti-Targets. Molecules 2019, 24, 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071282
Stevanovic S, Sencanski M, Danel M, Menendez C, Belguedj R, Bouraiou A, Nikolic K, Cojean S, Loiseau PM, Glisic S, et al. Synthesis, In Silico, and In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Leishmanial Activity of Oxadiazoles and Indolizine Containing Compounds Flagged against Anti-Targets. Molecules. 2019; 24(7):1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071282
Chicago/Turabian StyleStevanovic, Strahinja, Milan Sencanski, Mathieu Danel, Christophe Menendez, Roumaissa Belguedj, Abdelmalek Bouraiou, Katarina Nikolic, Sandrine Cojean, Philippe M. Loiseau, Sanja Glisic, and et al. 2019. "Synthesis, In Silico, and In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Leishmanial Activity of Oxadiazoles and Indolizine Containing Compounds Flagged against Anti-Targets" Molecules 24, no. 7: 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071282
APA StyleStevanovic, S., Sencanski, M., Danel, M., Menendez, C., Belguedj, R., Bouraiou, A., Nikolic, K., Cojean, S., Loiseau, P. M., Glisic, S., Baltas, M., & García-Sosa, A. T. (2019). Synthesis, In Silico, and In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Leishmanial Activity of Oxadiazoles and Indolizine Containing Compounds Flagged against Anti-Targets. Molecules, 24(7), 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071282