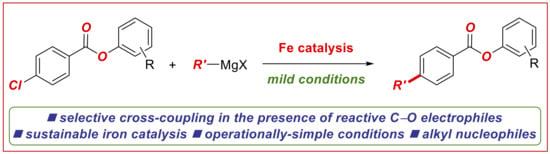
Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Aryl Chlorobenzoates with Alkyl Grignard Reagents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
4.2. General Procedure for Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling
4.3. General Procedure for Determination of Relative Reactivity
4.4. Characterization Data for Starting Materials
4.5. Characterization Data for Cross-Coupling Products
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fürstner, A.; Martin, R. Advances in Iron Catalyzed Cross Coupling Reactions. Chem. Lett. 2005, 34, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, B.D.; Fürstner, A. The Promise and Challenge of Iron-Catalyzed Cross Coupling. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaplik, W.M.; Mayer, M.; Cvengros, J.; Jacobi von Wangelin, A. Coming of Age: Sustainable Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 396–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plietker, B. Topic in Organometallic Chemistry Also Available Electronically. In Iron Catalysis–Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, E.B. Iron Catalysis II. Top. Organomet. Chem.; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 50. [Google Scholar]
- Marek, I.; Rappoport, Z. The Chemistry of Organoiron Compounds; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, I.; Knölker, H.J. Iron Catalysis in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3170–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legros, J.; Fidegarde, B. Iron-promoted C-C bond formation in the total synthesis of natural products and drugs. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 1541–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed C-O Bond Activation: Opportunity for Sustainable Catalysis. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3964–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürstner, A. Discussion Addendum for: 4-Nonylbenzoic Acid. Org. Synth. 2019, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A. Iron Catalysis in Organic Synthesis: A Critical Assessment of What It Takes To Make This Base Metal a Multitasking Champion. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A. Base-Metal Catalysis Marries Utilitarian Aspects with Academic Fascination. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 2362–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.R.; Schindler, C.S. Catalyst: Sustainable Catalysis. Chem 2017, 2, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molander, G.A.; Wolfe, J.P.; Larhed, M. (Eds.) Science of Synthesis: Cross-Coupling and Heck-Type Reactions; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- de Meijere, A.; Bräse, S.; Oestreich, M. (Eds.) Metal-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions and More; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Colacot, T.J. (Ed.) New Trends in Cross-Coupling; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, R.; Pathak, T.P.; Sigman, M.S. Advances in Transition Metal (Pd,Ni,Fe)-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions Using Alkyl-organometallics as Reaction Partners. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1417–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giri, R.; Thapa, S.; Kafle, A. Palladium- Catalysed, Directed C-H Coupling with Organometallics. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1395–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontek, A.; Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling in the Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals: In Pursuit of Sustainability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11116–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürstner, A.; Leitner, A. Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions of Alkyl-Grignard Reagents with Aryl Chlorides, Tosylates, and Triflates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A.; Leitner, A.; Mendez, M.; Krause, H. Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13856–13863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A.; Leitner, A. A Catalytic Approach to (R)-(+)-Muscopyridine with Integrated “Self-Clearance”. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A.; De Souza, D.; Parra-Rapado, L.; Jensen, J.T. Catalysis-Based Total Synthesis of Latrunculin, B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 5358–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaplik, W.M.; Mayer, M.; Jacobi von Wangelin, A. Domino Iron Catalysis: Direct Aryl-Alkyl Cross-Coupling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülak, S.; Jacobi von Wangelin, A. Chlorostyrenes in Iron-Catalyzed Biaryl Coupling Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gärtner, D.; Stein, A.L.; Grupe, S.; Arp, J.; Jacobi von Wangelin, A. Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Alkenyl Acetates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10545–10549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmina, O.M.; Steib, A.K.; Markiewicz, J.T.; Flubacher, D.; Knochel, P. Ligand-Accelerated Iron- and Cobalt-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions between N-Heteroaryl Halides and Aryl Magnesium Reagents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4945–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürstner, A.; Martin, R.; Krause, H.; Seidel, G.; Goddard, R.; Lehmann, C.W. Preparation, Structure, and Reactivity of Nonstabilized Organoiron Compounds. Implications for Iron-Catalyzed Cross Coupling Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8773–8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassani, C.; Bergonzini, G.; Wallentin, C.J. Active Species and Mechanistic Pathways in Iron-Catalyzed C–C Bond-Forming Cross-Coupling Reactions. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casitas, A.; Krause, H.; Goddard, R.; Fürstner, A. Elementary Steps in Iron Catalysis: Exploring the Links between Iron Alkyl and Iron Olefin Complexes for their Relevance in C–H Activation and C–C Bond Formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casitas, A.; Rees, J.A.; Goddard, R.; Bill, E.; DeBeer, D.; Fürstner, A. Two Exceptional Homoleptic Iron(IV) Tetraalkyl Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10108–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, S.B., III; Daifuku, S.L.; Sears, J.D.; Baker, T.M.; Carpenter, S.H.; Brennessel, W.W.; Neidig, M.L. The N-Methylpyrrolidone (NMP) Effect in Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling with Simple Ferric Salts and MeMgBr. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6496–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, J.D.; Muñoz, S.B.; Daifuku, S.L.; Shaps, A.A.; Carpenter, S.H.; Brennessel, W.W.; Neidig, M.L. The Effect of β-Hydrogen Atoms on Iron Speciation in Cross-Couplings with Simple Iron Salts and Alkyl Grignard Reagents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2769–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, B. N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- NMP is Classified as A Chemical of “Very High Concern” and A Proposal has been put forward to restrict the Use of NMP. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. Cyclic Ureas (DMI, DMPU) as Efficient, Sustainable Ligands in Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Coupling of Aryl Chlorides and Tosylates. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5361–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. 2-Methyltetrahydrofuran: A Green Solvent for Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontek, A.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)-C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Alkyl Grignard Reagents with Polyaromatic Tosylates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 48, 7271–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Chlorobenzamides with Alkyl Grignard Reagents: Development of Catalyst System, Synthetic Scope and Application. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)−C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Chlorobenzenesulfonamides with Alkyl Grignard Reagents: Entry to Alkylated Aromatics. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisz, E.; Podchorodecka, P.; Szostak, M. N-Methylcaprolactam as a Dipolar Aprotic Solvent for Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions: Matching Efficiency with Safer Reaction Media. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisz, E.; Kardela, M.; Piontek, A.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling at Low Catalyst Loading. Catl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisz, E.; Kardela, M.; Szostak, M. Ligand Effect on Iron-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions: Evaluation of Amides as O-Coordinating Ligands. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 5733–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Nolan, S.P.; Szostak, M. Well-Defined Palladium(II)-NHC (NHC = N-Heterocyclic Carbene) Precatalysts for Cross- Coupling Reactions of Amides and Esters by Selective Acyl CO–X. (X. = N., O) Cleavage. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Szostak, M. N-Acyl-Glutarimides: Privileged Scaffolds in Amide N-C Bond Cross-Coupling. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 20–21, 2352–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takise, R.; Muto, K.; Yamaguchi, J. Cross-Coupling of Aromatic Esters and Amides. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5864–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Rueping, M. Decarbonylative Cross-Couplings: Nickel Catalyzed Functional Group Interconversion Strategies for the Construction of Complex Organic Molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Szostak, M. Decarbonylative Cross-Coupling of Amides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 7998–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaike, K.; Muto, K.; Yamaguchi, J.; Itami, K. Decarbonylative C-H Coupling of Azoles and Aryl Esters: Unprecedented Nickel Catalysis and Application to the Synthesis of Muscoride, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13573–13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, K.; Yamaguchi, J.; Musaev, D.G.; Itami, K. Decarbonylative Organoboron Cross-Coupling of Esters by Nickel Catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, no. 7508. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takise, R.; Isshiki, R.; Muto, K.; Itami, K.; Yamaguchi, J. Decarbonylative Diaryl Ether Synthesis by Pd and Ni Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3340–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isshiki, R.; Muto, K.; Yamaguchi, J. Decarbonylative C–P Bond Formation Using Aromatic Esters and Organophosphorus Compounds. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halima, T.B.; Zhang, W.; Yalaoui, I.; Hong, X.; Yang, Y.-F.; Houk, K.N.; Newman, S.G. Palladium-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling of Aryl Esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halima, T.B.; Kishore, J.; Shkoor, V.M.; Newman, S.G. A Cross-Coupling Approach to Amide Bond Formation from Esters. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2176–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Makdissi, J.; Vandavasi, J.; Newman, S. Switchable Selectivity in the Pd-Catalyzed Alkylative Cross-Coupling of Esters. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4094–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardir, A.H.; Melvin, P.R.; Davis, R.M.; Hazari, N.; Beromi, M.M. Rapidly Activating Pd-Precatalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura and Buchwald-Hartwig Couplings of Aryl Esters. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 83, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatupheeraphat, A.; Liao, H.H.; Srimontree, W.; Guo, L.; Minenkov, Y.; Poater, A.; Cavallo, L.; Rueping, M. Ligand-Controlled Chemoselective C(acyl)-O Bond vs C(aryl)-C Bond Activation of Aromatic Esters in Nickel Catalyzed C(sp2)-C(sp3) Cross-Couplings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3724–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Rueping, M. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Decarbonylative Coupling Reactions: Concepts, Classifications, and Applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 7794–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z. Nickel-Catalyzed Decarbonylative Borylation and Silylation of Esters. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6692–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Meng, G.; Shi, S.; Ling, Y.; An, J.; Szostak, R.; Szostak, M. Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of Amides and Esters at Room Temperature: Correlation with Barriers to Rotation around C–N and C–O Bonds. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6525–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Lei, P.; Szostak, M. Pd-PEPPSI: A General Pd-NHC Precatalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura Cross- Coupling of Esters by C–O Cleavage. Organometallics 2017, 36, 3784–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shi, S.; Szostak, M. Pd-PEPPSI: Water-Assisted Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of Aryl Esters at Room Temperature using a Practical Palladium-NHC (NHC = N-Heterocyclic Carbene) Precatalyst. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 1538–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Szostak, M. Pd–PEPPSI: A General Pd–NHC Precatalyst for Buchwald–Hartwig Cross-Coupling of Esters and Amides (Transamidation) under the Same Reaction Conditions. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 10584–10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchspies, J.; Pyle, D.J.; He, H.; Szostak, M. Pd-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of Pentafluorophenyl Esters. Molecules. 2018, 23, 3134–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebman, J.; Greenberg, A. The Origin of Rotational Barriers in Amides and Esters. Biophys. Chem. 1974, 1, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Nikonov, G.I. Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones, Nitriles, and Esters Catalyzed by a Half-Sandwich Complex of Ruthenium. ChemCatChem. 2015, 7, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, J. Cu(OTf)2-Mediated Chan-Lam Reaction of Carboxylic Acids to Access Phenolic Esters. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 7472–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuvonen, H.; Neuvonen, K.; Pasanen, P. Substituent Influences on the Stability of the Ring and Chain Tautomers in 1,3-O,N-Heterocyclic Systems: Characterization by 13C-NMR Chemical Shifts, PM3 Charge Densities, and Isodesmic Reactions. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 3794–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.P.; Raizon, B.M.; Desarmeinen, M.; Feltz, P.; Headley, P.M.; Worms, P.; Lioyd, K.G.; Bartholini, G. New anticonvulsants: Schiff bases of γ-aminobutyric acid and γ-aminobutyramide. J. Med. Chem. 1980, 23, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J.; Su, W.; Ding, J. Palladium-Catalyzed Aromatic Esterification of Aldehydes with Organoboronic Acids and Molecular Oxygen. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




| Entry | Fe(acac)3 (mol%) | Ligand | mol % | Addition Time (min) | Time (min) | Yield (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 3 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 0 | 10 | 27 |
| 2 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 0 | 10 | 27 |
| 3 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 60 | 180 | 65 |
| 4 | 5 | DMI | 600 | 60 | 180 | 52 |
| 5 | 5 | DMI | 20 | 60 | 180 | 48 |
| 6 | 5 | - | - | 60 | 180 | 44 |
| 7 4 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 60 | 180 | 57 |
| 8 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 180 | 60 | 52 |
| 9 | 10 | DMI | 200 | 60 | 180 | 60 |
| 10 | 50 | DMI | 200 | 60 | 180 | 28 |
| 11 5 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 0 | 180 | 52 |
| 12 6 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 0 | 180 | <10 |
| 13 | - | - | - | 60 | 180 | 0 |
| 14 | - | DMI | 200 | 60 | 180 | 0 |
| 15 | 5 | NMP | 200 | 60 | 180 | 57 |

| Entry | Substrate | 2 | Product | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 2a |  | 63 |
| 2 |  | 2b |  | 68 |
| 3 |  | 2c |  | 81 |
| 4 |  | 2d |  | 51 |
| 5 |  | 2e |  | 80 |
| 6 |  | 2f |  | 90 |
| 7 |  | 2g |  | 83 |
| 8 |  | 2h |  | 76 |
| 9 2 |  | 2i |  | 37 |
| 10 2 |  | 2j |  | 82 |

| Entry | Fe(acac)3 (mol%) | Ligand | mol% | Time (min) | Yield (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | DMI | 200 | 180 | 98 (2) |
| 2 | 5 | DMPU | 200 | 180 | >98 (1) |
| 3 | 5 | TMU | 200 | 180 | >98 (<1) |
| 4 | 5 | NMP | 200 | 180 | 95 (4) |
| 5 | 5 | N-Methylcaprolactam | 200 | 180 | 92 (7) |
| 6 3 | 5 | Bis(OMeEt)-BA | 200 | 180 | 57 (<1) |
| 7 4 | 5 | Pip-BA | 200 | 180 | 75 (<1) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bisz, E.; Szostak, M. Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Aryl Chlorobenzoates with Alkyl Grignard Reagents. Molecules 2020, 25, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010230
Bisz E, Szostak M. Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Aryl Chlorobenzoates with Alkyl Grignard Reagents. Molecules. 2020; 25(1):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010230
Chicago/Turabian StyleBisz, Elwira, and Michal Szostak. 2020. "Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Aryl Chlorobenzoates with Alkyl Grignard Reagents" Molecules 25, no. 1: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010230
APA StyleBisz, E., & Szostak, M. (2020). Iron-Catalyzed C(sp2)–C(sp3) Cross-Coupling of Aryl Chlorobenzoates with Alkyl Grignard Reagents. Molecules, 25(1), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010230