Surfactantless Emulsions Containing Eugenol for Imidacloprid Solubilization: Physicochemical Characterization and Toxicity against Insecticide-Resistant Cimex lectularius
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Surfactantless Emulsions
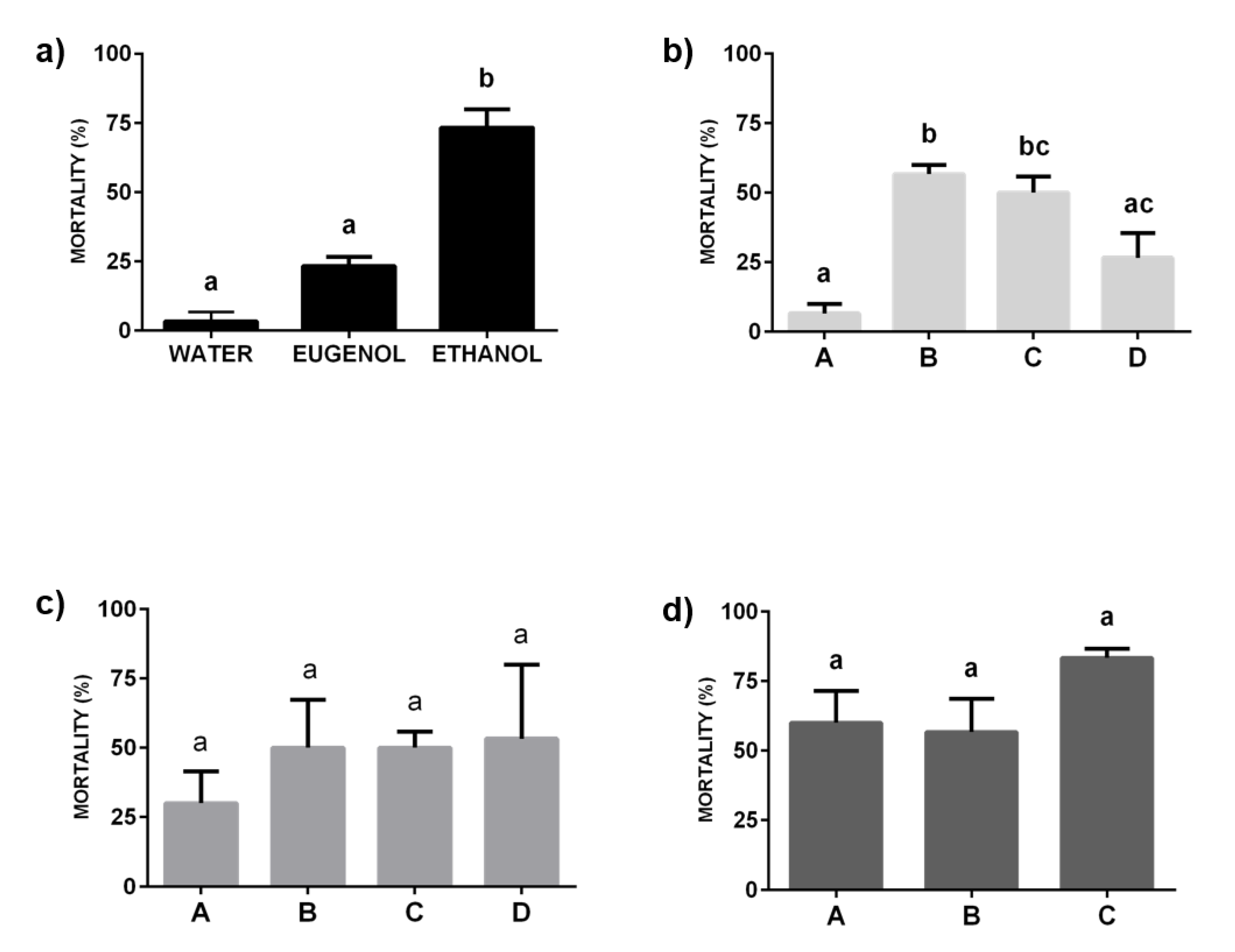
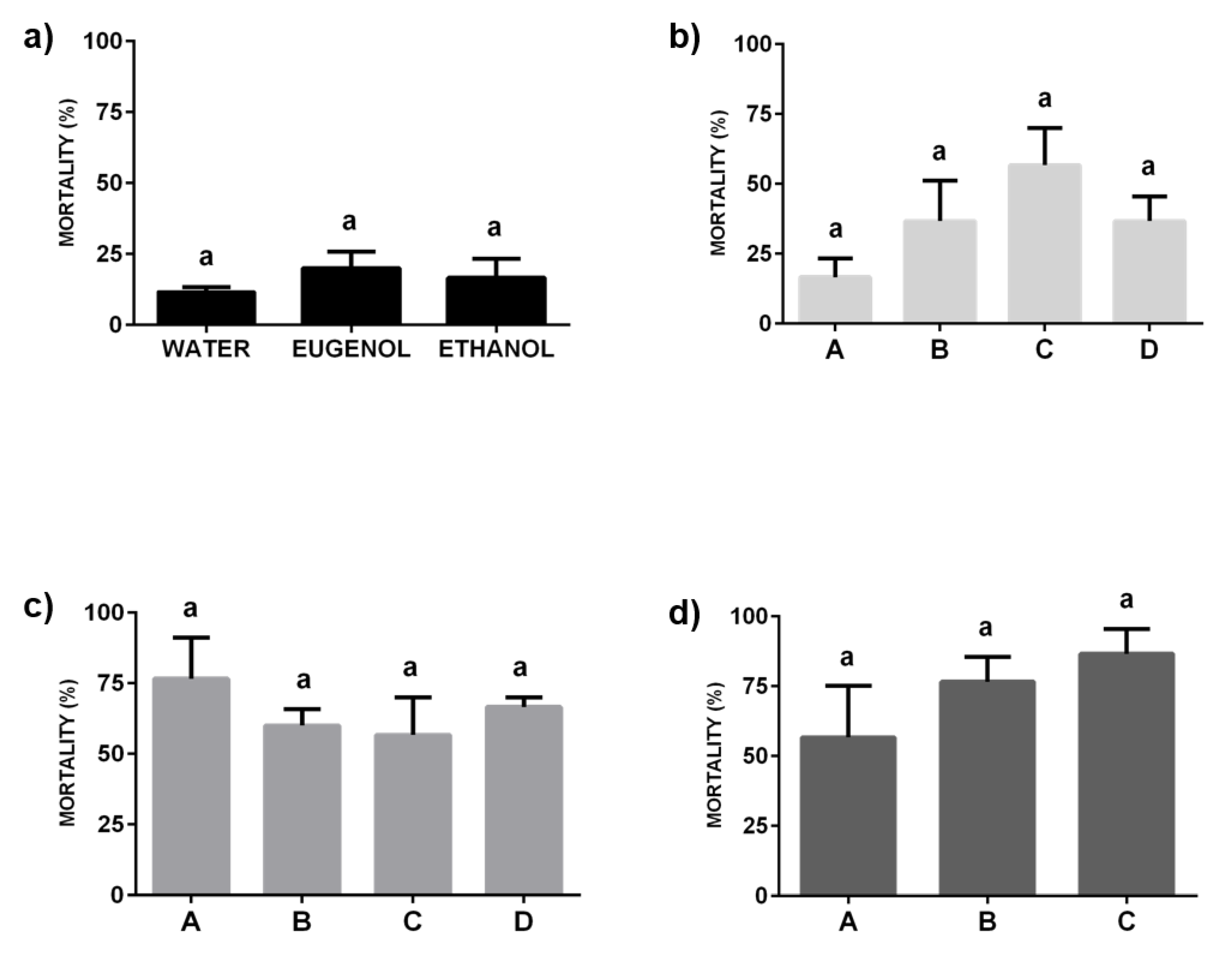
2.2. Insecticide Activity of Formulations against a Resistant Strain of C. lectularius
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Samples Preparation
3.3. Design of the Experiments
3.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.5. Insects
3.6. Toxicity Evaluation
3.6.1. Topical Application Bioassay
3.6.2. Spray Application Bioassay
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tisserand, R.B.; Balacs, T. Essential oil safety: A guide for health care professionals, 2nd ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, Scotland, London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Isman, M.B. Pesticides based on plant essential oils. Pesticide Outlook 1999, 10, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ayvaz, A.; Sagdic, O.; Karaborklu, S.; Ozturk, I. Insecticidal activity of the essential oils from different plants against three stored-product insects. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.; Tripathi, A.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, N. Essential Oils: A Novel Consumer and Eco-friendly Approach to Combat Postharvest Phytopathogens. J. Adv. Biol. Biotech. 2017, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela, R.; Benelli, G. Essential Oils as Ecofriendly Biopesticides? Challenges and Constraints. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, D.R.; Sparagano, O.A.E.; Port, G.; Okello, E.; Shiel, R.S.; Guy, J.H. Repellence of plant essential oils to Dermanyssus gallinae and toxicity to the non-target invertebrate Tenebrio molitor. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 162, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical Insecticides in the Twenty-First Century—Fulfilling Their Promise? Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristos, D.P.; Stamopoulos, D.C. Selection of Acanthoscelides obtectus (Say) for resistance to lavender essential oil vapour. J. Store. Prod. Res. 2003, 39, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-E.; Choi, W.-S.; Lee, H.-S.; Park, B.-S. Cross-resistance of a chlorpyrifos-methyl resistant strain of Oryzaephilus surinamensis (Coleoptera: Cucujidae) to fumigant toxicity of essential oil extracted from Eucalyptus globulus and its major monoterpene, 1, 8-cineole. J. Store. Prod. Res. 2000, 36, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T.G.E.; Field, L.M.; Williamson, M.S. The re-emergence of the bed bug as a nuisance pest: Implications of resistance to the pyrethroid insecticides. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R. Insecticide resistance in disease vectors of public health importance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2007, 63, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.C.; Nauen, R. IRAC: Mode of action classification and insecticide resistance management. Pest Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauen, R.; Denholm, I. Resistance of Insect Pests to Neonicotinoid Insecticides: Current Status and Future Prospects. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 58, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA-Registered Bed Bug Products. Available online: cfpub.epa.gov/oppref/bedbug/ (accessed on 14 May 2019).
- Hwang, S.W.; Svoboda, T.J.; De Jong, I.J.; Kabasele, K.J.; Gogosis, E. Bed bug infestations in an urban environment. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Potter, M.F.; Potter, D.A.; Haynes, K.F. Insecticide resistance in the bed bug: A factor in the pest’s sudden resurgence? J. Med. Entomol. 2007, 44, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doggett, S.L.; Russell, R.C. The resurgence of bed bugs, Cimex spp. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae) in Australia. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Urban Pests, Budapest, Hungary, 13–16 July 2008; Robinson, W.H., Bajomi, D., Eds.; OOK Pres: Budapest, Hungary, 2008; pp. 407–426. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, A. Moving from the old to the new: Insecticide research on bed bugs since the resurgence. Insects 2011, 2, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, K.; Doggett, S.L.; Veera Singham, V.; Lee, C.-Y. Insecticide resistance and resistance mechanisms in bed bugs, Cimex spp. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cáceres, M.; Santo-Orihuela, P.L.; Vassena, C.V. Evaluation of resistance to different insecticides and metabolic detoxification mechanism by use of synergist in the common bed bug (Heteroptera: Cimicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Yue, X. Insecticide resistance and cross resistance in the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.J.; Miller, D.M. Field evaluations of insecticide treatment regimens for control of the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius (L.). Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, M.; Sayyed, A.H.; Saleem, M.A.; Saeed, S. Cross resistance, inheritance and stability of resistance to acetamiprid in cotton whitefly, Bemisia tabaci Genn (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, K.; Veera Singham, G.; Doggett, S.L.; Lilly, D.G.; Lee, C.-Y. Effects of different surfaces and insecticide carriers on residual insecticide bioassays against bed bugs, Cimex spp. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternersen, J. Chemical Pesticides: Mode of Action and Toxicology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Elbert, A.; Haas, M.; Springer, B.; Thielert, W.; Nauen, R. Applied aspects of neonicotinoid uses in crop protection. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saillenfait, A.M.; Ndiaye, D.; Sabate, J.P. Pyrethroids: Exposure and health effects—An update. Int. J. Hyg. Envir. Health 2015, 218, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavoni, L.; Pavela, R.; Cespi, M.; Bonacucina, G.; Maggi, F.; Zeni, V.; Canale, A.; Lucchi, A.; Bruschi, F.; Benelli, G. Green Micro- and Nanoemulsions for Managing Parasites, Vectors and Pests. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samar, S.I. Essential Oil Nanoformulations as a Novel Method for Insect Pest Control in Horticulture. In Horticultural Crops; Baimey, H.K., Hamamouch, N., Kolombia, Y.A., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa, A.T.H. Green pesticides: Essential oils as biopesticides in insect-pest management. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 354–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnault-Roger, C.; Vincent, C.; Arnason, J.T. Essential oils in insect control: Low-risk products in a high-stakes world. An. Rev. Entom. 2012, 57, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Bloomquist, J.R. Plant essential oils affect the toxicities of carbaryl and permethrin against Aedes aegypti (Diptera:Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, N.; Hillier, N.K.; Cutler, G.C. Plant essential oils synergize and antagonize toxicity of different conventional insecticides against Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, E.J.; Gross, A.D.; Dunphy, B.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Coats, J.R. Comparison of the insecticidal characteristics of commercially available plant essential oils against Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.D.; Norris, E.J.; Kimber, M.J.; Dunphy, B.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Coats, J.R. Essential oils enhance the toxicity of permethrin against Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2017, 31, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynoso, M.M.N.; Lucia, A.; Zerba, E.N.; Alzogaray, R.A. Eugenol-hyperactivated nymphs of Triatoma infestans become intoxicated faster than non-hyperactivated nymphs when exposed to a permethrin-treated surface. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 3, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chansang, A.; Champakaew, D.; Junkum, A.; Jitpakdi, A.; Amornlerdpison, D.; Aldred, A.K.; Riyong, D.; Wannasan, A.; Intirach, J.; Muangmoon, R.; et al. Synergy in the adulticidal efficacy of essential oils for the improvement of permethrin toxicity against Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simamora, P.; Alvarez, J.M.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Solubilization of rapamycin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, J.J.; Abbott, S.; Shimizu, S. Mechanism of hydrophobic drug solubilization by small molecule hydrotropes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14915–14921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, A.B.; Jayakumar, C.; Gandhi, N.N. Hydrotropic effect and thermodynamic analysis on the solubility and mass transfer coefficient enhancement of ethylbenzene. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hefnawy, M.E.; Yousef, A. Characteristics of ternary clove/water/1-butanol microemulsions based drug delivery system for aspirin. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Critical Review of Techniques and Methodologies for Characterization of Emulsion Stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, A.; Argudo, P.G.; Guzmán, E.; Rubio, R.G.; Ortega, F. Formation of surfactant free microemulsions in the ternary system water/eugenol/ethanol. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 521, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; Anderson, T.D. High levels of resistance in the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius (Hemiptera: Cimicidae), to neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.R.; Goodman, M.H.; Potter, M.F.; Haynes, K.F. Population variation in and selection for resistance to pyrethroid-neonicotinoid insecticides in the bed bug. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, J. Long-term efficacy of various natural or “green” insecticides against bed bugs: A double-blind study. Insects 2014, 5, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelius, M.; Grace, J.K.; Yates, J.R. Toxicity of monoterpenoids and other natural products to the Formosan subterranean termite. J. Econ. Entomol. 1997, 90, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.J.; Coats, J.R. Insecticidal properties of several monoterpenoids to the house fly (Diptera: Muscidae), red flour beetle (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), and southern corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1994, 87, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Tsao, R.; Peterson, C.; Coats, J.R. Insecticidal activity of monoterpenoids to western corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), two spotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae), and house fly (Diptera: Muscidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1998, 90, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toloza, A.C.; Zygadlo, J.; Mougabure Cueto, G.N.; Biurrun, F.; Zerba, E.; Picollo, M.I. Fumigant and repellent properties of essential oils and component compounds against permethrin-resistant Pediculus humanus capitis (Anoplura: Pediculidae) from Argentina. J. Med. Entomol. 2006, 43, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.A.; da Silva, L.; Macêdo, M.J.F.; Lacerda-Neto, L.J.; dos Santos, M.A.C.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Cunha, F.A.B. Adulticide and repellent activity of essential oils against Ae aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae)—A review. South African J. Botany 2019, 124, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.; Zerba, E.N.; Alzogaray, R.A. Behavioral and toxicological responses of Rhodnius prolixus and Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) to ten monoterpene alcohols. J. Med. Entomol. 2013, 50, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, S.; Scharf, M.E.; Gondhalekar, A.D. Toxicity and neurophysiological impacts of plant essential oil components on bed bugs (Cimicidae: Hemiptera). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enan, E. Molecular and pharmacological analysis of an octopamine receptor from American cockroach and fruit fly in response to plant essential oils. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2005, 59, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Wang, C.; Cooper, R. Potential of essential oil-based pesticides and detergents for bed bug Control. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoh, S.P.; Choo, L.E.; Pang, F.Y.; Huang, Y.; Kini, M.R.; Ho, S.H. Insecticidal and repellent properties of nine volatile constituents of essential oils against the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana (L.). Pestic. Sci. 1998, 54, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, M.; Kapur, K.K.; Jalees, S.; Sharma, S.K. Laboratory evaluation of insecticidal properties of Ocimum basilicum L and O. sanctum L. plants essential oils and their major constituents against vector mosquito species. J. Entomol. Res. 1993, 17, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lucia, A.; Toloza, A.C.; Fanucce, M.; Fernández-Peña, L.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G.; Coviella, C.; Guzmán, E. Nanoemulsions based on thymol-eugenol mixtures: Characterization, stability and larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti. Bull. Insectology 2020, 73, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Berne, B.J.; Pecora, R. Dynamic Light Scattering with Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics; Dover Publications Inc.: Mineola, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.L.; Russell, R.M.; Preisler, H.K. Bioassays with Arthropods, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, W.S. A method for computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Med. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.J.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. lme4: Linear Mixed-effects Models using eigen and S4; R Package Version 1.0–5; Cran-R-Project: Zurich, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhardt, K.; Siva-Jothy, M.T. Biology of the bed bugs (Cimicidae). Ann Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 351–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available. |

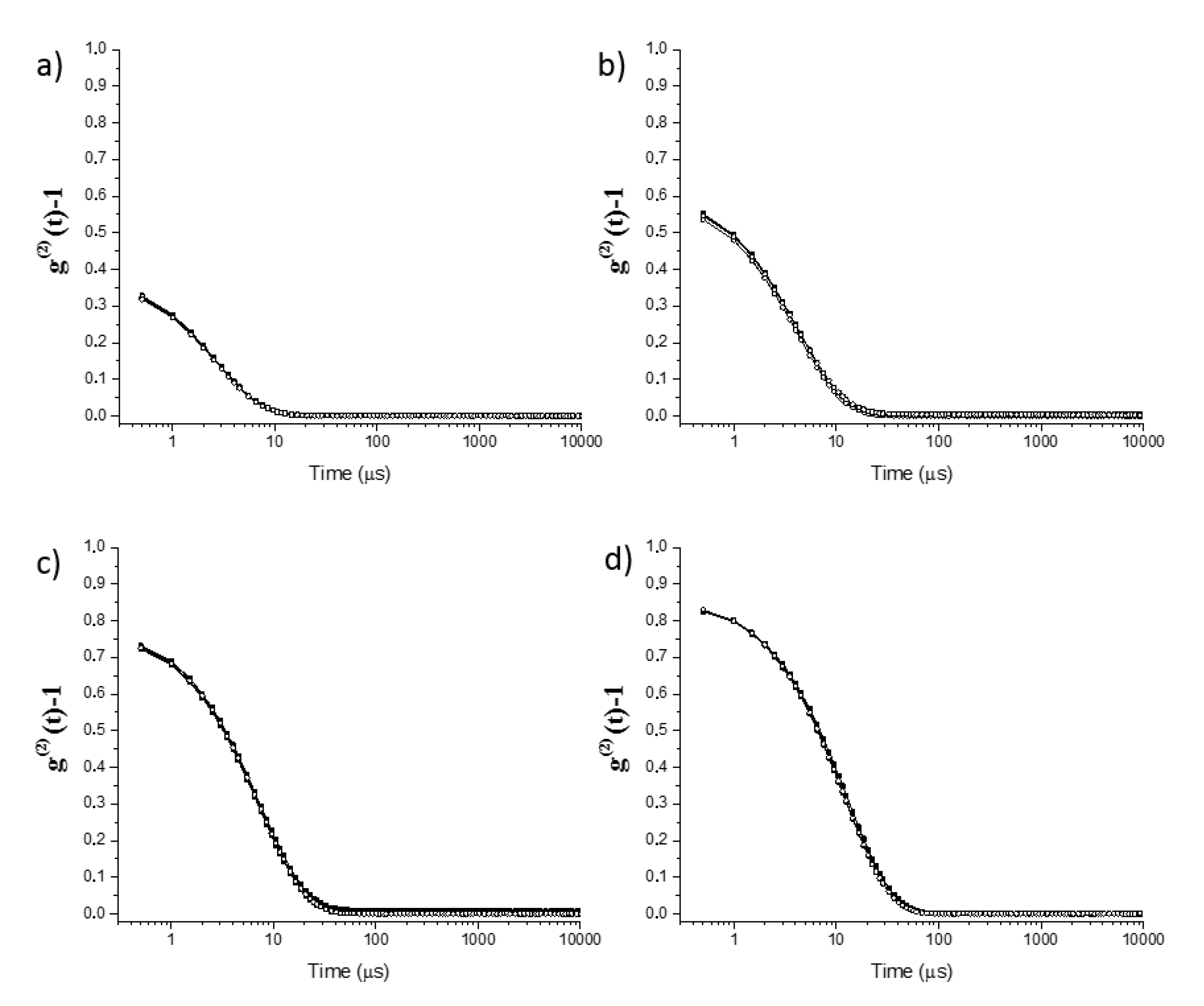
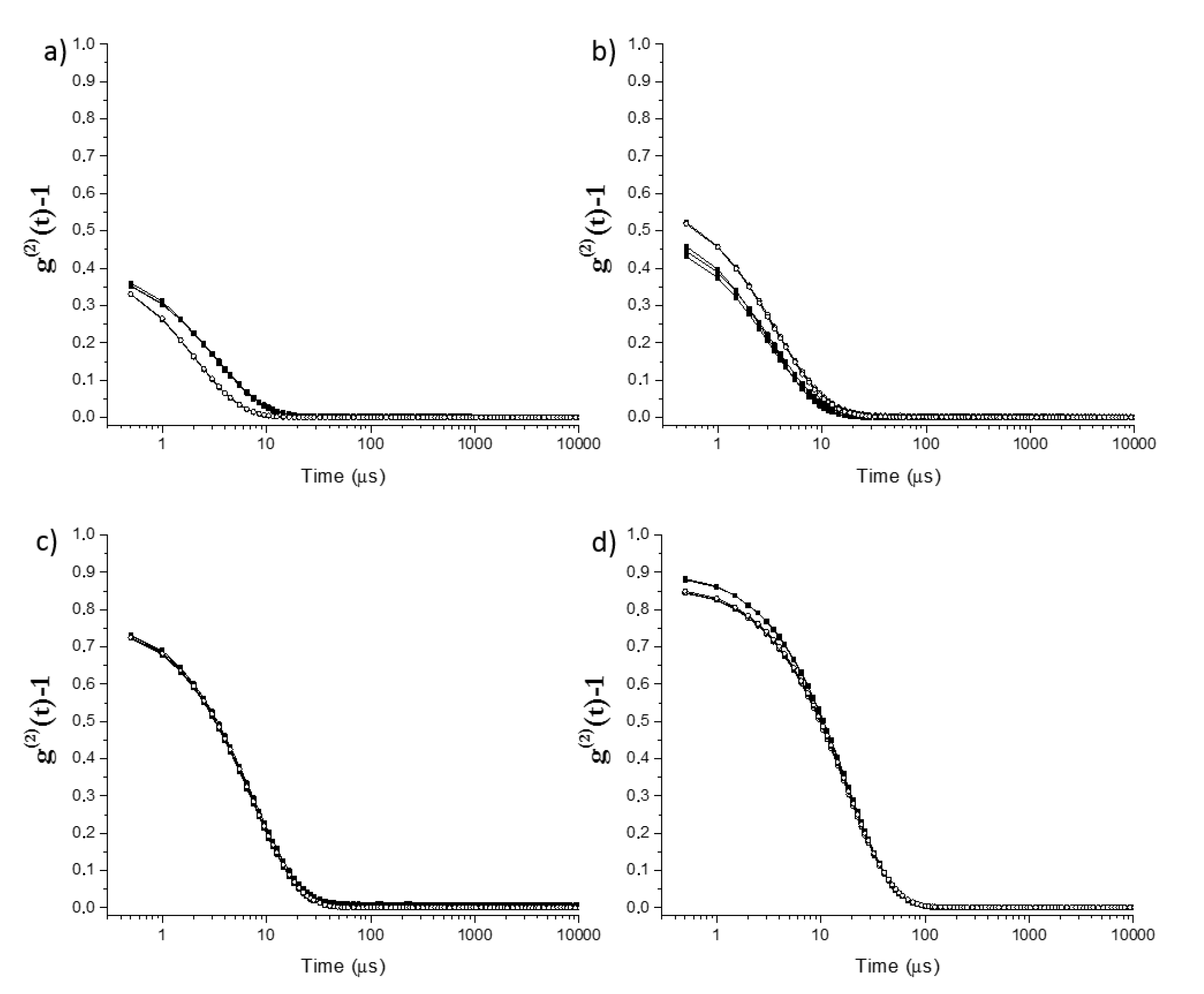
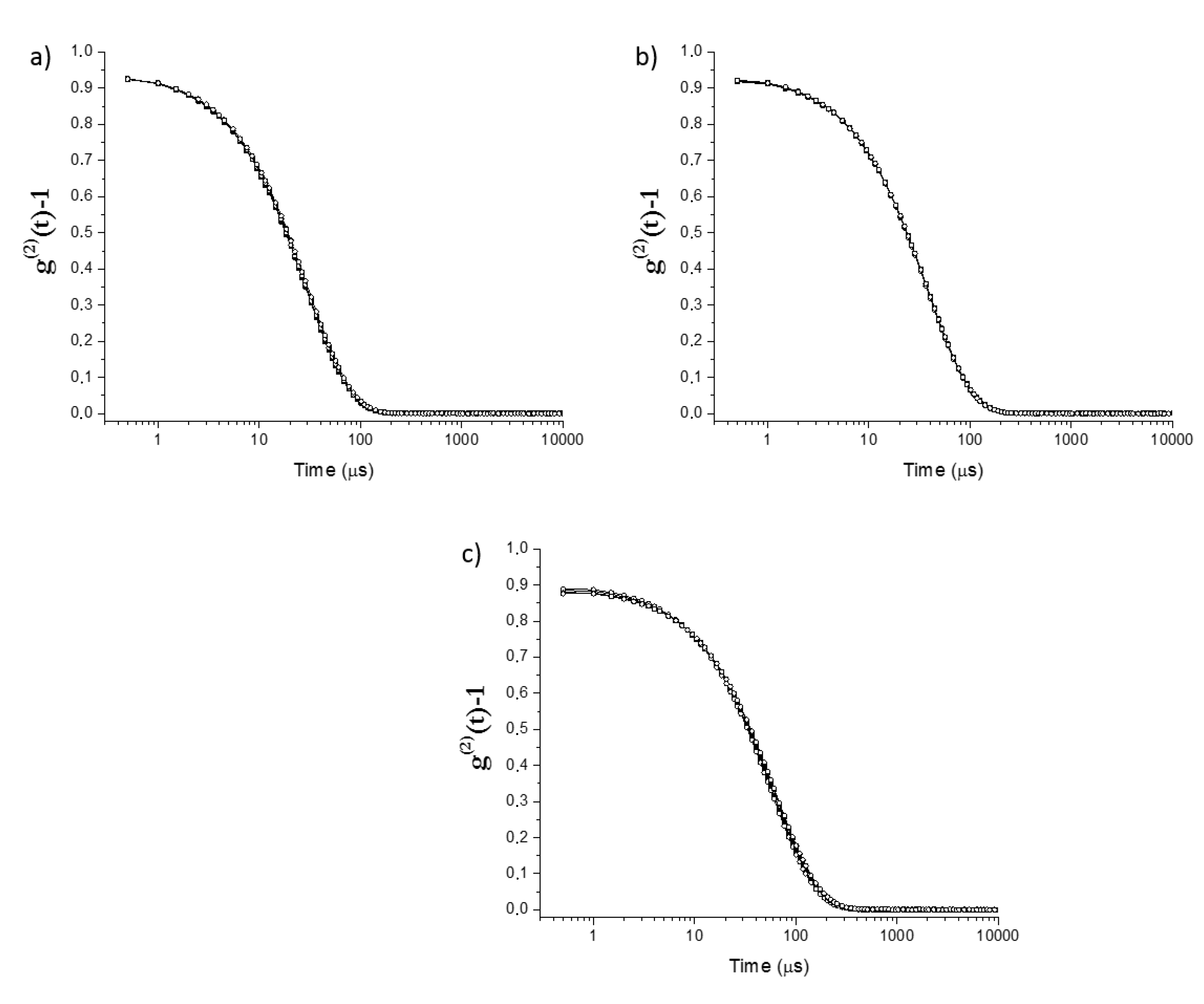
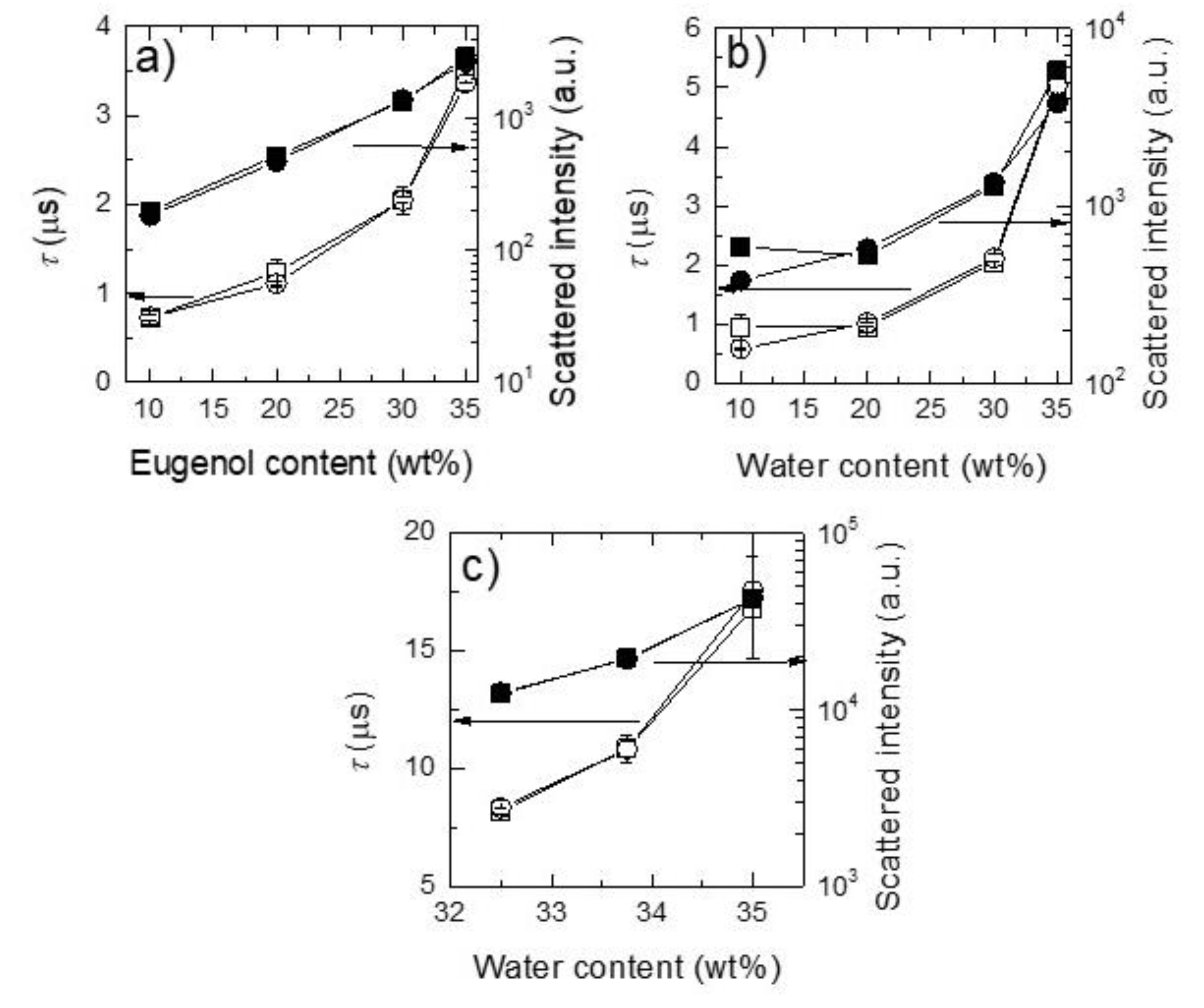

| Paths 1 | Sample | Region | Water (wt%) | Ethanol (wt%) | Eugenol (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | a | Pseudo-single | 30 | 60 | 10 |
| I | b | Pseudo-single | 30 | 50 | 20 |
| I | c | Pre-Ouzo | 30 | 40 | 30 |
| I | d | Pre-Ouzo | 30 | 35 | 35 |
| II | a | Pseudo-single | 10 | 60 | 30 |
| II | b | Pseudo-single | 20 | 50 | 30 |
| II | c | Pre-Ouzo | 30 | 40 | 30 |
| II | d | Pre-Ouzo | 35 | 35 | 30 |
| III | a | Pre-Ouzo | 32.5 | 32.5 | 35 |
| III | b | Pre-Ouzo | 33.75 | 32.5 | 33.75 |
| III | c | Pre-Ouzo | 35 | 32.5 | 32.5 |
| Variable | Factors | Parameter | D.F 1. | Z Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spray mortality | Intercept | 2.61 | 1 | 7.63 ** |
| Eugenol | 0.04 | 1 | 3.86 ** | |
| SI 2 | 6.75 × 10−6 | 1 | 1.06 | |
| Topic mortality | Intercept | 2.54 | 1 | 4.79 ** |
| Eugenol | 0.04 | 1 | 2.19 * | |
| SI 2 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 1 | 1.12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cáceres, M.; Guzmán, E.; Alvarez-Costa, A.; Ortega, F.; G. Rubio, R.; Coviella, C.; Santo Orihuela, P.L.; Vassena, C.V.; Lucia, A. Surfactantless Emulsions Containing Eugenol for Imidacloprid Solubilization: Physicochemical Characterization and Toxicity against Insecticide-Resistant Cimex lectularius. Molecules 2020, 25, 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102290
Cáceres M, Guzmán E, Alvarez-Costa A, Ortega F, G. Rubio R, Coviella C, Santo Orihuela PL, Vassena CV, Lucia A. Surfactantless Emulsions Containing Eugenol for Imidacloprid Solubilization: Physicochemical Characterization and Toxicity against Insecticide-Resistant Cimex lectularius. Molecules. 2020; 25(10):2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102290
Chicago/Turabian StyleCáceres, Mariano, Eduardo Guzmán, Agustín Alvarez-Costa, Francisco Ortega, Ramón G. Rubio, Carlos Coviella, Pablo L. Santo Orihuela, Claudia V. Vassena, and Alejandro Lucia. 2020. "Surfactantless Emulsions Containing Eugenol for Imidacloprid Solubilization: Physicochemical Characterization and Toxicity against Insecticide-Resistant Cimex lectularius" Molecules 25, no. 10: 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102290
APA StyleCáceres, M., Guzmán, E., Alvarez-Costa, A., Ortega, F., G. Rubio, R., Coviella, C., Santo Orihuela, P. L., Vassena, C. V., & Lucia, A. (2020). Surfactantless Emulsions Containing Eugenol for Imidacloprid Solubilization: Physicochemical Characterization and Toxicity against Insecticide-Resistant Cimex lectularius. Molecules, 25(10), 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102290









