Novel Class of Chalcone Oxime Ethers as Potent Monoamine Oxidase-B and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors
Abstract
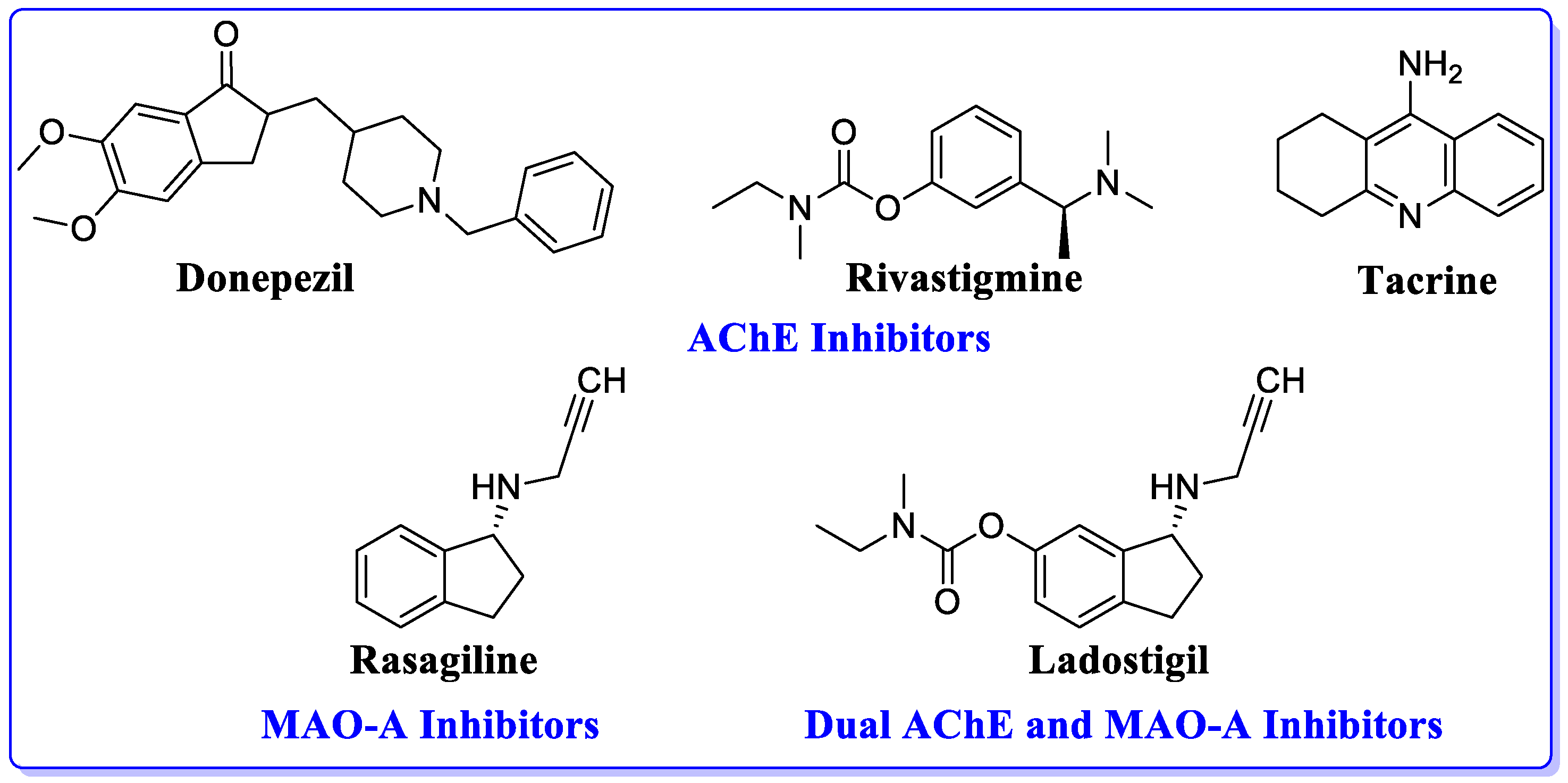
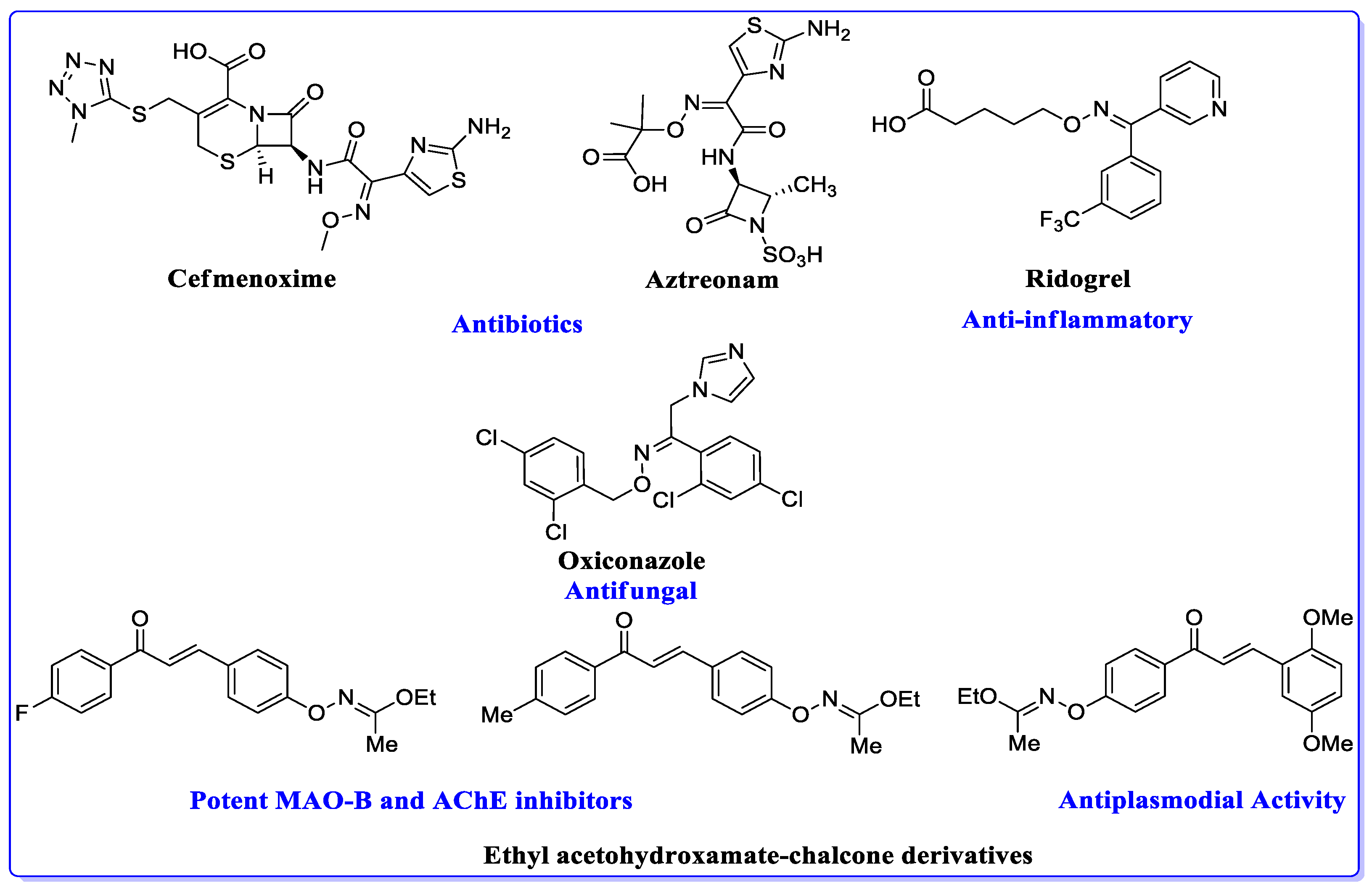
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
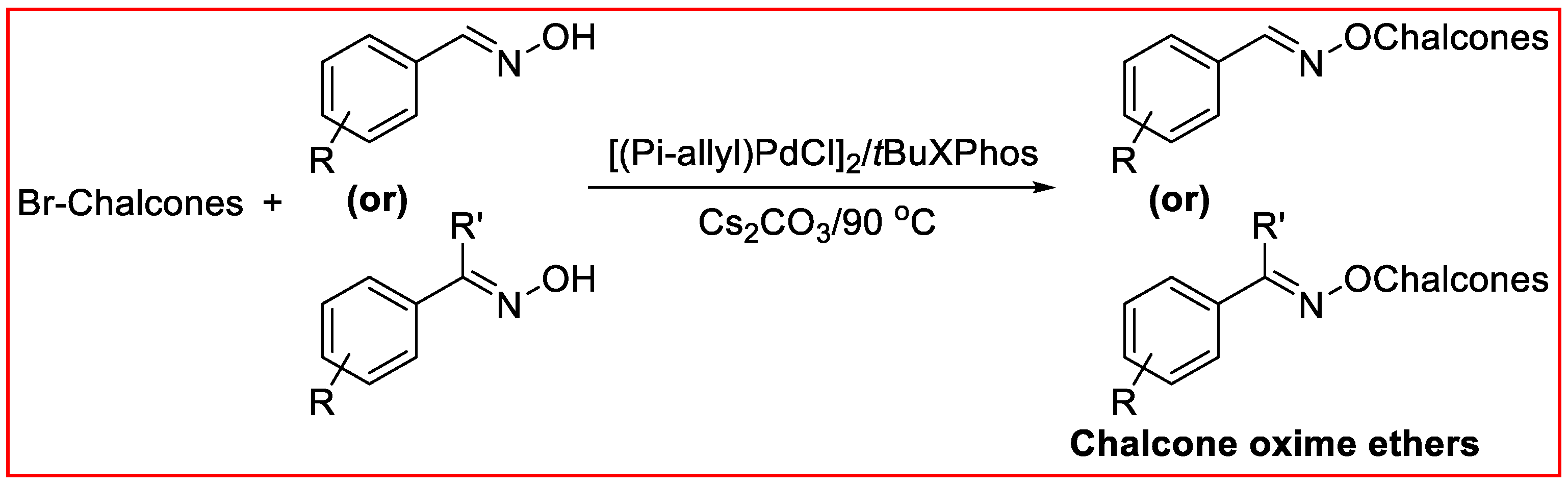
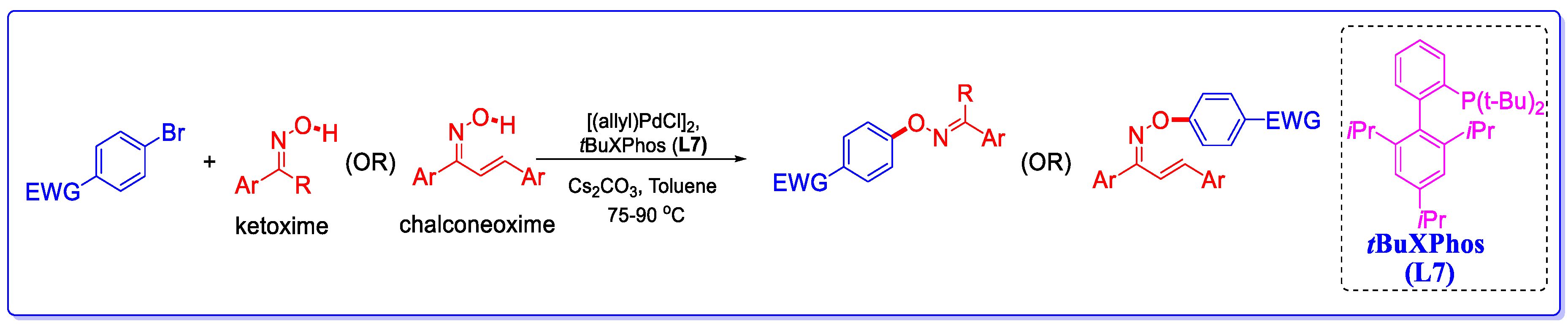
2.1. Synthesis of COEs
2.2. Inhibitory Activities against MAO-A, MAO-B and AChE
2.3. SARs for Inhibition Studies
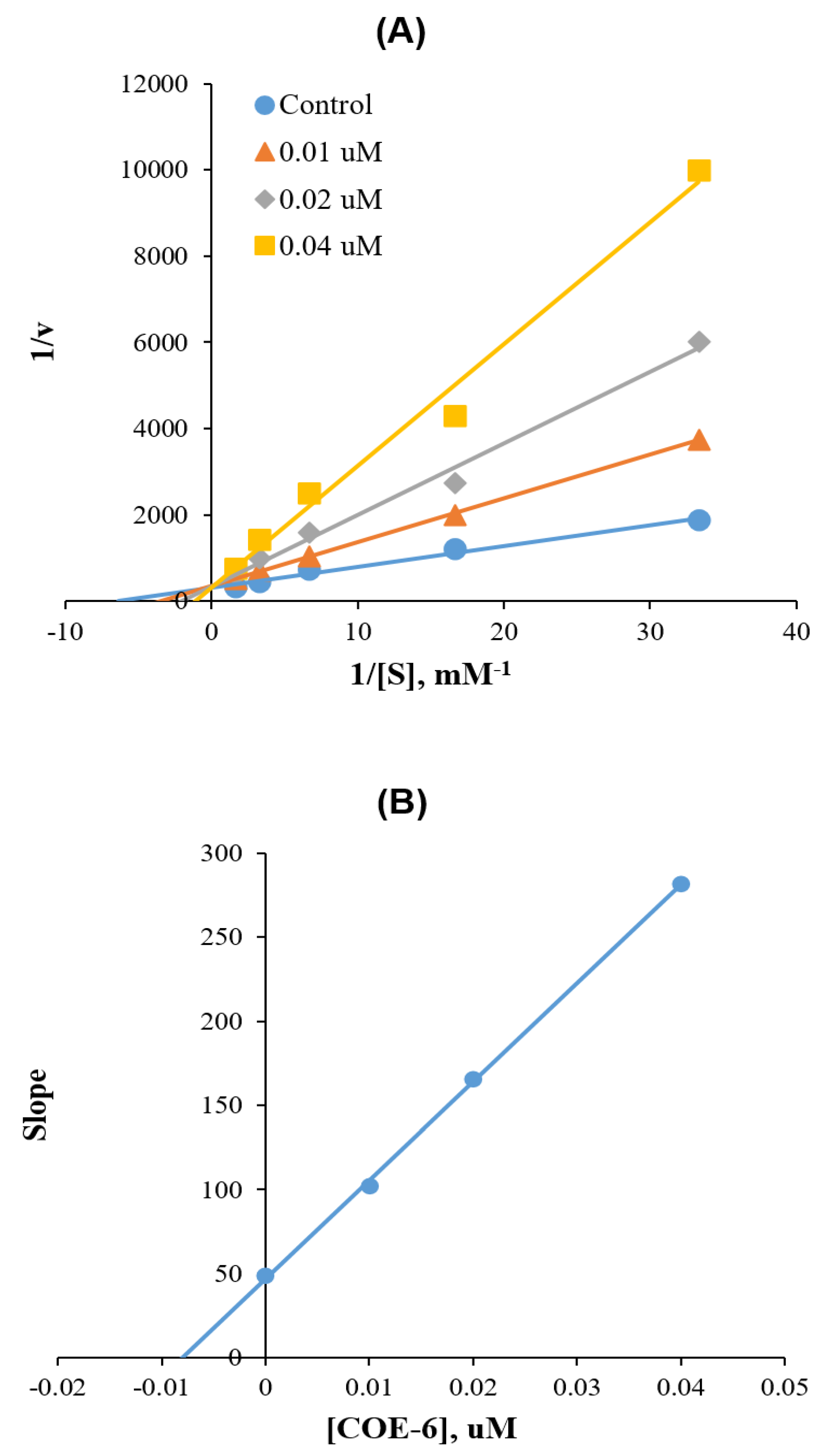
2.4. Kinetics of MAO-B Inhibitions
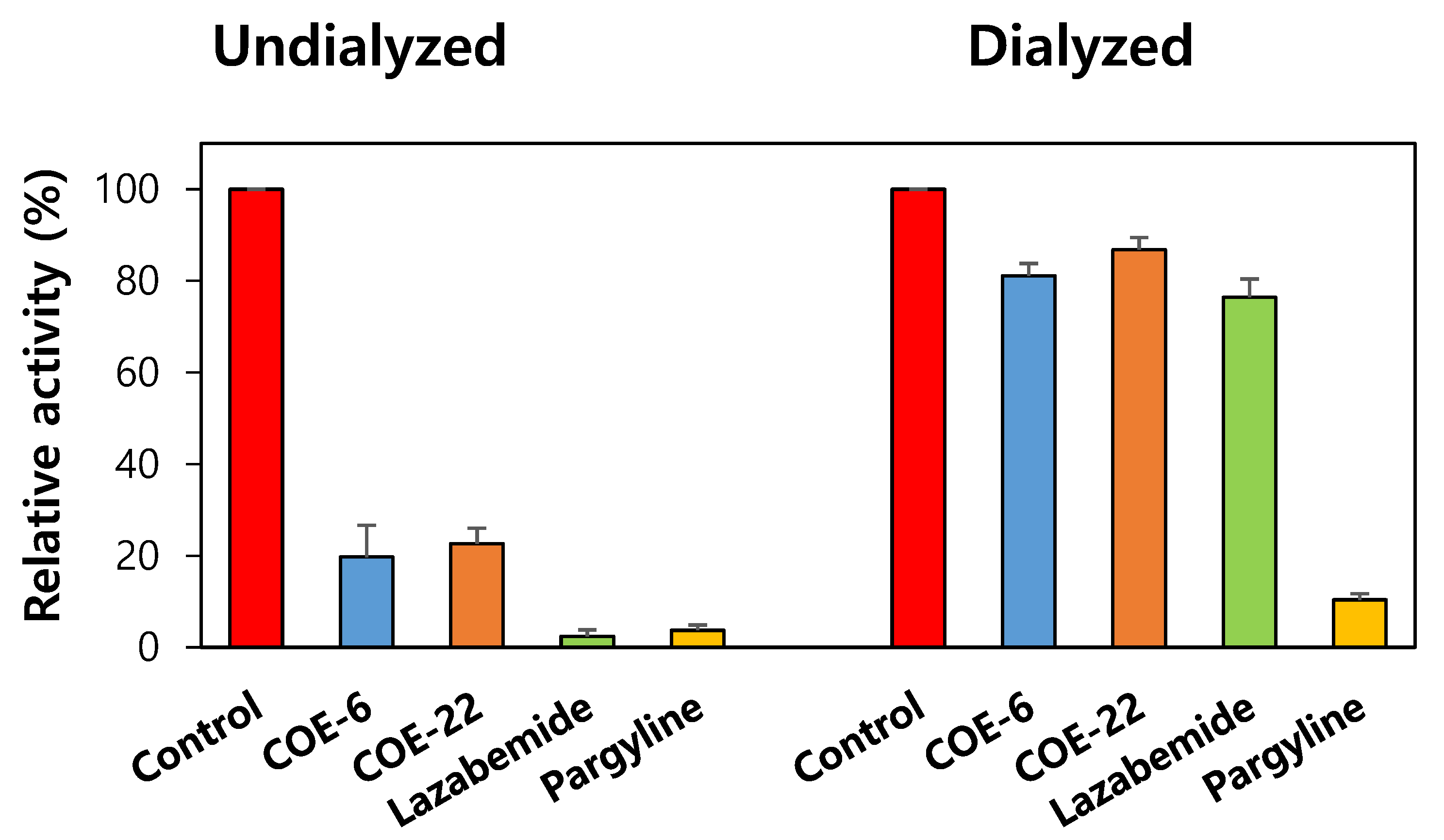
2.5. Reversibility Studies
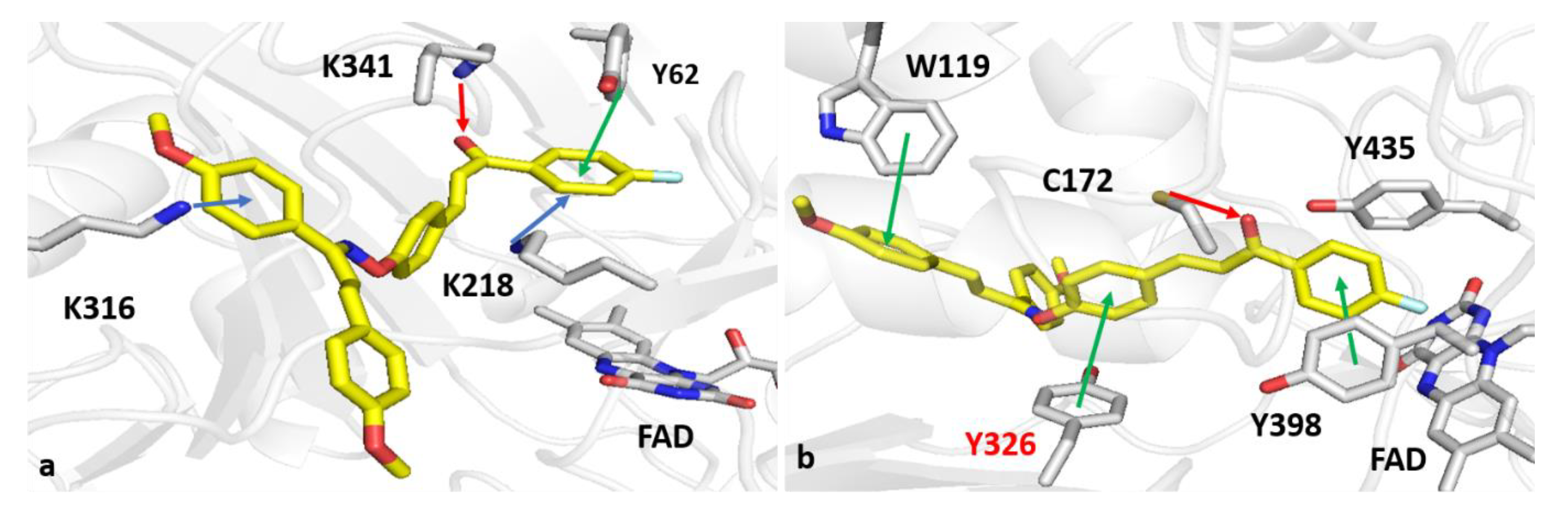
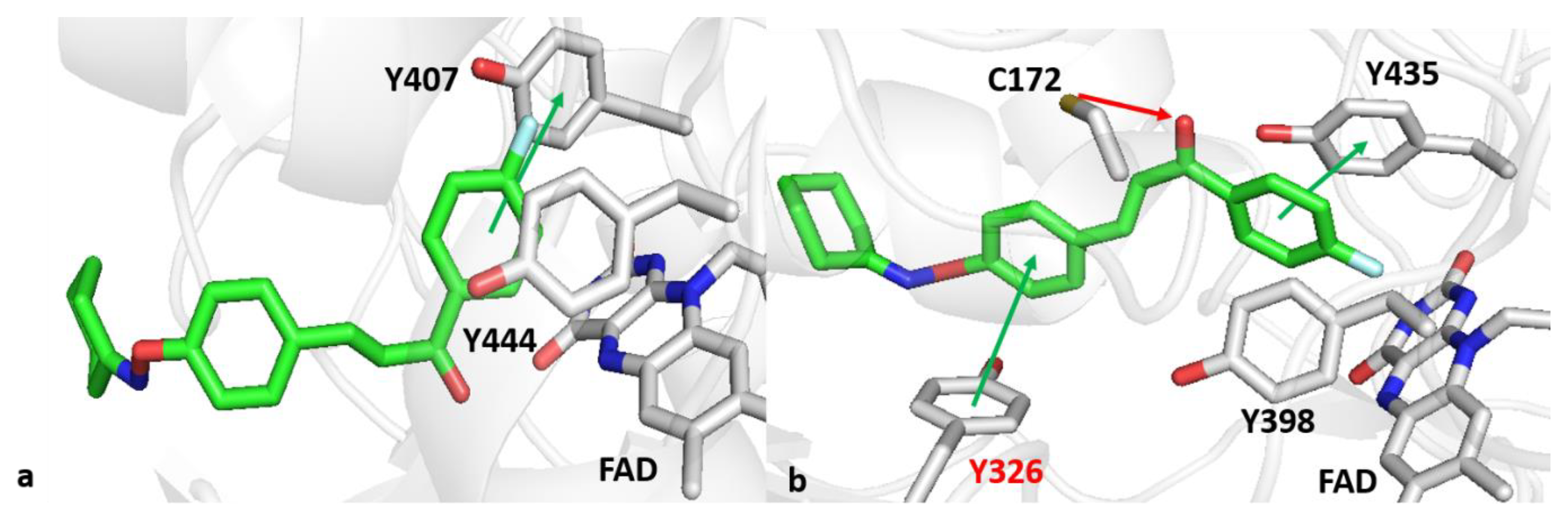
2.6. Computational Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Enzyme Assays
3.2. Analysis of Enzyme Inhibitions and Kinetics
3.3. Analysis of Inhibitor Reversibility
3.4. Computational Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangialasche, F.; Solomon, A.; Winblad, B.; Mecocci, P.; Kivipelto, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-Y. One-compound-multiple-targets strategy to combat Alzheimer’s disease. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5260–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Buccafusco, J.J. Multi-functional drugs for various CNS targets in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Mathew, G.E.; Uddin, M.S.; Inasu, S.T.; Kim, H.; Marathakam, A.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Carradori, S. Emerging therapeutic potentials of dual-acting MAO and AChE inhibitors in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2019, 352, e1900177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Matera, R.; Minarini, A.; Rosini, M.; Melchiorre, C. Alzheimer’s disease new approaches to drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Cavalli, A.; Valgimigli, L.L.; Bartolini, M.; Rosini, M.; Andrisano, V.; Recanatini, M.; Melchiorre, C. Multi-target-directed drug design strategy: From a dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitor to a trifunctional compound against Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 6446–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Maruyama, W.; Naoi, M. Neuropharmacological, neuroprotective and amyloid precursor processing properties of selective MAO-B inhibitor antiparkinsonian drug, rasagiline. Drugs Today 2005, 41, 369–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, A.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Capsoni, S.; Andrisano, V.; Bartolini, M.; Margotti, E.; Cattaneo, A.; Recanatini, M.; Melchiorre, C. A small molecule targeting the multifactorial nature of Alzheimer’s disease. Angew. Chem. Int. 2007, 46, 3689–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schyf, C.J.; Geldenhuys, W.J.; Youdim, M.B.H. Multifunctional drugs with different CNS targets for neuropsychiatric disorders. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimmock, J.R.; Elias, D.W.; Beazely, M.A.; Kandepu, N.M. Bioactivities of chalcones. Curr. Med. Chem. 1999, 6, 1125–1149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Suresh, J.; Anbazhagan, S.; Paulraj, J.; Krishnan, G.K. Heteroaryl chalcones: Mini review about their therapeutic voyage. BioMed. Prev. Nutr. 2014, 4, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandial, D.D.; Blair, C.A.; Zhang, S.; Krill, L.S.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zi, X. Molecular targeted approaches to cancer therapy and prevention using chalcones. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2014, 14, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Anand, A.; Kumar, V. Recent developments in biological activities of chalcones: A mini review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, D.K.; Bharti, S.K.; Asati, V. Chalcone scaffold as anti-infective agents: Structural and molecular target perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 496–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Haridas, A.; Suresh, J.; Mathew, G.E.; Ucar, G.; Jayaprakash, V. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory actions of chalcones: A mini review. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, F.; Fioravanti, R.; Bolasco, A.; Chimenti, P.; Secci, D.; Rossi, F.; Yáñez, M.; Orallo, F.; Ortuso, F.; Alcaro, S. Chalcones: A valid scaffold for monoamine oxidases inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.J.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A.; Bergh, J.J.; Lourens, A.C.U. Selected furanochalcone as inhibitors of monoamine oxidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4985–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, G.; Ahn, S.; Kim, B.G.; Park, H.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, A.H.; Koh, D.; Chong, Y.; Ahn, H.; Lim, Y. Chromenyl chalcones with inhibitory effects on monoamine oxidase B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7890–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Camilo, N.; Salas, C.O.; Sanhueza, C.; Espinosa-Bustos, C.; Sepulveda-Boza, S.; Reyes-Parada, M.; Gonzalez-Nilo, F.; Caroli-Rezende, M.; Fierro, A. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular simulation of chalcones and aurones as selective MAO-B inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 85, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Jang, B.K.; Cho, N.; Park, J.H.; Yeon, S.K.; Ju, E.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, G.; Pae, A.M.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Synthesis of a series of unsaturated ketone derivatives as selective and reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6486–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B. Unraveling the structural requirements of chalcone chemistry towards monoamine oxidase inhibition. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Mathew, G.E.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Suresh, J.; Vilapurathu, J.K.; Prakasan, A.; Suresh, J.K.; Thomas, A. Development of fluorinated methoxylated chalcones as selective monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors: Synthesis, biochemistry and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 62, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Uçar, G.; Yabanoğlu-Çiftçi, S.; Baysal, I.; Suresh, J.; Mathew, G.E.; Vilapurathu, J.K.; Nadeena, A.M.; Nabeela, P.; Lakshmi, V.; et al. Development of fluorinated thienylchalcones as monoamine oxidase-b inhibitors: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies. Lett. Org. Chem. 2015, 12, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Mathew, G.E.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Suresh, J.; Mathew, S. Potent and selective monoamine oxidase-b inhibitory activity: Fluoro- vs trifluoromethyl-4-hydroxylated chalcone derivatives. Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Haridas, A.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Adeniyi, A.A.; Soliman, M.E.S.; Joy, M.; Mathew, G.E.; Lakshmanan, B.; Jayaprakash, V. Exploration of chlorinated thienyl chalcones: A new class of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 680–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Haridas, A.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Joy, M.; Mathew, G.E.; Lakshmanan, B.; Jayaprakash, V. Synthesis, biochemistry, and computational studies of brominated thienyl chalcones: A new class of reversible MAO-B inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Uçar, G.; Mathew, G.E.; Mathew, S.; Purapurath, P.K.; Moolayil, F.; Mohan, S.; Varghese Gupta, S. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity: Methyl- versus chloro-chalcone derivatives. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, R.; Manju, S.L.; Uçar, G.; Baysal, I.; Mathew, B. Identification of indole based chalcones: Discovery of potent, selective and reversible class of MAO-B inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2016, 349, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Uçar, G.; Raphael, C.; Mathew, G.E.; Joy, M.; Machaba, K.E. Characterization of thienylchalcones as hMAO-B inhibitors: Synthesis, biochemistry and molecular dynamics studies. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 11113–11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, R.; Baek, S.C.; Manju, S.L.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Imidazole bearing chalcones as new class of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, J.; Baek, S.C.; Ramakrishnan, S.P.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Discovery of potent and reversible MAO-B inhibitors as furanochalcones. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Baek, S.C.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Lee, J.P.; Mathew, G.E.; Jayanthi, S.; Devaraji, D.; Raphael, C.; Vinod, D.; Kondarath, S.S.; et al. Potent and highly selective dual-targeting monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors: Fluorinated chalcones of morpholine versus imidazole. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2019, 352, e1800309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, R.; Petzer, J.P.; Petzer, A.; Aahraf, U.M.; Atari, E.; Alasmari, F.; Kumarasamy, S.; Sari, Y.; Khali, A. SAR and molecular mechanism studies of monoamine oxidase inhibition by selected chalcone analogs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayan, B.; Baek, S.C.; Kannappan, N.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O.; Subburaju, T.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Ethoxylated head of chalcones as a new class of multi-targeted MAO inhibitors. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 6614–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeta Baek, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Rangarajan, T.M.; Ayushee; Singh, R.P.; Singh, M.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Ethyl acetohydroxamate incorporated chalcones: Unveiling a novel class of chalcones for multitarget monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors against Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 8, 643–654. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.M.; Petrassi, H.M.; Palaninathan, S.K.; Mohamedmohaideen, N.N.; Purkey, H.E.; Nichols, C.; Chiang, K.P.; Walkup, T.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Sharpless, K.B.; et al. Bisaryloxime ethers as potent inhibitors of transthyretin amyloid fibril formation. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Kondo, M.; Kida, M.; Nakao, M.; Iwahi, T.; Nishi, T.; Noji, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Nozaki, Y. Cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel broad-spectrum cephalosporin: In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 19, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibl, A.M.; Ishag, A.H.; Durgham, S.M. Comparative in vitro antibacterial activity of aztreonam against clinical isolates of gram-negative bacteria. Chemotheraphy 1989, 35, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryskier, A. Roxithromycin: Review of its antimicrobial activity. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1998, 41, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carty, E.; Macey, M.; Mccartney, S.A.; Rampton, D.S. Ridogrel, a dual thromboxane synthase inhibitor and receptor antagonist: Anti-inflammatory profile in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hoogdalem, E.J.; van den Hoven, W.E.; Terpstra, I.J.; van Zijtveld, J.; Verschoor, J.S.C.; Visser, J.N. Nail penetration of the antifungal agent oxiconazole after repeated topical application in healthy volunteers, and the effect of acetylcysteine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 5, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strupczewski, J.T.; Allen, R.C.; Gardner, B.A.; Schmid, B.L.; Stache, U.; Glamkowski, E.J.; Jones, M.C.; Ellis, D.B.; Huger, F.P.; Dunn, R.W. Synthesis and neuroleptic activity of 3-(1-substituted-4-piperidinyl)-1,2-benzisoxazoles. J. Med. Chem. 1985, 28, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeta Rajendran, V.; Rangarajan, T.M.; Ayushee; Singh, R.P.; Singh, M. Synthesis of novel chalcones through palladium-catalyzed C–O cross-coupling reaction of bromo-chalcones with ethyl acetohydroxamate and their antiplasmodial evaluation against Plasmodium falcipuram in vitro. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeta Rangarajan, T.M.; Kaushik, K.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, M.; Singh, R.P. Efficient solvent- and temperature-tuned access to aldoxime ethers and phenolic functions by Pd-catalyzed C–O cross-coupling of aldoximes with aryl bromides and bromo-chalcones. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeta Rangarajan, T.M.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, M. An easy access to oxime ethers by Pd-catalyzed C–O cross-coupling of activated aryl bromides with ketoximes and chalcone oximes. Chin. J. Chem. 2020, 38, 830–836. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, B.; Carradori, S.; Guglielmi, P.; Uddin, M.S.; Kim, H. New aspects of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors. The key role of halogens to open the golden door. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiatordi, G.F.; Alberga, D.; Pisani, L.; Gadaleta, D.; Trisciuzzi, D.; Farina, R.; Carotti, A.; Lattanzi, G.; Catto, M.; Nicolotti, O. A rational approach to elucidate human monoamine oxidase molecular selectivity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 101, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Baek, S.C.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Lee, J.P.; Joy, M.; Rilda, P.R.A.; Randev, R.V.; Nithyamol, P.; Vijayan, V.; Inasu, S.T.; et al. Selected aryl thiosemicarbazones as a new class of multi-targeted monoamine oxidase inhibitors. MedChemComm 2018, 9, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Ryu, H.W.; Kang, M.G.; Park, D.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, H. Potent selective monoamine oxidase B inhibition by maackiain, a pterocarpan from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4714–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.C.; Lee, H.W.; Ryu, H.W.; Kang, M.G.; Park, D.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, M.L.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, H. Selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by hispidol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 15, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Feather-Stone, R.M., Jr. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.C.; Park, M.H.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, J.P.; Kang, M.G.; Park, D.; Park, C.M.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, H. Rhamnocitrin isolated from Prunus padus var. seoulensis: A potent and selective reversible inhibitor of human monoamine oxidase A. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 28, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.Y.; Ma, J.; Kondou, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamashita, E.; Tsukihara, T. Structure of human monoamine oxidase A at 2.2-A resolution: The control of opening the entry for substrates/inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5739–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Wang, J.; Pisani, L.; Caccia, C.; Carotti, A.; Salvati, P.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective non-covalent inhibitors: Safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5848–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2018-2, Prime; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Schrödinger Release 2018-2: Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |

| Chalcone Oxime Ethers (COEs) | Residual Activity (%) | IC50 (µM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAO-A (1.0 µM) | MAO-B (1.0 µM) | AChE (10 µM) | MAO-A | MAO-B | AChE | SIb | |
| Chalcone-ketoxime ethers | |||||||
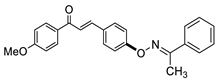 COE-1 | 94.4 ± 2.99 | 29.9 ± 5.25 | 77.6 ± 2.64 | >10 | 0.28 ± 0.041 | >40 | >35.7 |
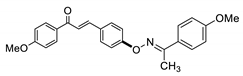 COE-2 | 69.9 ± 0.51 | 27.6 ± 2.44 | 66.5 ± 3.36 | >10 | 0.26 ± 0.055 | 15.2 ± 0.55 | >38.5 |
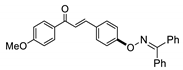 COE-3 | 87.3 ± 1.00 | 21.6 ± 4.88 | 77.1 ± 0.66 | >10 | 0.048 ± 0.021 | >40 | >208.3 |
 COE-4 | 83.7 ± 1.54 | 4.31 ± 1.22 | 62.1 ± 1.51 | 19.3 ± 0.21 | 0.059 ± 0.012 | >40 | 32.7 |
 COE-5 | 95.1 ± 2.68 | 57.5 ± 7.01 | 46.5 ± 0.71 | >10 | 1.12 ± 0.10 | 7.06 ± 1.50 | >8.9 |
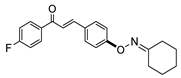 COE-6 | 76.8 ± 3.98 | −1.06 ± 1.84 | 79.4 ± 3.97 | 4.00 ± 0.021 | 0.018 ± 0.0020 | >40 | 222.2 |
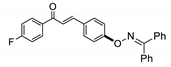 COE-7 | 91.7 ± 6.43 | 2.48 ± 0.15 | 76.2 ± 1.02 | 11.0 ± 1.22 | 0.028 ± 0.0016 | >40 | 392.9 |
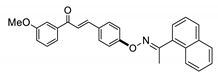 COE-8 | 68.6 ± 2.74 | 10.5 ± 0.21 | 70.7 ± 3.26 | 7.68 ± 0.34 | 0.042 ± 0.021 | >40 | 182.9 |
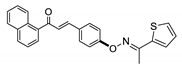 COE-9 | 71.4 ± 0.51 | 9.91 ± 1.83 | 46.7 ± 4.27 | 7.64 ± 0.16 | 0.037 ± 0.0057 | 8.39 ± 2.14 | 20.6 |
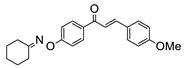 COE-10 | 67.1 ± 2.02 | 21.6 ± 1.22 | 47.6 ± 0.93 | >10 | 0.21 ± 0.010 | 9.42 ± 0.031 | >47.6 |
 COE-11 | 86.0 ± 6.58 | 68.5 ± 1.83 | 87.2 ± 0.47 | >10 | 1.82 ± 0.022 | >40 | >5.5 |
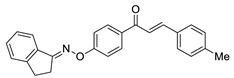 COE-12 | 95.7 ± 2.02 | 40.5 ± 0.10 | 72.0 ± 1.95 | >10 | 0.27 ± 0.056 | >40 | >37.0 |
 COE-13 | 46.2 ± 1.07 | 31.9 ± 9.75 | 57.6 ± 1.96 | 0.88 ± 0.030 | 0.13 ± 0.0069 | >40 | 6.8 |
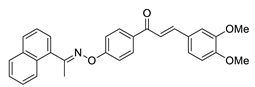 COE-14 | 91.1 ± 3.84 | 63.7 ± 1.39 | 62.2 ± 4.19 | >10 | 1.58 ± 0.031 | 13.2 ± 0.84 | >6.3 |
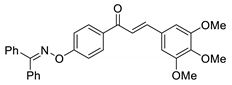 COE-15 | 95.0 ± 3.03 | 36.9 ± 9.49 | 56.9 ± 1.40 | >10 | 0.95 ± 0.029 | >40 | >10.5 |
| Aryl chalcone oxime ethers | |||||||
 COE-16 | 93.4 ± 3.44 | 97.8 ± 0.08 | 77.3 ± 6.62 | >10 | >10 | >40 | - |
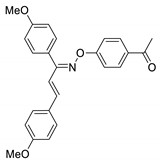 COE-17 | 80.9 ± 2.01 | 17.6 ± 2.77 | 80.3 ± 1.39 | >10 | 0.72 ± 0.015 | >40 | >13.9 |
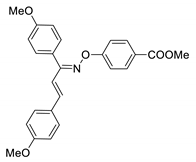 COE-18 | 88.1 ± 0.99 | 33.3 ± 0.52 | 58.3 ± 5.30 | >10 | 0.85 ± 0.12 | 10.6 ± 0.26 | >11.8 |
| Chalcone-chalconeoxime ethers | |||||||
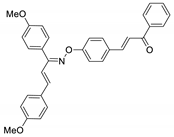 COE-19 | 85.3 ± 0.99 | 19.2 ± 3.06 | 39.0 ± 0.45 | >10 | 0.32 ± 0.015 | 5.35 ± 0.68 | >31.3 |
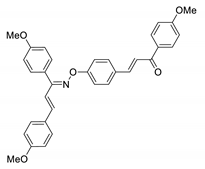 COE-20 | 89.7 ± 4.51 | 21.0 ± 0.42 | 60.6 ± 5.74 | >10 | 0.35 ± 0.011 | 11.2 ± 1.33 | >28.6 |
 COE-21 | 85.8 ± 1.47 | −2.19 ± 0.08 | 49.4 ± 2.90 | 15.9 ± 0.59 | 0.036 ± 0.0019 | 9.65 ± 1.20 | 441.7 |
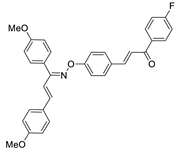 COE-22 | 81.8 ± 0.99 | 5.47 ± 0.21 | 35.7 ± 0.64 | 21.8 ± 1.55 | 0.028 ± 0.0042 | 4.39 ± 2.68 | 778.6 |
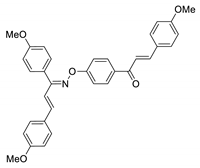 COE-23 | 85.1 ± 4.01 | 25.8 ± 4.78 | 57.3 ± 1.34 | >10 | 0.15 ± 0.021 | 9.16 ± 0.021 | >66.7 |
 COE-24 | 88.9 ± 0.98 | 87.4 ± 2.81 | 72.5 ± 2.91 | >10 | >10 | >40 | - |
| Toloxatone | - | - | - | 0.99 ± 0.080 | - | - | |
| Lazabemide | - | - | - | - | 0.042 ± 0.0028 | - | |
| Clorgyline | - | - | - | 0.0046 ± 0.00055 | 1.90 ± 0.78 | - | |
| Pargyline | - | - | - | 2.43 ± 0.17 | 0.020 ± 0.00071 | - | |
| Tacrine | - | - | - | - | - | 0.20 ± 0.019 | |
| Compound | Docking Score (kcal/mol) | ΔGbinding (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAO-A | MAO-B | MAO-A | MAO-B | |
| COE-6 | −10.128 | −11.728 | −58.64 | −82.65 |
| COE-22 | −7.785 | −13.452 | −60.57 | −87.94 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, J.M.; Rangarajan, T.M.; Chaudhary, R.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, M.; Singh, R.P.; Tondo, A.R.; Gambacorta, N.; Nicolotti, O.; Mathew, B.; et al. Novel Class of Chalcone Oxime Ethers as Potent Monoamine Oxidase-B and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Molecules 2020, 25, 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102356
Oh JM, Rangarajan TM, Chaudhary R, Singh RP, Singh M, Singh RP, Tondo AR, Gambacorta N, Nicolotti O, Mathew B, et al. Novel Class of Chalcone Oxime Ethers as Potent Monoamine Oxidase-B and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2020; 25(10):2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102356
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Jong Min, T. M. Rangarajan, Reeta Chaudhary, Rishi Pal Singh, Manjula Singh, Raj Pal Singh, Anna Rita Tondo, Nicola Gambacorta, Orazio Nicolotti, Bijo Mathew, and et al. 2020. "Novel Class of Chalcone Oxime Ethers as Potent Monoamine Oxidase-B and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors" Molecules 25, no. 10: 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102356
APA StyleOh, J. M., Rangarajan, T. M., Chaudhary, R., Singh, R. P., Singh, M., Singh, R. P., Tondo, A. R., Gambacorta, N., Nicolotti, O., Mathew, B., & Kim, H. (2020). Novel Class of Chalcone Oxime Ethers as Potent Monoamine Oxidase-B and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Molecules, 25(10), 2356. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102356








