Serum Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Intake of Black Ginseng Extracts in Beagle Dogs
Abstract
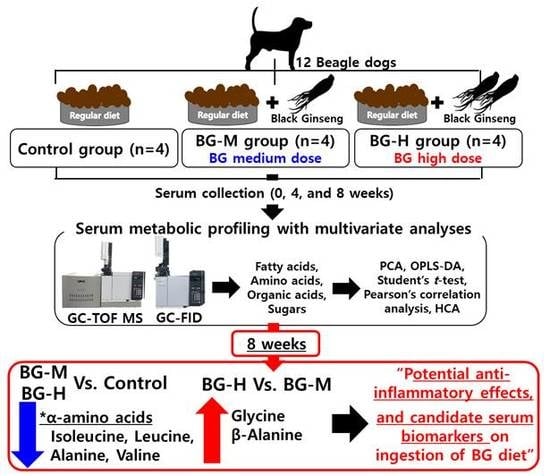
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Serum Metabolic Profiling
2.2. Multivariate Analyses
2.3. Identification of Metabolic Differences
2.4. Correlation between Serum Metabolites
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials
3.2. Preparation of BG, Experimental Design, Serum Collection
3.3. Chemicals and Reagents
3.4. Analysis of Hydrophilic Compounds
3.5. Analysis of LCFAs
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, P.; Shin, C.Y. A comprehensive review of the therapeutic and pharmacological effects of ginseng and ginsenosides in central nervous system. J. Ginseng. Res. 2013, 37, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Min, H. Ginseng, the’immunity boost’: The effects of Panax ginseng on immune system. J. Ginseng. Res. 2012, 36, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramesh, T.; Kim, S.W.; Hwang, S.Y.; Sohn, S.H.; Yoo, S.K.; Kim, S.K. Panax ginseng reduces oxidative stress and restores antioxidant capacity in aged rats. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Song, K.H.; Woo, J.K.; Park, M.H.; Rhee, M.H.; Choi, C.; Oh, S.H. Ginsenoside Rp1 from Panax ginseng exhibits anti-cancer activity by down-regulation of the IGF-1R/Akt pathway in breast cancer cells. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Abid, S.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Panax ginseng Cultivars in Korea and China. Molecules 2020, 25, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.K.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.; Hossain, M.A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Korean red ginseng plays an anti-aging role by modulating expression of aging-related genes and immune cell subsets. Molecules 2020, 25, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saba, E.; Jeon, B.R.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, K.; Goo, Y.K.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, C.K.; Roh, S.S.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Black ginseng extract ameliorates hypercholesterolemia in rats. J. Ginseng. Res. 2016, 40, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Saba, E.; Irfan, M.; Kim, M.; Chan, J.Y.; Jeon, B.S.; Choi, S.K.; Rhee, M.H. The anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of Korean black ginseng. Phytomedicine 2019, 54, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; Han, I.H.; Lee, D.; An, J.M.; Kim, S.N.; Shin, M.S.; Yamabe, N.; Hwang, G.S.; Yoo, H.H.; Choi, S.J.; et al. Beneficial effects of fermented black ginseng and its ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in LLC-PK1 cells. J. Ginseng. Res. 2016, 40, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.R.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, R.; Oh, H.I.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, K.J.; Sung, C.K. Anti-obesity effects of black ginseng extract in high fat diet-fed mice. J. Ginseng. Res. 2013, 37, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Mishra, M.K.; Aggarwal, H. Inflammation, immunity, and cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 6027305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, H.; Hadi, A.; Kord-Varkaneh, H.; Arab, A.; Afshari, M.; Ferguson, A.J.R.; Ghaedi, E. Effects of ginseng supplementation on selected markers of inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; He, G.; Yang, M.; Li, D. Natural products and anti-inflammatory activity. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 15, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shon, D.-H.; Choi, D.-W.; Kim, M.-H. Improvement of anti-inflammation activity of Gardeniae fructus extract by the treatment of β-Glucosidase. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 44, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, M.; Mutlu, E.A.; Benson, M.; Fields, J.Z.; Banan, A.; Keshavarzian, A. Use of herbal preparations in the treatment of oxidant-mediated inflammatory disorders. Complement. Ther. Med. 2007, 15, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Ying, Z.; Xiang, Z.; Hao, D.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ying, X. The anti-inflammation and pharmacokinetics of a novel alkaloid from Portulaca oleracea L. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.F.; Wu, G.Y.; Liao, Y.P.; Hou, Z.P.; Liu, H.J.; Yin, F.G.; Li, T.J.; Huang, R.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Deng, D.; et al. Effects of Chinese herbal ultra-fine powder as a dietary additive on growth performance, serum metabolites and intestinal health in early-weaned piglets. Livest. Sci. 2007, 108, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Wei, R.; Xie, X.; Wang, C.; Fan, S.; Zhang, X.; Su, J.; Liu, J.; Jia, W.; et al. Metabolome and gut microbiota variation with long-term intake of Panax ginseng extracts on rats. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3547–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.; Lopata, A.L.; Dasouki, M.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Metabolomics toward personalized medicine. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2019, 38, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sébédio, J.L. Metabolomics, Nutrition, and Potential Biomarkers of Food Quality, Intake, and Health Status. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 82, 83–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-J.; Cho, C.-W.; Hwang, J.-T.; Son, N.; Choi, J.H.; Shim, G.-S.; Han, C.-K. LC-MS-based metabolomic analysis of serum and livers from red ginseng-fed rats. J. Ginseng. Res. 2013, 37, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.E.; Kim, K.T.; Paik, H.D. Improved antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-adipogenic properties of hydroponic ginseng fermented by Leuconostoc mesenteroides KCCM 12010P. Molecules 2019, 24, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wang, G.J.; Xie, H.T.; Sun, J.G.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, X.L.; Li, H.; Lv, H.; Xu, M.J.; Wang, R. Determination of ginsenoside Rd in dog plasma by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry after solid-phase extraction and its application in dog pharmacokinetics studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 852, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Lee, K.S.; Nagaoka, T.; Tezuka, Y.; Uchiyama, M.; Kadota, S.; Saiki, I. Pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside deglycosylated by intestinal bacteria and its transformation to biologically active fatty acid esters. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, S.; Yu, M.; Lu, X.; Huo, T.; Ge, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, C.; Li, F. Urinary metabonomic study on biochemical changes in chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.M.; Zha, Q.L.; Chen, T.B.; Xiao, S.Y.; Xie, Y.; Luo, P.; Wang, Y.-P.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H. Discovery of markers for discriminating the age of cultivated ginseng by using UHPLC-QTOF/MS coupled with OPLS-DA. Phytomedicine 2018, 45, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Choi, B.-R.; Ma, S.; Lee, J.W.; Jo, I.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, G.-S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.Y. Metabolomics for age discrimination of ginseng using a multiplex approach to HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy, UPLC–QTOF/MS, and GC×GC–TOF/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, I.; Musso, H. New naturally occurring amino acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1983, 22, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, G. Cell and Molecular Biology: Concepts and Experiments, 7th ed.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, S.K.; Oberholzer, V.G. Ginseng--is there a use in clinical medicine? Postgrad. Med. J. 1988, 64, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, H.; Hiai, S.; Odaka, Y.; Yokozawa, T. Studies on the biochemical action of ginseng saponin: I. purification from ginseng extract of the active component stimulating serum protein biosynthesis. J. Biochem. 1975, 77, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, B.; Türler, A.; Schmidt, J.; Nazir, A.; Tsukamoto, T.; Moore, B.A.; Schnurr, C.; Kalff, J.C.; Bauer, A.J. Anti-inflammatory role of glycine in reducing rodent postoperative inflammatory ileus. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varanoske, A.N.; Wells, A.J.; Kozlowski, G.J.; Gepner, Y.; Frosti, C.L.; Boffey, D.; Coker, N.A.; Harat, I.; Hoffman, J.R. Effects of β-alanine supplementation on physical performance, cognition, endocrine function, and inflammation during a 24 h simulated military operation. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Suzuki, I.; Nakamura, T.; Bernier, F.; Aoshima, K.; Oda, Y. Identification of a new plasma biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease using metabolomics technology. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, M.; Du, G.; Zhong, G.; Yan, D.; Zeng, H.; Cai, W. Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-based metabolomic profiling reveals alterations in mouse plasma and liver in response to fava beans. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, W.-K.; So, K.M.; Kim, J.K. Trial data of the anti-obesity potential of a high resistant starch diet for canines using Dodamssal rice and the identification of discriminating markers in feces for metabolic profiling. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, H.-E.; Yoon, D.; Lee, B.; Kim, J.G.; Im, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, W.-K.; Kim, J.K. Serum Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Intake of Black Ginseng Extracts in Beagle Dogs. Molecules 2020, 25, 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163759
Kim YJ, Lee DY, Park H-E, Yoon D, Lee B, Kim JG, Im K-H, Lee Y-S, Lee W-K, Kim JK. Serum Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Intake of Black Ginseng Extracts in Beagle Dogs. Molecules. 2020; 25(16):3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163759
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ye Jin, Dae Young Lee, Ho-Eun Park, Dahye Yoon, Bumkyu Lee, Jae Geun Kim, Kyung-Hoan Im, Young-Seob Lee, Wan-Kyu Lee, and Jae Kwang Kim. 2020. "Serum Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Intake of Black Ginseng Extracts in Beagle Dogs" Molecules 25, no. 16: 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163759
APA StyleKim, Y. J., Lee, D. Y., Park, H.-E., Yoon, D., Lee, B., Kim, J. G., Im, K.-H., Lee, Y.-S., Lee, W.-K., & Kim, J. K. (2020). Serum Metabolic Profiling Reveals Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Intake of Black Ginseng Extracts in Beagle Dogs. Molecules, 25(16), 3759. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163759