Cu(I) Complexes of Multidentate N,C,N- and P,C,P-Carbodiphosphorane Ligands and Their Photoluminescence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
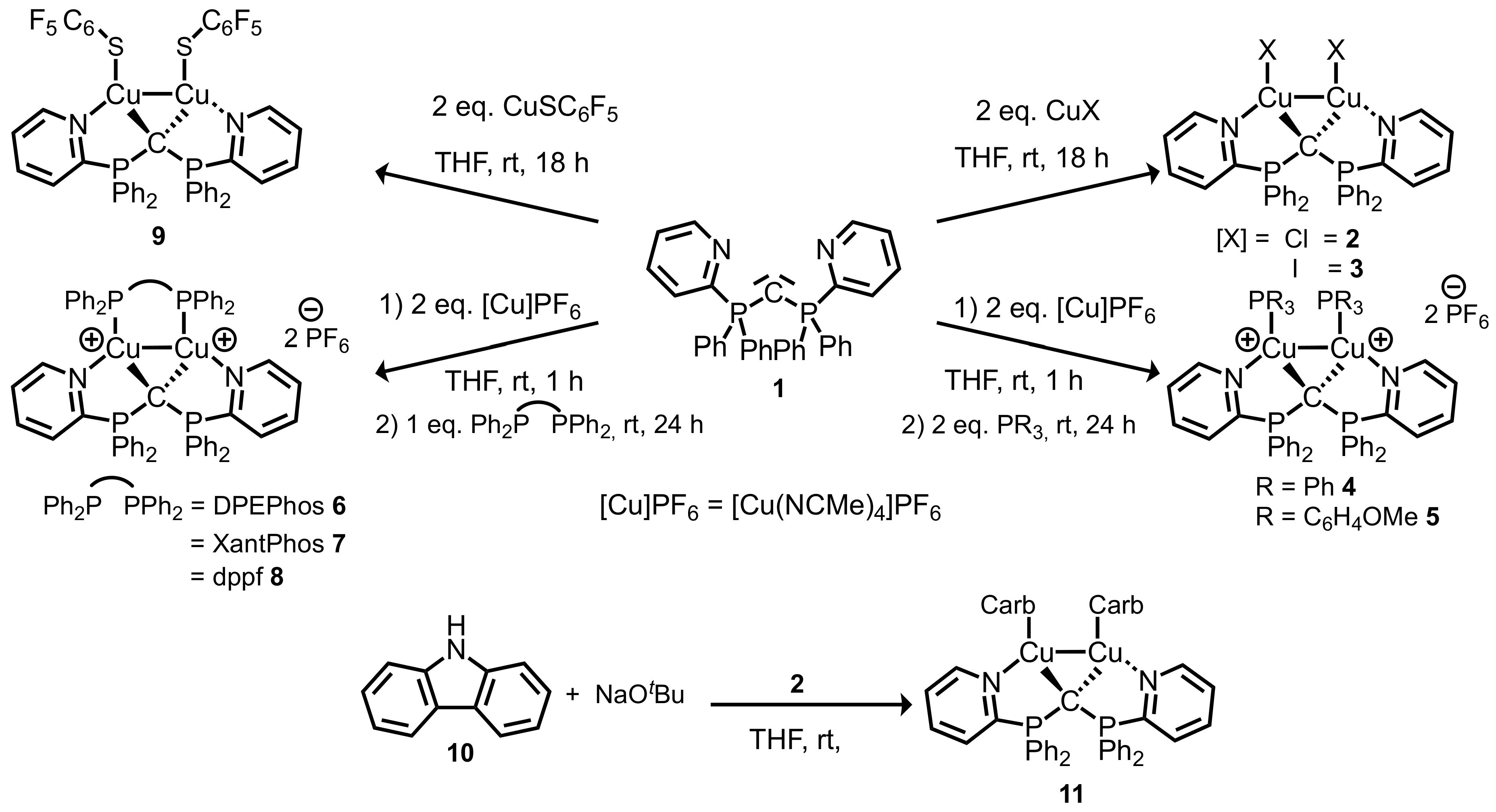
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of N,C,N-CDP Complexes
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of P,C,P–CDP Complexes
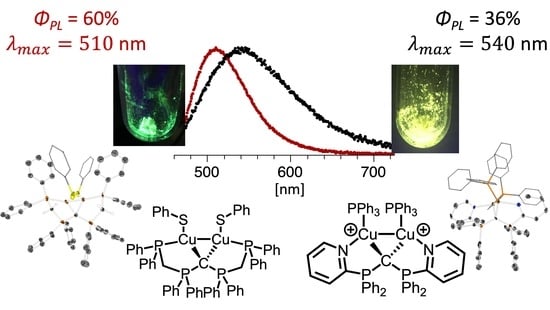
2.3. Photophysical Characterization of Selected CDP Complexes
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramirez, F.; Desai, N.B.; Hansen, B.; McKelvie, N. HEXAPHENYLCARBODIPHOSPHORANE, (C6H5)3PCP(C6H5)3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 3539–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonner, R.; Frenking, G. Divalent Carbon(0) Chemistry, Part 1: Parent Compounds. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3260–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonner, R.; Frenking, G. Divalent Carbon(0) Chemistry, Part 2: Protonation and Complexes with Main Group and Transition Metal Lewis Acids. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonner, R.; Frenking, G. C(NHC)2: Divalent Carbon(0) Compounds with N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands-Theoretical Evidence for a Class of Molecules with Promising Chemical Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8695–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenking, G.; Tonner, R. Divalent carbon(0) compounds. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 597–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonner, R.; Öxler, F.; Neumüller, B.; Petz, W.; Frenking, G. Carbodiphosphoranes: The Chemistry of Divalent Carbon(0). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 8038–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, R.; Knoll, F.; Schöler, H.; Wihler, H.-D. Vereinfachte Synthese von Bis(triphenylphosphoranyliden)methan. Angew. Chem. 1976, 88, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundermeyer, J.; Weber, K.; Peters, K.; Von Schnering, H.G. Modeling Surface Reactivity of Metal Oxides: Synthesis and Structure of an Ionic Organorhenyl Perrhenate Formed by Ligand-Induced Dissociation of Covalent Re2O7. Organometallics 1994, 13, 2560–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, W.; Frenking, G. ChemInform Abstract: Carbodiphosphoranes and Related Ligands. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 42, 49–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, W. Addition compounds between carbones, CL2, and main group Lewis acids: A new glance at old and new compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 291, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, V.H. Modern Ylide Chemistry, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, K.; Jones, N.D.; Ferguson, M.J.; McDonald, R.; Cavell, R.G. Chelate and Pincer Carbene Complexes of Rhodium and Platinum Derived from Hexaphenylcarbodiphosphorane, Ph3PCPPh3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5314–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavell, R.G. Pincer and Chelate Carbodiphosphorane Complexes of Noble Metals. In The Chemistry of Pincer Compounds, 1st ed.; Morales-Morales, D., Jensen, C.M., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, K.; Okitsu, H.; Miwa, H.; Kume, S.; Cavell, R.G.; Mizuta, T. Carbon(0)-Bridged Pt/Ag Dinuclear and Tetranuclear Complexes Based on a Cyclometalated Pincer Carbodiphosphorane Platform. Organometallics 2017, 36, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, W.; Neumuüller, B.; Klein, S.; Frenking, G. Syntheses and Crystal Structures of [Hg{C(PPh3)2}2][Hg2I6] and [Cu{C(PPh3)2}2]I and Comparative Theoretical Study of Carbene Complexes [M(NHC)2] with Carbone Complexes [M{C(PH3)2}2] (M = Cu+, Ag+, Au+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+). Organometallics 2011, 30, 3330–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, W.; Neumüller, B. New platinum complexes with carbodiphosphorane as pincer ligand via ortho phenyl metallation. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttger, S.C.; Poggel, C.; Sundermeyer, J. Ortho-directed Dilithiation of Hexaphenyl- carbodiphosphorane. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallinger, S.; Reitsamer, C.; Schuh, W.; Kopacka, H.; Wurst, K.; Peringer, P. Novel route to carbodiphosphoranes producing a new P,C,P pincer carbene ligand. Chem. Commun. 2007, 5, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsamer, C.; Schuh, W.; Kopacka, H.; Wurst, K.; Peringer, P. Synthesis and Structure of the First Heterodinuclear PCP−Pincer−CDP Complex with a Pd−Au d8−d10Pseudo-Closed-Shell Interaction. Organometallics 2009, 28, 6617–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsamer, C.; Schuh, W.; Kopacka, H.; Wurst, K.; Ellmerer, E.P.; Peringer, P. The First Carbodiphosphorane Complex with Two Palladium Centers Attached to the CDP Carbon: Assembly of a Single-Stranded di-Pd Helicate by the PCP Pincer ligand C(dppm)2. Organometallics 2011, 30, 4220–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsamer, C.; Stallinger, S.; Schuh, W.; Kopacka, H.; Wurst, K.; Obendorf, D.; Peringer, P. Novel access to carbodiphosphoranes in the coordination sphere of group 10 metals: Template synthesis and protonation of PCP pincer carbodiphosphorane complexes of C(dppm)2. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsamer, C.; Hackl, I.; Schuh, W.; Kopacka, H.; Wurst, K.; Peringer, P. Gold(I) and Gold(III) complexes of the [CH(dppm)2]+ and C(dppm)2 PCP pincer ligand systems. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 830, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maser, L.; Herritsch, J.; Langer, R. Carbodiphosphorane-based nickel pincer complexes and their (de)protonated analogues: Dimerisation, ligand tautomers and proton affinities. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 10544–10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maser, L.; Vondung, L.; Langer, R. The ABC in pincer chemistry—From amine- to borylene- and carbon-based pincer-ligands. Polyhedron 2018, 143, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Xie, X.; Burghaus, O.; Sundermeyer, J. Synthesis and Characterization of a N,C,N-Carbodiphosphorane Pincer Ligand and Its Complexes. Organometallics 2019, 38, 3768–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Pan, S.; Sun, X.; Zhao, L.; Frenking, G.; Zhu, C. Cerium–carbon dative interactions supported by carbodiphosphorane. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 16108–16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Yoo, S.; Lampande, R.; Kim, S. Vacuum Deposition. In Handbook of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes; Adachi, C., Hattori, R., Kaji, H., Tsujimura, T., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yersin, H. Highly Efficient OLEDs: Materials Based on Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Deaton, J.C.; Switalski, S.C.; Kondakov, D.Y.; Young, R.H.; Pawlik, T.D.; Giesen, D.J.; Harkins, S.B.; Miller, A.J.M.; Mickenberg, S.F.; Peters, J.C. E-Type Delayed Fluorescence of a Phosphine-Supported Cu2(μ-NAr2)2 Diamond Core: Harvesting Singlet and Triplet Excitons in OLEDs‖. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9499–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leitl, M.J.; Zink, D.M.; Schinabeck, A.; Baumann, T.; Volz, D.; Yersin, H. Copper(I) Complexes for Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence: From Photophysical to Device Properties. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerwieniec, R.; Leitl, M.J.; Homeier, H.H.H.; Yersin, H. Cu(I) complexes. Thermally activated delayed fluorescence. Photophysical approach and material design. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 325, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yersin, H.; Czerwieniec, R.; Shafikov, M.Z.; Suleymanova, A.F. TADF Material Design: Photophysical Background and Case Studies Focusing on CuI and AgI Complexes. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2017, 18, 3508–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Q.-K.; Zhou, L.-J.; Wu, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, C.-Z. Rational Design of Strongly Blue-Emitting Cuprous Complexes with Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence and Application in Solution-Processed OLEDs. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 3910–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gneuß, T.; Leitl, M.J.; Finger, L.H.; Yersin, H.; Sundermeyer, J. A new class of deep-blue emitting Cu(I) compounds—Effects of counter ions on the emission behavior. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 20045–20055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gneuß, T.; Leitl, M.J.; Finger, L.H.; Rau, N.; Yersin, H.; Sundermeyer, J. A new class of luminescent Cu(I) complexes with tripodal ligands—TADF emitters for the yellow to red color range. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 8506–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volz, D.; Chen, Y.; Wallesch, M.; Liu, R.; Fléchon, C.; Zink, D.M.; Friedrichs, J.; Flügge, H.; Steininger, R.; Göttlicher, J.; et al. Bridging the Efficiency Gap: Fully Bridged Dinuclear Cu(I)-Complexes for Singlet Harvesting in High-Efficiency OLEDs. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Ho, S.; Chen, Y.; Peng, C.; Yersin, H.; So, F. Highly Efficient Organic Light-Emitting Diode Using A Low Refractive Index Electron Transport Layer. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igawa, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Kawata, I.; Yashima, M.; Hoshino, M.; Osawa, M. Highly efficient green organic light-emitting diodes containing luminescent tetrahedral copper(i) complexes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Igawa, S.; Yashima, M.; Kawata, I.; Hoshino, M.; Osawa, M. Highly Efficient Green Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Containing Luminescent Three-Coordinate Copper(I) Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10348–10351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Komino, T.; Huang, S.; Matsunami, S.; Goushi, K.; Adachi, C. Triplet Exciton Confinement in Green Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Containing Luminescent Charge-Transfer Cu(I) Complexes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwieniec, R.; Yu, J.; Yersin, H. Blue-Light Emission of Cu(I) Complexes and Singlet Harvesting. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 8293–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, R.; Wu, X.-Y.; Liang, D.; Jia, J.-H.; Lu, C.-Z. A strongly greenish-blue-emitting Cu4Cl4 cluster with an efficient spin–orbit coupling (SOC): Fast phosphorescence versus thermally activated delayed fluorescence. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 6288–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinabeck, A.; Rau, N.; Klein, M.; Sundermeyer, J.; Yersin, H. Deep blue emitting Cu(i) tripod complexes. Design of high quantum yield materials showing TADF-assisted phosphorescence. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 17067–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamansky, S.; Djurovich, P.; Murphy, D.; Abdel-Razzaq, F.; Lee, H.-E.; Adachi, C.; Burrows, P.E.; Forrest, S.R.; Thompson, M. Highly phosphorescent bis-cyclometalated iridium complexes: Synthesis, photophysical characterization, and use in organic light emitting diodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yersin, H.; Rausch, A.F.; Czerwieniec, R.; Hofbeck, T.; Fischer, T. The triplet state of organo-transition metal compounds. Triplet harvesting and singlet harvesting for efficient OLEDs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2622–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yersin, H. Triplet Emitters for OLED Applications. Mechanisms of Exciton Trapping and Control of Emission Properties. Top. Curr. Chem. 2012, 241, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yersin, H.; Finkenzeller, W.J. Triplet Emitters for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes: Basic Properties. In Highly Efficient OLEDs; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, C.; Baldo, M.A.; Thompson, M.; Forrest, S.R. Nearly 100% internal phosphorescence efficiency in an organic light-emitting device. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 5048–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deaton, J.C.; Castellano, F.N. Archetypal Iridium(III) Compounds for Optoelectronic and Photonic Applications. In Iridium(III) in Optoelectronic and Photonics Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 83, pp. 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yan, Z.-P.; Wu, Z.-G.; Zheng, Y.-X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, J.-L.; Pan, Y.; Che, C.-M. Fast Synthesis of Iridium(III) Complexes Incorporating a Bis(diphenylphorothioyl)amide Ligand for Efficient Pure Green OLEDs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7184–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Chow, P.-K.; Kui, S.C.F.; Kwok, C.-C.; Che, C.-M. High-Efficiency Polymer Light-Emitting Devices with Robust Phosphorescent Platinum(II) Emitters Containing Tetradentate Dianionic O∧N∧C∧N Ligands. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6765–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fleetham, T.; Li, J. Efficient and Stable White Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Employing a Single Emitter. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2931–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yersin, H.; Rausch, A.F.; Czerwieniec, R. Organometallic Emitters for OLEDs: Triplet Harvesting, Singlet Harvesting, Case Structures, and Trends. In Physics of Organic Semiconductors; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 371–424. [Google Scholar]
- Baldo, M.A.; O’Brien, D.F.; You, Y.; Shoustikov, A.; Sibley, S.; Thompson, M.; Forrest, S.R. Highly efficient phosphorescent emission from organic electroluminescent devices. Nature 1998, 395, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.-M.; Kwok, C.-C.; Lai, S.-W.; Rausch, A.; Finkenzeller, W.; Zhu, N.; Yersin, H. Photophysical Properties and OLED Applications of Phosphorescent Platinum(II) Schiff Base Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.G. Photochemistry and Photophysics of Coordination Compounds: Platinum. In Photochemistry and Photophysics of Coordination Compounds II; Balzani, V., Campagna, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 205–268. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, L.; Williams, J.A.G. Luminescent Platinum Compounds: From Molecules to OLEDs. In Molecular Organometallic Materials for Optics; Bozec, H., Guerchais, V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 75–111. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Kui, S.C.F.; Ang, W.-H.; Ko, M.-Y.; Chow, P.-K.; Kwong, C.-L.; Kwok, C.-C.; Ma, C.; Guan, X.; Low, K.-H.; et al. Structurally robust phosphorescent [Pt(O^N^C^N)] emitters for high performance organic light-emitting devices with power efficiency up to 126 lm W−1 and external quantum efficiency over 20%. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4819–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Nomura, H.; Geng, Y.; Kim, J.U.; Nakanotani, H.; Adachi, C. Controlling Singlet–Triplet Energy Splitting for Deep-Blue Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, P.K.; Kim, D.; Coropceanu, V.; Brédas, J.-L. Up-Conversion Intersystem Crossing Rates in Organic Emitters for Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence: Impact of the Nature of Singlet vs Triplet Excited States. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turro, N.J. Modern Molecular Photochemistry of Organic Molecules; Benjamin/Cummings Pub. Co.: Melon Park, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.J.; Chen, C.Y.L.; Lin, I.J.B. Synthesis, Structure, and Spectroscopic Properties of Gold(I)-Carbene Complexes. Organometallics 1999, 18, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Ishii, A.; Tsukuda, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Tsubomura, T. Structural and spectroscopic properties of a copper(I)–bis(N-heterocyclic)carbene complex. Dalton Trans. 2009, 6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylova, V.A.; Djurovich, P.I.; Whited, M.T.; Thompson, M. Synthesis and characterization of phosphorescent three-coordinate Cu(i)–NHC complexes. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalano, V.J.; Munro, L.B.; Strasser, C.E.; Samin, A.F. Modulation of Metal–Metal Separations in a Series of Ag(I) and Intensely Blue Photoluminescent Cu(I) NHC-Bridged Triangular Clusters. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 8465–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, V.A.; Djurovich, P.I.; Aronson, J.W.; Haiges, R.; Whited, M.T.; Thompson, M. Structural and Photophysical Studies of Phosphorescent Three-Coordinate Copper(I) Complexes Supported by an N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligand. Organometallics 2012, 31, 7983–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamze, R.; Shi, S.; Kapper, S.C.; Sylvinson, D.; Estergreen, L.; Jung, M.; Tadle, A.; Haiges, R.; Djurovich, P.I.; Peltier, J.L.; et al. “Quick-Silver” from a Systematic Study of Highly Luminescent, Two-Coordinate, d10 Coinage Metal Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8616–8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Jung, M.C.; Coburn, C.; Tadle, A.; Sylvinson, M.R.D.; Djurovich, P.I.; Forrest, S.R.; Thompson, M. Highly Efficient Photo- and Electroluminescence from Two-Coordinate Cu(I) Complexes Featuring Nonconventional N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3576–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamze, R.; Peltier, J.L.; Sylvinson, D.; Jung, M.; Cardenas, J.; Haiges, R.; Soleilhavoup, M.; Jazzar, R.; Djurovich, P.I.; Bertrand, G.; et al. Eliminating nonradiative decay in Cu(I) emitters: >99% quantum efficiency and microsecond lifetime. Sciences 2019, 363, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitl, M.J.; Krylova, V.A.; Djurovich, P.I.; Thompson, M.; Yersin, H. Phosphorescence versus Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence. Controlling Singlet–Triplet Splitting in Brightly Emitting and Sublimable Cu(I) Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16032–16038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, B.; Gómez, V.; Platero-Prats, A.E.; Revés, M.; Echeverría, J.; Cremades, E.; Barragán, F.; Alvarez, S. Covalent radii revisited. Dalton Trans. 2008, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondi, A. van der Waals Volumes and Radii. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloveichik, G.L.; Eisenstein, O.; Poulton, J.T.; Streib, W.E.; Huffman, J.C.; Caulton, K.G. Multiple structural variants of LnCuI(.mu.-X)2CuILn (n = 1, 2). Influence of halide on a “soft” potential energy surface. Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, 3306–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Ferguson, M.J.; McDonald, R.; Cavell, R.G. Rare, Hexatomic, Boat-Shaped, Cross-Linked Bis(iminodiphenylphosphorano)methanediide Pincer Carbon Bridged Photoluminescent Copper Clusters Capped with Methyl or Halide Bridges. Organometallics 2010, 29, 4251–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the selected compounds might be available from the authors. |






| Cu–Cu | C–P1 | C–P2 | Cu–X 1 | Cu–C–Cu | P1–C–P2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2.5525(5) | 1.714(3) | 1.718(2) | 2.1504 | 80.26(9) | 121.51(14) |
| 3 | 2.5727(10) | 1.679(5) | 1.702(5) | 2.4501 | 78.64(19) | 128.5(3) |
| 4 | 2.6039(16) | 1.709(10) | 1.693(9) | 2.186 | 79.3(3) | 126.8(6) |
| 5 | 2.5768(5) | 1.707(3) | 1.710(3) | 2.2024 | 78.29(10) | 123.64(18) |
| 6 | 2.5798(6) | 1.710(4) | 1.712(4) | 2.1903 | 78.77(13) | 124.0(2) |
| 7 | 2.5580(3) | 1.7064(19) | 1.7211(18) | 2.1920 | 77.73(6) | 122.10(11) |
| 8 | 2.5882(16) | 1.730(6) | 1.717(6) | 2.1915 | 80.0(2) | 121.8(4) |
| 9 | 2.6667(7) | 1.710(3) | 1.710(3) | 2.1881 | 83.01(11) | 123.70(17) |
| 11 | 2.671(2) | 1.726(2) | 1.728(2) | 1.886 | 86.14(12) | 120.45(15) |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu–Cu | 2.8681(5) | 2.8816(12) | 2.989(2) |
| C–P1 | 1.718(2) | 1.716(3) | 1.707(12) |
| C–P2 | 1.717(2) | 1.717(2) | 1.718(12) |
| Cu–X 1 | 2.2041 | 2.4396(7) | 2.195 |
| Cu–C–Cu | 90.02(9) | 90.02(9) | 92.0(4) |
| P1–C–P2 | 122.86(14) | 126.3(4) | 126.9(7) |
| 17 | 18 | 14 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1–Cu | 2.304(2) | 2.196(3) | 2.0275 a |
| C1–P1 | 1.745(2) | 1.761(3) | 1.718(2) |
| C1–P2 | 1.745(2) | 1.777(3) | 1.717(2) |
| C2–P1 | 1.745(2) | 1.700(3) | 1.824(2) |
| C2–P3 | 1.846(2) | 1.699(3) | 1.846(2) |
| C3–P2 | 1.800(2) | 1.742(3) | 1.823(2) |
| C3–P4 | 1.847(2) | 1.737(3) | 1.847(2) |
| P3–Cu(1) | 2.2588(6) | 2.2774(9) | 2.2649(7) |
| P4–Cu(2) | 2.2629(6) | 2.2767(9) | 2.2701(7) |
| Cu–X | 2.2753(6) | 2.2509(9) | 2.204 a |
| P1–C1–P2 | 125.26(14) | 124.26(17) | 122.86(14) |
| P1–C2–P3 | 107.70(12) | 115.90(19) | 108.03(12) |
| P2–C3–P4 | 109.53(12) | 120.13(18) | 108.17(12) |
| P3–Cu–P4 | 113.07(2) | 116.76(3) | - |
| C1–Cu–P3 | 94.80(6) | 95.17(8) | 99.71(7) |
| C1–Cu–P4 | 94.87(6) | 94.41(8) | 98.92(7) |
| C1–Cu–X | 108.08(6) | 118.49(3) | 129.95 a |
| P3–Cu–X | 118.72(2) | 113.48(8) | 129.61(3) |
| P4–Cu–X | 120.21(2) | 113.87(3) | 127.98(3) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klein, M.; Demirel, N.; Schinabeck, A.; Yersin, H.; Sundermeyer, J. Cu(I) Complexes of Multidentate N,C,N- and P,C,P-Carbodiphosphorane Ligands and Their Photoluminescence. Molecules 2020, 25, 3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173990
Klein M, Demirel N, Schinabeck A, Yersin H, Sundermeyer J. Cu(I) Complexes of Multidentate N,C,N- and P,C,P-Carbodiphosphorane Ligands and Their Photoluminescence. Molecules. 2020; 25(17):3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173990
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlein, Marius, Nemrud Demirel, Alexander Schinabeck, Hartmut Yersin, and Jörg Sundermeyer. 2020. "Cu(I) Complexes of Multidentate N,C,N- and P,C,P-Carbodiphosphorane Ligands and Their Photoluminescence" Molecules 25, no. 17: 3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173990
APA StyleKlein, M., Demirel, N., Schinabeck, A., Yersin, H., & Sundermeyer, J. (2020). Cu(I) Complexes of Multidentate N,C,N- and P,C,P-Carbodiphosphorane Ligands and Their Photoluminescence. Molecules, 25(17), 3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173990