A New Co-Crystal of Synthetic Drug Rosiglitazone with Natural Medicine Berberine: Preparation, Crystal Structures, and Dissolution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
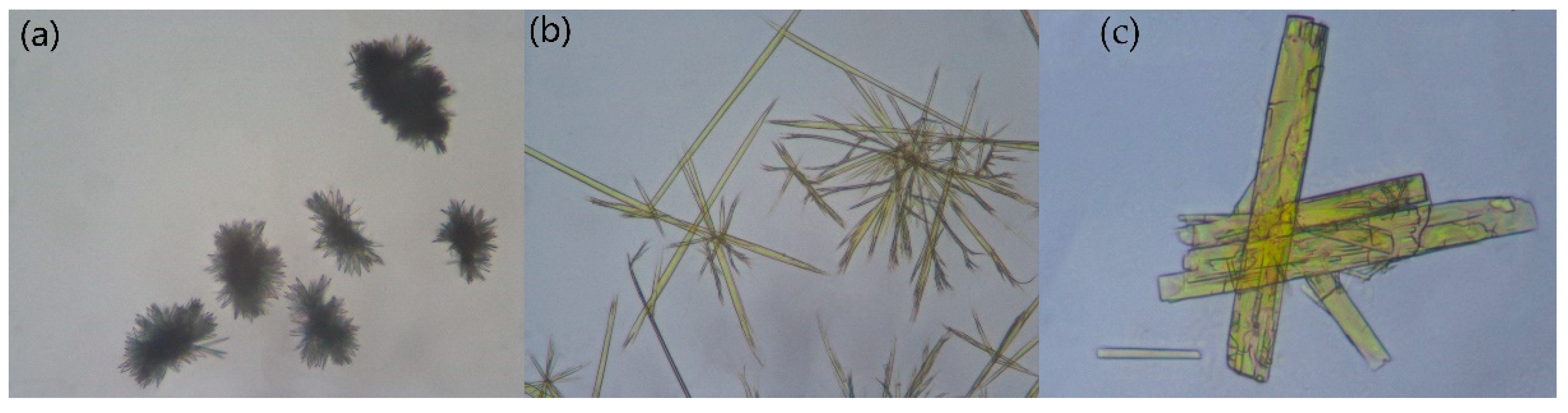
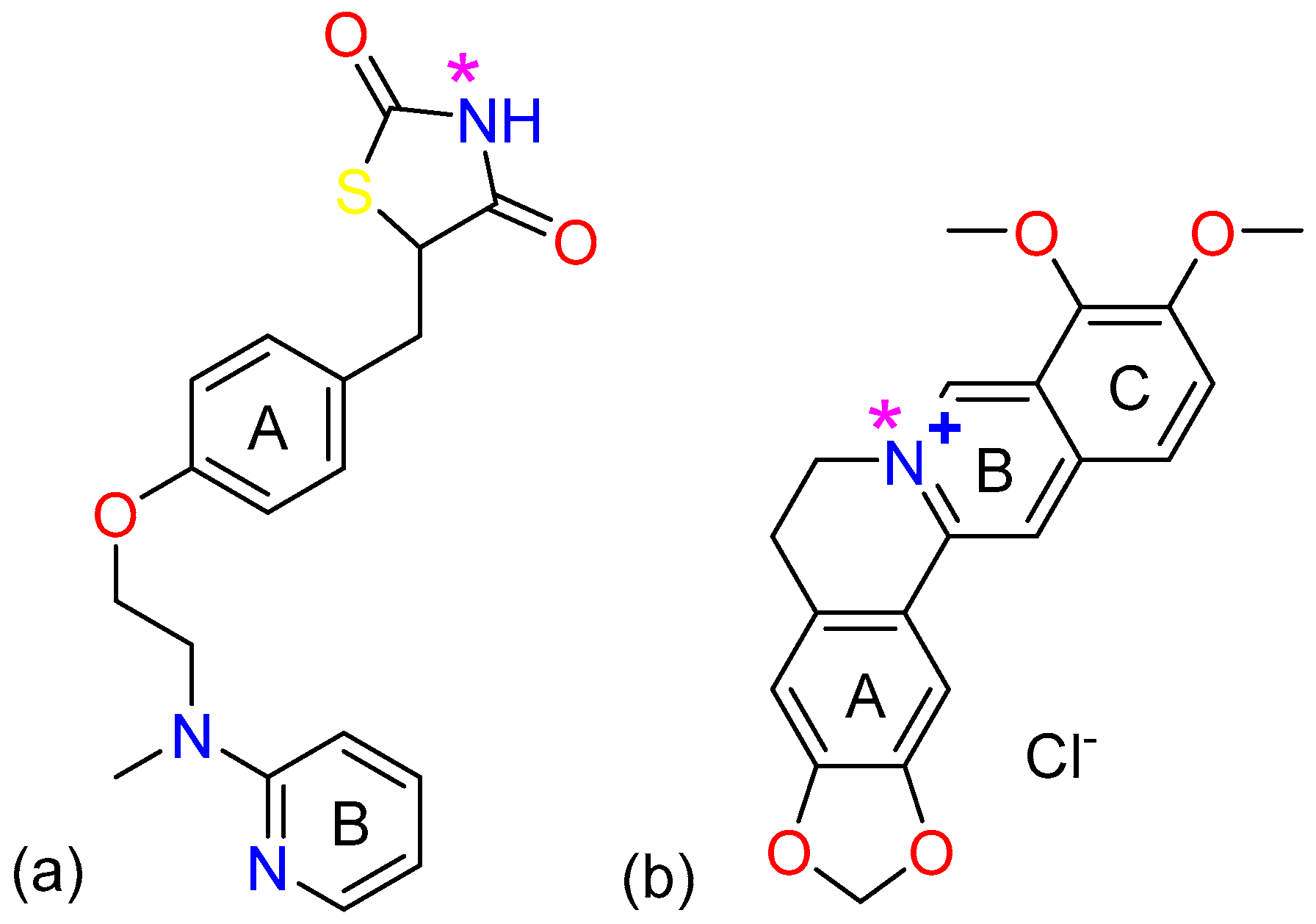
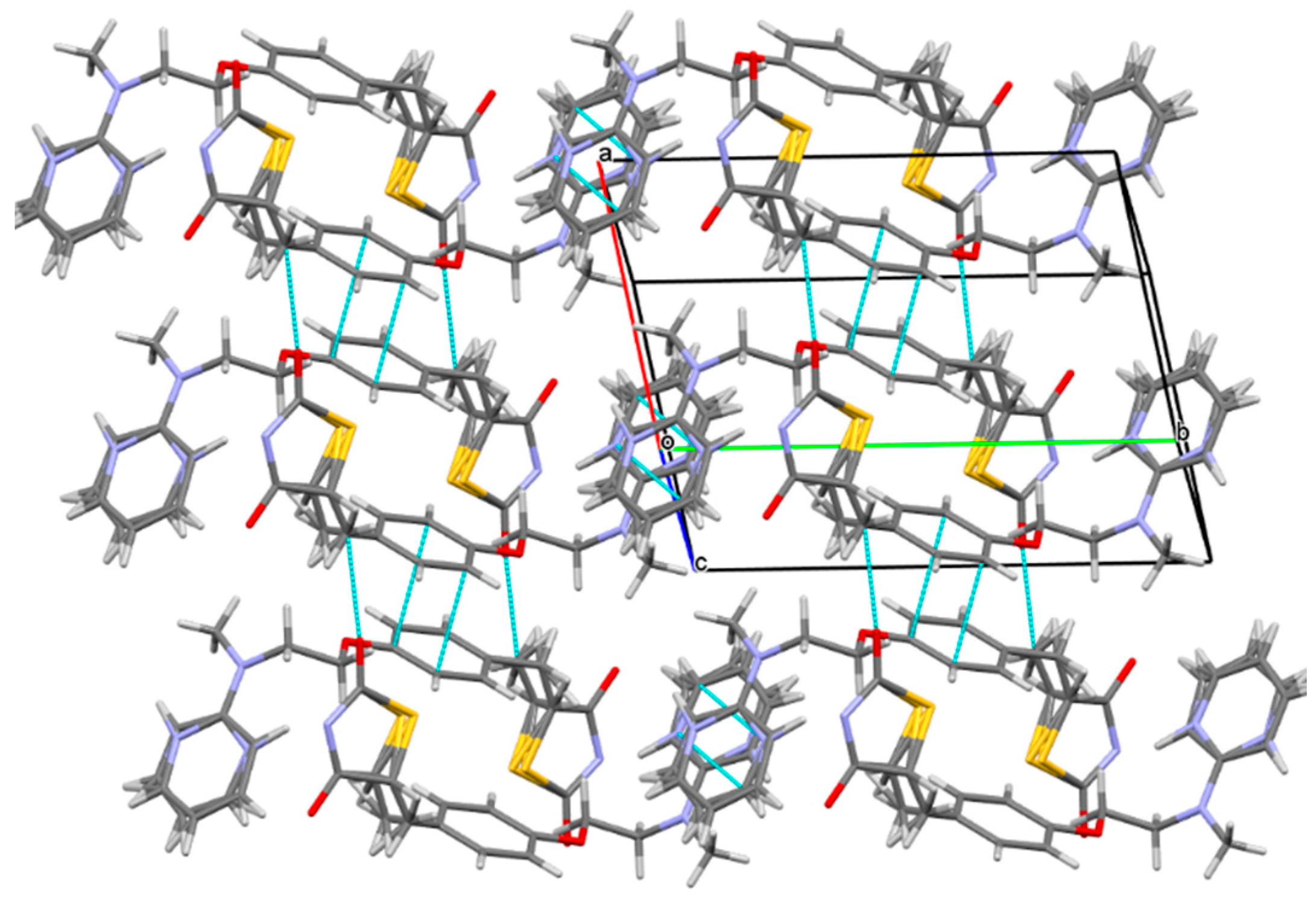
2.1. The Characterization Analysis of the Co-Crystal Structure
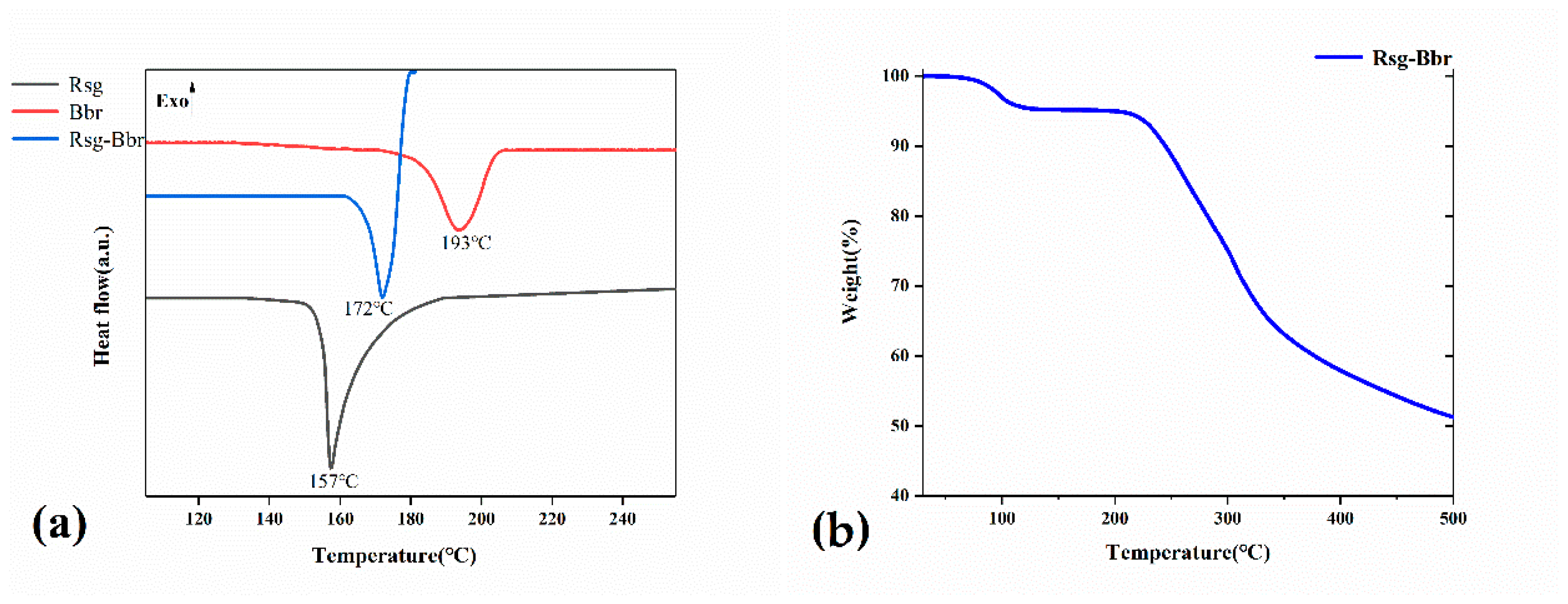
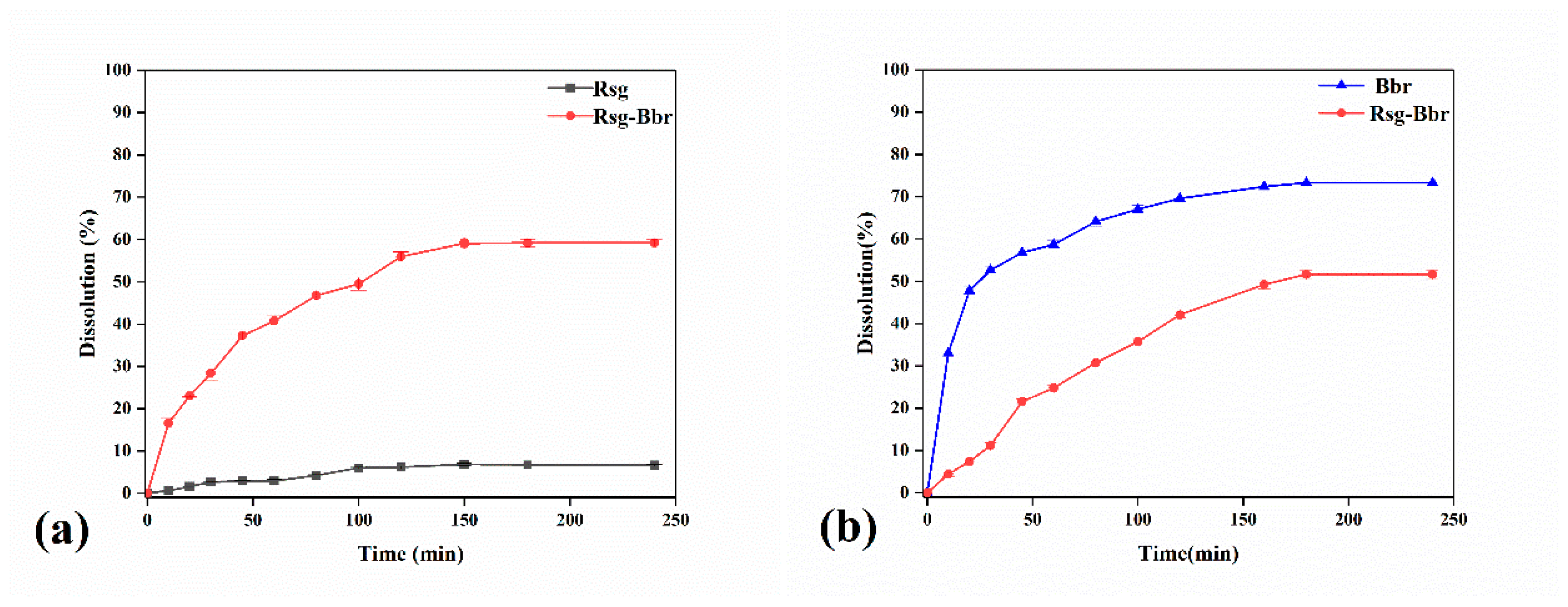
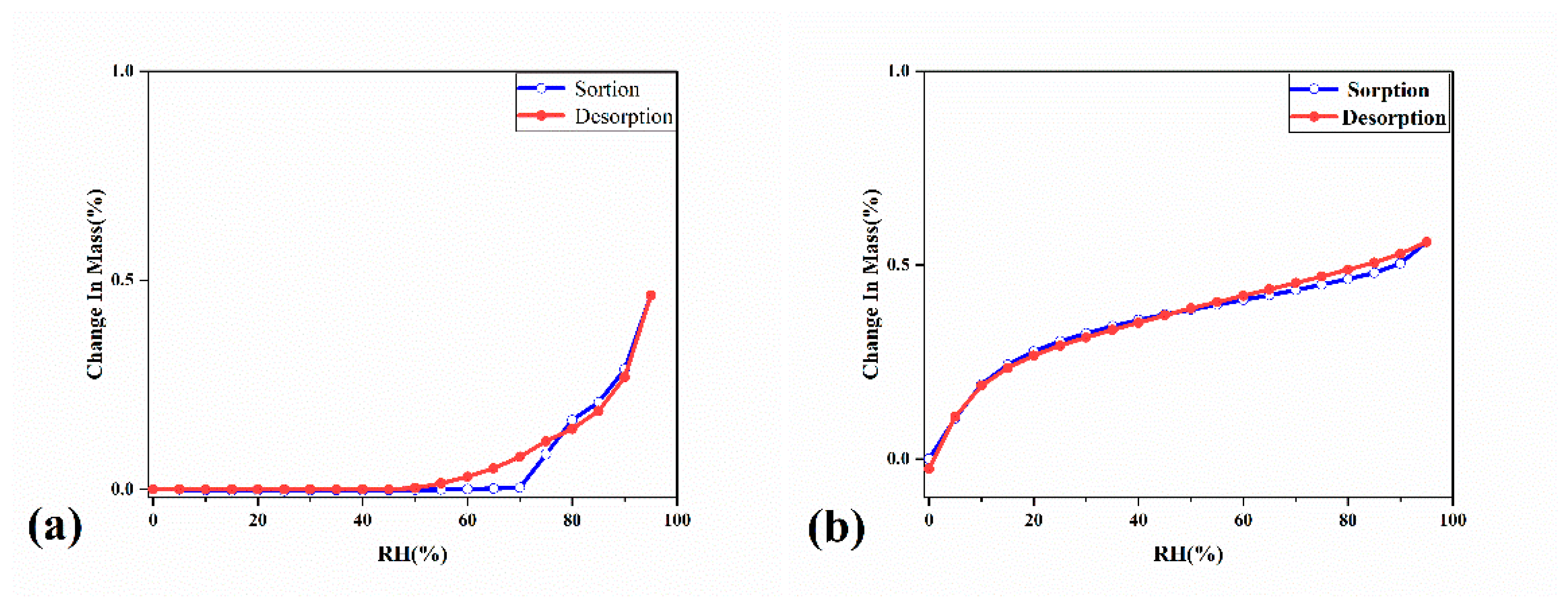
2.2. The Characterization Analysis of Crystal Dissolution and Hygroscopicity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods of Synthesis
3.3. Methods of Structural Analysis
3.3.1. Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.3.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
3.3.3. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.3.5. Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction (SCXRD)
3.3.6. Polarized Optical Microscopy (POM)
3.4. Methods of Physicochemical Properties
3.4.1. Dissolution Rate
3.4.2. Dynamic Water Vapor Sorption Isotherm (DVS)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aakeroy, C.B.; Salmon, D.J. Building co-crystals with molecular sense and supramolecular sensibility. Crystengcomm 2005, 7, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggirala, N.K.; Perry, M.L.; Almarsson, O.; Zaworotko, M.J. Pharmaceutical cocrystals: Along the path to improved medicines. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 640–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.C. Cocrystallization for successful drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozd, K.V.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. Novel drug-drug cocrystals of carbamazepine with para-aminosalicylic acid: Screening, crystal structures and comparative study of carbamazepine cocrystal formation thermodynamics. Crystengcomm 2017, 19, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, H.; Xu, Y.; Mei, X. Preparation and Solid-State Characterization of Dapsone Drug-Drug Co-Crystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 4562–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Cavanagh, K.L.; Rodriguez-Hornedo, N.; Matzger, A.J. Multidrug Cocrystal of Anticonvulsants: Influence of Strong Intermolecular Interactions on Physiochemical Properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 5012–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, O.D.; Furuish, T.; Yonemochi, E.; Terada, K.; Uekusa, H. Drug-Drug Multicomponent Crystals as an Effective Technique to Overcome Weaknesses in Parent Drugs. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplinsky, E. Sacubitril/valsartan in heart failure: Latest evidence and place in therapy. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2016, 7, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kario, K.; Sun, N.; Chiang, F.-T.; Supasyndh, O.; Baek, S.H.; Inubushi-Molessa, A.; Zhang, Y.; Gotou, H.; Lefkowitz, M.; Zhang, J. Efficacy and Safety of LCZ696, a First-in-Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor, in Asian Patients With Hypertension. Hypertension 2014, 63, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lou, B. Preparation, Crystal Structures, and Oral Bioavailability of Two Cocrystals of Emodin with Berberine Chloride. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 7481–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, B.B.; McGraw, T.E. Rosiglitazone, PPAR (gamma), and Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2667–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Wilkison, W.O.; Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12953–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balfour, J.A.B.; Plosker, G.L. Rosiglitazone. Drugs 1999, 57, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, F.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, W.; Fan, J.; Sun, G. Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L.; Chi, C.W.; Liu, T.Y. The anti-inflammatory potential of berberine in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2004, 203, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.-Y.; Wang, G.-J.; Sun, J.-G.; Huang, Z.-j.; Zhao, X.-C.; Gu, Y.; Liu, X.-D. Inhibitory action of berberine on glucose absorption. Yaoxue Xuebao 2003, 38, 911–914. [Google Scholar]
- Homma, N.; Kono, M.; Kadohira, H.; Yoshihara, S.; Masuda, S. The effect of berberine chloride on the intestinal flora of infants. Arzneim. Forsch. 1961, 11, 450–454. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.-x.; Wang, X.-m.; Jiang, T.; Gong, J.-f.; Nu, L.-y.; Li, N. Berberine Prevents Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Damage During Early Phase of Sepsis in Rat through the Toll-Like Receptors Signaling Pathway. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Xue, R.; Wu, J.-D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Wang, S.-K.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Song, D.-Q.; Wang, Y.-M.; et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2010, 59, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Fichna, J.; Storr, M. Effects of Berberine in the Gastrointestinal Tract—A Review of Actions and Therapeutic Implications. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Zhou, S.W.; Bin Zhang, K.; Tang, J.L.; Guang, L.X.; Ying, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.D. Chronic effects of berberine on blood, liver glucolipid metabolism and liver PPARs expression in diabetic hyperlipidemic rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine and metformin during the treatment of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Perumalla, S.R.; Lu, R.; Fang, J.; Sun, C.C. Sweet Berberine. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A-Found. Adv. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C-Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Empirical Formula | C39H40N4O8S |
|---|---|
| molecular weight | 724.81 |
| Crystal size/mm3 | 0.22 × 0.15 × 0.12 |
| Crystal system | triclinic |
| Space group | P − 1 |
| a/Å | 7.4411(4) |
| b/Å | 13.3185(6) |
| c/Å | 18.8457(10) |
| α/° | 98.950(4) |
| β/° | 98.400(4) |
| γ/° | 101.178(4) |
| V/Å3 | 1779.75(16) |
| Z | 2 |
| ρcalcg/cm3 | 1.353 |
| μ/mm−1 | 1.307 |
| F(000) | 764.0 |
| 2θ range for data collection/° | 7.628 to 134.16 |
| Index ranges | −8 ≤ h ≤ 8, −15 ≤ k ≤ 10, −22 ≤ l ≤ 22 |
| Reflections collected | 12524 |
| Independent reflections | 6335 [Rint = 0.0261, Rsigma = 0.0361] |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 6335/53/496 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | 1.038 |
| Final R indexes [I ≤ 2σ (I)] | R1 = 0.0584, wR2 = 0.1635 |
| Final R indexes [all data] | R1 = 0.0771, wR2 = 0.1833 |
| Largest diff. peak/hole / e Å−3 | 0.40/−0.26 |
| CCDC no. | 2007762 |
| D-H···A | d(D-H)/Å | d(H···A)/Å | d(D···A)/Å | D-H-A/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(11)-H(11)···O(6) 1 | 0.93 | 2.63 | 3.453(3) | 147.3 |
| C(14)-H(14)···O(5) 2 | 0.93 | 2.30 | 3.207(3) | 165.8 |
| C(24A^b)-H(24D^b)···O(5) 3 | 0.97 | 2.45 | 3.111(16) | 125.3 |
| C(7)-H(7)···O(8^a) 4 | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.258(12) | 137.9 |
| O(8A^b)-H(8AA^b)···N(4A^b) 5 | 1.05 | 2.19 | 3.06(4) | 139.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, X.; Jiang, L.; Cai, L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X. A New Co-Crystal of Synthetic Drug Rosiglitazone with Natural Medicine Berberine: Preparation, Crystal Structures, and Dissolution. Molecules 2020, 25, 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184288
Guan X, Jiang L, Cai L, Zhang L, Hu X. A New Co-Crystal of Synthetic Drug Rosiglitazone with Natural Medicine Berberine: Preparation, Crystal Structures, and Dissolution. Molecules. 2020; 25(18):4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184288
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Xiaoshu, Lan Jiang, Linhong Cai, Li Zhang, and Xiangnan Hu. 2020. "A New Co-Crystal of Synthetic Drug Rosiglitazone with Natural Medicine Berberine: Preparation, Crystal Structures, and Dissolution" Molecules 25, no. 18: 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184288
APA StyleGuan, X., Jiang, L., Cai, L., Zhang, L., & Hu, X. (2020). A New Co-Crystal of Synthetic Drug Rosiglitazone with Natural Medicine Berberine: Preparation, Crystal Structures, and Dissolution. Molecules, 25(18), 4288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184288





