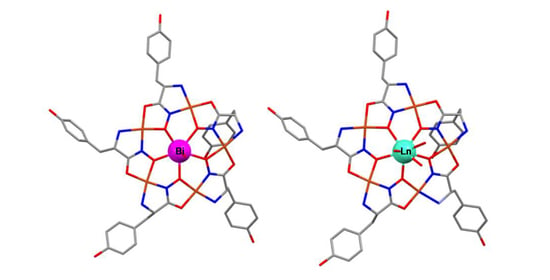
Water-Soluble Bismuth(III) Polynuclear Tyrosinehydroximate Metallamacrocyclic Complex: Structural Parallels to Lanthanide Metallacrowns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
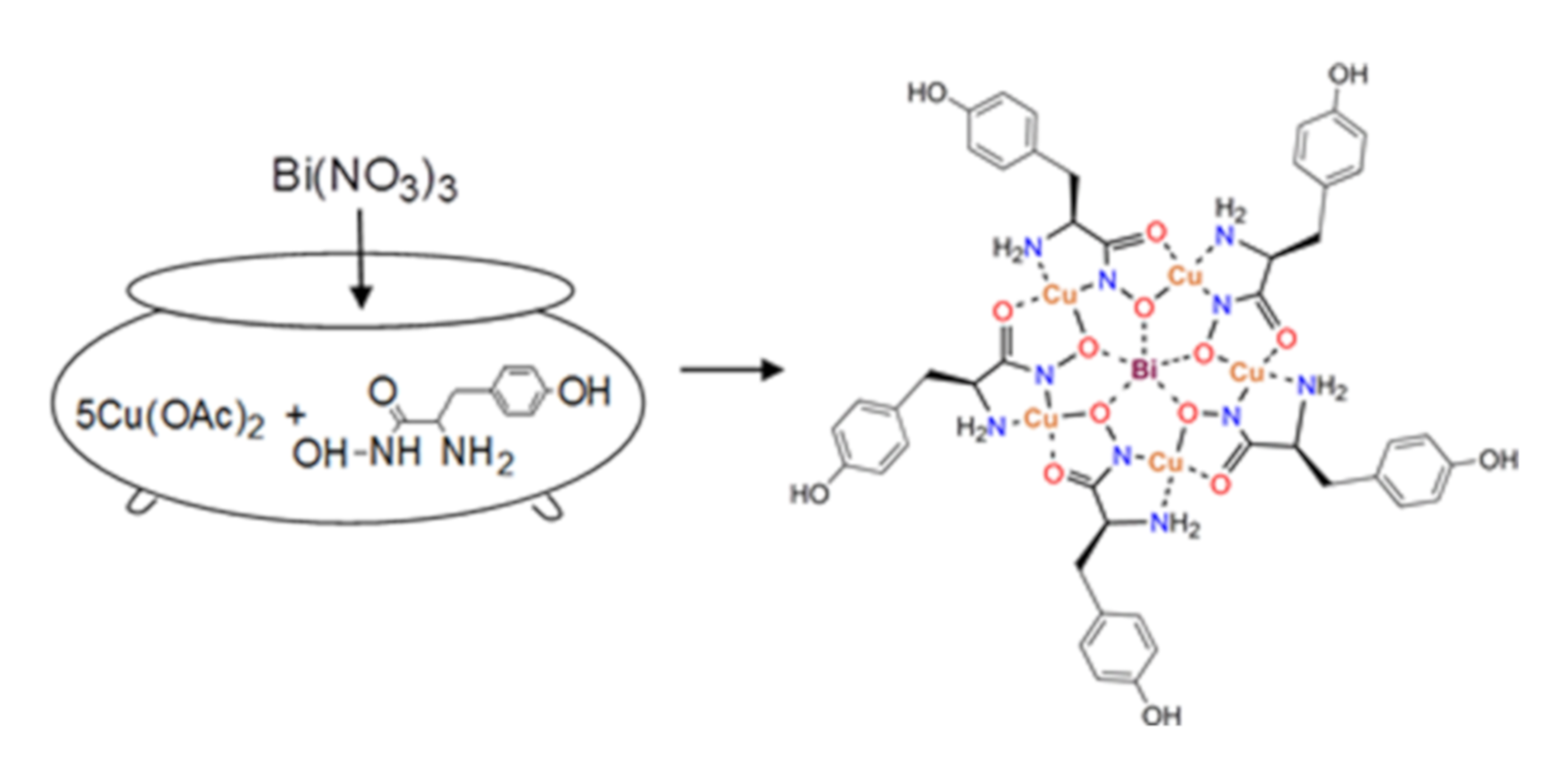
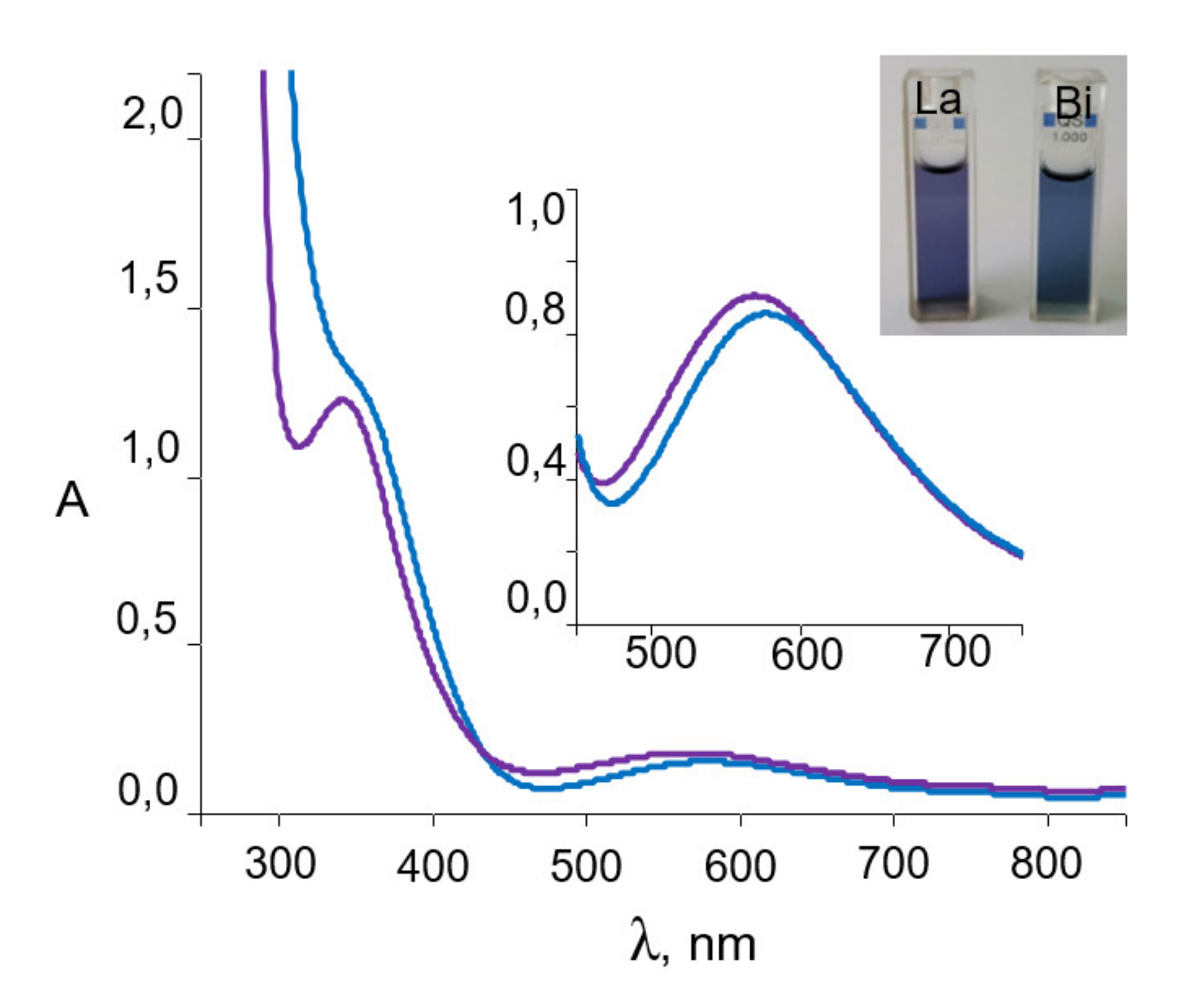
2.1. Synthesis and Spectroscopic Aspects
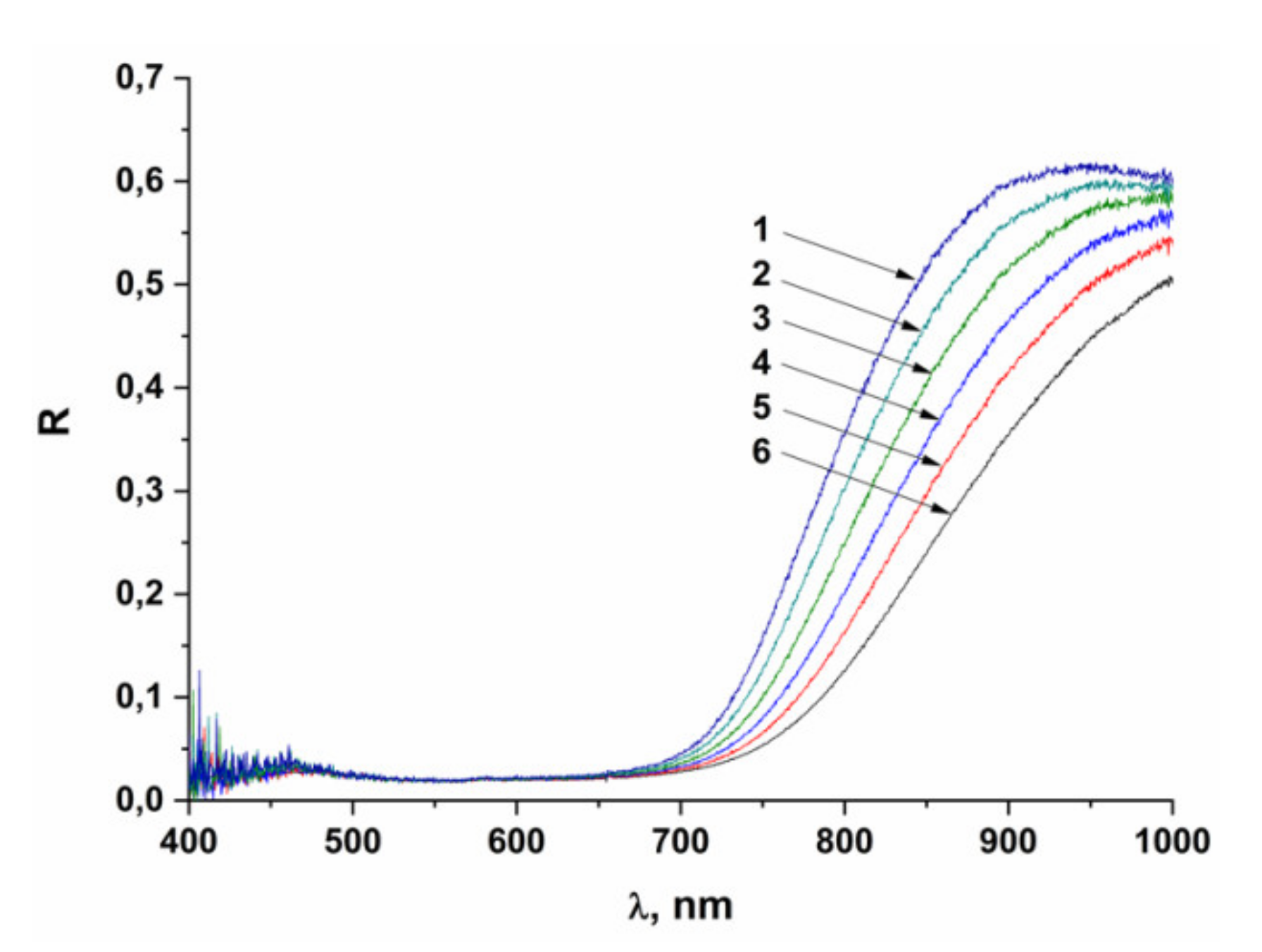
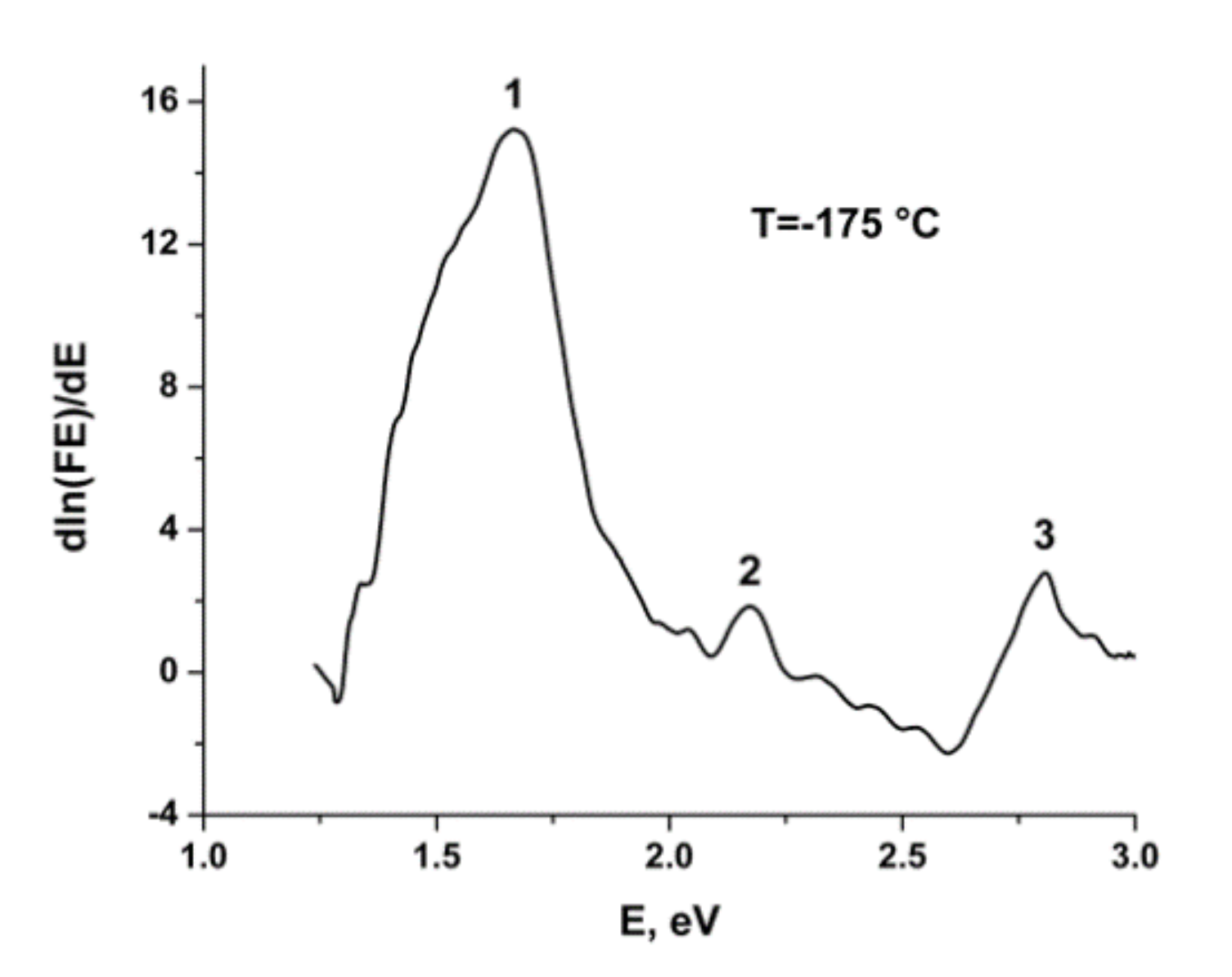
2.2. Thermochromic Properties
2.3. Structural Aspects: X-Ray Crystal Structure
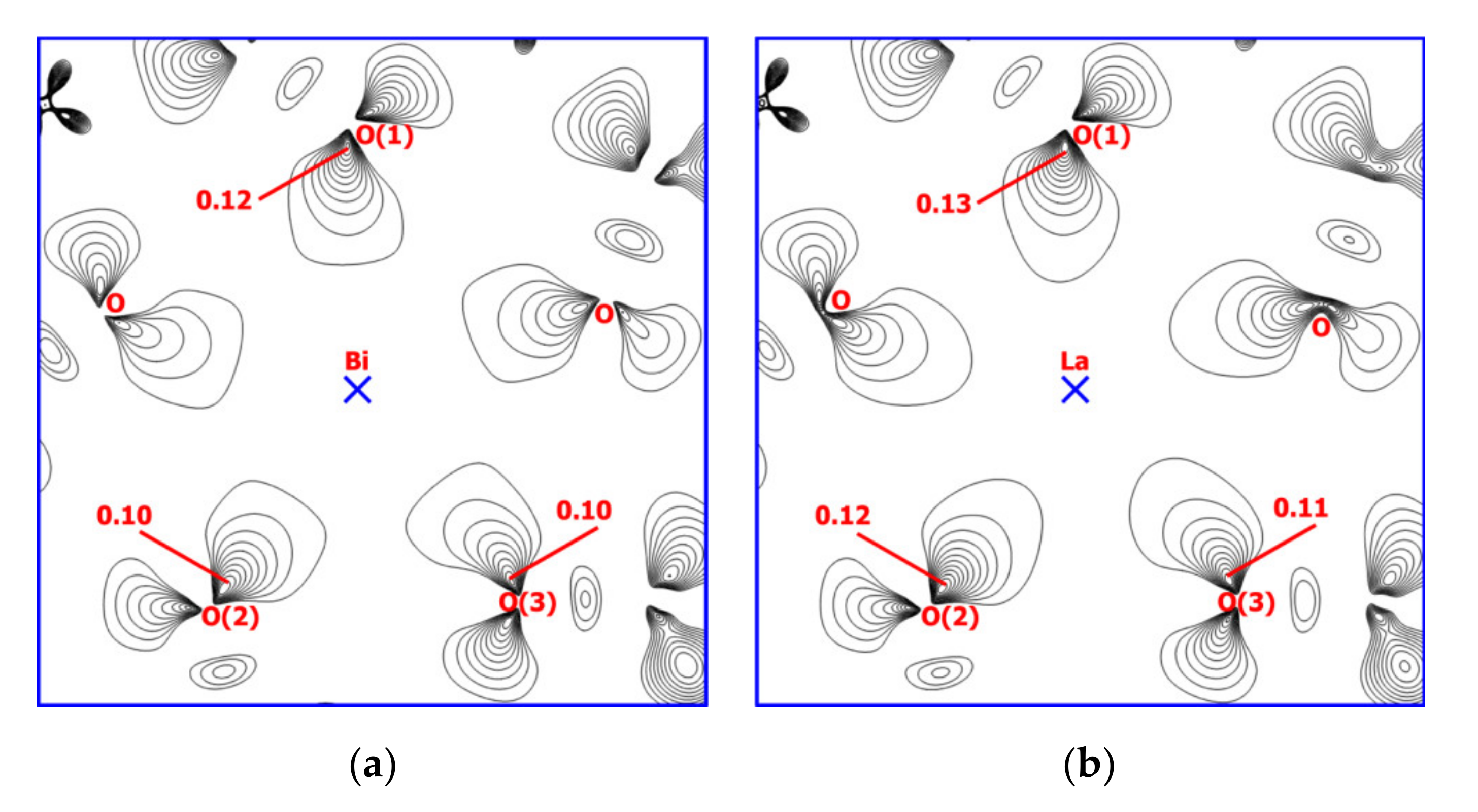
2.4. Theoretical Calculations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. X-ray Crystallographic Studies
3.3. Computational Methodology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mjos, K.D.; Orvig, C. Metallodrugs in Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4540–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaynor, D.; Griffith, D. The prevalence of metal-based drugs as therapeutic or diagnostic agents: Beyond platinum. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogan, D.M.; Griffith, D. Current and Potential Applications of Bismuth-Based Drugs. Molecules 2014, 19, 15258–15297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briand, G.G.; Burford, N. Bismuth Compounds and Preparations with Biological or Medicinal Relevance. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2601–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalik, M.; Masternak, J.; Barszcz, B.; Kowalik, J.M.A.B.B.M. Recent Research Trends on Bismuth Compounds in Cancer Chemoand Radiotherapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 729–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, P.J.; Li, H.; Sun, H. Coordination chemistry of metals in medicine: Target sites for bismuth. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 185, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Sun, H. Biocoordination chemistry of bismuth: Recent advances. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, H. Recent advances in bioinorganic chemistry of bismuth. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 16, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, Z.; Tircsó, G.; Rösch, F. The Use of the Macrocyclic Chelator DOTA in Radiochemical Separations. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2020, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimeček, J.; Hermann, P.; Seidl, C.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Morgenstern, A.; Wester, H.-J.; Notni, J. Efficient formation of inert Bi-213 chelates by tetraphosphorus acid analogues of DOTA: Towards improved alpha-therapeutics. EJNMMI Res. 2018, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavila, V.; Davidovich, R.L.; Gulea, A.; Whitmire, K.H. Bismuth(III) complexes with aminopolycarboxylate and polyaminopolycarboxylate ligands: Chemistry and structure. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 2782–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, M.; Motieiyan, E.; Bertolotti, F.; Marabello, D.; Rodrigues, V.H. Three new bismuth(III) pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate compounds: Synthesis, characterization and crystal structures. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1099, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-H.; Jiang, J.-H.; Li, X.; Tao, L.-M.; Xiao, S.-X.; Gu, H.-W.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, C.; Xie, J.-Q.; Peng, M.-N.; et al. Synthesis, crystal structure and biological properties of a bismuth(iii) Schiff-base complex. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 94267–94275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, A.; Ong, Y.C.; Blair, V.L.; Kedzierski, L.; Andrews, P.C. Bismuth(III) α-hydroxy carboxylates: Highly selective toxicity of glycolates towards Leishmania major. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 20, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; Blair, V.L.; Ferrero, R.; Junk, P.C.; Tabor, R.; Andrews, P.C. Synthesis and structural characterisation of bismuth(iii) hydroxamates and their activity against Helicobacter pylori. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 16903–16913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.; Blair, V.L.; Ferrero, R.L.; Mehring, M.; Andrews, P.C. Bismuth( iii ) benzohydroxamates: Powerful anti-bacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori and hydrolysis to a unique Bi 34 oxido-cluster [Bi 34 O 22 (BHA) 22 ( H -BHA) 14 (DMSO) 6 ]. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15232–15234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogan, D.M.; Twamley, B.; Fitzgerald-Hughes, D.; Griffith, D. Novel class of Bi( iii ) hydroxamato complexes: Synthesis, urease inhibitory activity and activity against H. pylori. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11008–11014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Martin, N.P.; Sadeghi, O.; Nyman, M. Bismuth for Controlled Assembly/Disassembly of Transition-Metal Oxo Clusters, Defining Reaction Pathways in Inorganic Synthesis and Nature. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 3471–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehring, M. From molecules to bismuth oxide-based materials: Potential homo- and heterometallic precursors and model compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 974–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ouyang, R.; Xu, L.; Guo, N.; Li, W.; Feng, K.; Ouyang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Miao, Y. Review: Bismuth complexes: Synthesis and applications in biomedicine. J. Coord. Chem. 2015, 68, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casely, I.J.; Ziller, J.W.; Mincher, B.J.; Evans, W.J. Bismuth Coordination Chemistry with Allyl, Alkoxide, Aryloxide, and Tetraphenylborate Ligands and the {[2,6-(Me2NCH2)2C6H3]2Bi}+Cation. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodwin, J.J.; Cutland, A.D.; Malkani, R.G.; Pecoraro, V.L. The development of chiral metallacrowns into anion recognition agents and porous materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 216, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, G.; Zaleski, C.M.; Pecoraro, V.L. Structural and Functional Evolution of Metallacrowns. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4933–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegoni, M.; Remelli, M. Metallacrowns of copper(II) and aminohydroxamates: Thermodynamics of self assembly and host–guest equilibria. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happ, P.; Plenk, C.; Rentschler, E. 12-MC-4 metallacrowns as versatile tools for SMM research. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 289, 238–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska, M.; Fritsky, I.O.; Gumienna-Kontecka, E.; Pavlishchuk, A.V. Metallacrown-based compounds: Applications in catalysis, luminescence, molecular magnetism, and adsorption. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 304–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkova, M.A. Water-Soluble Polynuclear Metallamacrocyclic Copper(II) and Lanthanide(III) Complexes Based on Amino Hydroxamic Acids. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2018, 44, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabrodina, G.S.; Katkova, M.A.; Baranov, E.V.; Zhigulin, G.Y.; Ketkov, S.Y. Synthesis and Molecular Structure of the First Metallamacrocyclic Bi(III)-Cu(II) 15-MC-5 Complex Derived from Pyrazinohydroxamic Acid. Macroheterocycles 2019, 12, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkova, M.A.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Muravyeva, M.S.; Shavyrin, A.; Baranov, E.V.; Khrapichev, A.A.; Ketkov, S.Y. Facile One-Pot Route toward Water-Soluble Lanthanide-Copper-Glycinehydrox¬imate 15-Metallacrown-5 Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 5202–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkova, M.A.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Baranov, E.V.; Muravyeva, M.S.; Kluev, E.A.; Shavyrin, A.; Zhigulin, G.Y.; Ketkov, S.Y. New insights into water-soluble and water-coordinated copper 15-metallacrown-5 gadolinium complexes designed for high-field magnetic resonance imaging applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkova, M.A.; Kremlev, K.V.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Rumyantcev, R.V.; Gazhulina, A.P.; Gusev, S.; Ketkov, S.Y.; Fomina, I.G.; Eremenko, I.L. Polynuclear Aminohydroximate Metallamacrocyclic Cu(II)-Ce(III) Complexes: A Facile Route to Intricate Nanostructures of Copper and Cerium Oxides. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkova, M.A.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Rumyantcev, R.V.; Zhigulin, G.Y.; Ketkov, S.Y.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Fomina, I.G.; Eremenko, I.L. pH-Responsive Switching Properties of a Water-Soluble Metallamacrocyclic Phenylalaninehydroximate La(III)-Cu(II) Complex: Insight into Tuning Protonation Ligand States. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4328–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkova, M.A.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Zhigulin, G.Y.; Rumyantsev, R.V.; Ketkov, S.Y. Water-Soluble Chiral Y(III)–Cu(II) Metallamacrocyclic Phenylalaninehydroximate Complex. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2019, 45, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayapov, V.R.; Usoltsev, A.N.; Adonin, S.A.; Sokolov, M.N.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Fedin, V.P.; Sokolov, M.N. Thermochromism of bromotellurates(iv): Experimental insights. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3927–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchenko, V.; Kalanda, N.; Yarmolich, M.; Balasoiu, M.; Lupu, N. Features of crystalline and magnetic structure of barium ferromolybdate in a wide temperature range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 477, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutland, A.D.; Malkani, R.G.; Kampf, J.W.; Pecoraro, V.L. Lanthanide [15]Metallacrown-5 Complexes Form Nitrate-Selective Chiral Cavities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2689–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.P.; Corradi, A.B.; Pelizzi, C.; Pelosi, G.; Tarasconi, P. Notes. Chemical and structural investigations on bismuth complexes of 2,6-di-acetylpyridine bis(2-thenoylhydrazone) and 2,6-diacetylpyridine bis(thiosemicarbazone). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1990, 3857–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.-F.; Maruyama, J.; Yamashita, T.; Shimada, S. Efficient Fixation of Carbon Dioxide by Hypervalent Organobismuth Oxide, Hydroxide, and Alkoxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6590–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breunig, H.J.; Königsmann, L.; Lork, E.; Nema, M.; Philipp, N.; Silvestru, C.; Soran, A.; Varga, R.A.; Wagner, R. Hypervalent organobismuth(iii) carbonate, chalcogenides and halides with the pendant arm ligands 2-(Me2NCH2)C6H4 and 2,6-(Me2NCH2)2C6H3. Dalton Trans. 2008, 14, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsanov, S.S. Van der Waals Radii of Elements. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 37, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkova, M.A.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Zhigulin, G.Y.; Baranov, E.V.; Trigub, M.M.; Terentiev, A.A.; Ketkov, S.Y. The first water-soluble polynuclear metallamacrocyclic Sr(ii)–Cu(ii) complex based on simple glycinehydroximate ligands. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 10479–10487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhigulin, G.Y.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Katkova, M.A.; Ketkov, S.Y. DFT studies of the electron density distribution and donor-acceptor interactions in water-soluble aminohydroximate metallamacrocyclic CaII and YIII complexes. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 68, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAINT. Data Reduction and Correction Program; Bruker AXS: Madison, WI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of silver and molybdenum microfocus X-ray sources for single-crystal structure determination. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laikov, D.N. Fast evaluation of density functional exchange-correlation terms using the expansion of the electron density in auxiliary basis sets. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1997, 281, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laikov, D.N.; Ustynyuk, Y.A. PRIRODA-04: A quantum-chemical program suite. New possibilities in the study of molecular systems with the application of parallel computing. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2005, 54, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laikov, D.N. A new class of atomic basis functions for accurate electronic structure calculations of molecules. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 416, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa, E.; Molins, E.; Lecomte, C. Hydrogen bond strengths revealed by topological analyses of experimentally observed electron densities. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 285, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borissova, A.O.; Korlyukov, A.A.; Antipin, M.Y.; Lyssenko, K.A. Estimation of Dissociation Energy in Donor−Acceptor Complex AuCl·PPh3via Topological Analysis of the Experimental Electron Density Distribution Function. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 11519–11522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntus, L.N.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Antipin, M.Y.; Bünzli, J.-C.G. Role of Inner- and Outer-Sphere Bonding in the Sensitization of EuIII-Luminescence Deciphered by Combined Analysis of Experimental Electron Density Distribution Function and Photophysical Data. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11095–11107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramov, Y.A. On the Possibility of Kinetic Energy Density Evaluation from the Experimental Electron-Density Distribution. Acta Cryst. 1997, 53, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, T.A. AIMAll; Version 10.05.04; TK Gristmill Software: Overland Park, KS, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Quantitative analysis of molecular surface based on improved Marching Tetrahedra algorithm. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2012, 38, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision B.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pollak, P.; Weigend, F. Segmented Contracted Error-Consistent Basis Sets of Double- and Triple-ζ Valence Quality for One- and Two-Component Relativistic All-Electron Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 3696–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


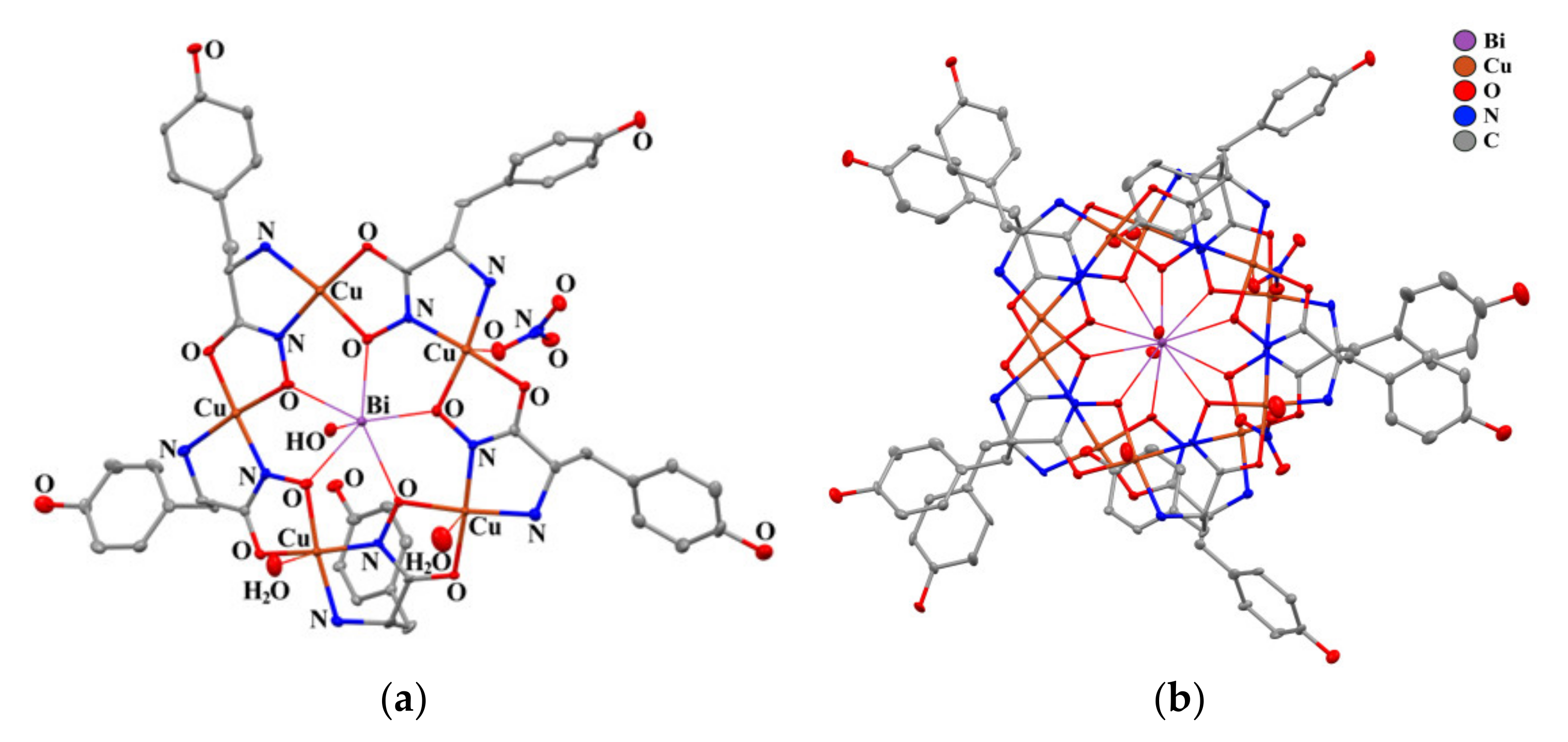



| Distances [A] and angles [°] | 1A (M = Bi) | 1B (M = Bi) | Bi(Cl)(H2O)[15- MCCu(II)Pyzha-5] [29] | Gd(H2O)3[15- MCCu(II)Tyrha-5] [37] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-O(oxime) | 2.387(7)–2.506(8) | 2.412(8)–2.543(8) | 2.429(8)–2.451(7) | 2.406(5)–2.440(7) |
| Cu-O(oxime) | 1.911(7)–1.935(8) | 1.915(8)–1.941(9) | 1.912(8)–1.928(7) | 1.908(5)–1.944(6) |
| Cu-O(carbonyl) | 1.905(8)–1.961(8) | 1.916(8)–1.952(8) | 1.935(7)–1.951(7) | 1.909(7)–1.959(9) |
| Cu-N(imine) | 1.903(9)–1.914(10) | 1.898(10)–1.912(10) | 1.906(8)–1.947(10) | 1.866(9)–1.904(6) |
| Cu-N(amine) | 1.990(9)–2.021(9) | 2.000(9)–2.027(10) | 2.006(9)–2.024(10) | 1.990(9)–2.037(9) |
| Cu-O(solv) | 2.48(1), 2.57(2) | 2.42(1), 2.56(1) | 2.16(2)–2.37(1) | 2.553(9) |
| M-O(OH/H2O) | 2.106(8) | 2.047(7) | 2.555(10) | 2.35(1)–2.54(2) |
| Cu-O(NO3) | 2.44(1), 2.88(1) | 2.425(8), 2.95(1) | 2.32(2)–2.403(8) | 2.477(7), 2.95(1) |
| Cu-O(Tyrha) | 2.762(8) | 2.655(8) | - | 2.825(7) |
| M...M (across the dimer cavity) | 7.1742(6) | - | 8.3933(6) | |
| M...M (between dimers) | 9.2437(8) | - | 8.5158(6) | |
| O(oxime)-Cu-N(imine) | 90.8(4)–91.0(4) | 90.6(4)–91.5(4) | 89.5(3)–90.9(4) | 89.3(3)–90.9(4) |
| O(oxime)-M-O(oxime) | 70.6(3)–73.8(3) | 71.0(3)–72.9(3) | 71.5(3)–72.9(3) | 70.7(2)–71.5(2) |
| Atoms | Distance, Å | ρ(rc), a.u. | ∇2ρ(rc), a.u. | ε |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-C 1 | 1.517–1.523/ | 0.250–0.252/ | –(0.508–0.494)/ | 0.106–0.107/ |
| 1.518–1.523 | 0.249–0.252 | –0.014 | 0.104–0.105 | |
| C-Nam 2 | 1.494–1.498/ | 0.244–0.246/ | –(0.485–0.475)/ | 0.016–0.019/ |
| 1.495–1.500 | 0.244–0.246 | –0.011 | 0.016–0.018 | |
| C-Nim 2 | 1.323/ | 0.358–0.359/ | –(1.177–1.172)/ | 0.277–0.279/ |
| 1.317–1.318 | 0.362 | –0.006 | 0.287–0.289 | |
| C-O | 1.283–1.284/ | 0.361–0.362/ | –(0.862–0.850)/ | 0.104–0.107/ |
| 1.285–1.286 | 0.36 | –0.011 | 0.099–0.102 | |
| N-O | 1.381–1.382/ | 0.323–0.324/ | –(0.131–0.128)/ | 0.069–0.070/ |
| 1.395–1.396 | 0.311–0.312 | –0.003 | 0.059–0.060 | |
| C-CR 3 | 1.549–1.552/ | 0.227–0.228/ | –(0.380–0.375)/ | 0.018–0.021/ |
| 1.547–1.550 | 0.228–0.230 | –0.008 | 0.018–0.021 | |
| C-Cring 4 | 1.508–1.509/ | 0.248/ | –(0.495–0.494)/ | 0.044–0.049/ |
| 1.508–1.510 | 0.247–0.248 | –0.003 | 0.043–0.048 |
| Atoms | Distance, Å | ρ(rc), a.u. | ∇2ρ(rc), a.u. | V(rc), a.u. | Eint, kcal/mol | ε |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi-Oox 1/ | 2.433–2.442/ | 0.049–0.050/ | 0.167–0.170/ | –(0.053–0.052)/ | 16.3–16.8/ | 0.182–0.184/ |
| La-Oox 1 | 2.432–2.438 | 0.056–0.057 | 0.187–0.189 | –0.001 | 19.8–20.2 | 0.240–0.241 |
| Cu-Oox 1 | 1.973–1.984/ | 0.084–0.086/ | 0.381–0.396/ | –(0.129–0.124)/ | 38.8–40.4/ | 0.047–0.048/ |
| 1.992–2.006 | 0.080–0.082 | 0.352–0.369 | –0.006 | 35.9–37.7 | 0.041–0.042 | |
| Cu-Ocarb 1 | 1.933–1.936/ | 0.094/ | 0.444–0.447/ | –(0.150–0.148)/ | 46.5–47.0/ | 0.014–0.018/ |
| 1.934–1.937 | 0.094 | 0.442–0.446 | –0.001 | 46.3–46.9 | 0.023–0.027 | |
| Cu-Nim | 1.890–1.892/ | 0.114–0.115/ | 0.474–0.477/ | –(0.195–0.194)/ | 60.9–61.3/ | 0.071–0.074/ |
| 1.896–1.897 | 0.113 | 0.464–0.468 | –0.191 | 59.9–60.1 | 0.071–0.074 | |
| Cu-Nam | 2.034–2.049/ | 0.083–0.086/ | 0.281–0.293/ | –(0.121–0.115)/ | 36.0–37.9/ | 0.020–0.023/ |
| 2.036–2.054 | 0.083–0.086 | 0.277–0.292 | –0.007 | 35.4–37.6 | 0.019–0.021 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katkova, M.A.; Zhigulin, G.Y.; Rumyantcev, R.V.; Zabrodina, G.S.; Shayapov, V.R.; Sokolov, M.N.; Ketkov, S.Y. Water-Soluble Bismuth(III) Polynuclear Tyrosinehydroximate Metallamacrocyclic Complex: Structural Parallels to Lanthanide Metallacrowns. Molecules 2020, 25, 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194379
Katkova MA, Zhigulin GY, Rumyantcev RV, Zabrodina GS, Shayapov VR, Sokolov MN, Ketkov SY. Water-Soluble Bismuth(III) Polynuclear Tyrosinehydroximate Metallamacrocyclic Complex: Structural Parallels to Lanthanide Metallacrowns. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194379
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatkova, Marina A., Grigory Y. Zhigulin, Roman V. Rumyantcev, Galina S. Zabrodina, Vladimir R. Shayapov, Maxim N. Sokolov, and Sergey Y. Ketkov. 2020. "Water-Soluble Bismuth(III) Polynuclear Tyrosinehydroximate Metallamacrocyclic Complex: Structural Parallels to Lanthanide Metallacrowns" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194379
APA StyleKatkova, M. A., Zhigulin, G. Y., Rumyantcev, R. V., Zabrodina, G. S., Shayapov, V. R., Sokolov, M. N., & Ketkov, S. Y. (2020). Water-Soluble Bismuth(III) Polynuclear Tyrosinehydroximate Metallamacrocyclic Complex: Structural Parallels to Lanthanide Metallacrowns. Molecules, 25(19), 4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194379