Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Sensor of Mercury (II) Based on Layer–by–Layer Deposition of Gold/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
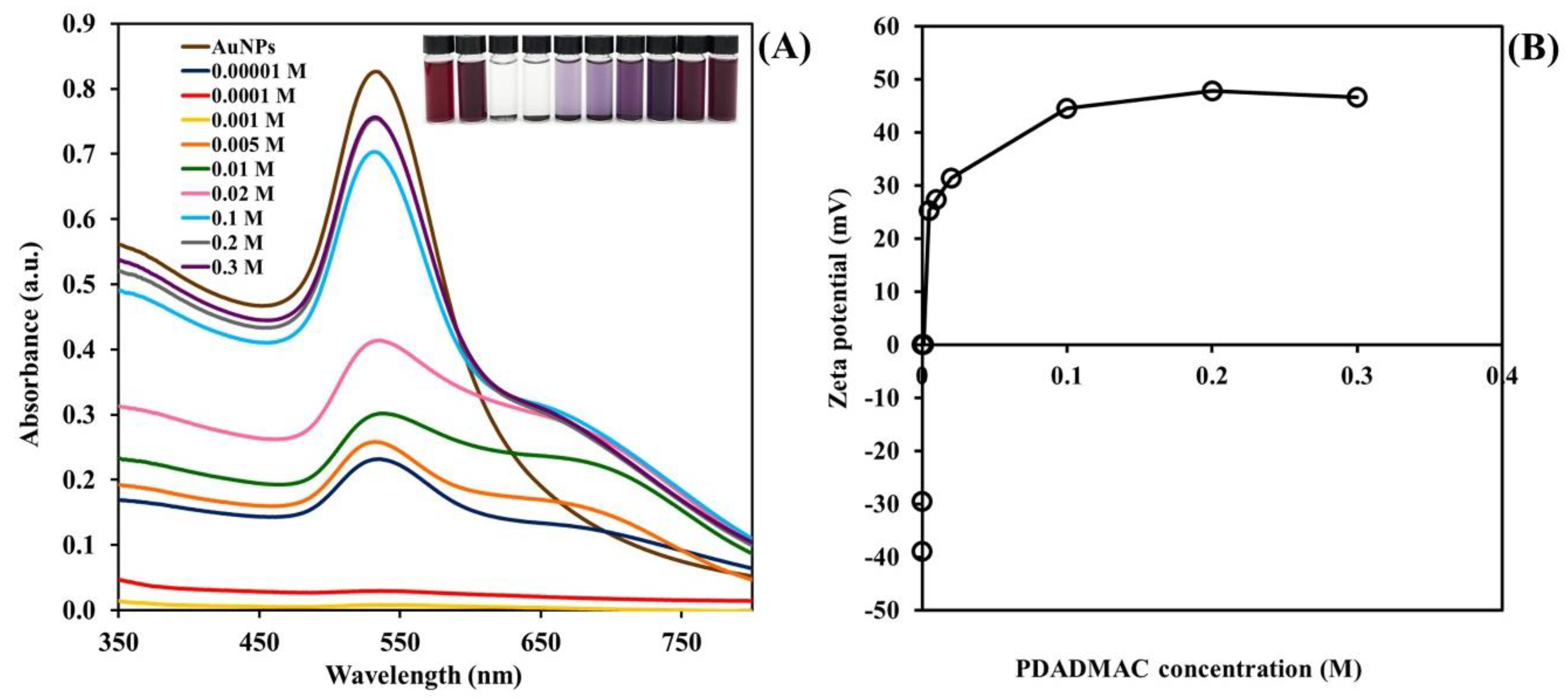
2.1. Effect of Concentration of PDADMAC on the Surface Modification of AuNPs
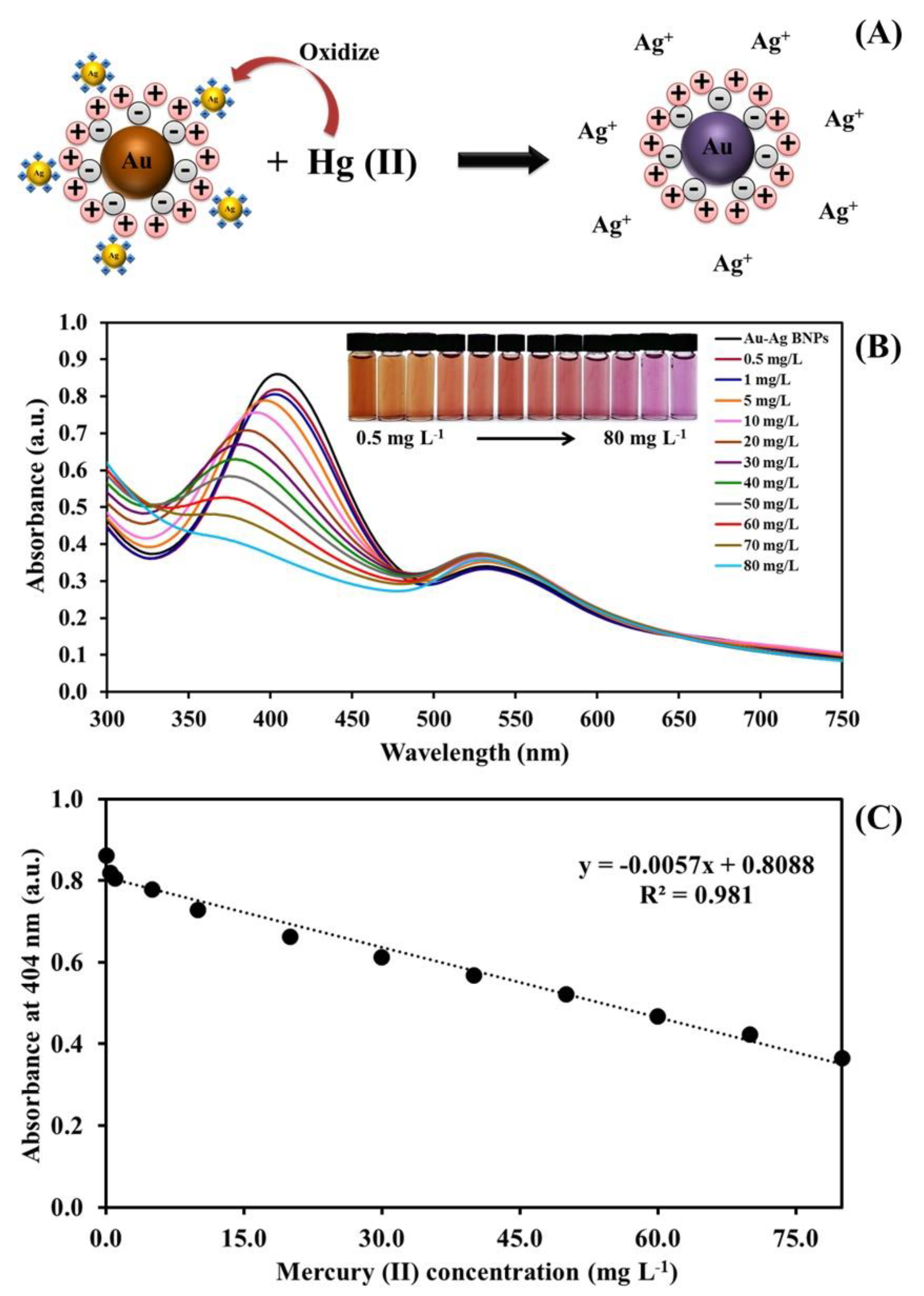
2.2. Characterization of the Synthesized Au–Ag Bimetallic Nanoparticles
2.3. Colorimetric Assay of Mercury (II) Detection
2.4. Optimization of the Sensing Conditions
2.5. Selectivity of Mercury (II) Detection
2.6. Analytical Performances of Gold/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles for Mercury (II) Assay
2.7. Application for the Detection of Mercury (II) in Aqueous Media
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of Gold/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles
3.3. Characterizations
3.4. Colorimetric Detection of Mercury (II)
3.5. Colorimetric Detection of Mercury (II) Selectivity of Mercury (II) Detection
3.6. Application for the Detection of Mercury (II) in Aqueous Media
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoichev, T.; Amouroux, D.; Martin-Doimeadios, R.C.R.; Monperrus, M.; Donard, O.F.X.; Tsalev, D.L. Fluorescence spectroscopy of biological tissues – a review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2006, 41, 591–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, K.V. Neurotoxic effects of mercury on auditory cortex networks growing on microelectrode arrays: A preliminary analysis. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2003, 25, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Hou, X.; Feng, X.; Zheng, C. Ultrasensitive speciation analysis of mercury in rice by headspace solid phase microextraction using porous carbons and gas chromatography-dielectric barrier discharge optical emission spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, F.P.; Jiao, B.Y.; Rao, J.Y.; Leng, G. Automated dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography - cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy for the determination of mercury species in natural water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1493, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, S.S.; Campiglia, A.D.; Barbosa, F. A simple method for methylmercury, inorganic mercury and ethylmercury determination in plasma samples by high performance liquid chromatography-cold-vapor-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 761, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, X.; Mo, F.; Huang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Fu, F. Ultra-sensitive speciation analysis of mercury by CE-ICP-MS together with field-amplified sample stacking injection and dispersive solid-phase extraction. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.P.; Yin, X.B.; Jiang, D.Q.; He, X.W. Speciation of mercury by hydrostatically modified electroosmotic flow capillary electrophoresis coupled with volatile species generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıca, D.Y.; Türker, A.R. Speciation and determination of inorganic mercury and methylmercury by headspace single drop microextraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry in water and fish. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Curdová, E.; Vavrušková, L.; Suchánek, M.; Baldrian, P.; Gabriel, J. ICP-MS determination of heavy metals in submerged cultures of wood-rotting fungi. Talanta 2004, 62, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. Colorimetric Detection of Mercury (II) Ion Using Unmodified Silver Nanoparticles and Mercury-Specific Oligonucleotides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Blue-to-red colorimetric sensing strategy for Hg2+ and Ag+ via redox-regulated surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hu, B. Sequential cloud point extraction for the speciation of mercury in seafood by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta B 2007, 62, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.F.; Da Costa, M.C.; Ferreira, D.C.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A. Fast ultrasound-assisted treatment of inorganic fertilizers for mercury determination by atomic absorption spectrometry and microwave-induced plasma spectrometry with the aid of the cold-vapor technique. Microchem. J. 2015, 118, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.M.; Koneswaran, M.; Narayanaswamy, R. A review on fluorescent nanoparticles for optical sensing applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 21624–21661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baptista, P.; Pereira, E.; Eaton, P.; Doria, G.; Miranda, A.; Gomes, I.; Quaresma, P.; Franco, R. Gold nanoparticles for the development of clinical diagnosis methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, C.; Chang, H. Gold nanoparticle probes for the detection of mercury, lead and copper ion. Analyst 2011, 136, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolessa, T.; Tana, Z.Q.; Yina, Y.G.; Liua, J.F. Single-drop gold nanoparticles for Headspace microextraction and colorimetric assay of mercury (II) in environmental waters. Talanta 2018, 176, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsri, E.; Popanyasak, J. Fabrication of silver nanoparticles/polyaniline composite thin films using layer-by-layer self-assembly technique for ammonia sensing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspect 2015, 467, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, Y.; Ding, N.; Cao, Q. Colorimetric detection of Cu2+ using 4-mercaptobenzoic acid modified silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspect 2011, 391, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gao, H.; Shen, W.; Lu, C.; Yuan, Q. Colorimetric detection of cysteine using noncrosslinking aggregation of fluorosurfactant-capped silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.A.; Singhal, R.K.; Kailasa, S.K. One-pot synthesis of silver nanoparticles using folic acid as a reagent for colorimetric and fluorimetric detections of 6-mercaptopurine at nanomolar concentration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhang, L.; Qu, L. Polyaniline/Ag composite nanotubes prepared through UV rays irradiation via fiber template approach and their NH3 gas sensitivity. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsri, E.; Seeharaj, P.; Sriwong, C. A sensitive and selective colorimetric sensor for reduced glutathione detection based on silver triangular nanoplates conjugated with gallic acid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspect 2018, 541, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lou, T.; Wu, Q.; Li, K.; Tan, L.; Sun, J. A facile label-free colorimetric sensor for Hg2+ based on Hg-triangularsilver nanoplates with amalgam-like structure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalkevich, N.; Shalkevich, A.; Si-Ahmedc, L.; Bu, T. Reversible formation of gold Nanoparticle surfactant composite assemblies for the preparation of concentrated colloidal solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 10175–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.E.; Zhan, J. Synthesis of Starch-Stabilized Ag Nanoparticles and Hg2+ Recognition in Aqueous Media. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2009, 4, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shipway, A.N.; Lahav, M.; Gabai, R.; Willner, I. Investigations into the Electrostatically Induce Aggregation of Au Nanoparticles. Langmuir. 2000, 16, 8789–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagers, K.; Chui, T. Effect of pH on the Stability of Gold Nanoparticles and Their Application for melamine Detection in Infant Formula. IOSR-JAC 2014, 7, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatti, M.; Sarkar, S.; Mahalingam, V. Glutathione modified ultrasmall Ce3+ and Tb nanocrystals for fluorescent determination of Hg (II) and Pb (II) ions. Microchim. Acta. 2016, 183, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Kang, S.; Oh, J.; Eom, M.S.; Oh, J.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, W.S.; Hong, S.; Han, M.S. A colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensor for detection of Hg2+ using counterion exchange of cationic polydiacetylene. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 4340–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, J.E.; Choi, M.G.; Ahn, S.; Chang, S.K. Selective chromogenic and flurogenic signalling of Hg2+ ions using a fluorescein-coumarin conjugate. Dyes Pigm. 2010, 84, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Yan, F.; Wang, M.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Rhodamine derivative functionalized chitosan as efficient sensor and Adsorbent for mercury (II) detection and removal. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






| Colorimetric Probe | LOD (µM) | Linear Range (µM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasmall Ce3+ and Tb3+ doped SrF2 nanocrystals capped with glutathione | 20.00 | 1–10 | [30] |
| Counterion exchange of cationic polydiacetylene | 8.30 | 0–65 | [31] |
| Dichlorofluorescein—coumarin conjugate | 4.30 | 0–100 | [32] |
| Rhodamine derivative functionalized chitosan | 3.42 | 0–6 | [33] |
| Au-Ag Bimetallic nanoparticle | 2.64 (0.53 mg L−1) | 0–398 | This work |
| Sample | This Work (mg L−1) | CV–AFS (mg L−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original* | Added | Found ** | Original* | Added | Found ** | |
| S1 | n.d. | 5.0 | 5.6 ± 0.2 | n.d. | 5.0 | 5.1 ± 0.2 |
| n.d. | 15.0 | 16.3 ± 0.4 | n.d. | 15.0 | 16.0 ± 0.1 | |
| S2 | n.d. | 5.0 | 6.3 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 5.0 | 5.9 ± 0.3 |
| n.d. | 15.0 | 15.6 ± 0.2 | n.d. | 15.0 | 15.8 ± 03 | |
| S3 | n.d. | 5.0 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | n.d. | 5.0 | 6.6 ± 0.2 |
| n.d. | 15.0 | 16.6 ± 1.1 | n.d. | 15.0 | 16.2 ± 0.4 | |
| S4 | n.d. | 5.0 | 5.9 ± 0.5 | n.d. | 5.0 | 7.2 ± 0.7 |
| n.d. | 15.0 | 16.4 ±0.3 | n.d. | 15.0 | 16.6 ± 0.2 | |
| S5 | n.d. | 5.0 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | n.d. | 5.0 | 6.9 ± 0.2 |
| n.d. | 15.0 | 16.2 ± 0.8 | n.d. | 15.0 | 16.7 ± 0.4 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathaweesansurn, A.; Vittayakorn, N.; Detsri, E. Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Sensor of Mercury (II) Based on Layer–by–Layer Deposition of Gold/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194443
Mathaweesansurn A, Vittayakorn N, Detsri E. Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Sensor of Mercury (II) Based on Layer–by–Layer Deposition of Gold/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194443
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathaweesansurn, Arjnarong, Naratip Vittayakorn, and Ekarat Detsri. 2020. "Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Sensor of Mercury (II) Based on Layer–by–Layer Deposition of Gold/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194443
APA StyleMathaweesansurn, A., Vittayakorn, N., & Detsri, E. (2020). Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric Sensor of Mercury (II) Based on Layer–by–Layer Deposition of Gold/Silver Bimetallic Nanoparticles. Molecules, 25(19), 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194443






