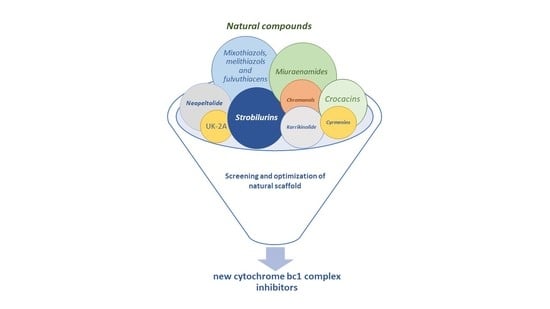
Natural Compound-Derived Cytochrome bc1 Complex Inhibitors as Antifungal Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Strobilurins
From Natural to Synthetic Strobilurins
3. Other Natural Products Inhibiting the Cytochrome bc1 Complex
3.1. Cyrmenin A, B1 and B2
3.2. Mixothiazols, Melithiazols and Fulvuthiacens
3.3. Miuraenamides
3.4. Crocacins
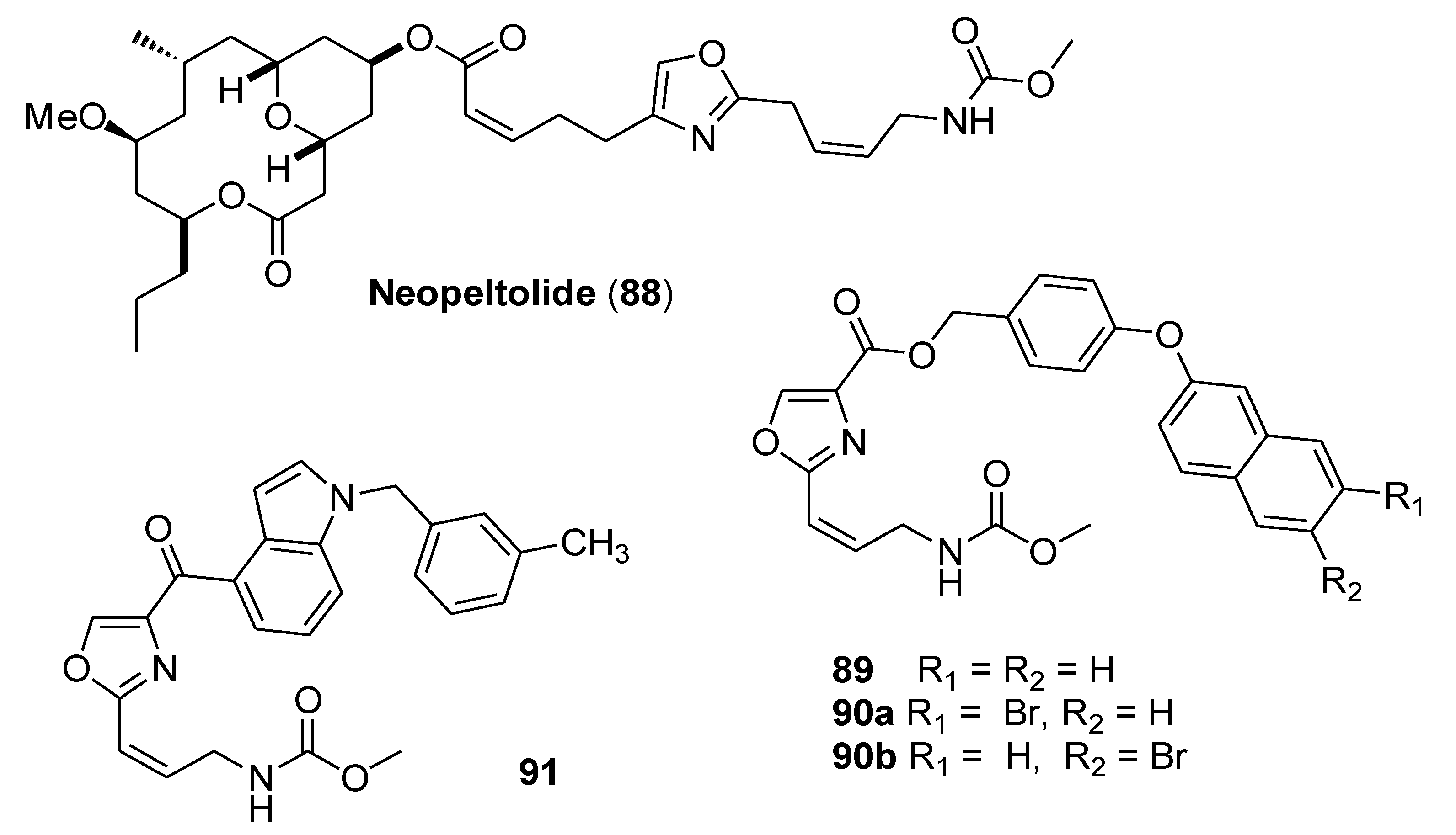
3.5. Neopeltolide
3.6. Chromanols
3.7. Karrikinolide
3.8. Picolinamide UK-2A
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calicioglu, O.; Flammini, A.; Bracco, S.; Bellù, L.; Sims, R. The future challenges of food and agriculture: An integrated analysis of trends and solutions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunte, C.; Palsdottir, H.; Trumpower, B.L. Protonmotive pathways and mechanisms in the cytochrome bc1 complex. FEBS Lett. 2003, 545, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorsbach, B.A.; Sparks, T.C.; Cicchillo, R.M.; Garizi, N.G.; Hahn, D.R.; Meyer, K.G. Natural products: A strategic lead generation approach in crop protection discovery. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, N.; Meunier, B.; Biagini, G.A. The cytochrome bc 1 complex as an antipathogenic target. FEBS Lett. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balba, H. Review of strobilurin fungicide chemicals. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2007, 42, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, H. Strobilurins and Other Complex III Inhibitors. In Modern Crop Protection Compounds; Kramer, W., Schimer, U., Eds.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 584–627. [Google Scholar]
- Anke, T.; Oberwinkler, F.; Steglich, W.; Schramm, G. The strobilurins—new antifungal antibiotics from the basidiomycete (PERS. Ex FR.) SING. J. Antibiot. 1977, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, D.W.; Clough, J.M.; Godwin, J.R.; Hall, A.A.; Hamer, M.; Parr-Dobrzanski, B. The strobilurin fungicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.-F.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.-L.; Yang, W.-C.; Huang, L.-S.; Wu, J.-W.; Berry, E.A.; Yang, G.-F. Computational Discovery of Picomolar Qo Site Inhibitors of Cytochrome bc1 Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Yang, W.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G. Design, synthesis, and bioevaluation of novel Strobilurin derivatives. Chin. J. Chem. 2012, 30, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Xu, L.-H.; Ye, L.-Y.; Wang, X.; Sha, Y.; Xiao, Z.-Y. Synthesis and Fungicidal Activities of Novel Indene-Substituted Oxime Ether Strobilurins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5247–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Xie, Y.-Q.; Gui, S.-Z.; Ye, L.-Y.; Huang, Z.-L.; Huang, Y.-B.; Che, L.-M. Synthesis and fungicidal activities of novel benzothiophene-substituted oxime ether strobilurins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.-Q.; Huang, Y.-B.; Liu, J.-S.; Ye, L.-Y.; Che, L.-M.; Tu, S.; Liu, C.-L. Design, synthesis and structure–activity relationship of novel oxime ether strobilurin derivatives containing substituted benzofurans. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.-Q.; Huang, Z.-L.; Yan, H.-D.; Li, J.; Ye, L.-Y.; Che, L.-M.; Tu, S. Design, synthesis, and biological activity of oxime ether strobilurin derivatives containing indole moiety as novel fungicide. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 85, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.M.; Tupe, S.G.; Jorwekar, S.U.; Sant, D.G.; Deshpande, S.R.; Maybhate, S.P.; Likhite, A.P.; Deshpande, M.V. Synthesis and antifungal potential of 1,2,3-triazole and 1,2,4- triazole thiol substituted strobilurin derivatives. Indian J. Chem. 2015, 54b, 908–917. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, G. Synthesis of novel (E)-α-(methoxyimino) benzeneacetate derivatives and their fungicidal activities. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2015, 37, 502–510. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, D.; Hua, X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, S.; Li, Z. Design, synthesis and fungicidal activity of novel strobilurin-1,2,4-triazole derivatives containing furan or thiophene rings. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2016, 32, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong Song, H.; Song, H.-X.; Shi, D.-Q. Synthesis and fungicidal activity of strobilurin analogues containing 1,2,4-triazole oxime ether moiety. J. Heterocyclic Chem. 2014, 51, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-X.; Shi, D.-Q. Synthesis and fungicidal activity of (E)-α-(Methoxyimino)-benzeneacetate derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazole Schiff base side chain. J. Heterocylic Chem. 2014, 51, 1345–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, G. Synthesis and biological activities of some novel (E)-α-(methoxyimino-)-benzeneacetate derivatives with modified 1,2,4-triazole moiety. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worthington, P. Sterol biosynthesis inhibiting triazole fungicides. In Bioactive Heterocyclic Compound Classes: Agrochemicals; Lamberth, C., Dinges, J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, M.; Wu, C.; Hua, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Z. Design, synthesis and bioactivities of novel strobilurin derivatives containing 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 37, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lei, S.; Liu, Y. Design, synthesis and fungicidal activities of novel 1,2,3-triazole functionalized strobilurins. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.-X.; Li, J.-Z.; Wang, H.-L. Design, synthesis, and antifungal activities of new β-methoxyacrylate analogues. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2013, 60, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.-S.; Liu, C.-L.; Li, H.-C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.-W.; Huang, G.; Chang, J.-B. The discovery of SYP-10913 and SYP-11277: Novel strobilurin acaricides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, S.; Li, Z. Synthesis and antifungal activities of novel strobilurin derivatives containing quinolin-2(1H)-one moiety. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2016, 32, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guoa, X.-F.; Fan, Z.-J.; Zhang, N.-L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Khazhieva, I.; Yurievich, M.Y.; Belskaya, N.P.; Bakulev, V.A. Synthesis and fungicidal activity of 3,4-dichloroisothiazole based strobilurins as potent fungicide candidates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3145–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clerici, F.; Gelmi, M.L.; Pellegrino, S.; Pocar, D. Chemistry of Biologically Active Isothiazoles. Top. Heterocycl. Chem. 2007, 9, 179–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektas, Y.; Eulgem, T. Synthetic plant defense elicitors. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Fan, Z.-J.; Guo, X.-F.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Xu, J.-H.; Song, Y.-Q.; Yurievich, M.Y.; Belskaya, N.P.; Bakulev, V.A. Synthesis of 1,2,3-thiadiazole and thiazole-based strobilurins as potent fungicide candidates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wang, W.; Bao, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, X. Synthesis and evaluation of essential oil-derived β-methoxyacrylate derivatives as high potential fungicides. Molecules 2017, 22, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isman, M.B. Plant essential oils for pest and disease management. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, K.; Li, Y.; Nan, Q.; Xu, J. Synthesis, fungicidal activity, structure-activity relationships (SARs) and density functional theory (DFT) studies of novel strobilurin analogues containing arylpyrazole rings. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Kong, X.; Cao, L.; Tian, S.; Ye, Y.; Qiao, C. Design, synthesis and fungicidal evaluation of novel pyraclostrobin analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Fu, B.; Li, J.-Q.; Qin, Z. Synthesis and fungicidal activity of (E)-methyl-2-(2-((1-cyano-2-hydrocarbylidenehydrazinyl)methyl)phenyl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetates. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3160–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, Y.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Arimori, S.; Kiguchi, S.; Harada, T.; Iwahashi, F. Discovery of methyltetraprole: Identification of tetrazolinone pharmacophore to overcome QoI resistance. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibold, T.; Sasse, F.; Reichenbach, H.; Höfle, G. Cyrmenins, novel antifungal peptides Containing a Nitrogen-Linked β-methoxyacrylate pharmacophore: Isolation and structural elucidation. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakor, N.S.; Musso, L.; Dallavalle, S. First Total Synthesis of Cyrmenin B1. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakor, N.S.; Dallavalle, S.; Musso, L.; Sardi, P. Synthesis and evaluation of structural requirements for antifungal activity of cyrmenin B1 analogues. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerth, K.; Irschik, H.; Trowitzsch, W.; Reichenbach, H. Myxothiazol, an antibiotic from Myxococcus fulvus (Myxobacterales). J. Antibiot. 1980, 33, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trowitzsch, W.; Hofle, G.; Sheldrick, W.S. The stereochemistry of myxothiazol. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 3829–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-W.; Woo, S.-H.; Lee, C.-O.; Cho, K.-Y.; Kim, B.-S. KR025, a New Cytotoxic Compound from Myxococcus fulvus. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, H.; Forche, E.; Reichenbach, H.; Hofle, G. Biosynthesis of myxothiazol Z, the ester-analog of myxothiazol A. Myxococcus fulvus Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 1681–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhlendorf, B.; Hermann, M.; Hecht, H.-J.; Sasse, F.; Forche, E.; Kunze, B.; Reichenbach, H.; Höfle, G. Antibiotics from gliding bacteria, 85[#] melithiazols A–N: New antifungal β-methoxyacrylates from myxobacteria. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 1999, 2601–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söker, U.; Sasse, F.; Kunze, B.; Höfle, G. Synthesis of melithiazol B and related compounds via oxidative degradation of myxothiazol A and Z. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 2000, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söker, U.; Sasse, F.; Kunze, B.; Höfle, G. Neighbouring-group assisted thiazole-ring cleavage by DIBAL-H: An expeditious synthesis of melithiazol C from myxothiazol A. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 2000, 2021–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panter, F.; Krug, D.; Müller, R. Novel methoxymethacrylate natural products uncovered by statistics-based mining of the Myxococcus fulvus secondary metabolome. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Fudou, R.; Ogawa, S.; Yamanaka, S.; Inukai, Y.; Ojika, M. Miuraenamides A and B, Novel Antimicrobial Cyclic Depsipeptides from a New Slightly Halophilic Myxobacterium: Taxonomy, Production, and Biological Properties. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojika, M.; Inukai, Y.; Kito, Y.; Hirata, M.; Iizuka, T.; Fudou, R.; Miuraenamides, R. Antimicrobial Cyclic Depsipeptides Isolated from a Rare and Slightly Halophilic Myxobacterium. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 3, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, B.; Jansen, R.; Höfle, G.; Reichenbach, H. Crocacin, a new electron transport inhibitor from crocatus (Myxobacteria). Production, isolation, physico-chemical and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, P.J.; Berry, E.A.; Cromartie, T.; Daldal, F.; Godfrey, C.R.A.; Lee, D.-W.; Phillips, J.; Taylor, E.A.; Viner, R. The role of molecular modeling in the design of analogues of the fungicidal natural products crocacins A and D. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 10345–10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, A.E.; Botelho, J.C.; Guzmaán, E.; Harmody, D.; Linley, P.; McCarthy, P.J.; Pitts, T.P.; Pomponi, S.A.; Reed, J.K. Neopeltolide, a Macrolide from a Lithistid Sponge of the Family Neopeltidae. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.-L.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Song, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-X.; Yang, J.-F.; Yang, G.-F. Natural product Neopeltolide as a cytochrome bc1 complex inhibitor: Mechanism of action and structural modification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.-Q.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhua, X.-L.; Yang, G.-F. Design and synthesis of potent inhibitors of bc1 complex based on natural product neopeltolide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müllebner, A.; Patel, A.; Stamberg, W.; Staniek, K.; Rosenau, T.; Netscher, T.; Gille, L. Modulation of the mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex activity by chromanols and related compounds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pŏsta, M.; Light, M.E.; Papenfus, H.B.; Van Staden, J.; Kohout, L. Structure–activity relationships of analogs of 3,4,5-trimethylfuran-2(5H)-one with germination inhibitory activities. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffidi, A.; Flematti, G.R.; Nelson, D.C.; Dixon, K.W.; Smith, S.M.; Ghisalberti, E.L. The synthesis and biological evaluation of labelled karrikinolides for the elucidation of the mode of action of the seed germination stimulant. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Shan, L.-Y.; Zhang, B.; Verpoort, F.; Yang, G.-F. Discovery of cytochrome bc1 complex inhibitors inspired by the natural product karrikinolide. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97580–97586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, M.; Abe, K.; Hanafi, M.; Shibata, K.; Tanaka, T.; Taniguchi, M. UK-2A, B, C and D, Novel Antifungal Antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. 517-02. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, W.J.; Meyer, K.G.; Slanec, T.J.; Meyer, S.T.; Wang, N.X.; Fitzpatrick, G.M.; Niyaz, N.M.; Nugent, J.; Ricks, M.J.; Rogers, R.B.; et al. Synthesis and biological activity of analogs of the antifungal antibiotic UK-2A. III. Impact of modifications to the macrocycle isobutyryl ester position. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, W.J.; Meyer, K.G.; Slanec, T.J.; Wang, N.X.; Meyer, S.T.; Niyaz, N.M.; Rogers, R.B.; Bravo-Altamirano, K.; Herrick, J.L.; Chenglin Yao, C. Synthesis and biological activity of analogs of the antifungal antibiotic UK-2A. I. Impact of picolinamide ring replacement. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, W.J.; Meyer, K.G.; Meyer, S.T.; Li, F.; Slanec, T.J.; Wang, N.X.; Yao, C. Synthesis and biological activity of analogs of the antifungal antibiotic UK-2A. II. Impact of modifications to the macrocycle benzyl position. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1831–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flampouri, E.; Mavrikou, S.; Mouzaki-Paxinou, A.-C.; Kintzios, S. Alterations of cellular redox homeostasis in cultured fibroblast-like renal cells upon exposure to low doses of cytochrome bc1 complex inhibitor kresoxim-methyl. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 113, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, L.; Quinn, B.; Li, Y.-F.; Zhang, M.; Elberry, M.; Yu, L.; Yu, C.-A.; Xia, D. Crystallographic Studies of Quinol Oxidation Site Inhibitors: A Modified Classification of Inhibitors for the Cytochrome bc1 Complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 341, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzote, L.; Stamberg, W.; Patel, A.; Rosenau, T.; Maes, L.; Cos, P.; Gille, L. Synthetic chromanol derivatives and their iInteraction with complex III in mitochondria from bovine, yeast, and Leishmania. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotsaert, F.A.J.; Ding, M.G.; Trumpower, B.L. Differential efficacy of inhibition of mitochondrial and bacterial cytochrome bc1 complexes by center N inhibitors antimycin, ilicicolin H and funiculosin. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—Bioenergetics 2008, 1777, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




















 | |||||
| In vitro | In vivo | ||||
| 25 mg/L | 6.25 mg/L | ||||
| Cpd | Pyricularia orizae | Botrytis cinerea | Erysiphe graminis | Colletotrichum lagenarium | Puccinia sorghi Schw. |
| 16a | 100 | 50 | 100 | 70 | / |
| 19a | 80 | 80 | 50 | 0 | 100 |
| 19b | 100 | 80 | 95 | 80 | 90 |
| 19c | 100 | 80 | 99 | 75 | 60 |
| enoxastrobin | 50 | 100 | 100 | 85 | 100 |
| In vitro | In vivo | ||||
| 6.25 mg/L | 6.25 mg/L | ||||
| Cpd | Pyricularia orizae | Botrytis cinerea | Erysiphe graminis | Colletotrichum lagenarium | Puccinia sorghi Schw. |
| 17 | 50 | 100 | 50 | 100 | 70 |
| 18 | / | 100 | 100 | 98 | 40 |
| enoxastrobin | 50 | 100 | 100 | 90 | 98 |
| Compd | X | Y | R | PP a | CH a | RC a | CO a | SS a | FG a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22a | H | O | C2H5 | 60.0 | 87.0 | 80.3 | 38.9 | 76.3 | 54.8 |
| 22b | H | O | i-C3H7 | 60.0 | 84.8 | 83.1 | 36.1 | 80.3 | 42.9 |
| 22c | H | O | i-C4H9 | 43.3 | 73.9 | 87.3 | 19.4 | 31.6 | 38.1 |
| 22d | Br | O | n-C4H9 | 63.3 | 69.6 | 90.1 | 25.0 | 82.9 | 61.9 |
| 22e | H | S | i-C4H9 | 56.7 | 50.0 | 94.4 | 33.3 | 56.6 | 57.1 |
| AZ | 63.3 | 56.5 | 81.7 | 72.2 | 82.9 | 73.8 |
| % Inhibition (50 mg/L) | EC50 (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compd | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | Rhizoctonia cerealis | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | Rhizoctonia cerealis |
| 23a | 100.0 | 98.8 | 7.67 | 15.93 |
| 23b | 98.8 | 97.7 | 7.35 | 9.35 |
| 23c | 100.0 | 87.2 | 6.15 | 13.45 |
| 24 | 82.7 | 95.3 | / | 9.20 |
| azoxystrobin | 96.3 | 70.9 | 4.67 | 22.86 |
| EC50 (µg/mL) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R.ca | P.ia | G.za | B.ca | S.sa | |
| 31 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 1.75 | 0.15 | / |
| 32 | 0.01 | / | 2.68 | / | / |
| AZ | 0.06 | 0.040 | 6.92 | 6.31 | 4.04 |
| Compd | % Inhibition (100 µM) | IC50 ± SD (µM) a | ΔGpred. b (Kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 42 | 11 | / | −23.84 |
| 43 | 99.9 | 0.95 ± 0.012 | −44.17 |
| pyraclostrobin | 99.9 | 1.76 ± 0.17nM | −35.85 |
| penthiopyrad | 95 | 1.56 ± 0.12 |
| Cpd | Sensitive Wild Type EC50 (ppm) a | G143A Mutant EC50 (ppm) | Resistant Factor b |
|---|---|---|---|
| strobilurin A | 0.02 | 0.2 | 10 |
| pyraclostrobin | 0.001 | 0.2 | 200 |
| 46 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 2.0 |
| 47 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1.0 |
| methyltetraprole (48) | 0.002 | 0.002 | 1.0 |
| Cpd | Botrytis cinerea Inibition Zone at 2 µg/disc (mm) | Citotoxicity IC50 (ng/mL) [b] | Inibition of NADH Oxidation IC50 (ng/mL) [c] | Lipophilicity Log POW [d] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 54[e] | 16 | 1 | 11 | 5.29 |
| 55 | 13 | 2 | 17 | 7.17 |
| 56 | 29 | 20 | 18 | 4.75 |
| 58 | 39 | 55 | 29 | 3.37 |
| 59 | 19 | 220 | 37 | 2.36 |
| 57 | 18 | 700 | 730 | 2.92 |
| 60 | 35 | 2000 | 250 | 3.97 |
| 63a | 42 | 500 | 42 | 3.62 |
| 63b | 42 | 400 | 85 | 3.81 |
| Kresoxim-methyl [e] | 33 | 400 | 72 | 3.70 |
| Compd | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose [µg per disk] | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1 | 10 | 0.13 | 5 | 2 | >50 | 50 |
Compd.  | Side Chain R | IC50 NADH oxidAse (nM) | Breakpoint Vine Downy Mildew (µM) | T50 Glass Slide (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 81 |  | 36 | 25 | 0.6 |
| 82 | n-C12H21- | 24 | >100 | 0.1 |
| 83 |  | 21 | >100 | 5 |
| 84 |  | 17 | 10 | 12 |
| 85 |  | 9 | 25 | 20 |
| 86 |  | 18 | 10 | NT |
| 87 |  | 16 | 10 | NT |
| Cpd | R | IC50 (µM) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| 89 | H | 0.045 ± 0.001 |
| 90a | 7-Br | 0.012 ± 0.002 |
| 90b | 6-Br | 0.016 ± 0.001 |
| 91 | 0.70 ± 0.012 | |
| AZ [b] | 0.205 ± 0.001 |
| Cpd | IC50 (µM) SCR | I% (10 µM) SCR | I% (10 µM) SQR | I% (10 µM) cyt bc1 | Selectivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 103a | 3.55 ± 0.11 | 76% | 14% | 66% | cyt bc1 |
| 103b | 9.39 ± 0.12 | 50% | <10% | 46% | cyt bc1 |
| 103c | 0.737 ± 0.011 | 82% | 39% | 83% | cyt bc1 |
| 103d | 1.10 ± 0.20 | 73% | 26% | 67% | cyt bc1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musso, L.; Fabbrini, A.; Dallavalle, S. Natural Compound-Derived Cytochrome bc1 Complex Inhibitors as Antifungal Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194582
Musso L, Fabbrini A, Dallavalle S. Natural Compound-Derived Cytochrome bc1 Complex Inhibitors as Antifungal Agents. Molecules. 2020; 25(19):4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194582
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusso, Loana, Andrea Fabbrini, and Sabrina Dallavalle. 2020. "Natural Compound-Derived Cytochrome bc1 Complex Inhibitors as Antifungal Agents" Molecules 25, no. 19: 4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194582
APA StyleMusso, L., Fabbrini, A., & Dallavalle, S. (2020). Natural Compound-Derived Cytochrome bc1 Complex Inhibitors as Antifungal Agents. Molecules, 25(19), 4582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25194582