A Computational Study of Metallacycles Formed by Pyrazolate Ligands and the Coinage Metals M = Cu(I), Ag(I) and Au(I): (pzM)n for n = 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Comparison with Structures Reported in the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center (CCDC)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of the Reported CSD Structures (Hits) and Their Refcodes
2.1.1. Copper, Only Cu(I) Structures (Cu(II) Structures Were Excluded)
2.1.2. Silver, Only Ag(I) Derivatives
2.1.3. Gold, Only Au(I) Structures (Au(III) Structures Were Excluded)
2.2. Calculated Structures (Minima in All Cases)
2.2.1. Geometries
2.2.2. Comparison of Calculated and Measured Geometries (Only Metal···Metal and Metal···Nitrogen Bond Lengths)
2.3. Energies
2.4. QTAIM Analysis
3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, J.; Lu, Z.; Wu, K.; Ning, G.-H.; Li, D. Coinage-Metal-Based Cyclic Trinuclear Complexes with Metal-Metal Interactions: Theories to Experiments and Structures to Functions. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9675–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkersen, H.; Groenveld, W.L.; Reedijk, J. Pyrazoles and imidazoles as ligands. Part XVIII. Neutral and anionic pyrazole coordinated to Cu(I) and Ag(I). Rec. Trav. Chim. Pays Bas. 1973, 92, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minghetti, G.; Banditelli, G.; Bonati, F. Metal derivatives of azoles. 3. The pyrazolato anion (and homologues) as a mono- or bidentate ligand: Preparation and reactivity of tri-. bi, and mononuclear gold(I) derivatives. Inorg. Chem. 1979, 18, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciocchi, N.; Moret, M.; Cairati, P.; Sironi, A.; Ardizzoia, G.A.; La Monica, G. The Multiphase Nature of the Cu(pz) and Ag(pz) (Hpz = Pyrazole) Systems: Selective Syntheses and Ab-Initio X-ray Powder Diffraction Structural Characterization of Copper(I) and Silver(I) Pyrazolates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 7668–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazalli, N.F.; Yuliati, L.; Lintang, H.O. Molecular Self-Assembly of Group 11 Pyrazolate Complexes as Phosphorescent Chemosensors for Detection of Benzene. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 299, 12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhi, J.S.; Patterson, M.R.; Dias, H.V.R. Coinage metal metallacycles involving a fluorinated 3,5-diarylpyrazolate. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 14814–14822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Saotome, M.; Takeda, S.; Young, D.J. Structures and Photoluminiscence of Coinage Metal(I) Phenylpyrazolato Trinuclear Complexes [M(3,5-Et2-4-Ph-pz)]3 and Arene Sandwich Complexes {[Ag(3,5-Et2-4-Ph-pz)]3}2(Ar) (Ar = Mesitylene and Toluene). Chem. Lett. 2020, 49, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberá, J.; Elduque, A.; Giménez, R.; Oro, L.A.; Serrano, J.L. Pyrazolate “Golden” Rings: Trinuclear Complexes That Form Columnar Mesophases at Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1996, 35, 2832–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberá, J.; Lantero, I.; Moyano, S.; Serrano, J.L.; Elduque, A.; Giménez, R. Silver pyrazolates as coordination-polymer luminiscent metallomesogens. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 14545–14553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán, E.; Barberá, J.; Serrano, J.L.; Elduque, A.; Giménez, R. Chiral Cyclic Trinuclear Gold(I) Complexes with a Helical Columnar Phase. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cored, J.; Crespo, O.; Serrano, J.L.; Elduque, A.; Giménez, R. Decisive Influence of the Metal in Multifunctional Gold, Silver, and Copper Metallacycles: High Quantum Yield Phosphorescence, Color Switching, and Liquid Crystalline Behavior. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 12632–12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovejero, P.; Mayoral, M.J.; Cano, M.; Lagunas, M.C. Luminescence of neutral and ionic gold(I) complexes containing pyrazole or pyrazolate-type ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 692, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramori, G.F.; Piccoli, R.M.; Segala, M.; Muñoz-Castro, A.; Guajardo-Maturana, R.; Andrada, D.M.; Frenking, G. Cyclic trinuclear copper(i), silver(i), and gold(i) complexes: A theoretical insight. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Dias, H.V.R.; Parasar, D.; Martín-Pastor, M. An experimental and computational NMR study of organometallic nine-membered rings: Trinuclear silver(I) complexes of pyrazolate ligands. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2020, 58, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, K.; Okano, M.; Martín-Pastor, M.; López-Sánchez, R.; Elguero, J.; Alkorta, I. Multinuclear magnetic resonance studies of five silver(I) trinuclear pyrazolate complexes. Struct. Chem. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Trujillo, C.; Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Elguero, J. Regium Bonds between Silver(I) Pyrazolates Dinuclear Complexes and Lewis Bases (N2, OH2, NCH, SH2, NH3, PH3, CO and CNH). Crystals 2020, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Trujillo, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Understanding Regium Bonds and their Competition with Hydrogen Bonds in Au2:HX Complexes. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Trujillo, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Rivalry between regium and hydrogen bonds established within diatomic coinage molecules and Lewis acids/bases. ChemPhysChem 2020. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, C.; Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Elguero, J.; Alkorta, I. The Lewis acidities of gold(I) and gold(III) derivatives: A theoretical study of complexes of AuCl and AuCl3. Struct. Chem. 2020, 31, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory; (International Series of Monographs on Chemistry, 22); Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, R.F.W. A quantum theory of molecular structure and its applications. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 893–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popelier, P.L.A. Atoms in Molecules: An Introduction, 1st ed.; Prentice Hall: Harlow, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Matta, C.F.; Boyd, R.J. An Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Foces-Foces, C.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Supramolecular structure of 1H-pyrazoles in the solid state: A crystallographic and ab initio study. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. 2000, 56, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Foces-Foces, C.; Infantes, L. Classification of hydrogen-bond motives in crystals of NH-pyrazoles: A mixed empirical and theoretical approach. Arkivoc 2006, ii, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Burini, A.; Fackler, J.P. Mixed-Metal Triangular Trinuclear Complexes: Dimers of Gold−Silver Mixed-Metal Complexes from Gold(I) Carbeniates and Silver(I) 3,5-Diphenylpyrazolates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5012–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Galassi, R.; Papa, F.; Burini, A.; Fackler, J.P. Gold(I) and Silver(I) Mixed-Metal Trinuclear Complexes: Dimeric Products from the Reaction of Gold(I) Carbeniates or Benzylimidazolates with Silver(I) 3,5-Diphenylpyrazolate. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 7770–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasar, D.; Jayaratna, N.B.; Muñoz-Castro, A.; Conway, A.E.; Mykhaailiuk, P.K.; Dias, H.V.R. Carbonyl complexes of copper(I) stabilized by bridging fluorinated pyrazolates and halide ions. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 6358–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoia, G.A.; Cenini, S.; La Monica, G.; Masciocchi, N.; Maspero, A.; Moret, M. Syntheses, Structures, and Reactivity of Polynuclear Pyrazolato Copper(I) Complexes, Including an ab-Initio XRPD Study of [Cu(dmnpz)](3) (Hdmnpz = 3,5-Dimethyl-4-nitropyrazole). Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 4284–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoia, G.A.; Cenini, S.; La Monica, G.; Masciocchi, N.; Moret, M. Synthesis, X-ray Structure, and Catalytic Properties of the Unprecedented Tetranuclear Copper(I) Species [Cu(dppz)]4 (Hdppz = 3,4-Diphenylpyrazole). Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, H.V.R.; Diyabalanage, H.V.K.; Eldabaja, M.G.; Elbjeirami, O.; Rawashdeh-Omary, M.A.; Omary, M.A. Brightly Phosphorescent Trinuclear Copper(I) Complexes of Pyrazolates: Substituent Effects on the Supramolecular Structure and Photophysics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7489–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, A.A.; Filippov, O.A.; Smol’yakov, A.F.; Baranova, K.F.; Titova, E.M.; Averin, A.A.; Shubina, E.S. Dinuclear CuI and AgI Pyrazolates Supported with Tertiary Phosphines: Synthesis, Structures, and Photophysical Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, R.; Simon, O.C.; Burini, A.; Tosi, G.; Conti, C.; Graiff, C.; Martins, N.M.R.; Da Silva, M.F.C.G.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Martins, L.M. Copper(I) and copper(II) metallacycles as catalysts for microwave assisted selective oxidation of cyclohexane. Polyhedron 2017, 134, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omary, M.A.; Rawashdeh-Omary, M.A.; Diyabalanage, H.V.K.; Dias, H.V.R. Blue Phosphors of Dinuclear and Mononuclear Copper(I) and Silver(I) Complexes of 3,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)pyrazolate and the Related Bis(pyrazolyl)borate. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 8612–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzoia, G.A.; Beccalli, E.M.; La Monica, G.; Masciocchi, N.; Moret, M. Synthesis of poly(3,5-dicarbomethoxypyrazolato)copper and its reactions with carbon monoxide and cyclohexyl isocyanide. Crystal structures of [Cu2(dcmpz)2(py)2(CO)] and [Cu(dcmpz)(RNC)]2 (Hdcmpz = 3,5-dicarbomethoxypyrazole, R = cyclohexyl). Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trose, M.; Nahra, F.; Poater, A.; Cordes, D.B.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cavallo, L.; Cazin, C.S. Investigating the Structure and Reactivity of Azolyl-Based Copper(I)-NHC Complexes: The Role of the Anionic Ligand. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8176–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colombo, V.; Galli, S.; Choi, H.J.; Han, G.D.; Maspero, A.; Palmisano, G.; Masciocchi, N.; Long, J.R. High thermal and chemical stability in pyrazolate-bridged metal-organic frameworks with exposed metal sites. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishima, A.; Fuyuhiro, A.; Kumagai, H.; Kawata, S. Bis[μ-3,5-bis-(2-pyrid-yl)pyrazolato]bis-(hydrogensulfato)-dicopper(II) methanol disolvate. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct. Rep. Online 2011, 67, m1523–m1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Zheng, J.; Peng, S.-K.; Zhu, X.-W.; Wan, M.-Y.; Lu, W.; Li, D. A chemopalette strategy for white light by modulating monomeric and excimeric phosphorescence of a simple Cu(I) cyclic trinuclear unit. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 4635–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, M.K.; Rettig, S.J.; Storr, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Trotter, J. Synthesis and X-ray crystal structure of the 3,5-dimethylpyrazolato copper(I) trimer, [Cu(pz″)]3. Can. J. Chem. 1990, 68, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujisawa, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Miyashita, Y.; Okamoto, K.-I. Crystal Structure of Pyrazolato-bridged Copper(I) Polynuclear Complexes. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, H.V.R.; A Polach, S.; Wang, Z. Coinage metal complexes of 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)pyrazolate ligand. J. Fluor. Chem. 2000, 103, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawitz, T.; Lemer, H.W.; Bolte, M. cyclo-Tri(μ2-3-phenyl-1H-pyrazole) tricopper(I). Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E 2006, 62, 1474–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, F.; Maspero, A.; Cervellino, A.; Guagliardi, A.; Masciocchi, N. Bending by Faulting: A Multiple Scale Study of Copper and Silver Nitropyrazolates. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 2913–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Miyashita, Y.; Okamoto, K.-I. Pyrazolate-bridged group 11 metal(I) complexes: Substituent effects on the supramolecular structures and physicochemical properties. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2010, 363, 2977–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspero, A.; Brenna, S.; Galli, S.; Penoni, A. Synthesis and characterization of new polynuclear copper(I) pyrazolate complexes and their catalytic activity in the cyclopropanation of olefins. J. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 672, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, A.A.; Smol’yakov, A.F.; Rodionov, A.N.; Kosenko, I.D.; Guseva, E.A.; Zubavichus, Y.V.; Dorovatovskii, P.V.; Filippov, O.A.; Shubina, E.S. Ferrocene-containing tri- and tetranuclear cyclic copper(i) and silver(i) pyrazolates. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2017, 66, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañon-Mancisidor, W.; Gómez-García, C.J.; Espallargas, M.G.; Vega, A.; Spodine, E.; Venegas-Yazigi, D.; Coronado, E. Structural re-arrangement in two hexanuclear Cu(II) complexes: From a spin frustrated trigonal prism to a strongly coupled antiferromagnetic soluble ring complex with a porous tubular structure. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omary, M.A.; Rawashdeh-Omary, M.A.; Gonser, M.W.A.; Elbjeirami, O.; Grimes, T.; Cundari, T.R.; Diyabalanage, H.V.K.; Gamage, C.S.P.; Dias, H.V.R. Metal Effect on the Supramolecular Structure, Photophysics, and Acid−Base Character of Trinuclear Pyrazolato Coinage Metal Complexes†. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 8200–8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujisawa, K. CSD Private Communication, 2016.
- Morishima, Y.; Young, D.J.; Fujisawa, K. Structure and photoluminescence of silver(i) trinuclear halopyrazolato complexes. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 15915–15928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Ishida, T.; Nogami, T. Supramolecular triangular and linear arrays of metal-radical solids using pyrazolato-silver(i) motifs. Dalton Trans. 2004, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.-P.; Wei, D.; Yang, G. Hexameric Silver(I) Pyrazolate: Synthesis, Structure, and Isomerization. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 11310–11316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Raptis, R.G. Synthesis and crystal structure of tetrameric silver(I) 3,5-di-tert-butyl-pyrazolate. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2007, 360, 2503–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, M.; Wöckel, S.; Konstanzer, V.; Dechert, S.; John, M.; Meyer, F. Structural Variations in Tetrasilver(I) Complexes of Pyrazolate-bridged Compartmental N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands. Z. Naturforsch. B 2009, 64, s1542–s1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, A.A.; Filippov, O.A.; Smol’yakov, A.F.; Averin, A.A.; Shubina, E.S. Synthesis, structures and luminescence of multinuclear silver(i) pyrazolate adducts with 1,10-phenanthroline derivatives. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8410–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, C.H.; Fuertes, S.; Beavers, C.M.; Hatcher, L.E.; Parlett, A.; Shepherd, H.J.; Christensen, J.; Teat, S.J.; Intissar, M.; Rodrigue-Witchel, A.; et al. Tunable Trimers: Using Temperature and Pressure to Control Luminescent Emission in Gold(I) Pyrazolate-Based Trimers. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 16933–16942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Raptis, R.G. Supramolecular assembly of trimeric gold(I) pyrazolates through aurophilic attractions. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fronczek, F.R. CSD Private Communication, 2014.
- Yang, G.; Raptis, R.G. Synthesis, structure and properties of tetrameric gold(I) 3,5-di-tert-butyl-pyrazolate. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2003, 352, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.H.; Raptis, R.G.; Fackler, J.P., Jr. Syntheses and X-ray structures of group 11 pyrazole and pyrazolate complexes. X-ray crystal structures of bis(3,5-diphenyl-pyrazole)copper(II) dibromide, tris(μ-3,5-diphenylpyrazolato-N,N′) trisilver(I)-2-tetrahydro-furan, tris(μ-3,5-diphenylpyrazolato-N,N′)trigold(I), and hexakis(μ-3,5-diphenyl-pyrazolato-N,N′)hexagold(I). Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasar, D.; Almotawa, R.M.; Jayaratna, N.B.; Ceylan, Y.S.; Cundari, T.R.; Omary, M.A.; Dias, H.V.R. Synthesis, Photophysical Properties, and Computational Analysis of Di- and Tetranuclear Alkyne Complexes of Copper(I) Supported by a Highly Fluorinated Pyrazolate. Organometallics 2018, 37, 4105–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, A.A.; Smol’yakov, A.F.; Baranova, K.F.; Filippov, O.A.; Shubina, E.S. Synthesis, structures and photophysical properties of phosphorus-containing silver 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)pyrazolates. Mendeleev Commun. 2018, 28, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. CSD Private Communication, 2019.
- Kandel, S.; Stenger-Smith, J.; Chakraborty, I.; Raptis, R.G. Syntheses and X-ray crystal structures of a family of dinuclear silver(I)pyrazolates: Assessment of their antibacterial efficacy against P. aeruginosa with a soft tissue and skin infection model. Polyhedron 2018, 154, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaratna, N.B.; Olmstead, M.M.; Kharisov, B.I.; Dias, H.V.R. Coinage Metal Pyrazolates [(3,5-(CF3)2Pz)M]3 (M = Au, Ag, Cu) as Buckycatchers. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 8277–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Baran, P.; Martínez, A.R.; Raptis, R.G. Substituent Effects on the Supramolecular Aggregation of AgI-Pyrazolato Trimers. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 13, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, H.V.R.; Gamage, C.S.P.; Keltner, J.; Diyabalanage, H.V.K.; Omari, I.; Eyobo, Y.; Dias, N.R.; Roehr, N.; McKinney, L.; Poth, T.; et al. Trinuclear Silver(I) Complexes of Fluorinated Pyrazolates. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 2979–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoia, G.A.; La Monica, G.; Maspero, A.; Moret, M.; Masciocchi, N. Silver(I) Pyrazolates. Synthesis and X-ray and (31)P-NMR Characterization of Triphenylphosphine Complexes and Their Reactivity toward Heterocumulenes. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.-X.; Ning, Y.-L.; Ying, J.; Hou, X.; Li, T.-J.; Wang, X.-L. Three multi-nuclear clusters and one infinite chain induced by a pendant 4-butyl-1H-pyrazole ligand for modification of Keggin anions. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.P.; Salbego, P.R.S.; De Moraes, G.A.; Bender, C.R.; Zambiazi, P.J.; Orlando, T.; Pagliari, A.B.; Frizzo, C.P.; Hörner, M. Understanding the crystalline formation of triazene N-oxides and the role of halogen···π interactions. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, J.P.P.; Salbego, P.R.S.; Orlando, T.; Rosa, J.M.L.; Fiss, G.F.; de Oliveira, J.P.G.; Vasconcellos, M.L.A.A.; Zanatta, N.; Bonacorso, H.G.; Martins, M.A.P. Substituent effects of 7-chloro-4-substituted quinolines. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 4094–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Solimannejad, M.; Provasi, P.; Elguero, J. Theoretical Study of Complexes and Fluoride Cation Transfer Between N2F+ and Electron Donors. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 7154–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugas, D.; Simon, S.; Duran, M. Electron Density Topological Properties are Useful to Assess the Difference Between Hydrogen and Dihydrogen Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 4506–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, I.; Alkorta, I.; Molins, E.; Espinosa, E. Universal Features of the Electron Density Distribution in Hydrogen-Bonding Regions: A Comprehensive Study Involving H⋅⋅⋅X (X=H, C, N, O, F, S, Cl, π) Interactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2442–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sanz, G.; Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J. Theoretical Study of Intramolecular Interactions in Peri-Substituted Naphthalenes: Chalcogen and Hydrogen Bonds. Molecules 2017, 22, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkorta, I.; Elguero, J.; Del Bene, J.E.; Mó, O.; Montero-Campillo, M.M.; Yáñez, M.; Romero, O.M. Mutual Influence of Pnicogen Bonds and Beryllium Bonds: Energies and Structures in the Spotlight. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 5871–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06 functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Accounts 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunning, T.H. Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. I. The atoms boron through neon and hydrogen. J. Chem. Phys. 1989, 90, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papajak, E.; Zheng, J.; Xu, X.; Leverentz, H.R.; Truhlar, D.G. Perspectives on Basis Sets Beautiful: Seasonal Plantings of Diffuse Basis Functions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 3027–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.A.; Puzzarini, C. Systematically convergent basis sets for transition metals. II. Pseudopotential-based correlation consistent basis sets for the group 11 (Cu, Ag, Au) and 12 (Zn, Cd, Hg) elements. Theor. Chem. Accounts 2005, 114, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Rev. A.03; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Keith, T.A. AIMAll, Version 19.10.12; TK Gristmill Software: Overland Park, KS, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
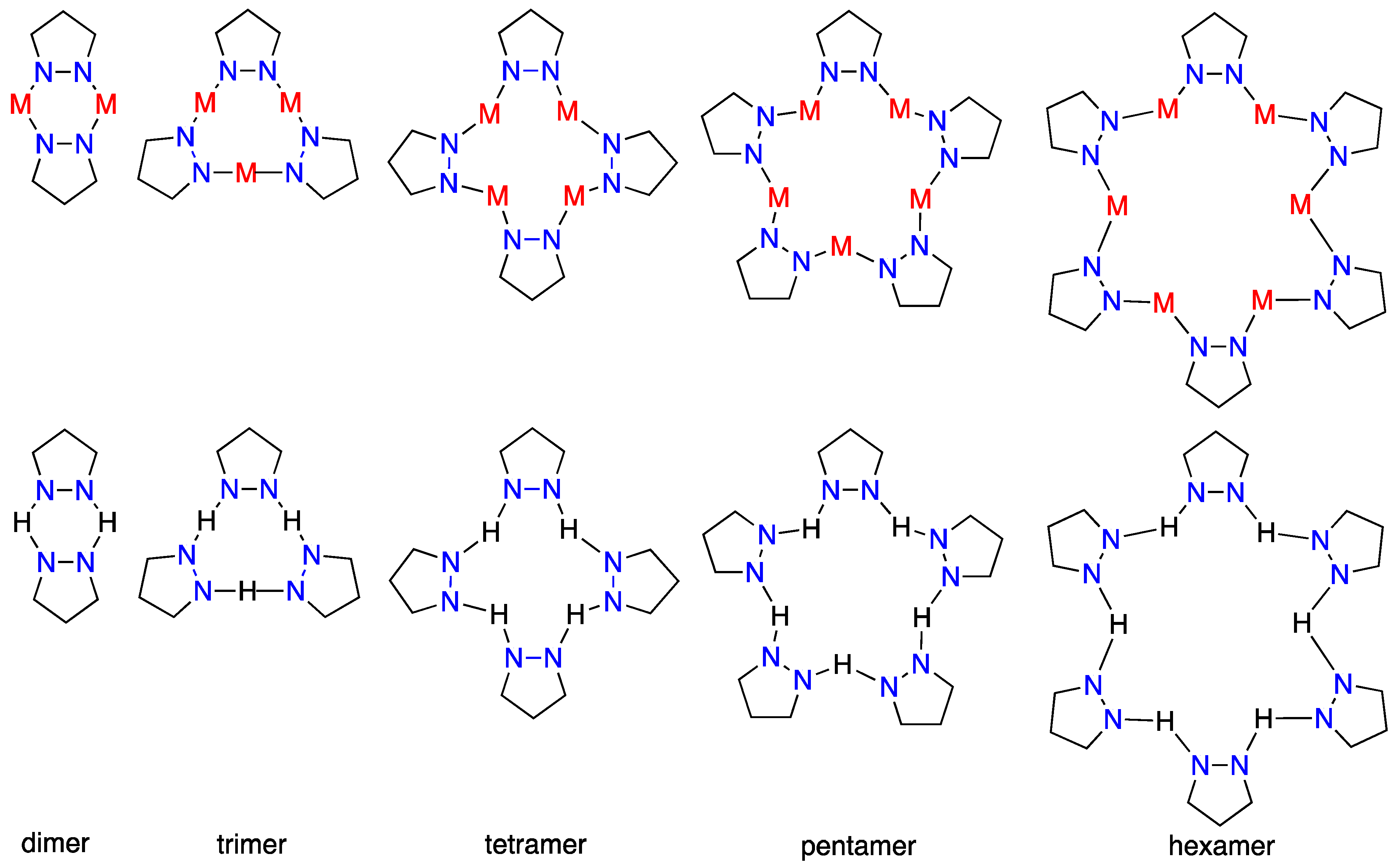
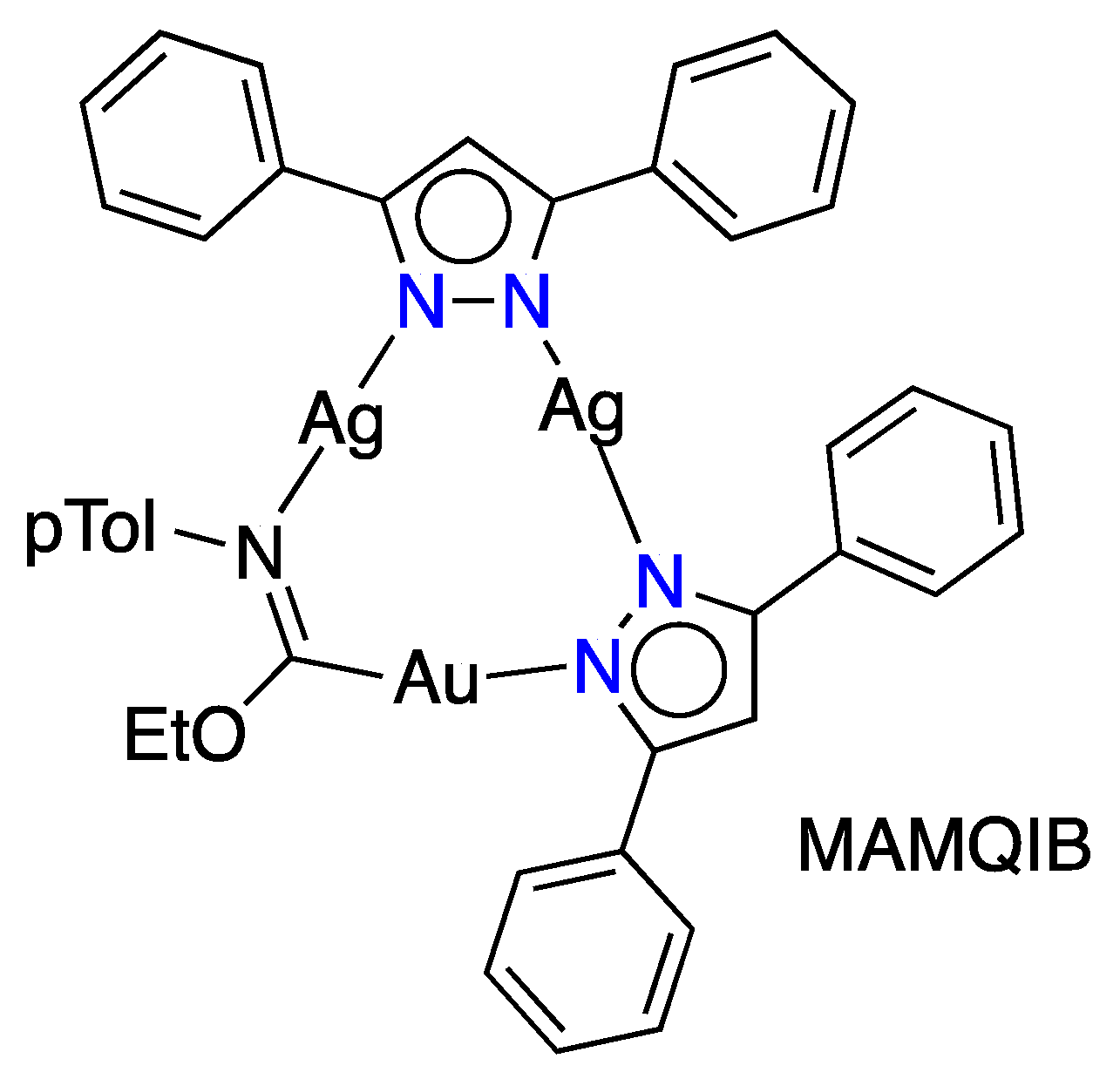
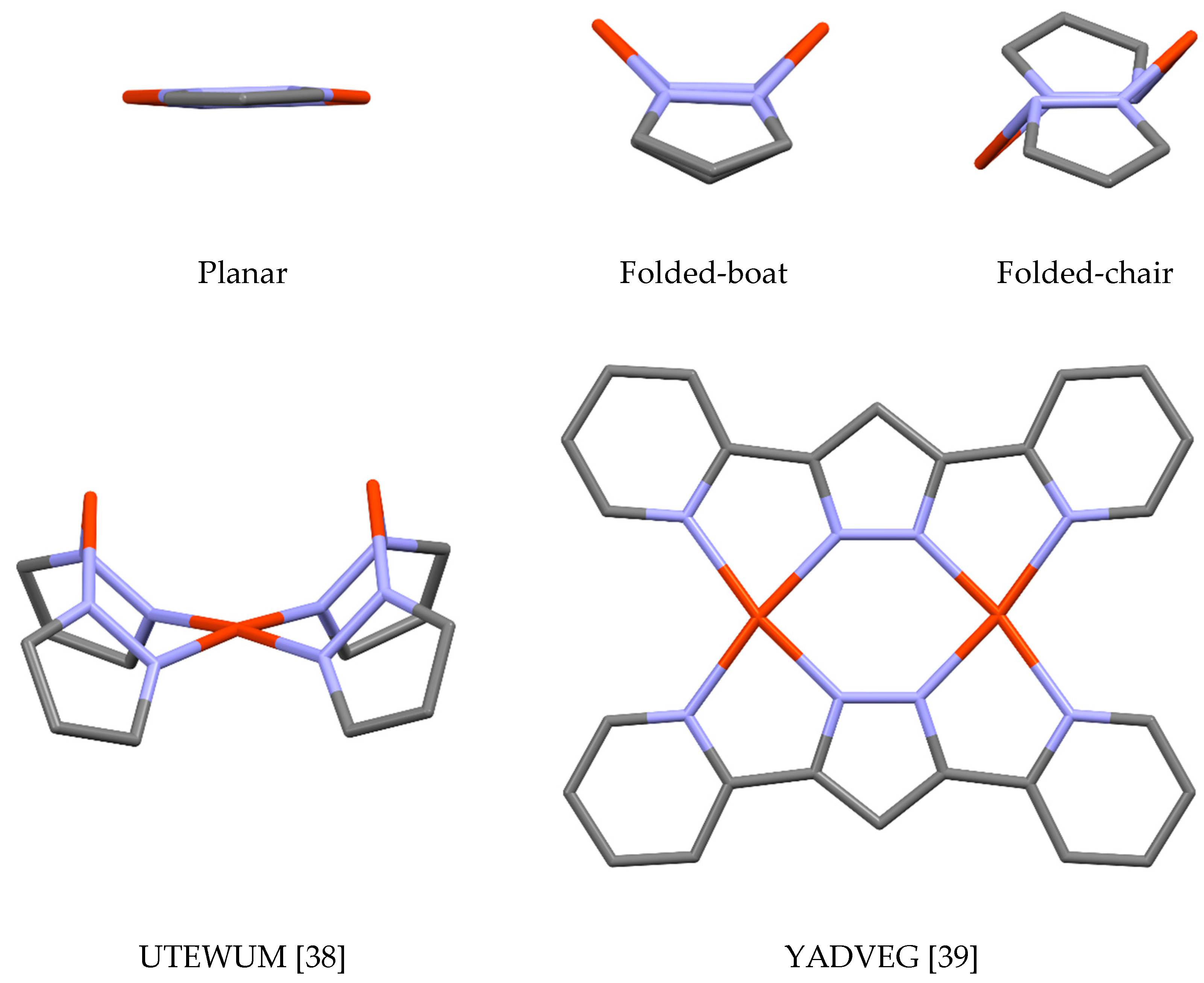
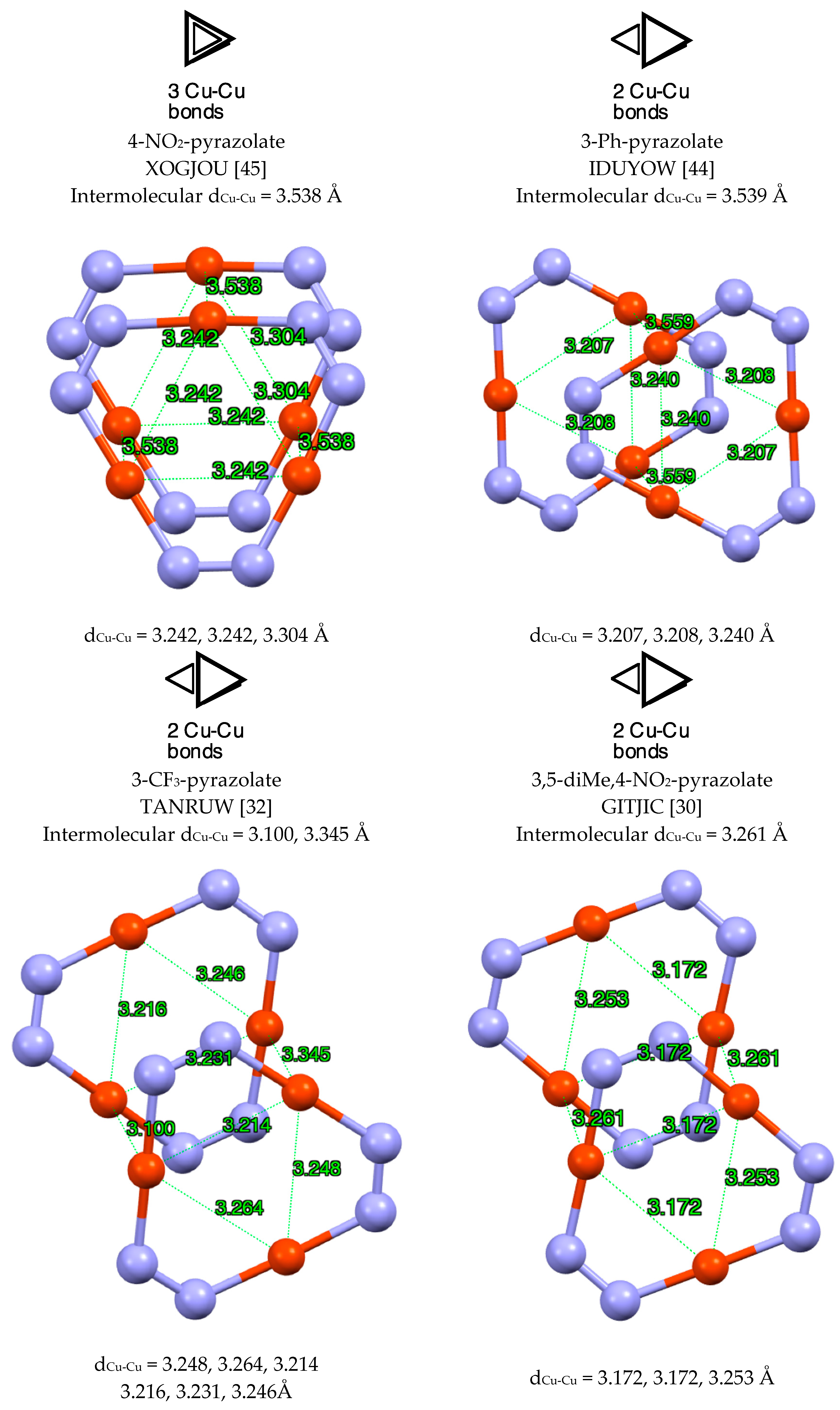
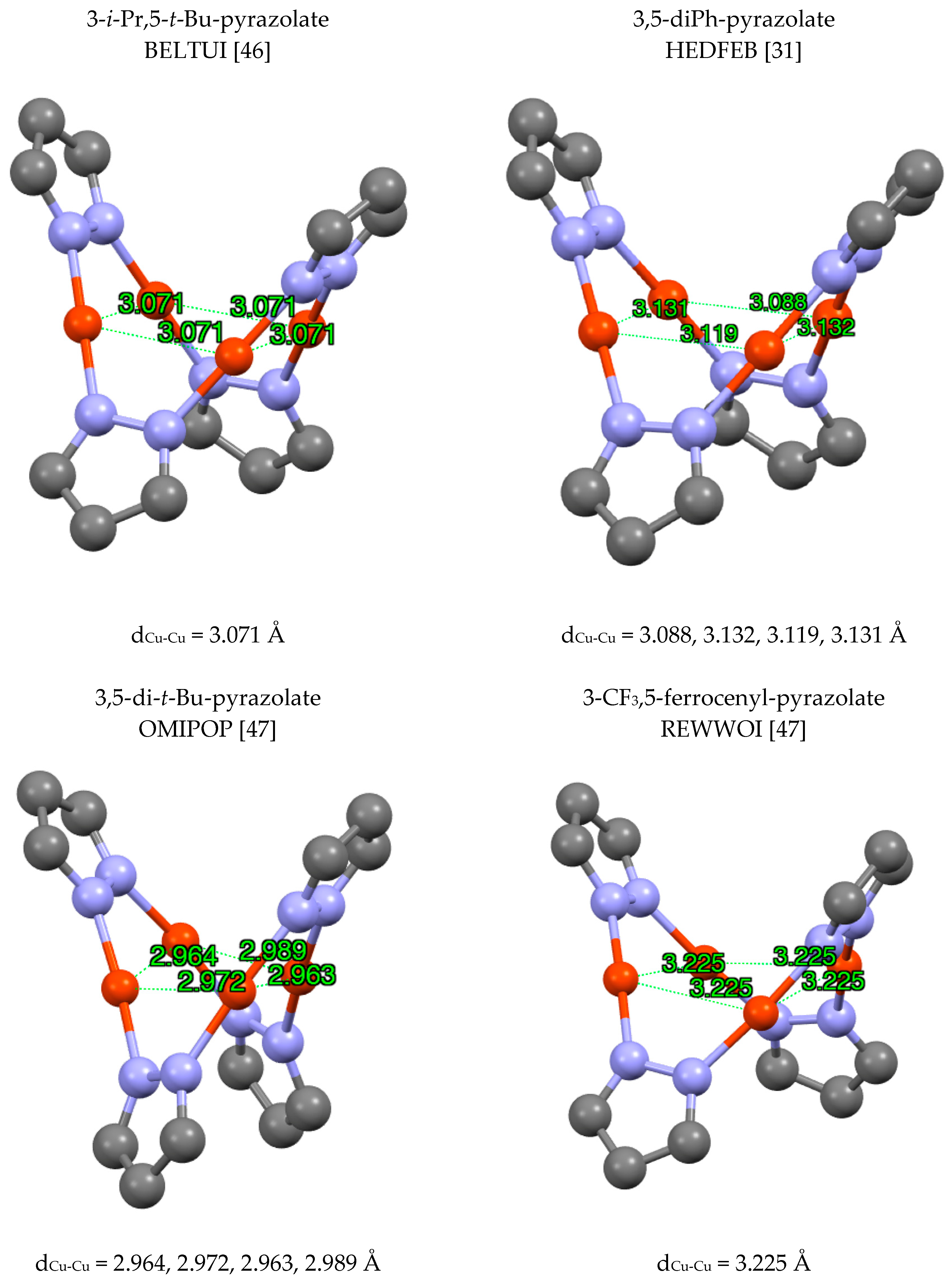
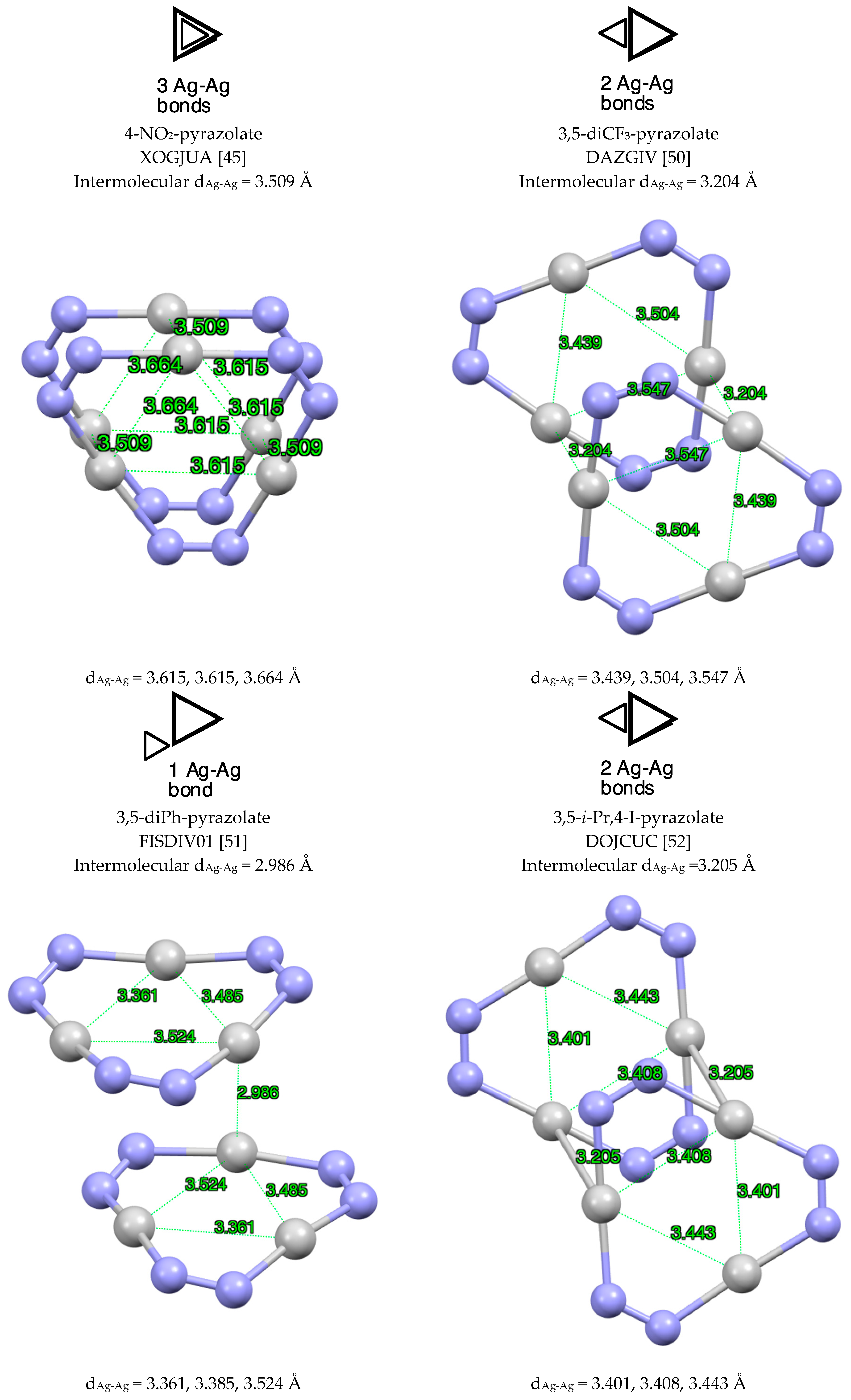


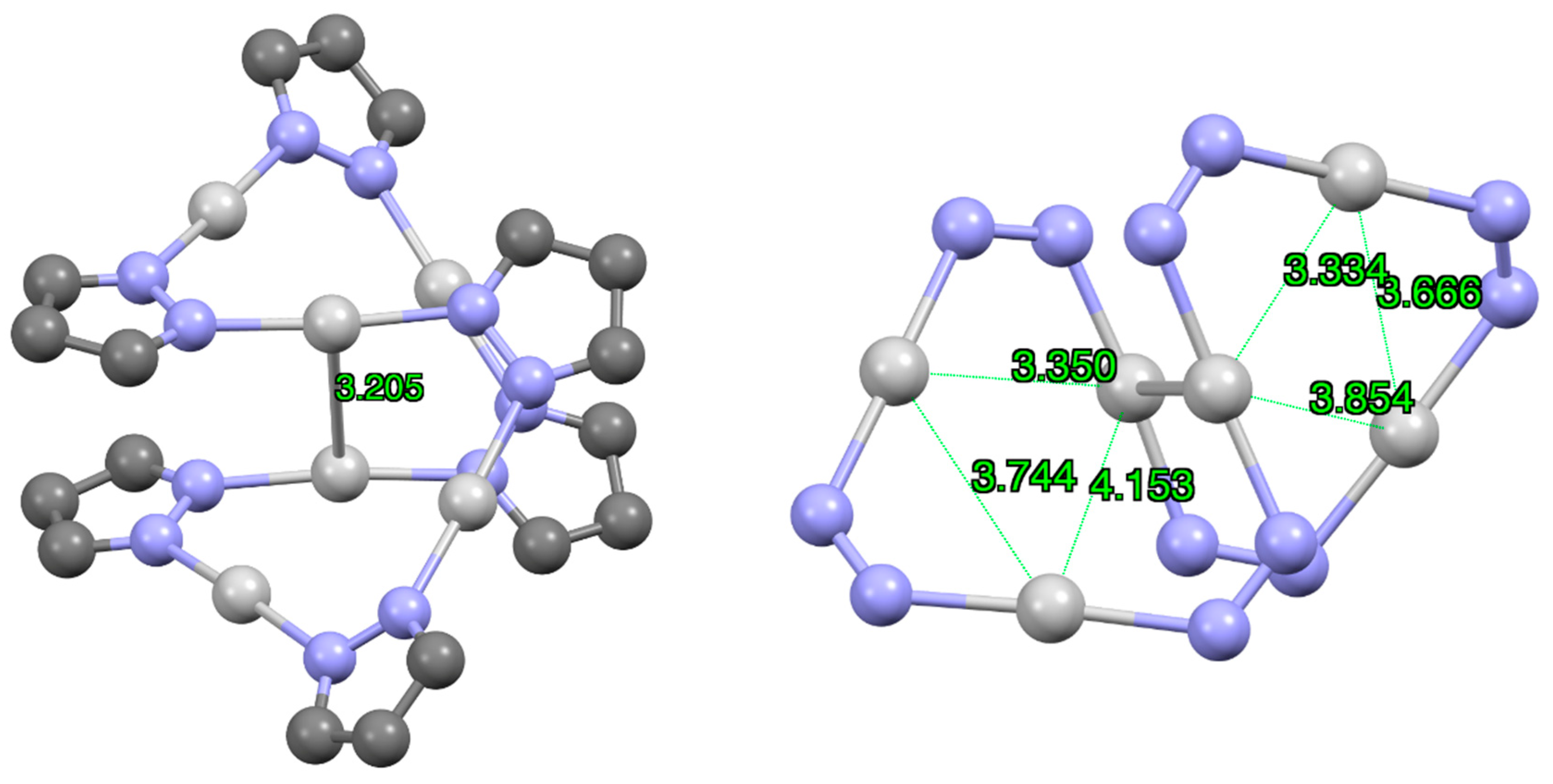
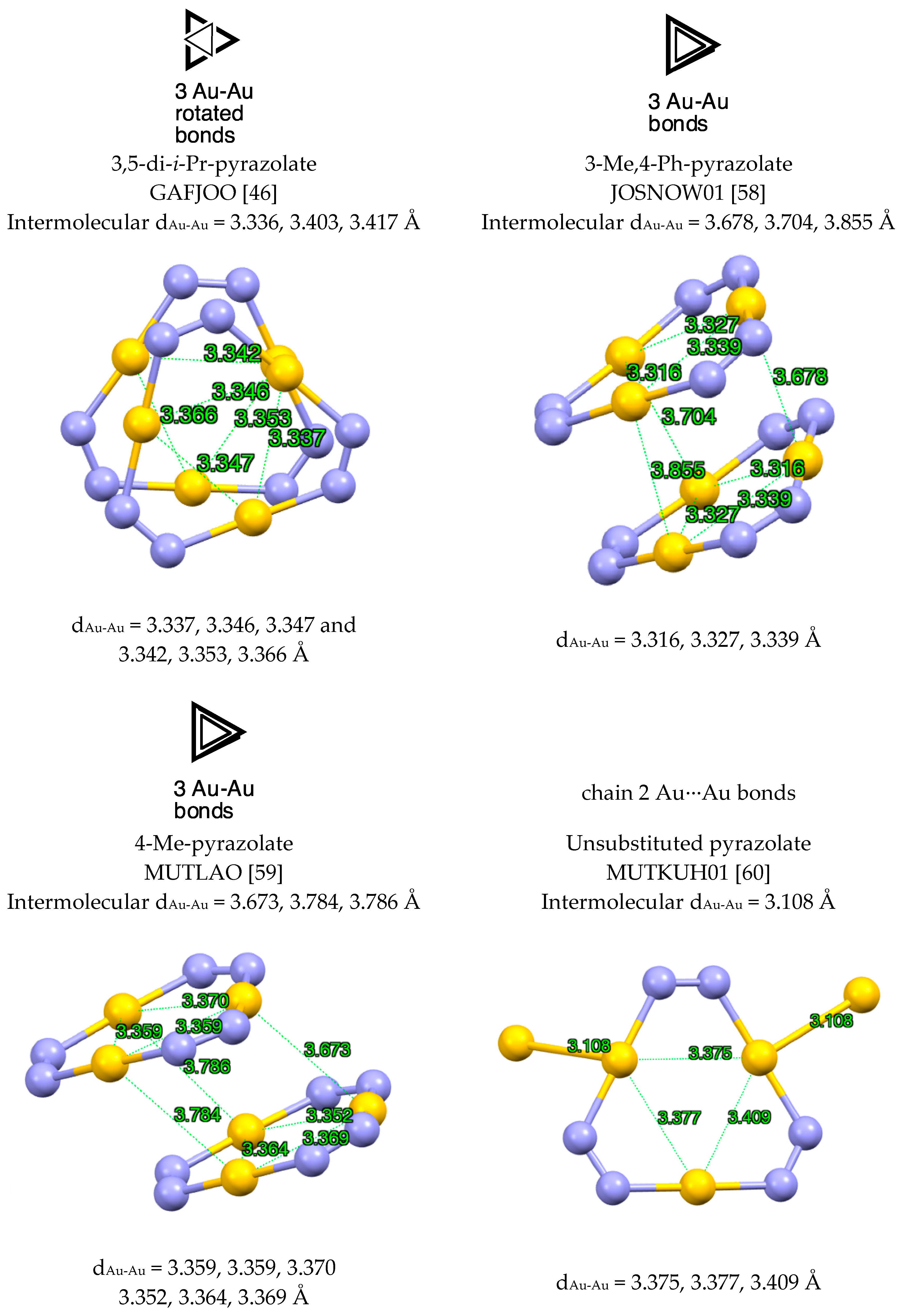

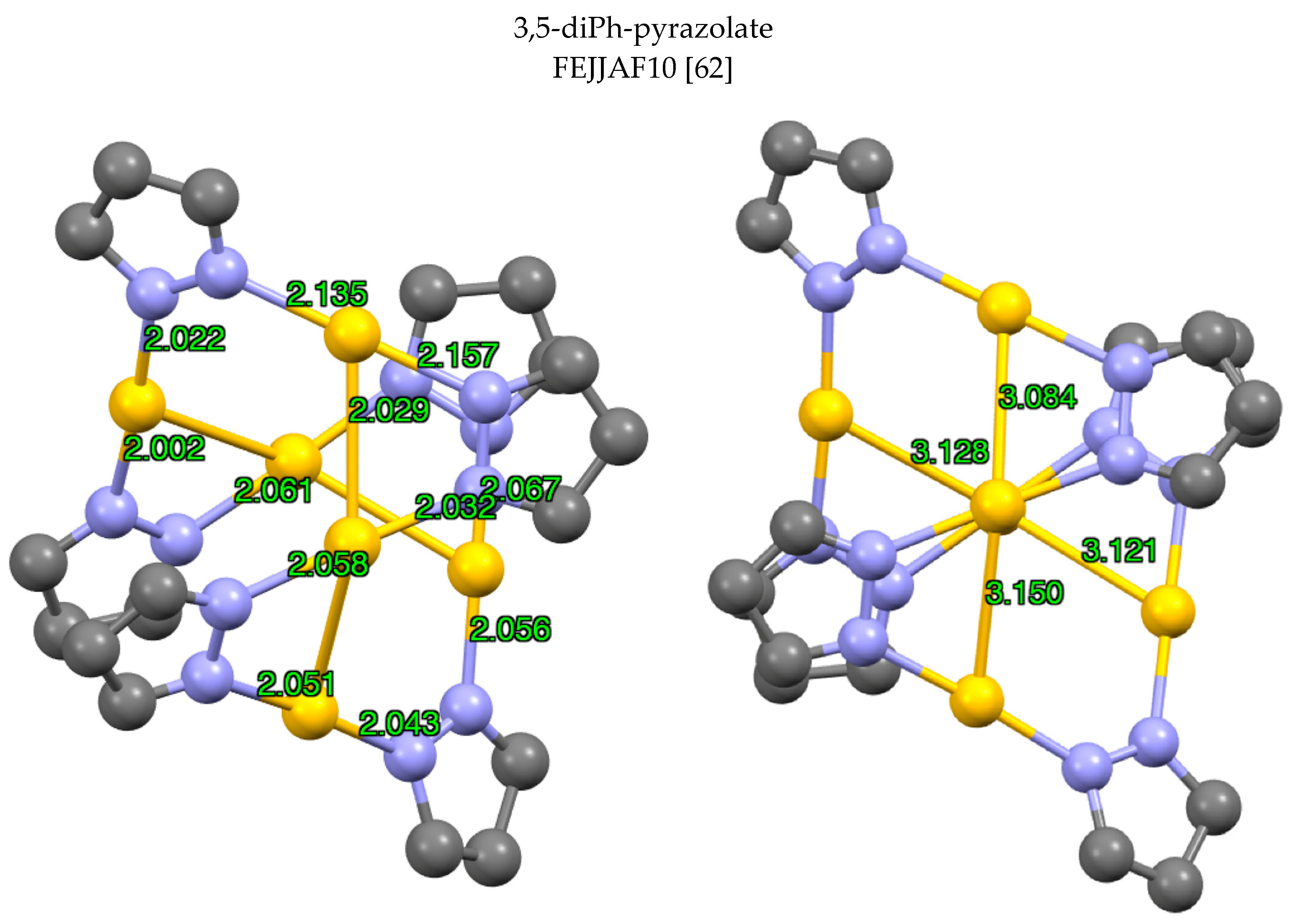
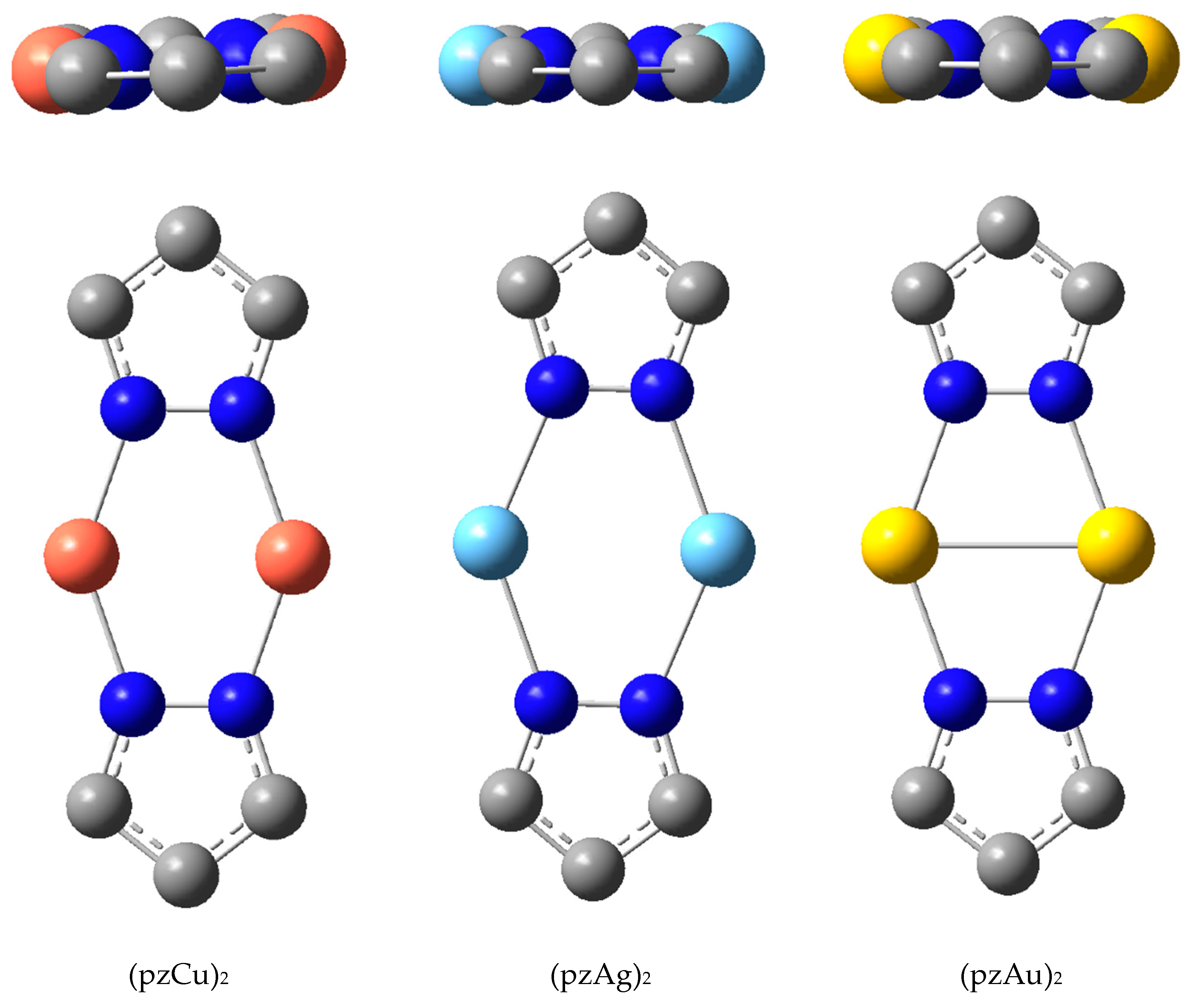

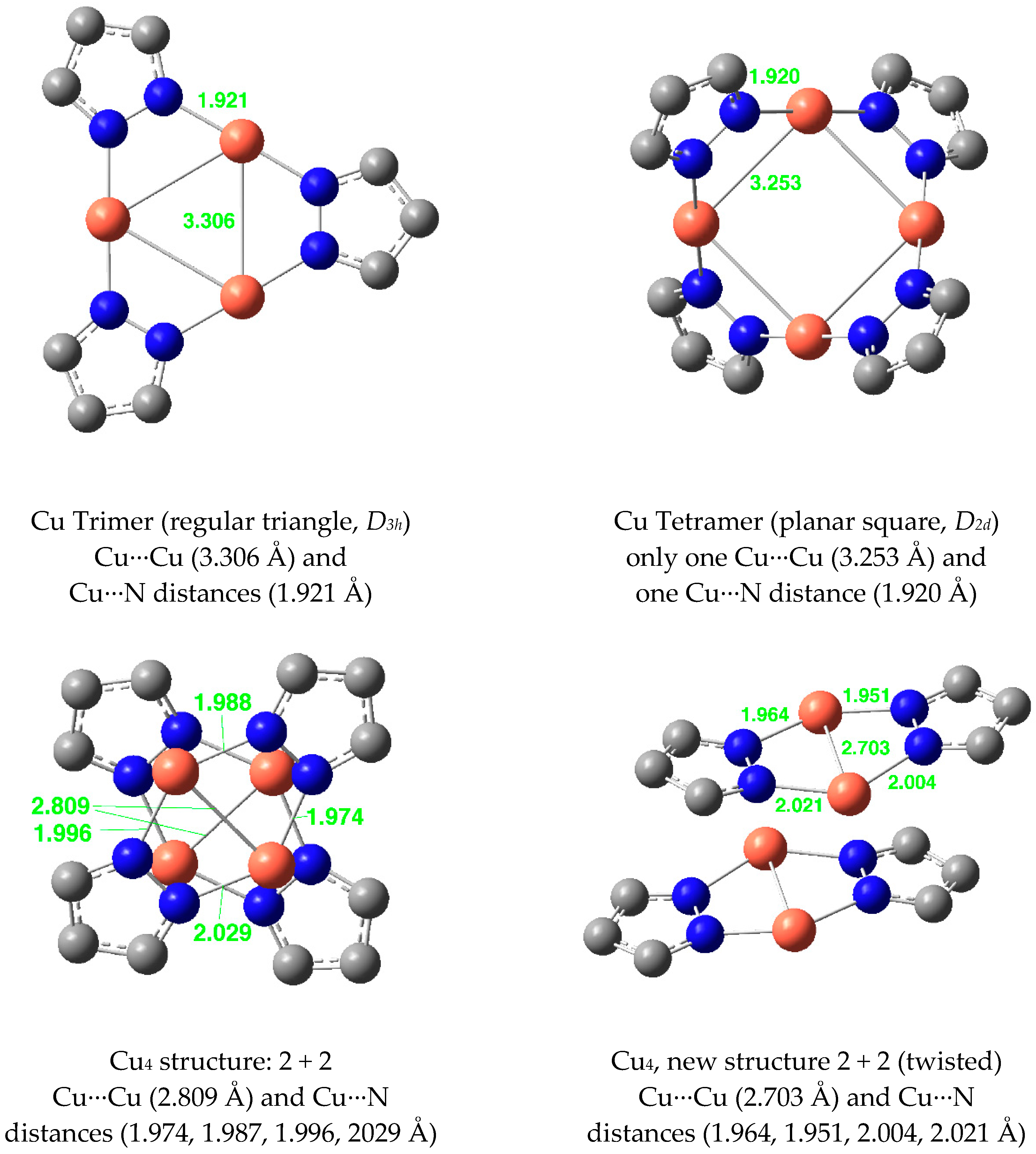
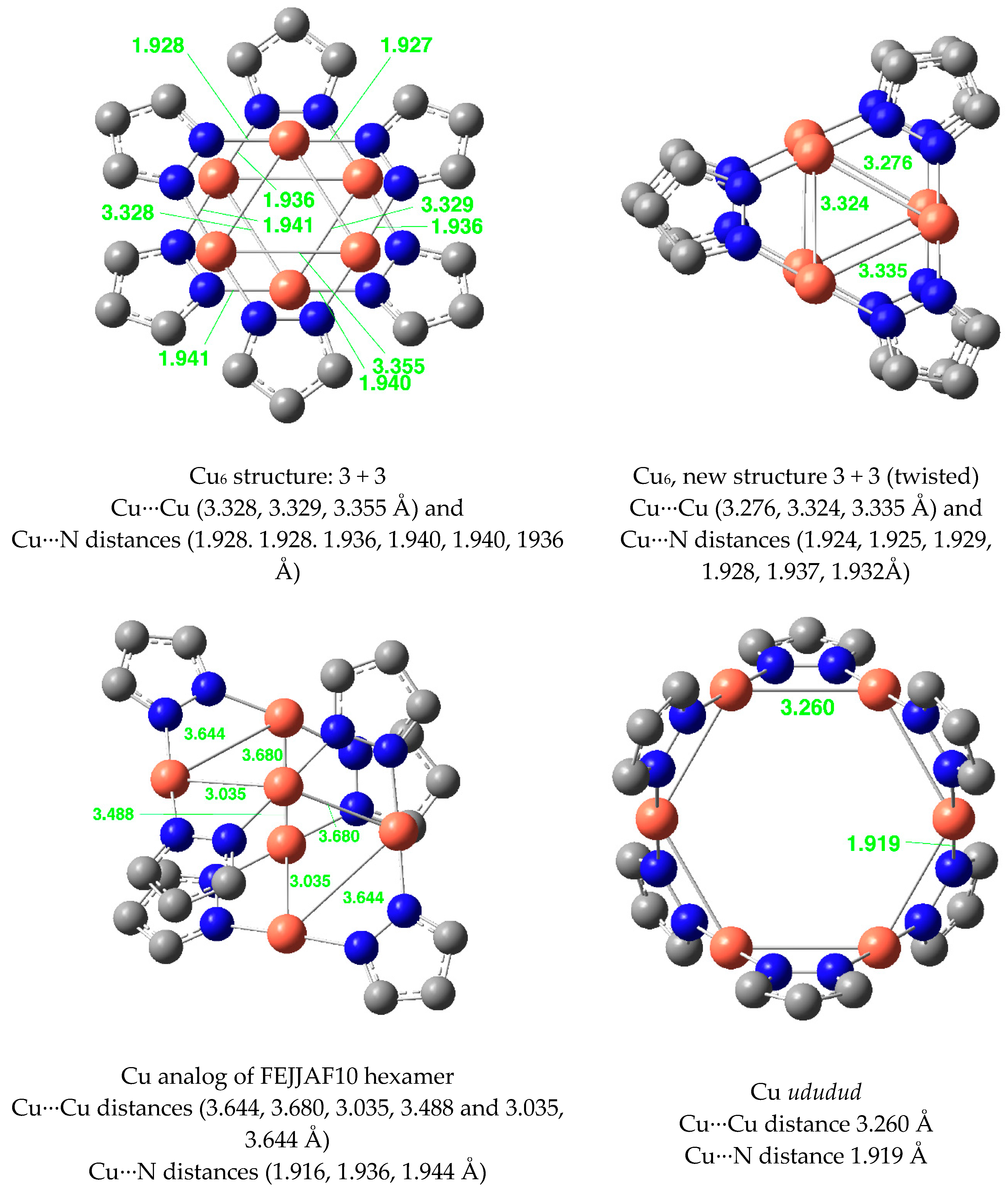
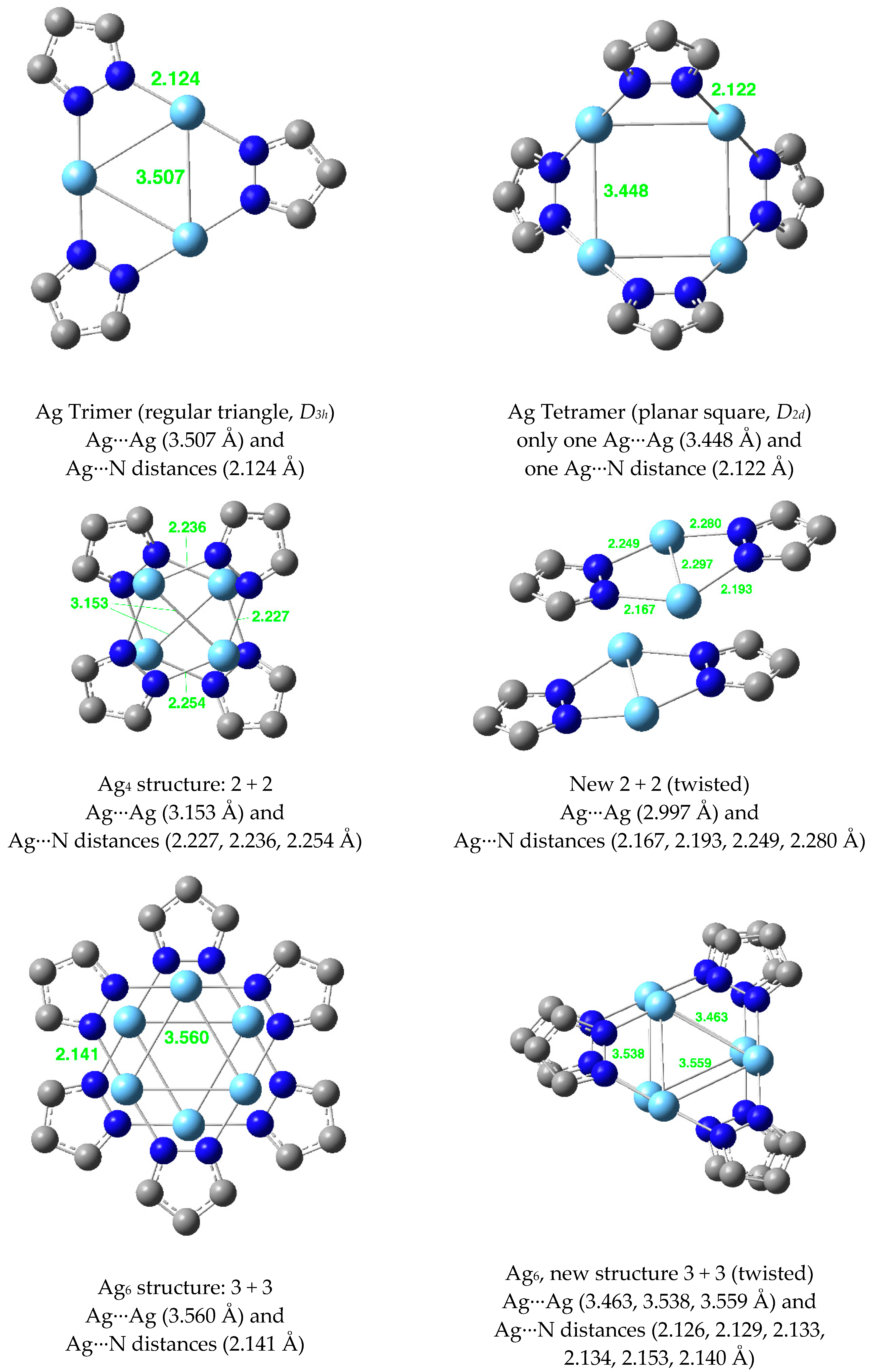
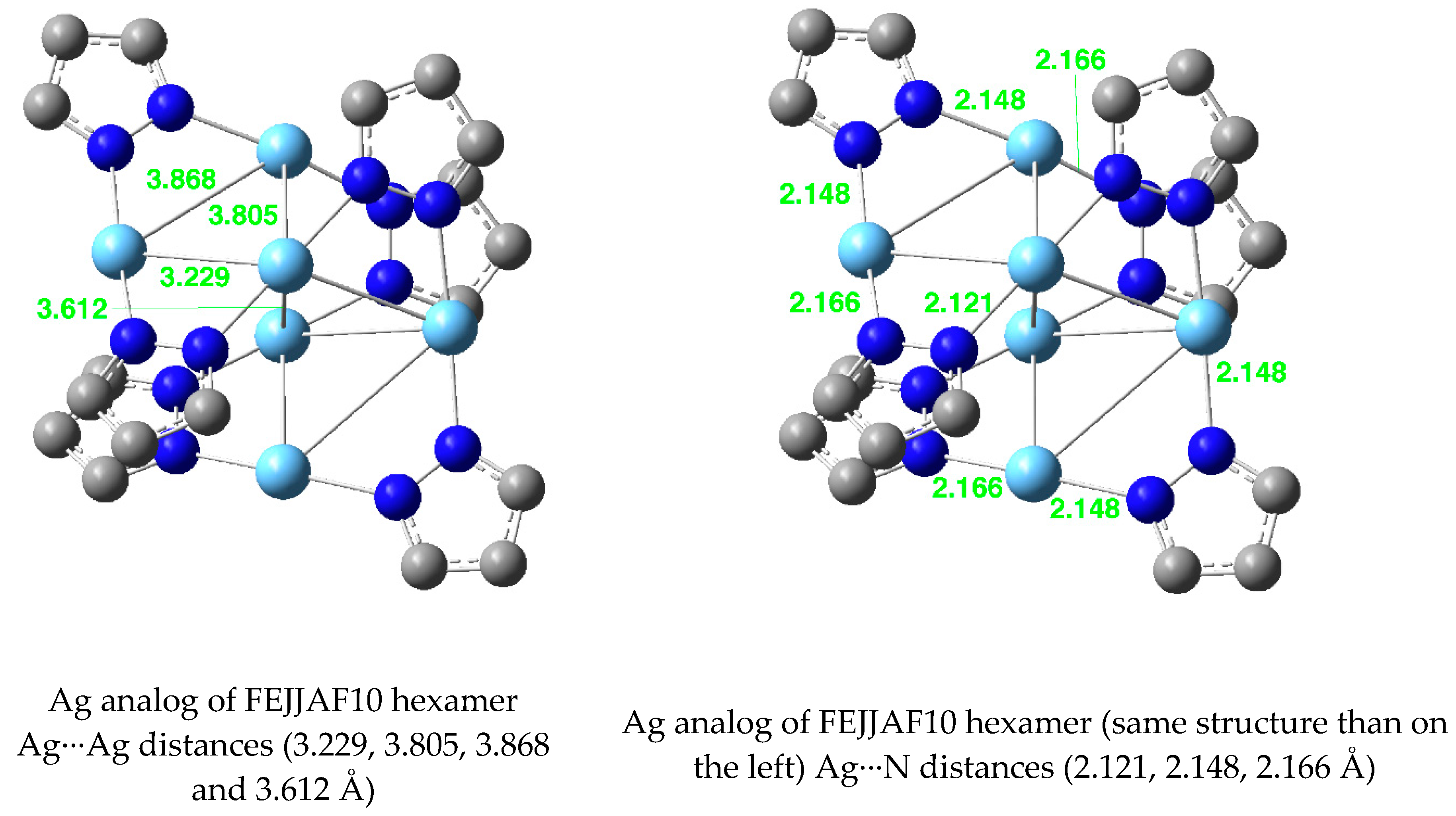
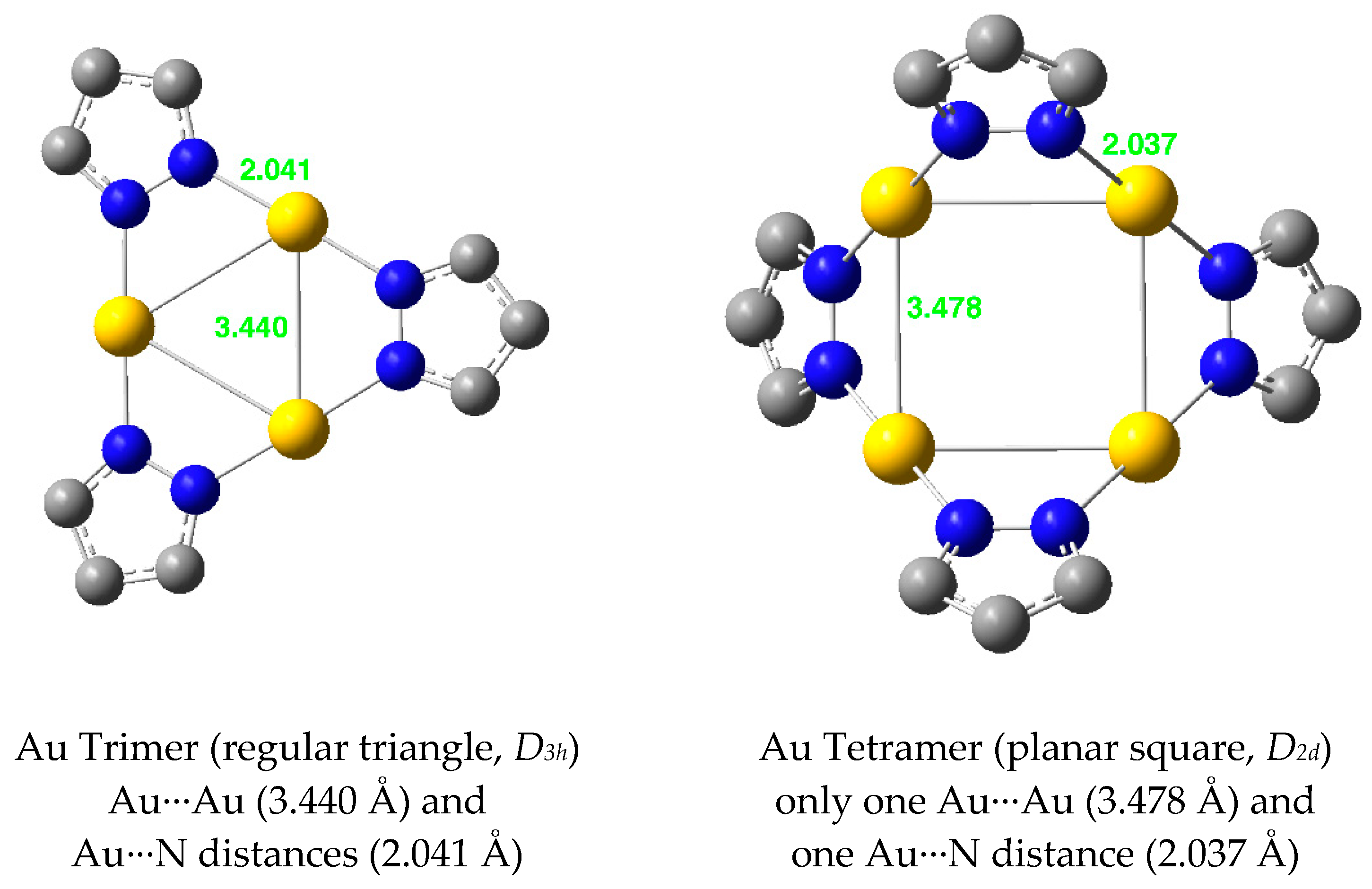
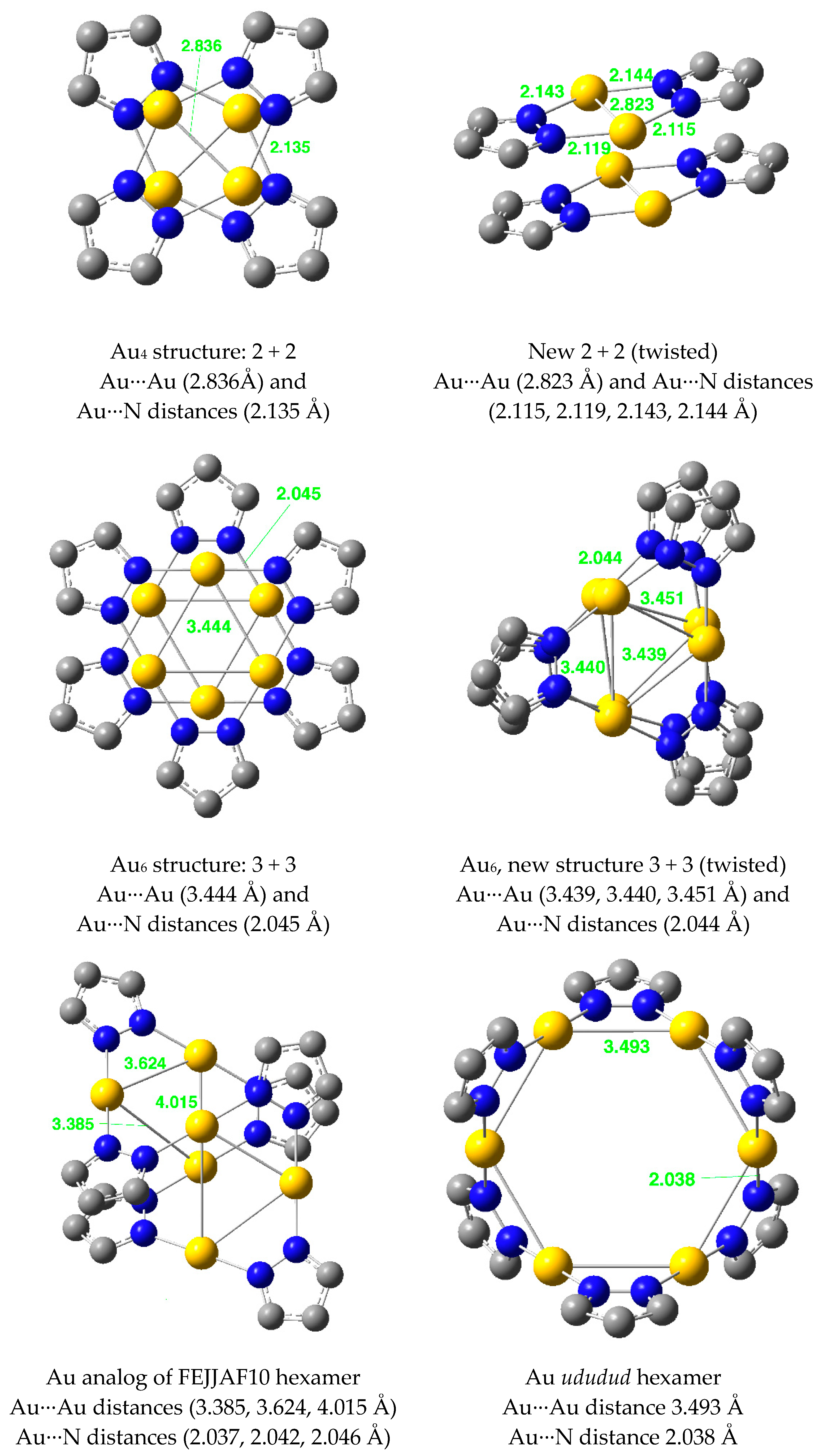

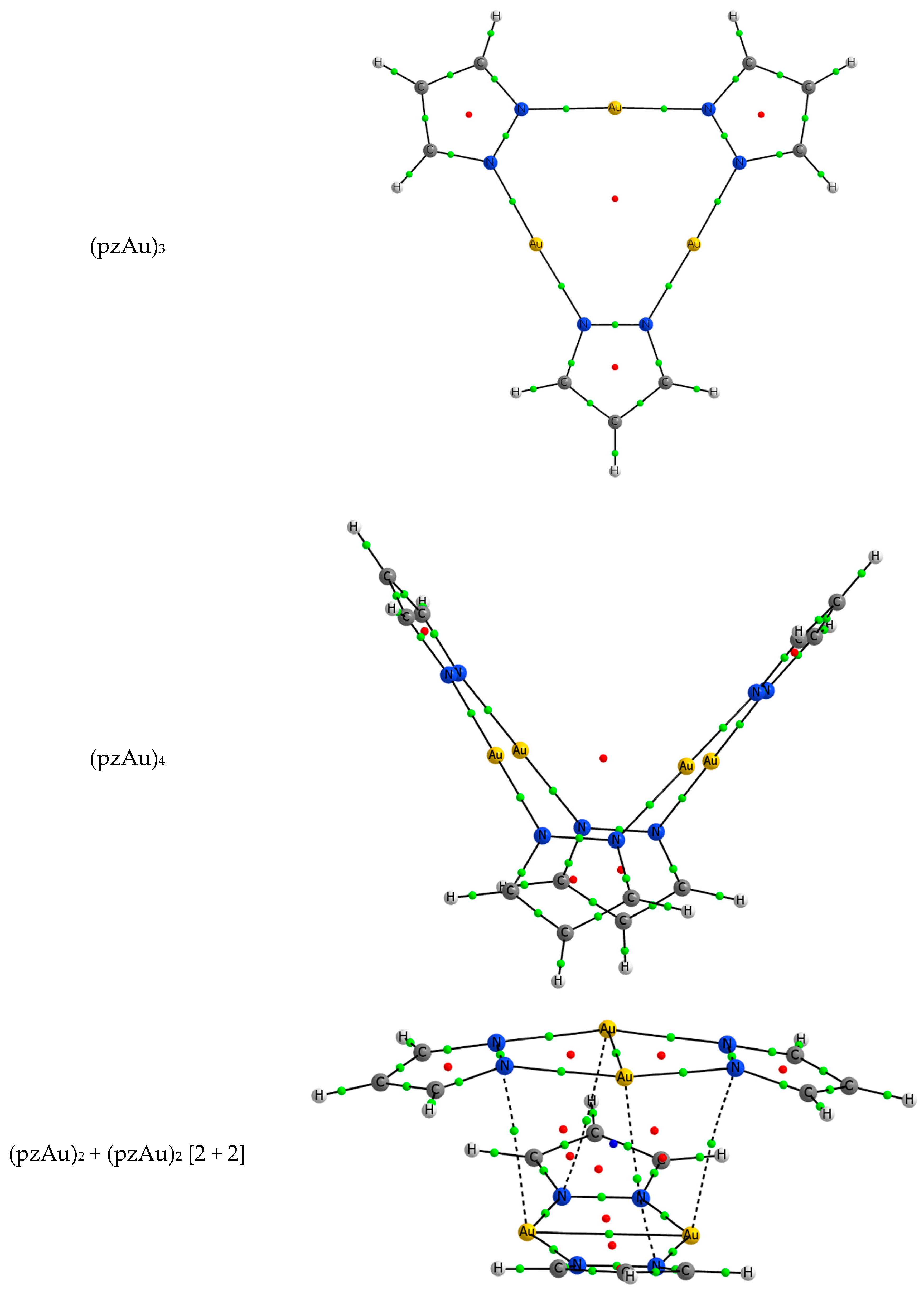

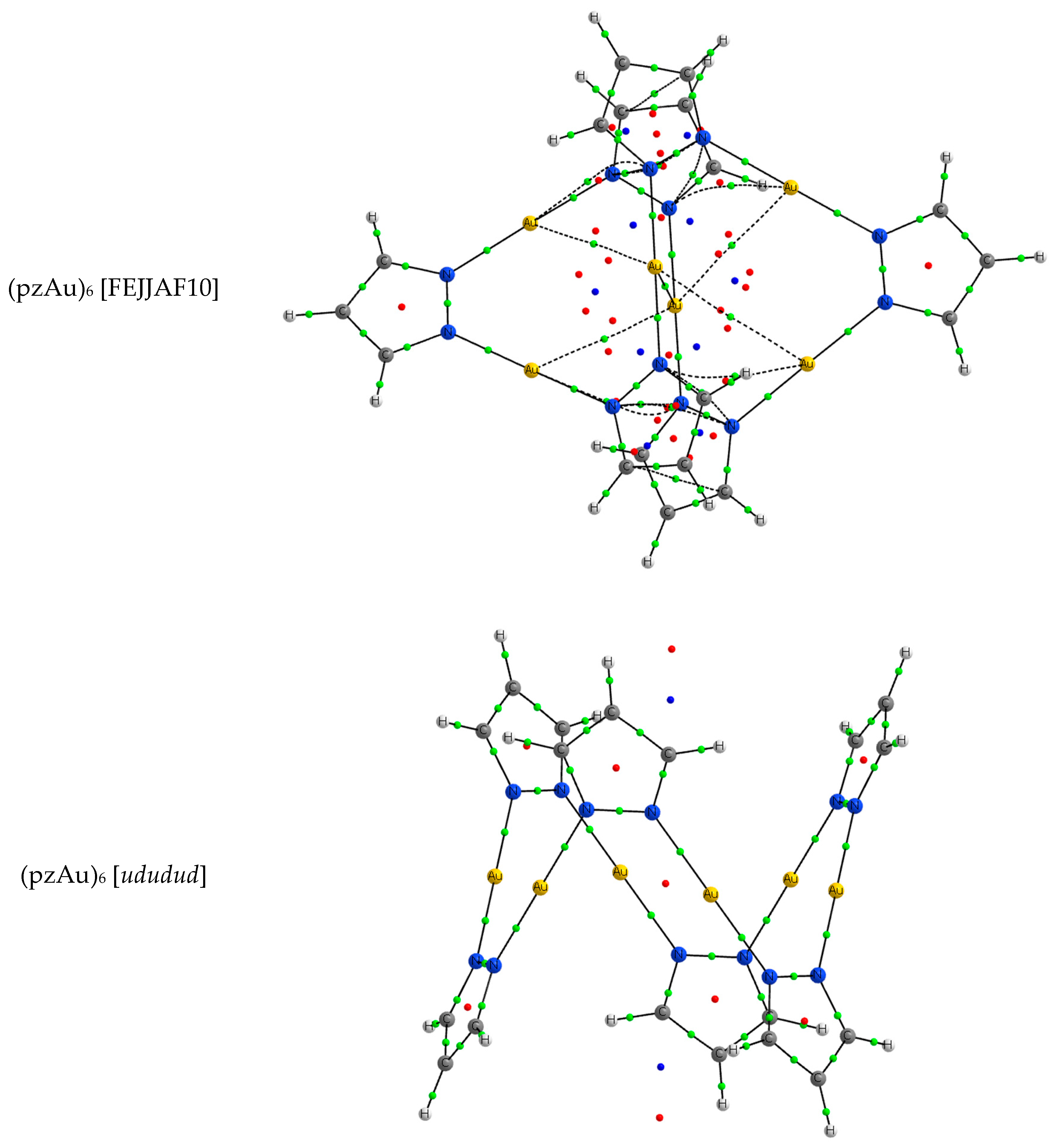
| Metal/H | Total | Dimers | Trimers | Tetramers | Pentamers | Hexamers (Refcodes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu(I) | 81 | 2 22 [27.2] | 1 41 [50.6] | 3 18 [22.2] | 5 0 [0.0] | 4 0 [0.0] |
| Ag(I) | 96 | 2 6 [6.2] | 1 72 [75.0] | 3 6 [6.2] | 5 0 [0.0] | 4 2 (QEJJEX [54], QEJJIB [54]) [2.1] |
| Au(I) | 37 | 4 0 [0.0] | 1 28 [75.7] | 2 8 [21.6] | 5 0 [0.0] | 3 1 (FEJJAF10 [62] [2.7] |
| H [26] | 38 | 1 16 [42.1] | 3 8 [21.1] | 2 13 [34.2] | 5 0 [0.0] | 4 1 [2.6] |
| Metal | Dimer | Trimer | Tetramer | Hexamer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | |
| Cu(I) | 2.656 | 1.963 | 3.306 | 1.921 | 3.352 | 1.920 | 3.447 | 1.932 |
| Ag(I) | 2.953 | 2.192 | 3.507 | 2.124 | 3.448 | 2.122 | 3.631 | 2.145 |
| Au(I) | 2.808 | 2.124 | 3.440 | 2.041 | 3.478 | 2.037 | 3.605 | 2.042 |
| Metal | Dimer (With Ligands) | Trimer | Tetramer | Hexamer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | |
| Cu(I) | 3.424 a | 1.974 a | 3.228 c | 1.858 c | 3.095 (3) | 1.849 (3) | - | - |
| Ag(I) | 3.824 b | 2.284 b | 3.520 d | 2.090 d | 3.274 (5) | 2.073 (5) | 3.615 (5) | 2.084 (5) |
| Au(I) | - | - | 3.356 e | 1.994 e | 3.185 (9) | 2.006 (5) | 3.121 (10) | 2.059 (10) |
| Metal | Dimer (With Ligands) | Trimer | Tetramer | Hexamer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | M-M | N-M | |
| Cu(I) | 3.726 a | 2.010 a | 3.251 c | 1.861 c | 3.394 f | 1.962 f | - | - |
| Ag(I) | 3.788 b | 2.245 b | 3.426 d | 2.200 d | None | None | None | None |
| Au(I) | - | - | 3.382 e | 2.004 e | None | None | None | None |
| Cu(I) | Ag(I) | Au(I) | H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-mer | ΔGrel | δΔGrel | ΔGrel | δΔGrel | ΔGrel | δΔGrel | ΔGrel | δΔGrel |
| Monomer | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Dimer | −211.4 | 0.0 | −171.6 | 0.0 | −165.5 | 0.0 | −3.5 | - |
| 1 + 1 | −149.2 | 124.3 | −126.4 | 90.4 | −108.0 | 115.0 | - | - |
| Trimer | −254.4 | - | −213.0 | - | −256.0 | - | −4.5 | - |
| Tetramer | −256.0 | 0.0 | −214.2 | 0.0 | −257.8 | 0.0 | −5.6 | - |
| 2 + 2 | −235.0 | 84.3 | −202.8 | 45.4 | −182.4 | 301.6 | - | - |
| 2 + 2 twisted | −229.4 | 106.7 | −193.2 | 83.6 | −182.1 | 302.8 | - | - |
| Pentamer | −259.4 | - | −218.5 | - | −253.9 | - | - | - |
| Hexamer | −269.3 | 31.3 | −230.0 | 33.5 | −269.3 | 21.6 | −2.0 | 10.6 |
| Hexamer ududud | −255.4 | 114.6 | −213.6 | 131.9 | −257.3 | 93.6 | −3.7 | 0.0 |
| 3 + 3 | −274.5 | 0.0 | −235.6 | 0.0 | −272.9 | 0.0 | - | - |
| 3 + 3 twisted | −271.3 | 19.4 | −232.2 | 20.0 | −272.6 | 1.8 | - | - |
| Metal/H | % Dimers | % Trimers | % Tetramers | % Pentamers | % Hexamers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu(I) | 2 [27.2] | 1 [50.6] | 3 [22.2] | 5 [0.0] | 4 [0.0] |
| Ag(I) | 2 [6.2] | 1 [75.0] | 3 [6.2] | 5 [0.0] | 4 [2.1] |
| Au(I) | 4 [0.0] | 1 [75.7] | 2 [21.6] | 5 [0.0] | 3 [2.7] |
| H | 1 [42.1] | 3 [21.1] | 2 [34.2] | 5 [0.0] | 4 [2.6] |
| ΔGrel dimers | ΔGrel trimers | ΔGrel tetramers | ΔGrel pentamers | ΔGrel hexamers | |
| Cu(I) | 5 211.4 | 4 254.4 | 3 256.0 | 2 259.4 | 1 269.3 |
| Ag(I) | 5 171.6 | 4 213.0 | 3 214.2 | 2 218.5 | 1 232.2 |
| Au(I) | 5 165.5 | 3 256.0 | 2 257.8 | 4 253.9 | 1 269.3 |
| H | 4 3.5 | 2 4.5 | 1 5.6 | - | 3 3.7 5 2.0 |
Sample Availability: Not available. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elguero, J.; Alkorta, I. A Computational Study of Metallacycles Formed by Pyrazolate Ligands and the Coinage Metals M = Cu(I), Ag(I) and Au(I): (pzM)n for n = 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Comparison with Structures Reported in the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center (CCDC). Molecules 2020, 25, 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215108
Elguero J, Alkorta I. A Computational Study of Metallacycles Formed by Pyrazolate Ligands and the Coinage Metals M = Cu(I), Ag(I) and Au(I): (pzM)n for n = 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Comparison with Structures Reported in the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center (CCDC). Molecules. 2020; 25(21):5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215108
Chicago/Turabian StyleElguero, José, and Ibon Alkorta. 2020. "A Computational Study of Metallacycles Formed by Pyrazolate Ligands and the Coinage Metals M = Cu(I), Ag(I) and Au(I): (pzM)n for n = 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Comparison with Structures Reported in the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center (CCDC)" Molecules 25, no. 21: 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215108
APA StyleElguero, J., & Alkorta, I. (2020). A Computational Study of Metallacycles Formed by Pyrazolate Ligands and the Coinage Metals M = Cu(I), Ag(I) and Au(I): (pzM)n for n = 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. Comparison with Structures Reported in the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center (CCDC). Molecules, 25(21), 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215108







