Amperometric Cytosensor for Studying Mitochondrial Interferences Induced by Plasticizers Bisphenol B and Bisphenol A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
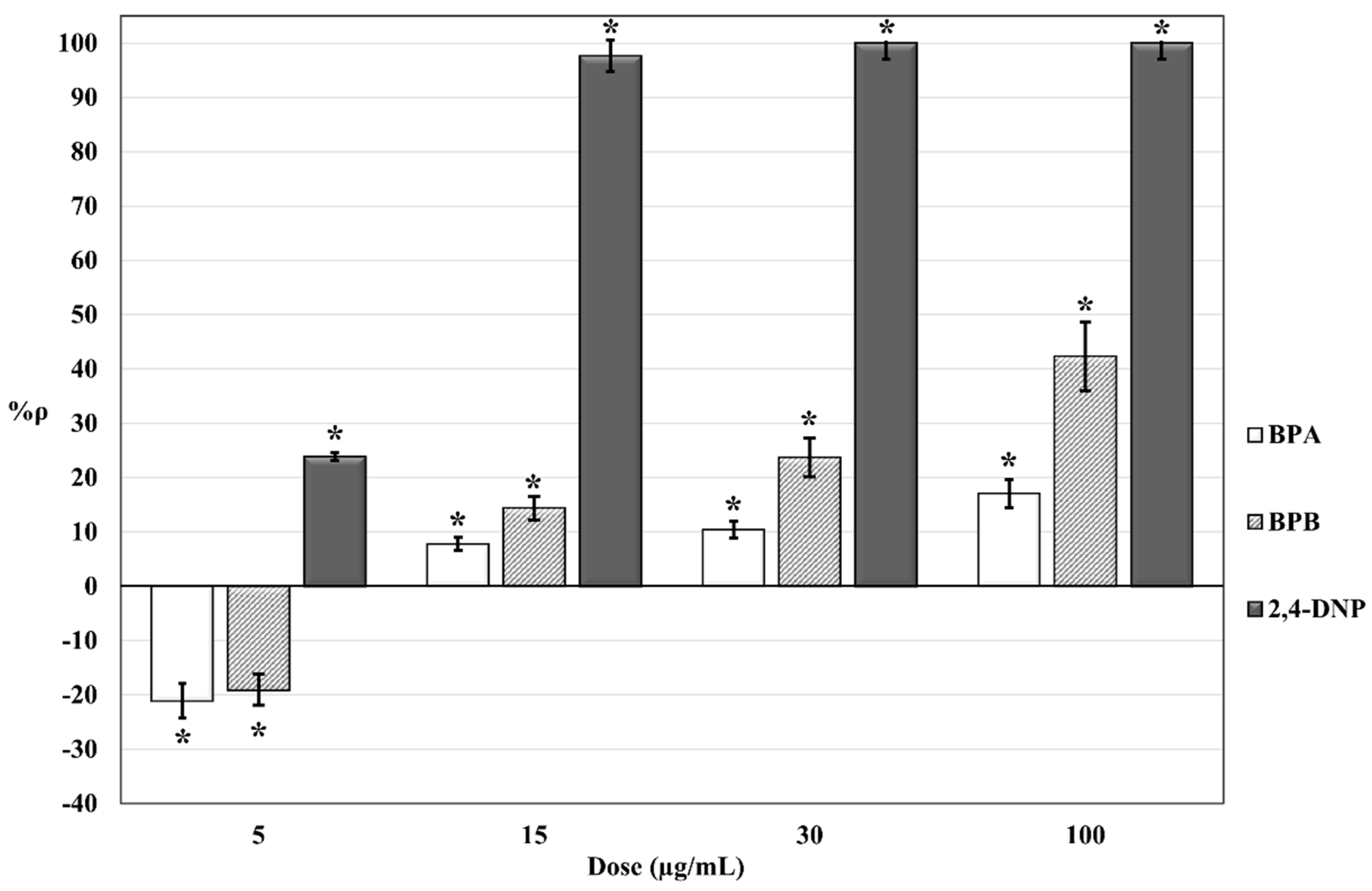
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Solutions
4.2. Assembly of Amperometric Cytosensors and Respirometric Bioassay Set-Up
- Blank yeast cell suspension: 12.50 mL of high-purity deionized water + 0.15 mL of 500 mg/mL of stock yeast cell suspensions
- Exposed yeast cell suspension: 12.50 mL of BPA, BPB, or 2,4-DNP solution + 0.15 mL of 500 mg/mL of stock yeast cell suspensions
- %ρ < 0: hyperstimulation of cellular respiration in exposed yeast cell suspensions is over the maximum physiological rate (compared to control yeast cell suspensions);
- %ρ = 0: no effects on cellular respiration in exposed yeast cell suspensions;
- 0 < %ρ < 100: inhibition of cellular respiration in exposed yeast cell suspensions.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuruto-Niwa, R.; Tateoka, Y.; Usuki, Y.; Nozawa, R. Measurement of bisphenol A concentrations in human colostrum. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, V.; Siefert, K.; Ransom, S.; Johnson, T.; Pinkerton, J.; Anderson, L.; Tao, L.; Kannan, K. Maternal bisphenol-A levels at delivery: A looming problem? J. Perinatol. 2008, 28, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caserta, D.; Ciardo, F.; Bordi, G.; Guerranti, C.; Fanello, E.; Perra, G.; Borghini, F.; La Rocca, C.; Tait, S.; Bergamasco, B.; et al. Correlation of endocrine disrupting chemicals serum levels and white blood cells gene expression of nuclear receptors in a population of infertile women. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahlhut, R.W.; Welshons, W.V.; Swan, S.H. Bisphenol A data in NHANES suggest longer than expected half-life, substantial nonfood exposure, or both. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Henare, K.L.; Thorstensen, E.B.; Ponnampalam, A.P.; Mitchell, M.D. Transfer of bisphenol A across the human placenta. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, 393.e1–393.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonca, K.; Hauser, R.; Calafat, A.M.; Arbuckle, T.E.; Duty, S.M. Bisphenol A concentrations in maternal breast milk and infant urine. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2014, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazzoli, C.; Petrini, C.; Mantovani, A. Sustainable development and next generation’s health: A long-term perspective about the consequences of today’s activities for food safety. Annali dell’Istituto Superiore di Sanità 2009, 45, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Materials, E.E.P.O.F.C. Scientific opinion on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Goetz, N.; Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Bisphenol A: How the most relevant exposure sources contribute to total consumer exposure. Risk Anal. 2010, 30, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouokam, G.B.; Ajaezi, G.C.; Mantovani, A.; Orisakwe, O.E.; Frazzoli, C. Use of Bisphenol A-containing baby bottles in Cameroon and Nigeria and possible risk management and mitigation measures: Community as milestone for prevention. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 481, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjit, N.; Siefert, K.; Padmanabhan, V. Bisphenol-A and disparities in birth outcomes: A review and directions for future research. J. Perinatol. 2009, 30, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: Food exposure and impact on human health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercogliano, R.; Santonicola, S. Investigation on bisphenol A levels in human milk and dairy supply chain: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.; Almeida, C.; Mendes, E.; Fernandes, J. Simultaneous determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol B in beverages and powdered infant formula by dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction and heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, H.; Beausoleil, C.; Habert, R.; Minier, C.; Picard-Hagen, N.; Michel, C. Evidence for Bisphenol B endocrine properties: Scientific and regulatory perspectives. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ike, M.; Chen, M.Y.; Danzl, E.; Sei, K.; Fujita, M. Biodegradation of a variety of bisphenols under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grumetto, L.; Montesano, D.; Seccia, S.; Albrizio, S.; Barbato, F. Determination of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol B residues in canned peeled tomatoes by reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10633–10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.C.; Cunha, C.; Ferreira, A.R.; Fernandes, J.O. Determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol B in canned seafood combining QuEChERS extraction with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 2453–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumetto, L.; Gennari, O.; Montesano, D.; Ferracane, R.; Ritieni, A.; Albrizio, S.; Barbato, F. Determination of five bisphenols in commercial milk samples by liquid chromatography coupled to fluorescence detection. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobellis, L.; Colacurci, N.; Trabucco, E.; Carpentiero, C.; Grumetto, L. Measurement of bisphenol A and bisphenol B levels in human blood sera from healthy and endometriotic women. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.; Fernandes, J.O. Quantification of free and total bisphenol A and bisphenol B in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) and heart-cutting multidimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (MD–GC/MS). Talanta 2010, 83, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Liu, F.; Guo, Y.; Moon, H.-B.; Nakata, H.; Wu, Q.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of eight bisphenol analogues in indoor dust from the united states and several asian countries: Implications for human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9138–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, S.; Mizutare, T.; Makishima, M.; Suzuki, N.; Fujimoto, N.; Igarashi, K.; Ohta, S. Potent estrogenic metabolites of bisphenol A and bisphenol B formed by rat liver S9 fraction: Their structures and estrogenic potency. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 78, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, S.; Suzuki, T.; Sanoh, S.; Kohta, R.; Jinno, N.; Sugihara, K.; Yoshihara, S.; Fujimoto, N.; Watanabe, H.; Ohta, S. Comparative study of the endocrine-disrupting activity of bisphenol A and 19 related compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 84, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenmai, A.K.; Dybdahl, M.; Pedersen, M.; Van Vugt-Lussenburg, B.M.A.; Wedebye, E.B.; Taxvig, C.; Vinggaard, A.M. Are structural analogues to bisphenol A safe alternatives? Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 139, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.W.; Shu, M.; Luo, H.; Ye, H.; Ge, W.; Perkins, R.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Estrogenic activity data extraction and in silico prediction show the endocrine disruption potential of bisphenol A replacement compounds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1784–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Pirzada, M.; Jahan, S.; Ullah, H.; Turi, N.; Ullah, W.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Zakria, M.; Lodhi, K.Z.; Khan, M.M. Impact of low-dose chronic exposure to bisphenol A and its analogue bisphenol B, bisphenol F and bisphenol S on hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular activities in adult rats: A focus on the possible hormonal mode of action. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, G.; Gentile, F.; Pizzimenti, S.; Canuto, R.A.; Daga, M.; Arcaro, A.; Cetrangolo, G.P.; Lepore, A.; Ferretti, C.; Dianzani, C.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases: Spotlight on fatty acid oxidation and lipoperoxidation products. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Tayama, S. Metabolism and cytotoxicity of bisphenol A and other bisphenols in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 2000, 74, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooe, H.; Taira, T.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.M.; Ariga, H. Induction of reactive oxygen species by bisphenol A and abrogation of bisphenol A-induced cell injury by DJ-1. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 88, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Hu, D.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X. Effects of exogenous bisphenol A on the function of mitochondria in root cells of soybean (Glycine max L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, A.F.; Iwachow, M.A.; Venara, M.; Rey, R.A.; Schteingart, H.F. Bisphenol A effect on glutathione synthesis and recycling in testicular Sertoli cells. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2010, 34, e102–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacova, J.; Jambor, T.; Knazicka, Z.; Tvrda, E.; Kolesarova, A.; Lukac, N. Dose- and time-dependent effects of bisphenol A on bovine spermatozoa in vitro. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhlas, S.; Usman, A.; Ahmad, M. In vitro study to evaluate the cytotoxicity of BPA analogues based on their oxidative and genotoxic potential using human peripheral blood cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 60, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragone, R.; Cheng, R.; Grasso, G.; Frazzoli, C. Diuron in water: Functional toxicity and intracellular detoxification patterns of active concentrations assayed in tandem by a yeast-based probe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 3731–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grasso, G.; Caracciolo, L.; Cocco, G.; Frazzoli, C.; Dragone, R. Towards simazine monitoring in agro-zootechnical productions: A yeast cell bioprobe for real samples screening. Biosensors 2018, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragone, R.; Frazzoli, C.; Grasso, G.; Rossi, G. Sensor with intact or modified yeast cells as rapid device for toxicological test of chemicals. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2014, 3, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragone, R.; Grasso, G. Biosensoristic devices: Monitoring and diagnostics in agro-zootechnical productions. In Cameroon-Nigeria-Italy Scientific Cooperation: Veterinary Public Health and Sustainable Food Safety to Promote “One Health/One Prevention”; Frazzoli, C., Asongalem, A.E., Orisakwe, O.E., Eds.; Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Rome, Italy, 2012; Volume 12, pp. 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Frazzoli, C.; Dragone, R.; Mantovani, A.; Massimi, C.; Campanella, L. Functional toxicity and tolerance patterns of bioavailable Pd(II), Pt(II), and Rh(III) on suspended Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells assayed in tandem by a respirometric biosensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragone, R.; Grasso, G.; Muccini, M.; Toffanin, S. Portable bio/chemosensoristic devices: Innovative systems for environmental health and food safety diagnostics. Front. Public Health 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragone, R.; Ermilov, L.; Grasso, G.; Maggioni, S.; Mantovani, A.; Frazzoli, C. Antioxidant power as biochemical endpoint in bread for screening and early managing quality and toxicant-related safety anomalies in food production. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 94, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulachev, V.P. Uncoupling: New approaches to an old problem of bioenergetics. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 1998, 1363, 100–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moses, V.; Smith, M.J.H. Uncoupling reagents and metabolism. 2. Effects of 2:4-dinitrophenol and salicylate on glucose metabolism in baker’s yeast. Biochem. J. 1960, 76, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bereketoglu, C.; Arga, K.Y.; Eraslan, S.; Mertoglu, B. Analysis of transcriptional profiles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae exposed to bisphenol A. Curr. Genet. 2016, 63, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M. Uncoupling to survive? The role of mitochondrial inefficiency in ageing. Exp. Gerontol. 2000, 35, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadenbach, B. Intrinsic and extrinsic uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2003, 1604, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brookes, P.S. Mitochondrial H+ leak and ROS generation: An odd couple. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aon, M.; Cortassa, S.; O’Rourke, B. Redox-optimized ROS balance: A unifying hypothesis. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2010, 1797, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, B.M.; Overkamp, K.M.; Van Maris, A.J.; Kötter, P.; Luttik, M.A.; Van Dijken, J.P.; Pronk, J.T. Stoichiometry and compartmentation of NADH metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 25, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaz, S. Modeling kinetics of subcellular disposition of chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 1793–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamura, E.; Kakitsubo, R.; Nakahara, M. NMR Determination of the delivery site of bisphenol A in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Langmuir 1999, 15, 8332–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, E.; Wakai, C.; Matubayasi, N.; Sugiura, Y.; Nakahara, M. Limited slowdown of endocrine-disruptor diffusion in confined fluid lipid membranes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 248101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broniatowski, M.; Sobolewska, K.; Flasiński, M.; Wydro, P. Studies on the interactions of bisphenols with anionic phospholipids of decomposer membranes in model systems. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.; Koorengevel, M.; De Kruijff, B.; De Kroon, A. Transbilayer movement of phosphatidylcholine in the mitochondrial outer membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is rapid and bidirectional. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 1999, 1421, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, A.S.; Zhou, J.; Gohil, V.M.; Chen, S.; Greenberg, M.L. Cellular functions of cardiolipin in yeast. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2009, 1793, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshkin, V.; Greenberg, M.L. Cardiolipin prevents rate-dependent uncoupling and provides osmotic stability in yeast mitochondria. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paradies, G.; Paradies, V.; De Benedictis, V.; Ruggiero, F.M.; Petrosillo, G. Functional role of cardiolipin in mitochondrial bioenergetics. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2014, 1837, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Not available. |


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dragone, R.; Grasso, G.; Frazzoli, C. Amperometric Cytosensor for Studying Mitochondrial Interferences Induced by Plasticizers Bisphenol B and Bisphenol A. Molecules 2020, 25, 5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215185
Dragone R, Grasso G, Frazzoli C. Amperometric Cytosensor for Studying Mitochondrial Interferences Induced by Plasticizers Bisphenol B and Bisphenol A. Molecules. 2020; 25(21):5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215185
Chicago/Turabian StyleDragone, Roberto, Gerardo Grasso, and Chiara Frazzoli. 2020. "Amperometric Cytosensor for Studying Mitochondrial Interferences Induced by Plasticizers Bisphenol B and Bisphenol A" Molecules 25, no. 21: 5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215185
APA StyleDragone, R., Grasso, G., & Frazzoli, C. (2020). Amperometric Cytosensor for Studying Mitochondrial Interferences Induced by Plasticizers Bisphenol B and Bisphenol A. Molecules, 25(21), 5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25215185







