Abstract
The enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) plays a central role in metabolism of bioactive lipid signaling molecules. The substrate-specific hydrolase activity of sEH converts epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) to less bioactive dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids. EETs exhibit anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antihypertensive, cardio-protective and organ-protective properties. Accordingly, sEH inhibition is a promising therapeutic strategy for addressing a variety of diseases. In this review, we describe small molecule architectures that have been commonly deployed as sEH inhibitors with respect to angiogenesis, inflammation and cancer. We juxtapose commonly used synthetic scaffolds and natural products within the paradigm of a multitarget approach for addressing inflammation and inflammation induced carcinogenesis. Structural insights from the inhibitor complexes and novel strategies for development of sEH-based multitarget inhibitors are also presented. While sEH inhibition is likely to suppress inflammation-induced carcinogenesis, it can also lead to enhanced angiogenesis via increased EET concentrations. In this regard, sEH inhibitors in combination chemotherapy are described. Urea and amide-based architectures feature prominently across multitarget inhibition and combination chemotherapy applications of sEH inhibitors.
1. Arachidonic Acid Pathway and Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids (EETs)
Arachidonic acid (ARA) is an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFAs) and metabolized by three major classes of enzymes including cyclooxygenases (COXs), lipoxygenases (LOXs, and cytochrome P450s (CYPs), resulting in the formation of various inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins, prostacyclin, lipoxins and leukotrienes [1]. Through the cytochrome P450s pathways, ARA can be converted to two kinds of eicosanoid acids: epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenase, and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) by CYP α-oxidases [2]. The cytochrome P450-derived HETEs are proinflammatory mediators, whereas EET is vasodilatory towards specific cells and tissues. Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a prominent enzyme involved in the degradation of anti-inflammatory EETs and is considered as the major pathway inactivating EETs to corresponding diols inducing the infiltration of proinflammatory mediators. Expression of both pro and anti-inflammatory mediators are influenced by various factors such as rheumatic diseases, myocardial infarction, angina, aging, obesity and pharmacotherapy [3]. Enhanced inflammatory cell infiltration causes chronic inflammation and inflammation-induced carcinogenesis. Thus, sEH targeting is commonly suggested for preventing inflammation-induced carcinogenesis [4].
The CYP2C and CYP2J enzymes convert arachidonic acid to four EET regioisomers, namely 5,6-EET, 8,9-EET, 11,12-EET, and 14,15-EET [5,6]. Elevated EET levels in breast cancer tissues are associated with upregulation of specific CYPs, and downregulation of sEH, and are also associated with aggressive cell behavior in patients [7]. EETs are also reported to promote the pathogenesis of various human cancers [8,9,10].
2. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH)
Epoxide hydrolases have been detected in prokaryotes and eukaryotes ranging from plants to mammals [11,12,13]. In mammals, these include soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH), cholesterol epoxide hydrolase, and leukotriene A4 (LTA4) hydrolase. These enzymes mediate the addition of water to both exogenous and endogenous epoxides, leading to the corresponding vicinal diols [14]. sEH effectively utilizes 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-EETs, while 5,6-EET is a poor substrate.
sEH is composed of two structurally and functionally independent domains with two distinct activities. The C-terminal domain is responsible for hydrolase activity, while the N-terminal domain shows phosphatase activity [15]. While sEH exhibits broad tissue distribution, high levels of sEH are found in intestine, liver, kidney, brain and vasculature with lower levels in lung, spleen and testes [5]. In human hepatocytes and renal proximal tubules, sEH localizes to both the cytosol and peroxisomes. However, it is exclusively cytosolic in other sEH-containing cells such as pancreatic islet cells, intestinal epithelium, anterior pituitary cells, adrenal gland, endometrium, lymphoid follicles, prostate ductal epithelium and blood vessels [5].
The C-terminus epoxide hydrolase motif of sEH transforms four regioisomers of EETs, namely, 5,6-, 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-EETs, to the corresponding dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs), whereby the biological effects of EETs are diminished, eliminated or altered [16]. Spectroscopic studies and crystallographic studies have revealed the catalytic site and reaction mechanism of epoxide ring opening activity by sEH [17,18]. The reaction takes place via an SN2-type reaction based on the cooperative action of a catalytic triad composed of Tyr382, Tyr465, and Asp334. Tyr382 and/or Tyr465 form hydrogen bonds with the epoxide oxygen and activate the epoxide of the substrate through polarization. Nucleophilic attack by Asp334 of the enzyme on an epoxide carbon, usually at the least sterically hindered and most reactive carbon, leads to the formation of a covalent hydroxyl-alkyl enzyme intermediate. The nucleophile Asp334 is oriented and activated by a His523-Asp495 pair. Subsequently, a water molecule activated by His523 attacks the alkyl-enzyme intermediate to form a tetrahedral intermediate, which finally collapses to release the corresponding diol product [19,20]. Mutation of either tyrosine to a phenylalanine leads to a 90% loss of enzyme activity [19]. A recent study based on molecular dynamics simulation suggests that the protonation of His523 is essential for the proper orientation of Asp333 [21]. sEH hydrolase activity has been shown to be dependent on sEH dimerization. Disrupting sEH dimerization may serve as a novel therapeutic strategy for reducing sEH hydrolase activity [22].
3. Role of EETs in Angiogenesis and Inflammation
Organisms are routinely exposed to endogenous and exogenous epoxide-containing compounds such as EETs. An epoxide (or oxirane) possesses distinctive reactivity patterns owing to the highly polarized oxygen-carbon bonds in addition to a highly strained ring [20]. Reactive epoxides such as 8,9-, 11,12-, 14,15-EETs, and some exogenous epoxides, are responsible for electrophilic reactions with DNA and proteins, leading to mutagenic, toxic and carcinogenic effects [20].
EETs generate an anti-inflammatory effect on the endothelium by inhibiting cytokine-induced NF-κB transcription factor [23]. The transcription factor NF-κB is a key component of the cellular response to damage, stress and inflammation. NF-κB activation is mediated by inhibitory kappa B (IκB) kinase (IKK), which is, in turn, activated in response to a variety of pathogenic factors. Activated IKK phosphorylates an inhibitory protein, IκB, which results in IκB degradation and thereby allows NF-κB to translocate to the nucleus and to induce the synthesis of proinflammatory molecules [24]. EETs block the inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (IκB) kinase IKK-mediated phosphorylation of IkBα, maintaining NF-κβ in an inactive state [21]. Considering that EETs are secreted from endothelial cells, a natural connect is expected between EETs and angiogenesis [25,26,27,28,29]. The signaling pathway that forms this connect varies depending on the species, type of endothelium and the EET regioisomer responsible for initiating the process [24]. Overall, three signaling pathways play a role in EET-mediated angiogenesis [24]. The first pathway is a cAMP-dependent pathway that activates the cAMP response-element binding protein (CREBP) and COX-2 expression. This pathway is activated by EETs produced by CYP2C9, especially 11,12- EET [30]. The second pathway is also activated by EETs produced by CYP2C9, but involves PI3K and Akt, leading to an increase in cyclin D1 expression [26]. The third pathway is a p38 MAPK pathway that is activated by 8,9-EET and 11,12-EET [31].
The sphingosine kinases (SphK1 and SphK2) are a distinctive group of lipid kinases responsible for ATP-dependent phosphorylation of sphingosine to produce Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). SphK1 has emerged as a significant signaling enzyme because of its contribution to the growth, metastasis and chemoresistance of various human cancers [32,33]. Sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) participates in the activation of the inflammatory response via sphingosine-1-phosphate formation. Notably, SphK1 is also an important mediator of 11,12-EET induced angiogenic pathways in human endothelial cell (EC) [34]. The expression of a dominant-negative SphK1 or knockdown of SphK1 by siRNA, inhibited 11,12-EET-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration, tube formation in vitro and Matrigel plug angiogenesis in vivo [34]. 14,15-EET is reported to induce angiogenesis through several pathways and receptors, including TRPV1 [35], Src, PI3K/Akt signaling in parallel with mTOR-S6K1 activation and Src-dependent STAT-3-mediated VEGF expression [24]. These observations point to a biphasic effect of EETs (Figure 1). In particular, inhibition of sEH, and the subsequent increase in EET concentration, results in enhanced angiogenesis, thereby stimulating primary tumor growth and metastasis.
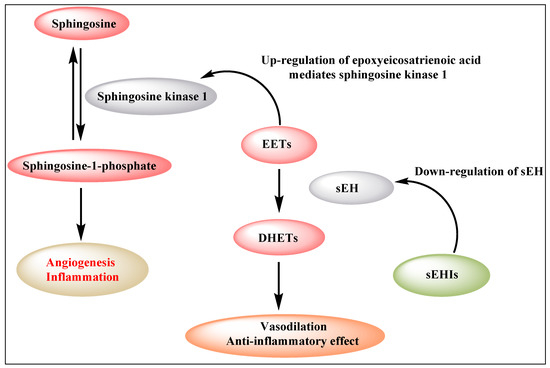
Figure 1.
Biphasic effect of EETs (EETs: epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; sEH: soluble epoxide hydrolase; DHETs: dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids).
4. sEH in Inflammation-Driven Carcinogenesis
Materials inflammation-driven cancer is based on the infiltration of white neutrophilic granulocytes, and involvement of cytokines and chemokines [36]. Soluble epoxy hydrolase is a prominent proinflammatory enzyme that is responsible for the infiltration of inflammatory mediators. Inhibition of sEH significantly reduces the conversion of EETs to corresponding DHETs, thereby highlighting sEH as an important target for addressing inflammation and carcinogenesis [4]. Node et al. demonstrated that physiological concentrations of EETs or overexpression of CYP2J2 inhibist inflammation by decreasing cytokine-induced endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression, and preventing leukocyte adhesion to vascular walls and tissues by a mechanism involving inhibition of transcription factor NF-kB and IkB kinase [23]. Inhibition of inflammation is suggested based on multiple pathways that result in suppressing inflammatory cell recruitment, modulating the arachidonic acid metabolite profile and further targeting the PPAR-gamma and NF-kB pathways, which, in turn lead to an inhibition of COX-2, 5-LOX, iNOS and VCAM-1 (Figure 2) [5].
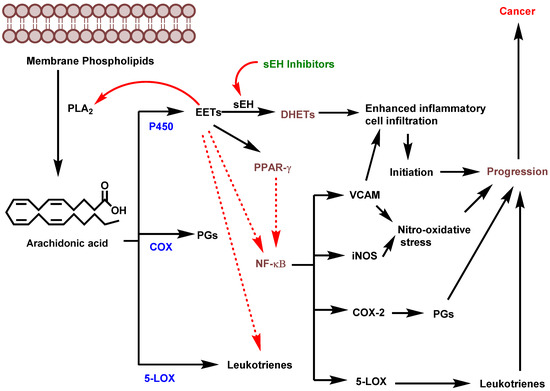
Figure 2.
Potential role of sEH in inflammation-driven carcinogenesis (PLA2: phospholipase A2; EETs: epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; sEH: soluble epoxide hydrolase; DHETs: dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids; COX: cyclooxygenase; LOX: lipoxygenase; PGs: prostaglandins; PPAR-γ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; NF-κβ: (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; VCAM: vascular cell adhesion molecule; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase). (Figure adapted from [5]).
5. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors (sEHIs)
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors (sEHIs) have been leveraged for addressing a variety of diseases including hypertension [37,38,39], cancer [7,25,40], dyslipidemia [41], pain [42,43,44,45,46], immunological disorders [47], neurological diseases [45,48,49,50], diabetes [51,52,53,54] and eye diseases [55,56]. Urea, carbamate and amide derivatives represent the most potent class of pharmacophores reported as sEHIs [57,58,59]. Crystal structures of urea derivatives bound to sEH revealed that the carbonyl oxygen of the urea group accepts hydrogen bonds from Tyr residues (381, 465), and the nitrogen atom of NH group donates a hydrogen bond to Asp333. Urea derivatives mimic the transition state for epoxide ring opening and exert their inhibitory property [60]. Based on the L-shaped hydrophobic pocket of sEH, lipophilic functional groups, such as adamantyl, biphenyl or halogens, can enhance the potency of urea-based inhibitors. Crystal structure of nonurea inhibitors, for example benzoxazole amide and fulvestrant, bound to sEH have been reported [61,62]. Xing and coworkers applied structure-based virtual screening to design combinatorial libraries to discover benzoxazole based novel and potent soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors. The benzoxazole nitrogen atom and the amide oxygen atom form concurrent hydrogen bonds with Tyr381 and Tyr465, respectively. The benzoxazole ring nitrogen atom and the amide nitrogen form hydrogen bonds with His523 and Asp333, respectively [61]. In contrast, fulvestrant complexed with sEH showed that the oxygen atom of the sulfoxide (S=O) group forms hydrogen bonds with tyrosines 383 and 466 [62]. Interestingly, a hydrogen bond interaction between the sulfur atom of sulfoxide group and Asp335 was also observed.
Trans-3-phenylglycidols and chalcone oxides were first reported as sEHIs, and it was demonstrated that substituted chalcone oxides are more potent inhibitors of sEH enzyme than trans-3-phenylglycidols [63,64,65]. A large number of urea derivatives have been shown to possess sEH inhibitory activity (Figure 3) [66,67,68,69,70]. One of the earliest urea derivative DCUs showed excellent in vivo inhibitory activity against sEH enzyme, albeit constrained by unfavorable pharmacokinetic properties [16]. Similarly, another urea-based potent inhibitor CDU was hampered by rapid metabolization in hepatic microsomes [71]. Fatty acid analogs, AUDA displayed excellent sEH inhibitory activity but were restricted in their applicability due to fatty acid β-oxidation and P450 oxidation-based instability of the adamantane group. A higher accumulation of fatty acid epoxides, and a relatively lower amount of the corresponding diol, was observed in urine after 24 h of treatment of AUDA in AngII-infused rats [72]. Substitution of a long alkyl chain by a polar group positioned approximately 7 Å from the urea carbonyl group improved the physical properties of inhibitors leading to incorporation of the ether functional group in AEPU [73]. Replacement of ether chain by conformationally restricted substituents as in APAU, c-AUCB, t-AUCB, and TPPU resulted in favorable pharmacokinetic properties along with low nanomolar potency [38,74,75,76,77]. Several trisubstituted urea derivatives have been reported with excellent potency and attractive bioavailability [77,78,79,80]. Urea derivatives containing fluorene and adamantane groups increased the sEH inhibitory activity by a factor of 4.5 [81]. The replacement of adamantyl and 4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl groups with natural bicyclic lipophilic groups provided a series of sEHIs with similar potency and 10-fold more water solubility compared to the original compounds [82]. On a similar note, Codony and coworkers developed 2-oxaadamant-1-yl urea-based molecules and reported that the replacement of a methylene unit of the adamantane group by an oxygen atom increased the solubility, permeability, and stability with nanomolar sEH inhibitory potency [83]. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening has been used for discovery of 6-amino-2-((4-chlorobenzyl)thio)-5-phenylpyrimidin-4(3H)-one and urea-based potent sEHIs [84]. Although structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies provided a significant number of selective and potent urea-based sEHIs, their low solubility and poor metabolic stability continue to hamper pharmacological use in vivo. A variety of amide and α-keto or α-hydroxy amide derivatives are recognized as potent sEHIs (Figure 4) [59,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94].
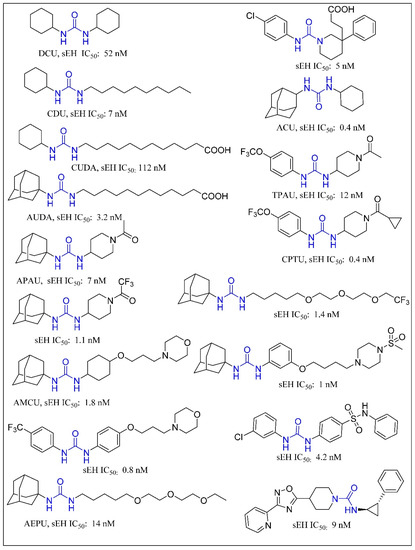
Figure 3.
Urea based soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors.
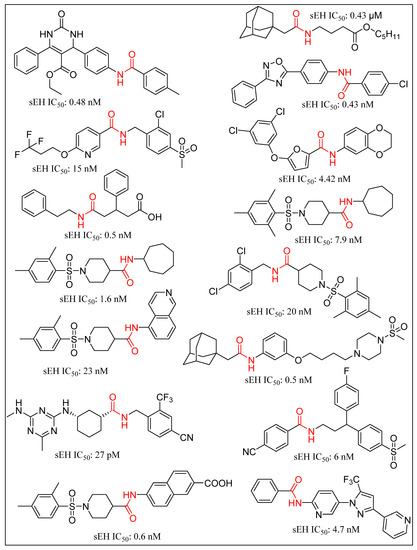
Figure 4.
Amide based soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors.
Other moieties that have shown promising sEHI activity include aminobenzisoxazole, acyl hydrazones, 4-benzamidobenzoic acid hydrazide, adamantyl thioureas and sulphoxide derivatives [61,62,95,96,97,98] The ligand-based pharmacophore model has recently led to identification of novel N-benzoyl-2-phenylhydrazine-1-carboxamide and ethyl (R)-6-methyl-2-(3-(p-tolyl)ureido)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylate as potential sEHIs with IC50 values of less than 5 µM [99]. A variety of small molecule inhibitors of human sEH with reported X-ray crystal structures (PDB ID) and IC50 values are depicted in Figure 5 [15,58,59,61,62,78,100,101,102,103,104,105]. The chemical space for sEHIs has been further expanded by the recent work of Scholz and coworkers on demonstration of carboranes as non-natural 3-D pharmacophores and sEH inhibition by carboranylcarboxamide compounds [106].
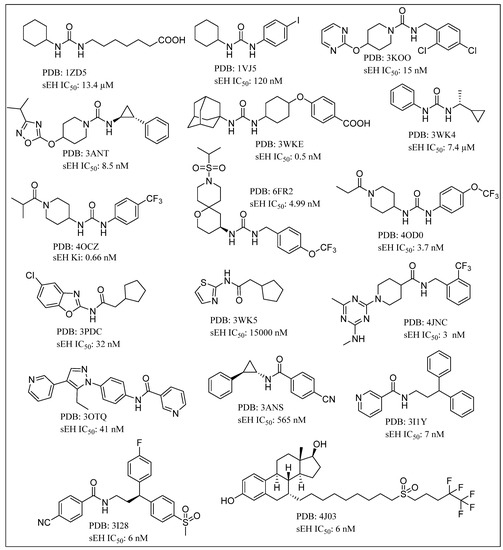
Figure 5.
Chemical structure of small molecule inhibitors of human soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in X-ray crystal structure complexes with PDB and IC50 values.
Research on natural product-based sEHIs development has sought to address the typical drawbacks of synthetic small molecule inhibitors. A plethora of natural products, including stilbenes, carbazole, anthraquinones, selaginellin, cycloartane triterpene, capsaicin, dihydrocapsaicin, anthocyanin derivatives and phenolic glycosides derivatives, possess sEHI activity (Figure 6) [107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119]. Interestingly, very few natural products bear the urea or carbamate groups that form the mainstay of synthetic sEHIs. Moracin and coumarin derivatives from mulberry leaves have been identified as significant sEHIs [120]. Sun and coworkers collected protostane-type triterpenoids from Alisma orientale and reported their potential sEH inhibitory activities [121]. Natural products have also provided a platform for exploration of mimics towards sEH inhibition. A series of partially saturated analogues containing epoxide bioisosteres were synthesized and evaluated for in vitro inhibition of sEH by Falck and coworkers [122]. Similarly, a new generation of EET mimics incorporating modifications to the carboxylate were prepared and evaluated for inhibition of sEH [123]. A number of frontier approaches, such as DNA-encoded small-molecule libraries, have been adopted towards identification of sEHIs [124]. Belyanskaya and coworkers deployed the encoded library technology (ELT) for the discovery and early clinical development of an inhibitor of the enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase (GSK2256294). This particular platform combines DNA encoding, combinatorial organic chemistry and affinity-based selection, and can efficiently yield high quality molecules with favorable pharmacological properties [125].
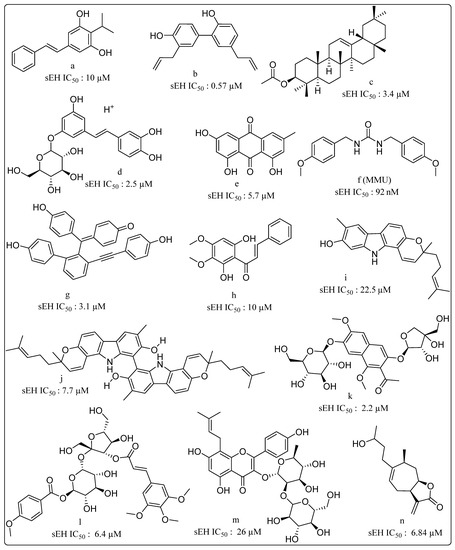
Figure 6.
Natural products displaying soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitory properties (a) Isopropylstilbene from Photorhabdus, (b) Honokiol isolated from Magnolia officinalis, (c) β-amyrin acetate isolated from Acer mandshuricum, (d,e) from Rheum undulatum, (f) MMU from Pentadiplandra brazzeana Baillon, (g) Selaginellin derivatives from Selaginella tamariscina, (h) (E)-1-(2,6-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-one from Docynia indica (Wall.) Decne. (i) Isomahanine and (j) Bisisomahanine from the aerial parts of Glycosmis stenocarpa, (k) the seeds of Cassia tora, (l) phenolic glycosides from Polygala tenuifolia. (m) Prenyl-flavonoids from Epimedium koreanum Nakai (n) 4H-tomentosin from Inula helenium.
Giancarlo and coworkers developed a distinctive dual inhibitory mechanism of the endogenous 15-deoxy-Δ12,14 prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) whereby hsEH can be inhibited by reversible docking of 15d-PGJ2 in the catalytic pocket, as well as by covalent locking of the same compound onto cysteine residues C423 and C522 remote to the active site. This mode of inhibition expands the scope of development of new allosteric inhibitors of hsEH [126].
6. Dual Inhibition/Modulation of sEH as Part of Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutics
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors have been studied in combination with other target-specific inhibitors as potential multitarget therapies. The consideration of sEH in anti-inflammatory drug development is notable in this regard. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and selective cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) inhibitors (coxibs), which are capable to block COX-2 mediated conversion of ARA to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), are widely used to treat inflammation and pain [127]. NSAIDs are associated with several gastrointestinal injury-based adverse effects including ulceration, bleeding, inflammation and even perforation [128].
sEHIs have been suggested as being capable of synergistic reduction of the side effects of NSAIDs [129,130,131]. Inhibition of EET catabolism via sEHIs, results in a significant increase in their anti-inflammatory properties, providing scope for effective treatment of inflammatory disease and associated cancers. Synergistic activity of sEHIs with COX inhibitors are effective against obesity-induced colonic inflammation. The latter is a major risk factor for colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, chronic colitis and pancreatitis. A variety of amide and urea-based small molecule dual sEHIs have been reported in this context (Figure 7). Hwang et al. reported urea-containing pyrazole derivatives as dual inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 and sEH [132]. Novel urea-diarylpyrazole hybrids exhibit dual COX-2/sEH inhibition with improved anti-inflammatory activity and highly reduced cardiovascular risks [133]. Leukotrienes (LTs) are proinflammatory lipid mediators, regulate the innate immune response and play a pathophysiological role in chronic inflammatory diseases such as asthma and atherosclerosis. The 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) facilitates ARA conversion by 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) to proinflammatory leukotrienes (LTs). Inhibition of FLAP has been reported to efficiently abolish LT formation in vitro and in vivo. Thus, dual inhibition of FLAP and sEH is likely to represent a powerful anti-inflammatory strategy due to simultaneous suppression of proinflammatory LTs and dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids while maintaining anti-inflammatory EETs [134]. Garscha et al. have reported the in vivo pharmacological profile of difapolin that dually targets FLAP and sEH and are promising for treatment of inflammation-related diseases [135]. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening has been used for developing dual inhibitors of the 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein and sEH [136]. Notably, N-[4-(benzothiazol-2-ylmethoxy)-2-methylphenyl]-N′-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)urea shows an IC50 of 200 nM in a cell-based FLAP test system and 20 nM for sEH activity in a cell-free assay. It was demonstrated that LTA4H specifically converts the instable epoxide LTA4 toward the proinflammatory LTB4. Thus, dual inhibition of LTA4H and sEH is likely to have superior effects in resolving inflammation due to accumulation of the anti-inflammatory EETs and blockage of the chemoattractant LTB4. Hiesinger et al. developed amide derivatives with a benzothiazole core as a dual inhibitor of sEH and LTA4 hydrolase, thereby demonstrating another future route for development of anti-inflammatory agents [137]. Hefke et al. deployed computer-aided fragment growing strategies to design amide based dual inhibitors of sEH and LTA4 hydrolase [138]. Other strategies in this regard include benzimidazole derivatives as dual sEH/5-Lipoxygenase inhibitors using virtual screening [139]. Substituted fluorobenzimidazoles derivatives have been reported as dual inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase and sEH [140]. A hybrid imidazo-[1,2a]-pyridine-based dual inhibitor of sEH and 5-lipoxygenase exhibits high potency in vitro [141]. Other sEH/5-LO dual inhibitors include fragment-based development of 2-aminothiazole derivatives [142]. Meirer et al. developed a dual 5-LO/sEH inhibitor KM55 which significantly inhibits the LPS-induced adhesion of leukocytes to endothelial cells by blocking leukocyte activation [143]. Dual inhibitors for sEH and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) have been shown to synergize responses to inflammatory and neuropathic pain [144,145] Dual inhibitors focused on sEH have sought to leverage the role of targets that are implicated in regulation of inflammation. For example, sEH and p38β kinase have been demonstrated as two key regulators of inflammation. TPPU has been reported as both a human sEH and p38β kinase inhibitor with nanomolar potencies and distinct selectivity [146]. On a similar theme, Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) activation is associated with antisteatotic and antifibrotic effects which promise synergies with a sEHI based anti-inflammatory strategy. Schmidt and coworkers developed an amide-based dual modulator of farnesoid X receptor and soluble epoxide hydrolase to counter nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [147]. Recently, dual FXR activators/sEH inhibitors have been reported that are derived from the antiasthma drug Zafirlukast. These inhibitors possess favorable dual potency towards FXR and sEH while reducing the original cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonism of the lead drug [148]. Inceoglu and coworkers demonstrated that coadministration of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and sEH inhibitors results in an enhanced analgesic effect compared to the individual treatments [149]. Further, bioavailable sEH/PDE4 dual inhibitors have been reported for management of pain as well as tools for investigating the biology of pain [150].
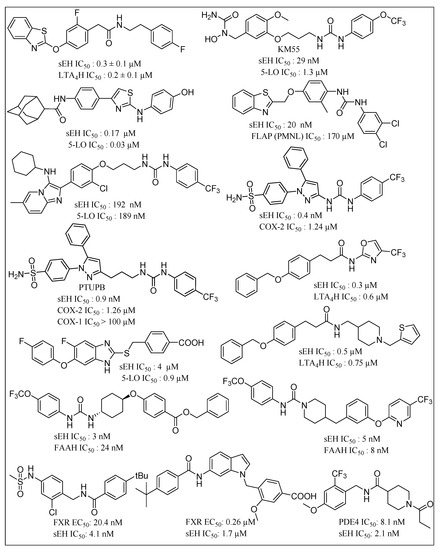
Figure 7.
Chemical structures of small molecule based dual COX-2/sEH inhibitor, 5-LO/sEH inhibitor, FLAP/sEH inhibitor, sEH/ LTA4H inhibitors, sEH/FAAH inhibitors, sEH/PDE4 inhibitors, and FXR activator/sEH inhibitor. (COX: cyclooxygenase; sEH: soluble epoxide hydrolase; 5-LO: 5-lipoxygenase; FLAP: 5-lipoxygenase activating protein; LTA4H: leukotriene A4 hydrolase; FAAH: fatty acid amide hydrolase; PDE4: phosphodiesterase 4; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor).
7. Dual Inhibition of sEH in Combination Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy promotes tumorigenesis, angiogenesis and metastasis via apoptotic tumor cell-induced macrophage chemotaxis and proinflammatory cytokines [151,152,153]. Gartung and coworkers reported that ovarian tumor cell debris generated by first-line platinum and taxane-based chemotherapy accelerates tumor progression by stimulating a macrophage-derived surge of proinflammatory cytokines and bioactive lipids [154]. Targeting the debris-mediated surge of protumorigenic factors, including inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, proangiogenic growth factors and danger signals (e.g., alarmins), offers an approach for enhancing the efficacy of cytotoxic therapies. The combined pharmacological abrogation of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and sEH pathways has been shown to prevent the debris-induced surge of both cytokines and lipid mediators by macrophages. PTUPB prevents the chemotherapy-induced cytokine/lipid surge and suppresses debris-stimulated ovarian tumor growth by acting as a surge protector against therapy-induced protumorigenic mediators, ultimately improving patient survival by preventing tumor recurrence [154].
While cisplatin is among the most prominent chemotherapeutic agents, cisplatin-based therapy is highly toxic, underlying the need for improvement in efficacy of cisplatin-therapies [155]. The modulation of the arachidonic acid pathway is considered one of the crucial strategies to avoid toxicity associated with cisplatin therapy [156]. The overexpression of COX-2 in tumor or stromal cells is responsible for tumor angiogenesis [157]. COX-2 inhibitors block production of angiogenic factors, leading to the inhibition of proliferation, migration and vascular tube formation. Nevertheless, coxibs failed in human clinical trials for several cancers [158,159]. Furthermore, sEHIs synergize the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects associated with coxibs, Refs. [129,130] prevent gastrointestinal erosion, Ref. [131] and alter prostacyclin (PGI2) and thromboxane A2 (TBX2) ratios associated with blood clotting [129]. Thus, the dual COX-2/sEH inhibition strategy can maximize antitumor activity and lower toxic effects of selective COX-2 inhibition, and ultimately may also protect normal tissues from cisplatin toxicity. The chemical structures of some small molecules used in dual inhibition of sEH as part of combination chemotherapy are shown in Figure 8. Combined administration of PTUPB (sEH/COX inhibitor) and cisplatin, increased apoptosis and decreased phosphorylation in the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways when compared with controls. Notably, PTUPB treatment did not alter platinum-DNA adduct levels, which is the most critical step in platinum-induced cell death [156].
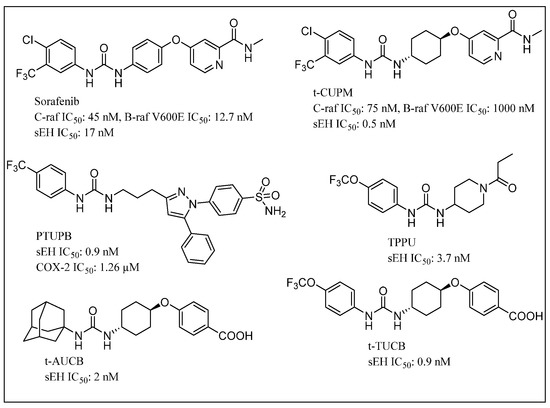
Figure 8.
Chemical structures of small molecules used in dual inhibition of sEH in combination chemotherapy.
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal malignant neoplasms. Chronic pancreatitis and mutant Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog KRAS gene (Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog) are the most common entities involved in pancreatic carcinogenesis, with more than 90% of human pancreatic carcinomas carrying the KRAS gene mutation [160,161]. Mutations of KRAS lead to constitutive activation of KRAS and persistent stimulation of downstream signaling pathways that initiate carcinogenesis via sustained proliferation, metabolic reprogramming, antiapoptosis, remodeling of the tumor microenvironment, evasion of the immune response, cell migration and metastasis [162]. The mutant RAS-activated RAF1 proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase (c-RAF)-mitogen-activated protein kinase’s kinase (MEK)-extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) pathway appears crucial for initiating carcinogenesis. Signaling through c-RAF-MEK-ERK, but not b-RAF, is shown to be essential for tumor initiation via mutant Kras, while c-RAF is responsible for transmitting signals from mutant KRAS to MEK-ERK [163]. In the process of long-standing chronic inflammation, aberrant metabolites of arachidonic acid play a crucial role in promoting carcinogenesis. EETs are capable of exerting an effective anti-inflammatory effect by reducing cytokine-induced endothelial cell adhesion molecule (VCAM) and reducing nuclear factor kappa-B kinase and nuclear factor kappa-B kinase inhibitor activity. Therefore, the development of a dual c-RAF/sEH inhibitor would be crucial for suppressing mutant Kras-initiated carcinogenesis [164].
ω-3 epoxy fatty acid metabolites derived from ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) metabolism by cytochrome P450 epoxygenases have been suggested to play a crucial role in inhibiting pancreatic cancer growth. Several studies have suggested the importance of ω-3 epoxide as highly potent metabolites against inflammation and carcinogenesis, particularly via targeting inflammatory signals [165,166,167]. The combined use of ω-3 PUFAs with sEHIs offers a promising strategy for pancreatic cancer treatment and prevention. ω-3 epoxy metabolites prevent pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) growth via inhibition of the RAS/RAF/ MEK/ERK pathway [168]. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are considered immunonutrients and are commonly used in the nutritional therapy of cancer patients. Interestingly, the 2017 European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) guidelines for cancer patients discuss the use of omega-3 PUFAs for cancer-cachexia treatment, leaving aside other cancer-related complications that could potentially be managed by omega-3 PUFA supplementation [169].
The use of Bleomycin (BLM) in cancer chemotherapy is constrained by its pulmonary toxicity. A recent study showed that AUDA can reduce pulmonary toxicity in the BLM-induced lung fibrosis in mice model [170]. t-AUCB suppresses human glioblastoma cell growth by activating NF-κβ-p65 [171]. The combination of selective COX-2 inhibitors such as celecoxib and a potent sEHI, namely t-AUCB, synergistically suppresses primary tumor growth and metastasis [127,172]. An orally bioavailable COX-2 and sEH dual inhibitor, PTUPB, displayed excellent potency in reducing inflammatory pain and tumor growth in comparison to the combination of celecoxib and t-AUCB [127,132]. PTUPB has been reported to potentiate cisplatin-based treatment without increasing toxicity in vivo, thereby emphasizing the scope of sEHIs in combination chemotherapy [156]. Another report revealed that the sEHIs, TPPU and t-TUCB, nullify a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced colonic inflammation in mice model. This suggests the importance of sEH in obesity-induced colonic inflammation, which is a major risk factor for the progression and development of colorectal cancer [173]. A dual inhibitor of sEH and RAF1 proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase (c-RAF), t-CUPM, significantly inhibited chronic pancreatitis and reduced pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms (PanIN). This approach possibly signals a revolutionary development in preventing and treating pancreatic cancer [164,174]. The VEGF receptor and Raf inhibitor sorafenib showed excellent inhibitory properties on hsEH. Sorafenib treatment was found to reverse lipopolysaccharide-induced hypotension based on the anti-inflammatory effect resulting from soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition [40]. Activity of sorafenib is thought to stabilize endogenous epoxygenated fatty acids (EpFAs) including antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic EETs [129]. These results suggest the possible scope of sorafenib to control highly angiogenic malignancies including renal cancer.
8. Conclusions
The ARA pathway and EETs are deeply interlinked with a variety of physiological outcomes ranging from vasodilation, angiogenesis and inflammation. sEH is a crucial component of the ARA pathway, and sEH inhibition forms a classical strategy for blocking the infiltration of inflammatory mediators. Due to the interconnections between sEH activity, angiogenesis and inflammation-induced carcinogenesis, multitarget therapies involving sEHIs hold promise for treatment of inflammation and a variety of cancers. While urea, carbamate and amide derivatives have been widely reported as sEHIs, these scaffolds have also been successfully leveraged for developing dual inhibitors towards sEH and suitable ARA pathway targets such as FLAP, LTA4 hydrolase and 5-LO. Further, the combination of sEHIs and NSAIDs is capable of synergistically suppressing primary tumor growth and metastasis with reduced toxicity. Multikinase inhibitors in combination with sEHIs offer a promising treatment strategy for hepatocellular and renal cell carcinoma. The use of polyunsaturated fatty acids in combination with sEH inhibition, as well as the dual inhibition of sEH and c-RAF, are potent approaches for preventing pancreatic cancer. Thus, small molecule sEHIs can be effectively leveraged as dual inhibitors and as components of combination chemotherapy. The widespread tissue and cytosolic distribution of sEH emphasizes the need for sEHIs possessing superior solubility and metabolic stability that can facilitate sEH inhibition-based multi-target therapies to achieve better results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.D.M., R.C. and B.D.; writing—original draft preparation, A.D.M., R.C. and B.D.; writing—review and editing, A.D.M., R.C. and B.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by CSIR through grant No. 02(0342)/18/EMR-II and APC was funded by IIT Gandhinagar.
Acknowledgments
B.D. is grateful to CSIR for financial support through grant No. 02(0342)/18/EMR-II.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| sEH | soluble epoxy hydrolase |
| EET | epoxyeicosatrienoic acid |
| ARA | arachidonic acid |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| LOX | lipoxygenase |
| 5-LO | 5-lipoxygenase |
| CYP | cytochrome P450 |
| HETEs | hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids |
| LTA4 | leukotriene A4 |
| hsEH | human soluble epoxy hydrolase |
| DHETs | dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid |
| Sphk1 | Sphingosine kinase 1 |
| FLAP | 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein |
| KRAS | Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| sEHIs | soluble epoxy hydrolase inhibitors |
| DCU | 1,3-Dicyclohexylurea |
| CDU | 1-cyclohexyl-3-dodecyl-urea |
| AUDA | 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido) dodecanoic acid |
| AEPU | 1-adamantanyl-3-(5-(2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)ethoxy)pentyl)urea |
| APAU | 1-(1-Acetypiperidin-4-yl)-3-adamantanylurea |
| TPPU | 1-(1-propanoylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]urea |
| PTUPB | 4-(5-phenyl-3-(3-[3-(4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ureido]-propyl)S-pyrazol-1-yl) benzenesulfonamide |
| t-AUCB | trans-4-[4-(3-Adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-cyclohexyloxy]-benzoic acid |
| t-TUCB | trans-4-[4-[3-(4-Trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-ureido]-cyclohexyloxy]-benzoic acid |
| CPTU | 1-(1-(cyclopropanecarbonyl)piperidin-4-yl)-3-(4 (trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)urea |
| TPAU | (1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-acetylpiperidin-4-yl)urea |
| ACU | 1-adamantyl-3-cyclohexylurea |
| AMAU | N-((1-acetylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-N’-(adamant-1-yl)urea |
| CUPM | 5-[4-[3-(4-chloro-3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-ureido]-cyclohexyloxy]-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid methylamide |
References
- Needleman, P.; Truk, J.; Jakschik, B.A.; Morrison, A.R.; Lefkowith, J.B. Arachidonic acid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1986, 55, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imig, J.D. Epoxides and soluble epoxide hydrolase in cardiovascular physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 101–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulmatycki, K.M.; Jamali, F. Drug disease interactions: Role of inflammatory mediators in disease and variability in drug response. Inflammation 2005, 23, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liao, J.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Bai, H.; Yang, A.; Hammock, B.D.; Yang, G.Y. Reduction of inflammatory bowel disease-induced tumor development in IL-10 knockout mice with soluble epoxide hydrolase gene deficiency. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwood, S.; Liao, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Yang, G.Y. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and soluble epoxide hydrolase: Potential therapeutic targets for inflammation and its induced carcinogenesis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2010, 2, 447. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, A.A.; Fang, X.; Snyder, G.D.; Weintraub, N.L. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): Metabolism and biochemical function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 55–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, D.; Dou, X.; Niu, N.; Huang, W.; Bai, J.; Zhang, G. Elevated 14, 15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid by increasing of cytochrome P450 2C8, 2C9 and 2J2 and decreasing of soluble epoxide hydrolase associated with aggressiveness of human breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Panigrahy, D.; Edin, M.L.; Lee, C.R.; Huang, S.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Butterfield, C.E.; Barnes, C.M.; Mammoto, A.; Mammoto, T.; Luria, A.; et al. Epoxyeicosanoids stimulate multiorgan metastasis and tumor dormancy escape in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.-X.; Lee, C.R.; Seubert, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chao, Z.-R.; Tao, D.-D.; Gong, J.-P.; et al. Cytochrome P-450 epoxygenases protect endothelial cells from apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha via MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H142–H151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-G.; Chen, C.-L.; Card, J.W.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.-X.; Fu, X.-N.; Ning, Y.-G.; Xiao, X.; Zeldin, D.C.; Wang, D.W. Cytochrome P450 2J2 promotes the neoplastic phenotype of carcinoma cells and is up-regulated in human tumors. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4707–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.W.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Epoxide hydrolases: Their roles and interactions with lipid metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2005, 44, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammock, B.D.; Grant, D.; Storms, D. Epoxide hydrolases. Compr. Toxicol. 1997, 3, 283–305. [Google Scholar]
- Fretland, A.J.; Omiecinski, C.J. Epoxide hydrolases: Biochemistry and molecular biology. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2000, 129, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.C.; Hammock, B.D. Discovery of inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase: A target with multiple potential therapeutic indications. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1789–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, G.A.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Christianson, D.W. Structure of human epoxide hydrolase reveals inferences on bifunctional catalysis in epoxide and phosphate ester hydrolysis. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 4716–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, F.; Huse, L.M.; Morisseau, C.; Draper, A.J.; Newman, J.W.; Parker, C.; Graham, L.; Engler, M.M.; Hammock, B.D.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates hydrolysis of vasoactive epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borhan, B.; Jones, A.D.; Pinot, F.; Grant, D.F.; Kurth, M.J.; Hammock, B.D. Mechanism of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase formation of an α-hydroxy ester-enzyme intermediate through Asp-333. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26923–26930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiriadi, M.A.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Christianson, D.W. Detoxification of environmental mutagens and carcinogens: Structure, mechanism, and evolution of liver epoxide hydrolase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10637–10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Morisseau, C.; Maxwell, J.E.; Argiriadi, M.A.; Christianson, D.W.; Hammock, B.D. Biochemical evidence for the involvement of tyrosine in epoxide activation during the catalytic cycle of epoxide hydrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23082–23088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Epoxide hydrolases: Mechanisms, inhibitor designs, and biological roles. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 311–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiøtt, B.; Bruice, T.C. Reaction mechanism of soluble epoxide hydrolase: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14558–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.W.; Subrahmanyam, R.M.; Summers, S.A.; Xiao, X.; Alkayed, N.J. Soluble epoxide hydrolase dimerization is required for hydrolase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7697–7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Node, K.; Huo, Y.; Ruan, X.; Yang, B.; Spiecker, M.; Ley, K.; Zeldin, D.C.; Liao, J.K. Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science 1999, 285, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, A.A.; Norris, A.W. Action of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on cellular function. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C996–C1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahy, D.; Greene, E.R.; Pozzi, A.; Wang, D.W.; Zeldin, D.C. EET signaling in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, I.; Busse, R. Endothelium-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and vascular function. Hypertension 2006, 47, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Hoshi, T.; Weintraub, N.L.; Spector, A.A.; Lee, H.C. Activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in rat cardiac ventricular myocytes. J. Physiol. 2001, 53, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, U.R.; Fisslthaler, B.; Barbosa-Sicard, E.; Falck, J.R.; Fleming, I.; Busse, R. Cytochrome P450 epoxygenases 2C8 and 2C9 are implicated in hypoxia-induced endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 5489–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, U.R.; Fleming, I. From endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) to angiogenesis: Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and cell signaling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, U.R.; Falck, J.R.; Schmidt, R.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. Cytochrome P4502C9-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Macias-Perez, I.; Abair, T.; Wei, S.; Su, Y.; Zent, R.; Falck, J.R.; Capdevila, J.H. Characterization of 5, 6-and 8, 9-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (5, 6-and 8, 9-EET) as potent in vivo angiogenic lipids. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27138–27146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L.; Wu, X.; Qiu, L.; Di, W. Sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)/S1P receptor axis is involved in ovarian cancer angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 74947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Chen, S.; You, B.; Sun, J. Activation of sphingosine kinase-1 mediates induction of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 78, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.H.; Lee, K.I.; Shyue, S.K.; Chen, H.Y.; Wei, J.; Lee, T.S. Implication of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 in 14, 15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid-induced angiogenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Qin, C.; Li, W.; Jia, T.; Nan, Q.; Qiang, R. Soluble epoxide hydrolase: Potential target for inflammation and inflammation-driven cancer. J. Carcinog. Mutagen. 2017, 8, 1000294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imig, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Capdevila, J.H.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition lowers arterial blood pressure in angiotensin II hypertension. Hypertension 2002, 39, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiamvimonvat, N.; Ho, C.M.; Tsai, H.J.; Hammock, B.D. The soluble epoxide hydrolase as a pharmaceutical target for hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2007, 50, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carroll, M.A.; Chander, P.N.; Falck, J.R.; Sangras, B.; Stier, C.T. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, AUDA, prevents early salt-sensitive hypertension. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, J.Y.; Park, S.H.; Morisseau, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Hammock, B.D.; Weiss, R.H. Sorafenib has soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity, which contributes to its effect profile In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Vincelette, J.; Cheng, Y.; Mehra, U.; Chen, D.; Anandan, S.K.; Gless, R.; Webb, H.K.; Wang, Y.X. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuated atherosclerosis, abdominal aortic aneurysm formation, and dyslipidemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inceoglu, B.; Jinks, S.L.; Schmelzer, K.R.; Waite, T.; Kim, I.H.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase reduces LPS-induced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in a rat model of inflammatory pain. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inceoglu, B.; Jinks, S.L.; Ulu, A.; Hegedus, C.M.; Georgi, K.; Schmelzer, K.R.; Wagner, K.; Jones, P.D.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids modulate two distinct analgesic pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18901–18906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, T.E.; Morisseau, C.; Liu, J.Y.; Inceoglu, B.; Jones, P.D.; Sanborn, J.R.; Hammock, B.D. 1-Aryl-3-(1-acylpiperidin-4-yl) urea inhibitors of human and murine soluble epoxide hydrolase: Structure-Activity relationships, pharmacokinetics, and reduction of inflammatory pain. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 7067–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.M.; McReynolds, C.B.; Schmidt, W.K.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for pain, inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 180, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Inceoglu, B.; Gill, S.S.; Hammock, B.D. Epoxygenated fatty acids and soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition: Novel mediators of pain reduction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2816–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, M.; Ren, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.; Xiong, Z.; Ishima, T.; Pu, Y.; Hwang, S.H.; Toyoshima, M.; Iwayama, Y.; et al. Key role of soluble epoxide hydrolase in the neurodevelopmental disorders of offspring after maternal immune activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7083–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Ma, M.; Yang, J.; Nonaka, R.; Yamaguchi, A.; Ishikawa, K.I.; Kobayashi, K.; Murayama, S.; Hwang, S.H.; Saiki, S.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5815–E5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K. Role of soluble epoxide hydrolase in metabolism of PUFAs in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarriello, S.; Tuazon, J.P.; Corey, S.; Schimmel, S.; Rajani, M.; Gorsky, A.; Incontri, D.; Hammock, B.D.; Borlongan, C.V. Humble beginnings with big goals: Small molecule soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors for treating CNS disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 172, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, Q. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor protects against blood-brain barrier dysfunction in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes via the AMPK/HO-1 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savina, Y.; Duflot, T.; Bounoure, F.; Kotzki, S.; Thiébaut, P.A.; Serreau, P.A.; Skiba, M.; Picquenot, J.M.; Cornic, M.; Morisseau, C.; et al. Impact of the acute local inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase on diabetic skin microcirculatory dysfunction. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minaz, N.; Razdan, R.; Hammock, B.D.; Mujwar, S.; Goswami, S.K. Impact of diabetes on male sexual function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Protective role of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 115, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Dziumbla, S.; Lin, J.; Bibli, S.I.; Zukunft, S.; De Mos, J.; Awwad, K.; Frömel, T.; Jungmann, A.; Devraj, K.; et al. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase prevents diabetic retinopathy. Nature 2017, 552, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Corson, T.W. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition for ocular diseases: Vision for the future. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, R.S.; Park, B.; Sheik Pran Babu, S.P.; Si, Y.; Kharwadkar, R.; Mitter, S.K.; Lee, B.; Sun, W.; Qi, X.; Boulton, M.E.; et al. Chemical proteomics reveals soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for ocular neovascularization. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.H.; Park, Y.K.; Hammock, B.D.; Nishi, K. Structure-Activity relationships of cycloalkylamide derivatives as inhibitors of the soluble epoxide hydrolase. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gomez, G.A.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Christianson, D.W. Human soluble epoxide hydrolase: Structural basis of inhibition by 4-(3-cyclohexylureido)-carboxylic acids. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldrup, A.B.; Soleymanzadeh, F.; Taylor, S.J.; Muegge, I.; Farrow, N.A.; Joseph, D.; McKellop, K.; Man, C.C.; Kukulka, A.; De Lombaert, S. Structure-Based optimization of arylamides as inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5880–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argiriadi, M.A.; Morisseau, C.; Goodrow, M.H.; Dowdy, D.L.; Hammock, B.D.; Christianson, D.W. Binding of alkylurea inhibitors to epoxide hydrolase implicates active site tyrosines in substrate activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 15265–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; McDonald, J.J.; Kolodziej, S.A.; Kurumbail, R.G.; Williams, J.M.; Warren, C.J.; O’Neal, J.M.; Skepner, J.E.; Roberds, S.L. Discovery of potent inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase by combinatorial library design and structure-based virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisseau, C.; Pakhomova, S.; Hwang, S.H.; Newcomer, M.E.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase by fulvestrant and sulfoxides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3818–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dietze, E.C.; Kuwano, E.; Casas, J.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of cytosolic epoxide hydrolase by trans-3-phenylglycidols. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Du, G.; Newman, J.W.; Hammock, B.D. Mechanism of mammalian soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition by chalcone oxide derivatives. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 356, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokkumar, K.; Prathyusha, L.T.; Umamaheshwari, M.; Sivashanmugam, T.; Subhadradevi, V.; Jagannath, P.; Madeswaran, A.; Salesheir, F. Design, ADMET and docking studies on some novel chalcone derivatives as soluble epoxide hydrolase enzyme inhibitors. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2012, 57, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, S.-X.; Cao, B.; Morisseau, C.; Jin, Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Long, Y.-Q. Structure-based optimization of the piperazino-containing 1,3-disubstituted ureas affording sub-nanomolar inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 3, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, P.D.; Hsing-Ju, T.; Zung, N.D.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Synthesis and SAR of conformationally restricted inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5212–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, P.D.; Wolf, N.M.; Morisseau, C.; Whetstone, P.; Hock, B.; Hammock, B.D. Fluorescent substrates for soluble epoxide hydrolase and application to inhibition studies. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 343, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Goodrow, M.H.; Newman, J.W.; Wheelock, C.E.; Dowdy, D.L.; Hammock, B.D. Structural refinement of inhibitors of urea-based soluble epoxide hydrolases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulu, A.; Appt, S.; Morisseau, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Jones, P.D.; Rose, T.E.; Dong, H.; Lango, J.; Yang, J.; Tsai, H.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and in vivo potency of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in cynomolgus monkeys. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Morisseau, C.; Newman, J.W.; Hammock, B.D. In Vitro metabolism of the mammalian soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, 1-cyclohexyl-3-dodecyl-urea. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olearczyk, J.J.; Field, M.B.; Kim, I.H.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Imig, J.D. Substituted adamantyl-urea inhibitors of the soluble epoxide hydrolase dilate mesenteric resistance vessels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Morisseau, C.; Watanabe, T.; Hammock, B.D. Design, synthesis, and biological activity of 1, 3-disubstituted ureas as potent inhibitors of the soluble epoxide hydrolase of increased water solubility. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2110–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.J.; Hwang, S.H.; Morisseau, C.; Yang, J.; Jones, P.D.; Kasagami, T.; Kim, I.H.; Hammock, B.D. Pharmacokinetic screening of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in dogs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wan, D.; Yang, J.; McReynolds, C.B.; Barnych, B.; Wagner, K.M.; Morisseau, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Sun, J.; Blöcher, R.; Hammock, B.D. In vitro and in vivo metabolism of a potent inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase, 1-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-(4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenyl) urea. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Whitcomb, R.; MacIntyre, E.; Tran, V.; Do, Z.N.; Sabry, J.; Patel, D.V.; Anandan, S.K.; Gless, R.; Webb, H.K. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of AR9281, an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase, in single- and multiple-dose studies in healthy human subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, G.Y.; Liu, T.; Duan, J.X.; Zhou, H.F.; Lee, K.S.; Hammock, B.D.; Fang, X.; Jiang, J.X.; Guan, C.X. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor 1-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-3-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 363, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldrup, A.B.; Soleymanzadeh, F.; Farrow, N.A.; Kukulka, A.; De Lombaert, S. Optimization of piperidyl-ureas as inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.C.; Ding, F.X.; Wang, S.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; Xu, S.; Chen, H.S.; Tong, X.; et al. Discovery of a highly potent, selective, and bioavailable soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor with excellent ex vivo target engagement. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5009–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.C.; Ding, F.X.; Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Chen, H.S.; Tong, X.; Tong, V.; Mitra, K.; Kumar, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. Discovery of spirocyclic secondary amine-derived tertiary ureas as highly potent, selective and bioavailable soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3398–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmistrov, V.V.; Butov, G.M. Synthesis and properties of N-[R-adamantan-1 (2)-yl]-N′-(2-fluorophenyl) ureas—Target-Oriented soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 54, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmistrov, V.V.; Morisseau, C.; Karlov, D.; Pitushkin, D.; Vernigora, A.; Rasskazova, E.; Butov, G.M.; Hammock, B.D. Bioisosteric substitution of adamantane with bicyclic lipophilic groups improves water solubility of human soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codony, S.; Pujol, E.; Pizarro, J.; Feixas, F.; Valverde, E.; Loza, M.I.; Brea, J.M.; Saez, E.; Oyarzabal, J.; Pineda-Lucena, A.; et al. 2-Oxaadamant-1-yl Ureas as soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors: In Vivo evaluation in a murine model of acute pancreatitis. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9237–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltenberger, B.; Garscha, U.; Temml, V.; Liers, J.; Werz, O.; Schuster, D.; Stuppner, H. Discovery of potent soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors by pharmacophore-based virtual screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, E.; Hedayati, M.; Rad, L.H.; Shahhosseini, S.; Faizi, M.; Tabatabai, S.A. Novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors with a dihydropyrimidinone scaffold: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaar, A.L.; Yang, L.; Boardley, R.L.; Goyal, N.S.; Robertson, J.; Baldwin, S.J.; Newby, D.E.; Wilkinson, I.B.; Tal-Singer, R.; Mayer, R.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and adverse event profile of GSK2256294, a novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, N.; Paliwal, S.; Sharma, S.; Verma, K.; Gururani, R.; Tiwari, A.; Verma, A.; Chauhan, M.; Singh, A.; Kumar, D.; et al. Discovery of novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors as potent vasodilators. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, S.N.; Lee, S.B.; Samokhvalov, V.; Chaudhary, K.R.; El-Sikhry, H.; Weldon, S.M.; Seubert, J.M. Novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor protects mitochondrial function following stress. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 90, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Heirtzler, F.R.; Morisseau, C.; Nishi, K.; Tsai, H.J.; Hammock, B.D. Optimization of amide-based inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase with improved water solubility. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3621–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, S.K.; Webb, H.K.; Do, Z.N.; Gless, R.D. Unsymmetrical non-adamantyl N, N′-diaryl urea and amide inhibitors of soluble expoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 4259–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, E.; Amrolah, S.M.; Nazari, M.; Tabatabi, S.A. Novel amide derivatives of 3-phenylglutaric acid as potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Mol. Divers. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecic, S.; Deng, S.-X.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Landry, D.W. Design, synthesis and evaluation of non-urea inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, G.; Smith, D.H.; Yan, F.; Rinderspacher, A.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X.; Deng, S.X.; et al. Discovery of potent non-urea inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2354–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pecic, S.; Pakhomova, S.; Newcomer, M.E.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Zhu, Z.; Rinderspacher, A.; Deng, S.-X. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of piperidine-derived non-urea soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.C.; Ding, F.X.; Deng, Q.; Xu, S.; Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; Pai, L.Y.; Alonso-Galicia, M.; et al. A strategy of employing aminoheterocycles as amide mimics to identify novel, potent and bioavailable soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5716–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Ma, W.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Ban, S.R.; Feng, X.E.; Li, Q.S. Synthesis and biological activity of 4-substituted benzoxazolone derivatives as a new class of sEH inhibitors with high anti-inflammatory activity in vivo. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2380–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzer, K.R.; Kubala, L.; Newman, J.W.; Kim, I.H.; Eiserich, J.P.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase is a therapeutic target for acute inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9772–9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmistrov, V.V.; Morisseau, C.; Pitushkin, D.; Karlov, D.; Fayzullin, R.R.; Butov, G.M.; Hammock, B.D. Adamantyl thioureas as soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2302–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwati, S.; Siddiqui, M.I. Identification of potential soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors by ligand-based pharmacophore model and biological evaluation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 38, 4956–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, D.; Tsuda, Y.; Shiyama, T.; Nishimura, T.; Chiyo, N.; Tominaga, Y.; Sawada, N.; Mimoto, T.; Kusunose, N. A practical use of ligand efficiency indices out of the fragment-based approach: Ligand efficiency-guided lead identification of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Tanabe, E. Structural insights into binding of inhibitors to soluble epoxide hydrolase gained by fragment screening and X-ray crystallography. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.S.; Liu, J.-Y.; Wagner, K.M.; Pakhomova, S.; Dong, H.; Morisseau, C.; Fu, S.H.; Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Ulu, A.; et al. Optimized Inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase improve in vitro target residence time and in vivo efficacy. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7016–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukin, A.; Kramer, J.; Hartmann, M.; Weizel, L.; Hernandez-Olmos, V.; Falahati, K.; Burghardt, I.; Kalinchenkova, N.; Bagnyukova, D.; Zhurilo, N.; et al. Discovery of polar spirocyclic orally bioavailable urea inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalji, R.K.; McAtee, J.J.; Belyanskaya, S.; Brandt, M.; Brown, G.D.; Costell, M.H.; Ding, Y.; Dodson, J.W.; Eisennagel, S.H.; Fries, R.E.; et al. Discovery of 1-(1, 3, 5-triazin-2-yl) piperidine-4-carboxamides as inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3584–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.Y.; Man, C.C.; Fleck, R.W.; Farrow, N.A.; Ingraham, R.H.; Kukulka, A.; Proudfoot, J.R.; Betageri, R.; Kirrane, T.; Patel, U.; et al. Substituted pyrazoles as novel sEH antagonist: Investigation of key binding interactions within the catalytic domain. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6379–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M.S.; Wingen, L.M.; Brunst, S.; Wittman, S.; Cardoso, I.L.A.; Weizel, L.; Proschak, E. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors with carboranes as non-natural 3-D pharmacophores. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 185, 111766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, L.B.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Nguyet, N.T.M.; Yang, S.Y.; Ma, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity of phenolic glycosides from Polygala tenuifolia and in silico approach. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Morisseau, C.; Huang, H.; Hammock, B.D. Screening of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory ingredients from traditional Chinese medicines for anti-inflammatory use. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Morisseau, C.; Inceoglu, B.; Kamita, S.G.; De Nicola, G.R.; Nyegue, M.; Hammock, B.D. Potent natural soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors from Pentadiplandra brazzeana Baillon: Synthesis, quantification, and measurement of biological activities in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, N.P.; Kim, J.H.; Luyen, B.T.T.; Dat, N.T.; Kim, Y.H. In silico investigation of cycloartane triterpene derivatives from Cimicifuga dahurica (Turcz.) Maxim. roots for the development of potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscató, E.L.; Büttner, D.; Brüggerhoff, A.; Klingler, F.M.; Weber, J.; Scholz, B.; Živković, A.; Marschalek, R.; Stark, H.; Steinhilber, D.; et al. From a multipotent stilbene to soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors with antiproliferative properties. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, I.S.; Ryu, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kang, J.S.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H. In vitro and in silico investigation of anthocyanin derivatives as soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Ma, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.K. Discovery of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors from natural products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 64, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.-K.; Kim, Y.H. Constituents of the seeds of Cassia tora with inhibitory activity on soluble epoxide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5097–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, A.R.; Kim, J.H.; Yan, X.-T.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory components from Rheum undulatum and in silico approach. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, C.W.; Tai, B.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Choi, G.-S.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity of selaginellin derivatives from Selaginella tamariscina. Molecules 2015, 20, 21405–21414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Morgan, A.M.A.; Tai, B.H.; Van, D.T.; Cuong, N.M.; Kim, Y.H. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase activity by compounds isolated from the aerial parts of Glycosmis stenocarpa. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Shao, B.; Zhang, B.-J.; Liu, T.-T.; Sun, C.-P.; Huang, H.-L.; Wu, J.-R.; Liang, J.-H.; Ma, X.-C. Natural soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors from Inula helenium and their interactions with soluble epoxide hydrolase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.D.; Li, W.; Kim, J.E.; Yang, S.Y.; Ma, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Prenyl-flavonoids from Epimedium koreanum Nakai and their soluble epoxide hydrolase and tyrosinase inhibitory activities. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.X.; Heo, M.; Go, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Li, W. Coumarin and moracin derivatives from mulberry leaves (Morus alba L.) with soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-P.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Yi, J.; Yan, J.-K.; Wang, Y.-L.; Morisseau, C.; Liu, Z.-B.; Hammock, B.D.; Ma, X.-C. Protostane-Type triterpenoids as natural soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors: Inhibition potentials and molecular dynamics. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falck, J.R.; Kodela, R.; Manne, R.; Atcha, K.R.; Puli, N.; Dubasi, N.; Manthati, V.L.; Capdevila, J.H.; Yi, X.Y.; Goldman, D.H.; et al. 14,15-Epoxyeicosa-5,8,11-trienoic acid (14,15-EET) surrogates containing epoxide bioisosteres: Influence upon vascular relaxation and soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5069–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck, J.R.; Koduru, S.R.; Mohapatra, S.; Manne, R.; Atcha, R.; Manthati, V.L.; Capdevila, J.H.; Christian, S.; Imig, J.D.; Campbell, W.B. 14,15-Epoxyeicosa-5,8,11-trienoic acid (14,15-EET) surrogates: Carboxylate modifications. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6965–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litovchick, A.; Dumelin, C.E.; Habeshian, S.; Gikunju, D.; Guie, M.A.; Centrella, P.; Zhang, Y.; Sigel, E.A.; Cuozzo, J.W.; Keefe, A.D.; et al. Encoded library synthesis using chemical ligation and the discovery of sEH inhibitors from a 334-million member library. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belyanskaya, S.L.; Ding, Y.; Callahan, J.F.; Lazaar, A.L.; Israel, D.I. Discovering drugs with DNA-encoded library technology: From concept to clinic with an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abis, G.; Charles, R.L.; Kopec, J.; Yue, W.W.; Atkinson, R.A.; Bui, T.T.; Lynham, S.; Popova, S.; Sun, Y.B.; Fraternali, F.; et al. 15-deoxy-Δ 12, 14-Prostaglandin J 2 inhibits human soluble epoxide hydrolase by a dual orthosteric and allosteric mechanism. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Panigrahy, D.; Hwang, S.H.; Yang, J.; Mahakian, L.M.; Wettersten, H.I.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Ingham, E.S.; Tam, S.; et al. Dual inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 and soluble epoxide hydrolase synergistically suppresses primary tumor growth and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11127–11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.D.; Liao, J.; Tong, X.; Xu, D.; Sun, L.; Li, H.; Yang, G.Y. Epoxy-Oxylipins and soluble epoxide hydrolase metabolic pathway as targets for NSAID-induced gastroenteropathy and inflammation-associated carcinogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzer, K.R.; Inceoglu, B.; Kubala, L.; Kim, I.H.; Jinks, S.L.; Eiserich, J.P.; Hammock, B.D. Enhancement of antinociception by coadministration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13646–13651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Inceoglu, B.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition, epoxygenated fatty acids and nociception. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 96, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.K.; Wan, D.; Yang, J.; Da Silva, C.A.T.; Morisseau, C.; Kodani, S.D.; Yang, G.Y.; Inceoglu, B.; Hammock, B.D. Anti-Ulcer efficacy of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor TPPU on diclofenac-induced intestinal ulcers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 357, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Wagner, K.M.; Morisseau, C.; Liu, J.Y.; Dong, H.; Wecksler, A.T.; Hammock, B.D. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of urea-containing pyrazoles as dual inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 and soluble epoxide hydrolase. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3037–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelazeem, A.H.; Safi El-Din, A.G.; Abdel-Fattah, M.M.; Amin, N.H.; El-Moghazy, S.M.; El-Saadi, M.T. Discovery of novel urea-diarylpyrazole hybrids as dual COX-2/sEH inhibitors with improved anti-inflammatory activity and highly reduced cardiovascular risks. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 205, 112662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Yang, J.; Inceoglu, B.; Qiu, H.; Ulu, A.; Hwang, S.-H.; Chiamvimonvat, N.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase enhances the anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin and 5-lipoxygenase activation protein inhibitor in a murine model. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garscha, U.; Romp, E.; Pace, S.; Rossi, A.; Temml, V.; Schuster, D.; Konig, S.; Gerstmeier, J.; Liening, S.; Werner, M.; et al. Pharmacological profile and efficiency in vivo of diflapolin, the first dual inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein and soluble epoxide hydrolase. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temml, V.; Garscha, U.; Romp, E.; Schubert, G.; Gerstmeier, J.; Kutil, Z.; Matuszczak, B.; Waltenberger, B.; Stuppner, H.; Werz, O.; et al. Discovery of the first dual inhibitor of the 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein and soluble epoxide hydrolase using pharmacophore-based virtual screening. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiesinger, K.; Schott, A.; Kramer, J.S.; Blocher, R.; Witt, F.; Wittman, S.K.; Steinhilber, D.; Pogoryelov, D.; Gerstmeier, J.; Werz, O.; et al. Design of dual inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase and LTA4 hydrolase. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefke, L.; Hiesinger, K.; Zhu, W.F.; Kramer, J.S.; Proschak, E. Computer-Aided fragment growing strategies to design dual inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase and LTA4 hydrolase. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, D.; Wisniewska, J.M.; Hahn, S.; Achenback, J.; Buscato, E.; Klingler, F.-M.; Hofmann, B.; Steinhilber, D.; Proschak, E. Dual-Target virtual screening by pharmacophore elucidation and molecular shape filtering. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandha, B.; Ramareddy, S.A.; Hazra, K. Synthesis of substituted fluorobenzimidazoles as inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase and soluble epoxide hydrolase for anti-inflammatory activity. Arch. Pharm. 2018, 351, 1800030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirer, K.; Rodl, C.B.; Wisniewska, J.M.; George, S.; Hafner, A.-K.; Buscato, E.; Klingler, F.-M.; Hahn, S.; Berressem, D.; Wittmann, S.K.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of novel dual inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase and 5-lipoxygenase. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achenback, J.; Klingler, F.-M.; Blocher, R.; Moser, D.; Hafner, A.K.; Rodl, C.B.; Kretschmer, S.; Kruger, B.; Lohr, F.; Stark, H.; et al. Exploring the chemical space of multitarget ligands using self-organizing maps. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirer, K.; Glatzel, D.; Kretschmer, S.; Wittmann, S.K.; Hartmann, M.; Blocher, R.; Angioni, C.; Geisslinger, G.; Steinhilber, D.; Hofmann, B.; et al. Design, synthesis and cellular characterization of a dual inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase and soluble epoxide hydrolase. Molecules 2017, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodani, S.D.; Bhakta, S.; Hwang, S.H.; Pakhomova, S.; Newcomer, M.E.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Identification and optimization of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors with dual potency towards fatty acid amide hydrolase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodani, S.D.; Wan, D.; Wagner, K.M.; Hwang, S.H.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Design and potency of dual soluble epoxide hydrolase/fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 14076–14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Xu, M.; Morisseau, C.; Hwang, S.H.; Hammock, B.D.; Li, Q.X. 1-Trifluoromethoxyphenyl-2-(1-propionylpiperidin-4-yl) urea, a selective and potent dual inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase and p38 kinase intervenes in Alzheimer’s signaling in human nerve cells. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4018–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.; Rotter, M.; Weiser, T.; Wittmann, S.; Weizel, L.; Kaiser, A.; Heering, J.; Goebel, T.; Angioni, C.; Wurglics, M.; et al. A dual modulator of farnesoid X receptor and soluble epoxide hydrolase to counter nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7703–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierle, S.; Helmstadter, M.; Schmidt, J.; Hartmann, M.; Horz, M.; Kaiser, A.; Weizel, L.; Heitel, P.; Proschak, A.; Hernandez-Olmos, V.; et al. Dual farnesoid X receptor/soluble epoxide hydrolase modulators derived from Zafirlukast. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, B.; Wagner, K.; Schebb, N.H.; Morisseau, C.; Jinks, S.L.; Ulu, A.; Hegedus, C.; Rose, T.; Brosnan, R.; Hammock, B.D. Analgesia mediated by soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors is dependent on cAMP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5093–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocher, R.; Wagner, K.M.; Gopireddy, R.R.; Harris, T.R.; Wu, H.; Barnych, B.; Hwang, S.H.; Xiang, Y.K.; Proschak, E.; Morisseau, C.; et al. Orally available soluble epoxide hydrolase/phosphodiesterase 4 dual inhibitor treats inflammatory pain. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3541–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, H.; Jones, J.D.; Purica, M.C.; Weidner, S.; Koh, A.J.; Kuo, R.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Daignault-Newton, S.; Pienta, K.J.; et al. Apoptosis-induced CXCL5 accelerates inflammation and growth of prostate tumor metastases in bone. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, J.C.; Young, C.; Hicks, D.; Owens, P.; Williams, A.; Vaught, D.B.; Morrison, M.M.; Lim, J.; Williams, M.; Brantley-Sieders, D.M.; et al. Efferocytosis produces a prometastatic landscape during postpartum mammary gland involution. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4737–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.I.; Liao, J.; Berry, J.E.; Li, X.; Koh, A.J.; Michalski, M.E.; Eber, M.R.; Soki, F.N.; Sadler, D.; Sud, S.; et al. Cyclophosphamide creates a receptive microenvironment for prostate cancer skeletal metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartung, A.; Yang, J.; Sukhatme, V.P.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Fernandes, D.; Chang, J.; Schmidt, B.A.; Hwang, S.H.; Zurakowski, D.; Huang, S.; et al. Suppression of chemotherapy-induced cytokine/lipid mediator surge and ovarian cancer by a dual COX-2/sEH inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, G.Y.; Woodward, N.; Coward, J.I. Cisplatin versus carboplatin: Comparative review of therapeutic management in solid malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 102, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Ma, A.H.; Yu, W.; Zimmermann, M.; Yang, J.; Hwang, S.H.; Zhu, D.; Lin, T.Y.; Malfatti, M.; et al. COX-2/sEH dual inhibitor PTUPB potentiates the antitumor efficacy of cisplatin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Chaki, R.; Mandal, V.; Mandal, S.C. COX-2 as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol. Rep. 2010, 62, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridelli, C.; Gallo, C.; Ceribelli, A.; Gebbia, V.; Gamucci, T.; Ciardiello, F.; Carozza, F.; Favaretto, A.; Daniele, B.; Galetta, D.; et al. Factorial phase III randomised trial of rofecoxib and prolonged constant infusion of gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: The GEmcitabine-COxib in NSCLC (GECO) study. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.X.; Loehrer, P.; Seitz, D.; Helft, P.; Juliar, B.; Ansari, R.; Pletcher, W.; Vinson, J.; Cheng, L.; Sweeney, C. A phase II trial of irinotecan, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin combined with celecoxib and glutamine as first-line therapy for advanced colorectal cancer. Oncology 2005, 69, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Maisonneuve, P.; Cavallini, G.; Ammann, R.W.; Lankisch, P.G.; Andersen, J.R.; Dimagno, E.P.; Andren-Sandberg, A.; Domellof, L.; Group, I.P.S. Pancreatitis and the risk of pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, S.R.; Wang, L.; Multani, A.S.; Combs, C.; Deramaudt, T.B.; Hruban, R.H.; Rustgi, A.K.; Chang, S.; Tuveson, D.A. Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pylayeva-Gupta, Y.; Grabocka, E.; Bar-Sagi, D. RAS oncogenes: Weaving a tumorigenic web. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasco, R.B.; Francoz, S.; Santamaría, D.; Cañamero, M.; Dubus, P.; Charron, J.; Baccarini, M.; Barbacid, M. C-Raf, but not B-Raf, is essential for development of K-Ras oncogene-driven non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Hwang, S.H.; Li, H.; Liu, J.Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Yang, G.Y. Inhibition of chronic pancreatitis and murine pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia by a dual inhibitor of c-RAF and soluble epoxide hydrolase in LSL-KrasG12D/Pdx-1-Cre mice. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Panigrahy, D.; Mahakian, L.M.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Lee, K.S.S.; Wettersten, H.I.; Ulu, A.; Hu, X.; Tam, S.; et al. Epoxy metabolites of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) inhibit angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6530–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Sirois, M.; Échavé, V.; Albadine, R.; Rousseau, E. 17, 18-Epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid targets PPARγ and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase to mediate its anti-inflammatory effects in the lung: Role of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Arita, M.; Isobe, Y.; Iwamoto, R.; Goto, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Urabe, D.; Inoue, M.; Arai, H. Eicosapentaenoic acid is converted via ω-3 epoxygenation to the anti-inflammatory metabolite 12-hydroxy-17, 18-epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Sun, L.; Liao, J.; Li, H.; You, X.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Hwang, S.H.; Jones, R.D.; Hammock, B.; et al. Inhibition of pancreatic carcinoma growth through enhancing ω-3 Epoxy polyunsaturated fatty acid profile by inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3651–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.D.; Campos, M.M. Protective effects of omega-3 fatty acids in cancer-related complications. Nutrients 2019, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.W.; Jia, Y.L.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, J.X.; Shen, J.; Jin, Y.C.; Guan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Q.M. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor AUDA decreases bleomycin-induced pulmonary toxicity in mice by inhibiting the p38/Smad3 pathways. Toxicology 2017, 389, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Xing, B.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, G.; Gu, B.; Zhang, G.; Wei, D.; Gu, P.; et al. t-AUCB, an improved sEH inhibitor, suppresses human glioblastoma cell growth by activating NF-κB-p65. J. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 108, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; DuBois, R.N. Eicosanoids and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hwang, S.H.; Qi, W.; Wan, D.; Kim, D.; Sun, J.; Sanidad, K.Z.; et al. Lipidomic profiling reveals soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target of obesity-induced colonic inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5283–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Wecksler, A.T.; Zhang, G.; Morisseau, C.; Nguyen, L.V.; Fu, S.H.; Hammock, B.D. Synthesis and biological evaluation of sorafenib-and regorafenib-like sEH inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3732–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).