Solubility and Thermal Degradation of Quercetin in CO2-Expanded Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
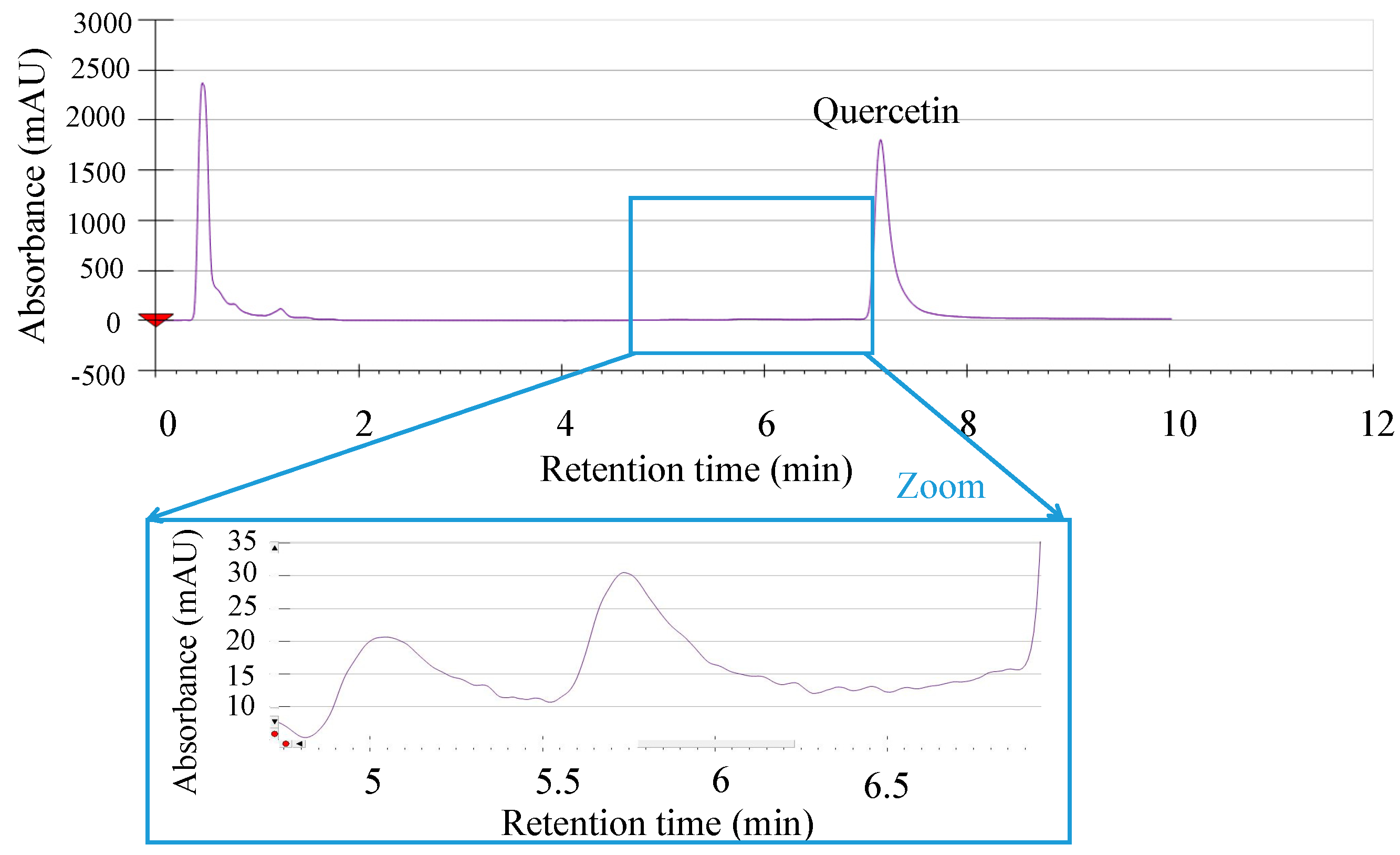
2.1. Thermal Degradation Measurements
2.2. Solubility Measurements
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Equipment Setup
3.3. Thermal Degradation Measurements
3.4. UHPLC-QTOF/MS Analysis
3.5. Solubility Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darband, S.G.; Kaviani, M.; Yousefi, B.; Sadighparvar, S.; Pakdel, F.G.; Attari, J.A.; Mohebbi, I.; Naderi, S.; Majidinia, M. Quercetin: A functional dietary flavonoid with potential chemo-preventive properties in colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Phys. 2018, 233, 6544–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Song, Y.; Liang, Y.N.; Li, R. Quercetin treatment improves renal function and protects the kidney in a rat model of adenine-induced chronic kidney disease. Med. Sci. Mon. 2018, 24, 4760–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Yakoub, A.R.; Abdehedi, O.; Jridi, M.; Elfalleh, W.; Nasri, M.; Ferchichi, A. Flavonoids, phenols, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities in various extracts from Tossa jute leave (Corchorus olitorus L.). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 118, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrova, E.V.; Maksimenko, E.V.; Borisenko, S.N.; Lekar, A.V.; Borisenko, N.I.; Minkin, V.I. Extraction of Rutin and Quercetin Antioxidants from the Buds of Sophora Japonica (Sophora japonica L.) by Subcritical Water. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 11, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, R.N. Gerd Brunner: Gas Extraction—An Introduction to Fundamentals of Supercritical Fluids and the Application to Separation Processes. Topics in Physical Chemistry, Vol. 4, eds. H. Baumgärtel, E. U. Franck, W. Grünbein. Steinkopff, Darmstadt/Springer, New York, 1994, 387 S., DM 64,—. Berichte Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 1090–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Musialik, M.; Kuzmicz, R.; Pawlowski, T.S.; Litwinienko, G. Acidity of hydroxyl groups: An overlooked influence on antiradical properties of flavonoids. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turturică, M.; Stănciuc, N.; Bahrim, G.; Râpeanu, G. Effect of thermal treatment on phenolic compounds from plum (prunus domestica) extracts—A kinetic study. J. Food Eng. 2016, 171, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramešová, Š.; Sokolová, R.; Degano, I.; Bulíčková, J.; Žabka, J.; Gál, M. On the stability of the bioactive flavonoids quercetin and luteolin under oxygen-free conditions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Acqua, S.; Miolo, G.; Innocenti, G.; Caffieri, S. The photodegradation of quercetin: Relation to oxidation. Molecules 2012, 17, 8898–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, K.; King, J.W.; Howard, L.R.; Monrad, J.K. Solubility and solution thermodynamic properties of quercetin and quercetin dihydrate in subcritical water. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmara, R.S.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R. Solubility of quercetin in water + methanol and water + ethanol from (292.8 to 333.8) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 3934–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebil, L.; Humeau, C.; Anthony, J.; Dehez, F.; Engasser, J.M.; Ghoul, M. Solubility of flavonoids in organic solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafer, A.; Fornari, T.; Berna, A.; Stateva, R.P. Solubility of quercetin in supercritical CO2+ ethanol as a modifier: Measurements and thermodynamic modelling. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2004, 32, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.H.; Acree Jr, W.E. On the solubility of quercetin. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 197, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, T. Quantitative HPLC analysis of phenolic acids, flavonoids and ascorbic acid in four different solvent extracts of two wild edible leaves, Sonchus arvensis and Oenanthe linearis of North-Eastern region in India. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 6, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, A.; Jaafar, H.Z.E.; Rahmat, A. Effects of solvent type on phenolics and flavonoids content and antioxidant activities in two varieties of young ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) extracts. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam, B.; Chaudhari, R.V.; Chaudhari, A.S.; Akien, G.R.; Xie, Z. Supercritical fluids and gas-expanded liquids as tunable media for multiphase catalytic reactions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 115, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.V.M.; Duarte, C.M.M. Dense CO₂ as a Solute, Co-Solute or Co-Solvent in Particle Formation Processes: A Review. Materials 2011, 4, 2017–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamimi, S.; Abellan Mayoral, A.; Cunico, L.P.; Turner, C. Carbon Dioxide Expanded Ethanol Extraction: Solubility and Extraction Kinetics of α-Pinene and cis-Verbenol. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4336–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.J.; Tu, W.C.; Levers, O.; Bröhl, A.; Hallett, J.P. Green and Sustainable Solvents in Chemical Processes. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 747–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunico, L.P.; Acosta, M.C.; Turner, C. Experimental measurements and modeling of curcumin solubility in CO2-expanded ethanol. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 130, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shehada, S.; Clark, J.H.; Paggiola, G.; Sherwood, J. Tunable solvents: Shades of green. Chem. Eng. Proc. Proc. Intens. 2016, 99, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.S.; Foss, F.W., Jr.; Schug, K.A. Thermally accelerated oxidative degradation of quercetin using continuous flow kinetic electrospray-ion trap-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spec. 2013, 24, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchner, N.; Krumbein, A.; Rohn, S.; Kroh, L.W. Effect of thermal processing on the flavonols rutin and quercetin. Rap. Comm. Mass. Spec. 2006, 20, 3229–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Kubben, N.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Bast, A. Oxidized quercetin reacts with thiols rather than with ascorbate: Implication for quercetin supplementation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2003, 308, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wianowska, D.; Dawidowicz, A.L.; Bernacik, K.; Typek, R. Determining the true content of quercetin and its derivatives in plants employing SSDM and LC–MS analysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.H. Degradation kinetics of fisetin and quercetin in solutions affected by medium pH, temperature and co-existing proteins. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2016, 81, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sandahl, M.; Sjöberg, P.J.R.; Turner, C. Pressurised hot water extraction in continuous flow mode for thermolabile compounds: Extraction of polyphenols in red onions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, P.G.; Jessop, D.A.; Fu, D.; Phan, L. Solvatochromic parameters for solvents of interest in green chemistry. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvezdanović, J.B.; Marković, D.Z.; Cvetković, D.J.; Stanojević, J.S. UV-induced change in the antioxidant activity of quercetin toward benzophenone-initiated lipid peroxidation. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2012, 77, 1571–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CO2 (% mol) | Temperature (K) | k (min −1) 10−4 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2-Expanded Ethanol | CO2-Expanded Ethyl Lactate | ||
| 10 | 308 | Not observed | Not observed |
| 30 | Not observed | Not observed | |
| 50 | Not observed | Not observed | |
| 10 | 323 | 0.44 | 7.05 |
| 30 | Not observed | 2.94 | |
| 50 | Not observed | Not observed | |
| 10 | 343 | 4.83 | 9.33 |
| 30 | Not observed | 6.83 | |
| 50 | Not observed | 4.09 | |
| CO2 (% mol) | Temperature (K) | Solubility (Molar Fraction) 10−4 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2-Expanded Ethanol | CO2-Expanded Ethyl Lactate | ||
| 10 | 308 | 10.61 ± 0.16 | 43.22 ± 0.16 |
| 30 | 7.74 ± 0.06 | 19.24 ± 0.07 | |
| 50 | 5.53 ± 0.06 | 8.93 ± 0.12 | |
| 10 | 323 | 10.67 ± 0.69 (calc. 10.80) | 41.71 ± 0.12 (50.68) |
| 30 | 13.07 ± 0.09 | 27.74 ± 0.09 (30.09) | |
| 50 | 6.13 ± 0.08 | 11.16 ± 0.02 | |
| 10 | 343 | 11.87 ± 0.50 (calc. 13.56) | 37.49 ± 0.06 (48.51) |
| 30 | 14.00 ± 0.15 | 21.98 ± 0.26 (26.55) | |
| 50 | 8.06 ± 0.03 | 10.18 ± 0.01 (11.40) | |
Sample Availability: Not available. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cunico, L.P.; Cobo, A.M.; Al-Hamimi, S.; Turner, C. Solubility and Thermal Degradation of Quercetin in CO2-Expanded Liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235582
Cunico LP, Cobo AM, Al-Hamimi S, Turner C. Solubility and Thermal Degradation of Quercetin in CO2-Expanded Liquids. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235582
Chicago/Turabian StyleCunico, Larissa P., Andrés Medina Cobo, Said Al-Hamimi, and Charlotta Turner. 2020. "Solubility and Thermal Degradation of Quercetin in CO2-Expanded Liquids" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235582
APA StyleCunico, L. P., Cobo, A. M., Al-Hamimi, S., & Turner, C. (2020). Solubility and Thermal Degradation of Quercetin in CO2-Expanded Liquids. Molecules, 25(23), 5582. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235582






