Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Ayahuasca Beverages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Alkaloid Derivatives and Other Compounds
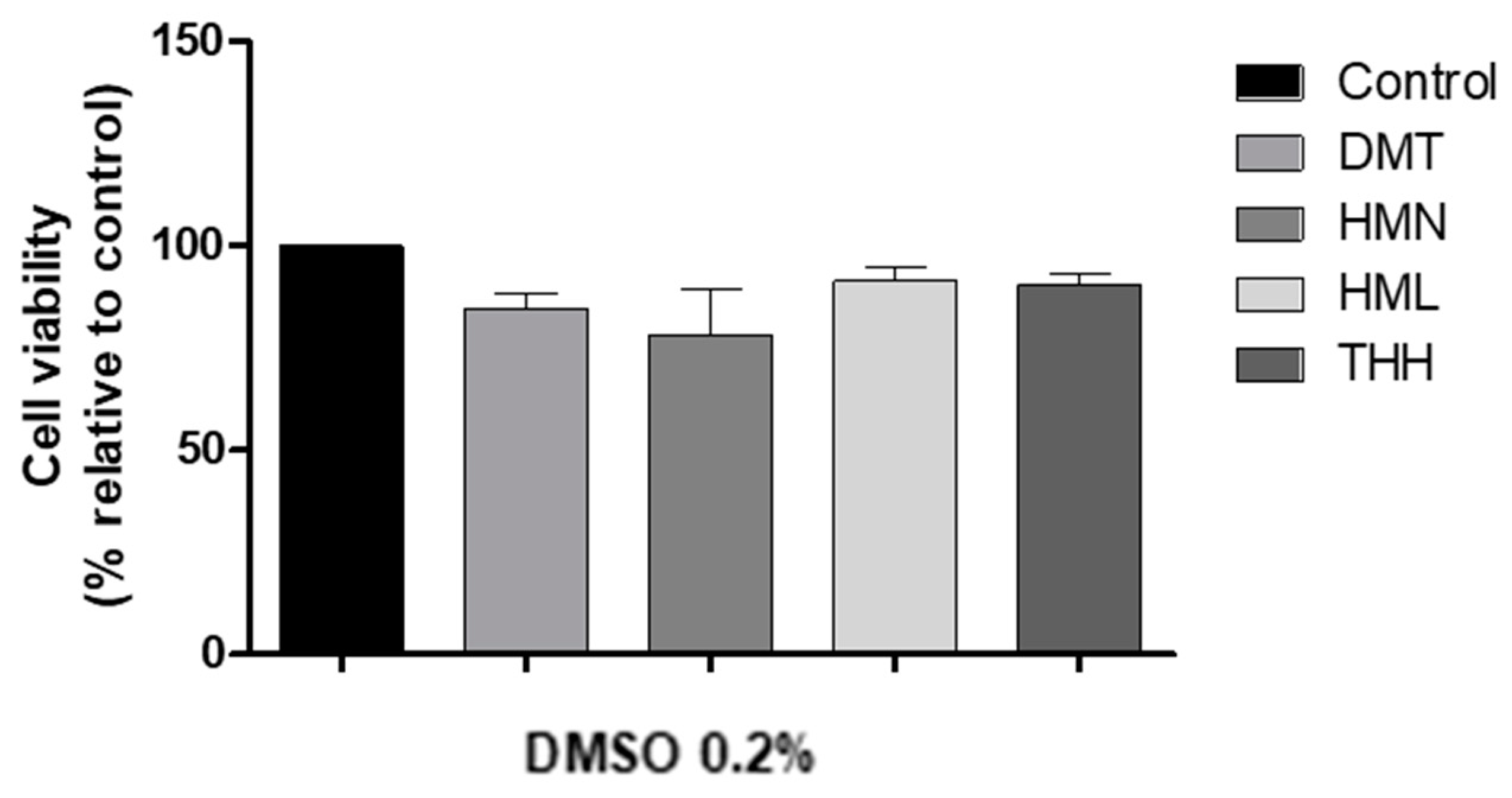
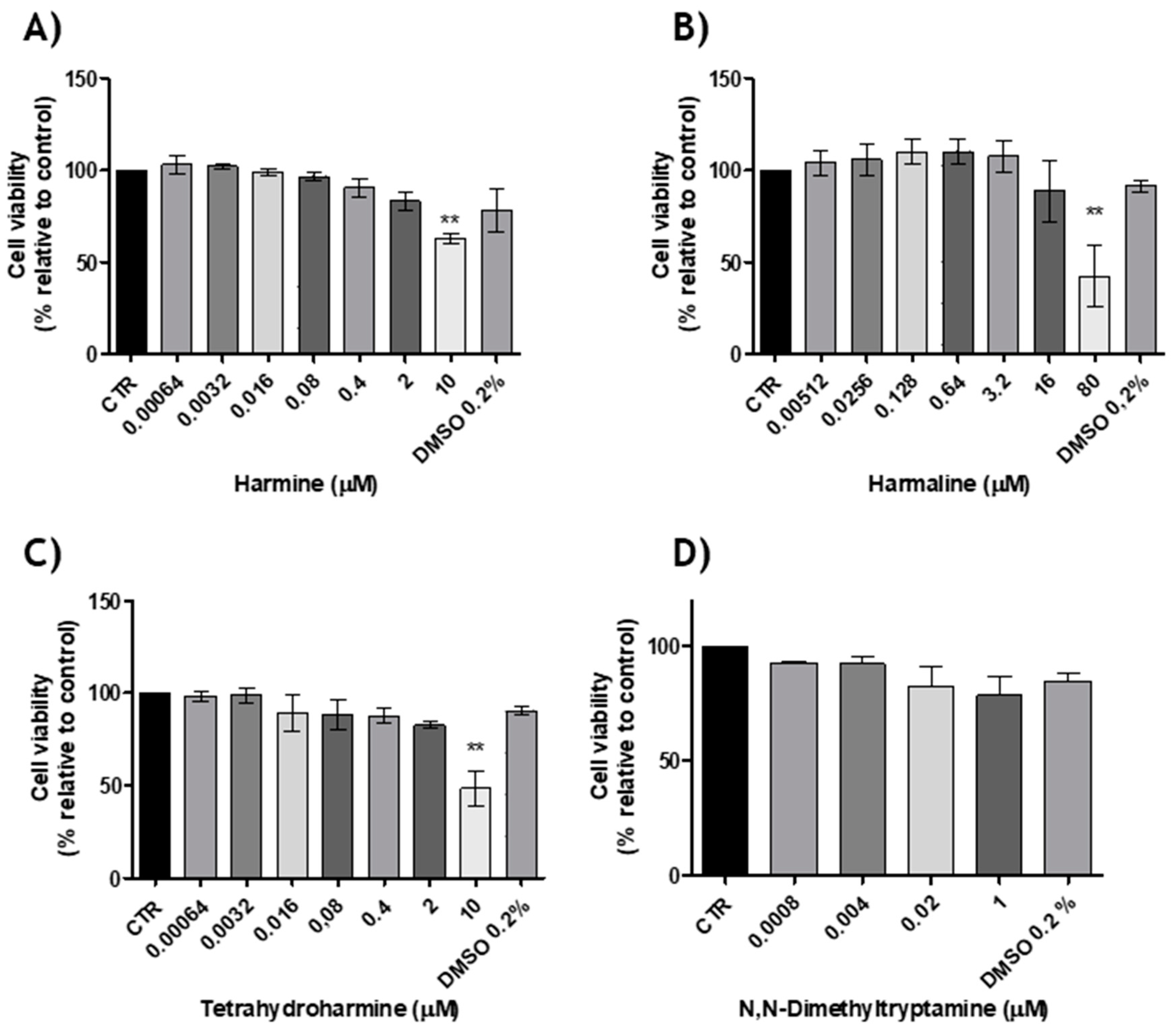
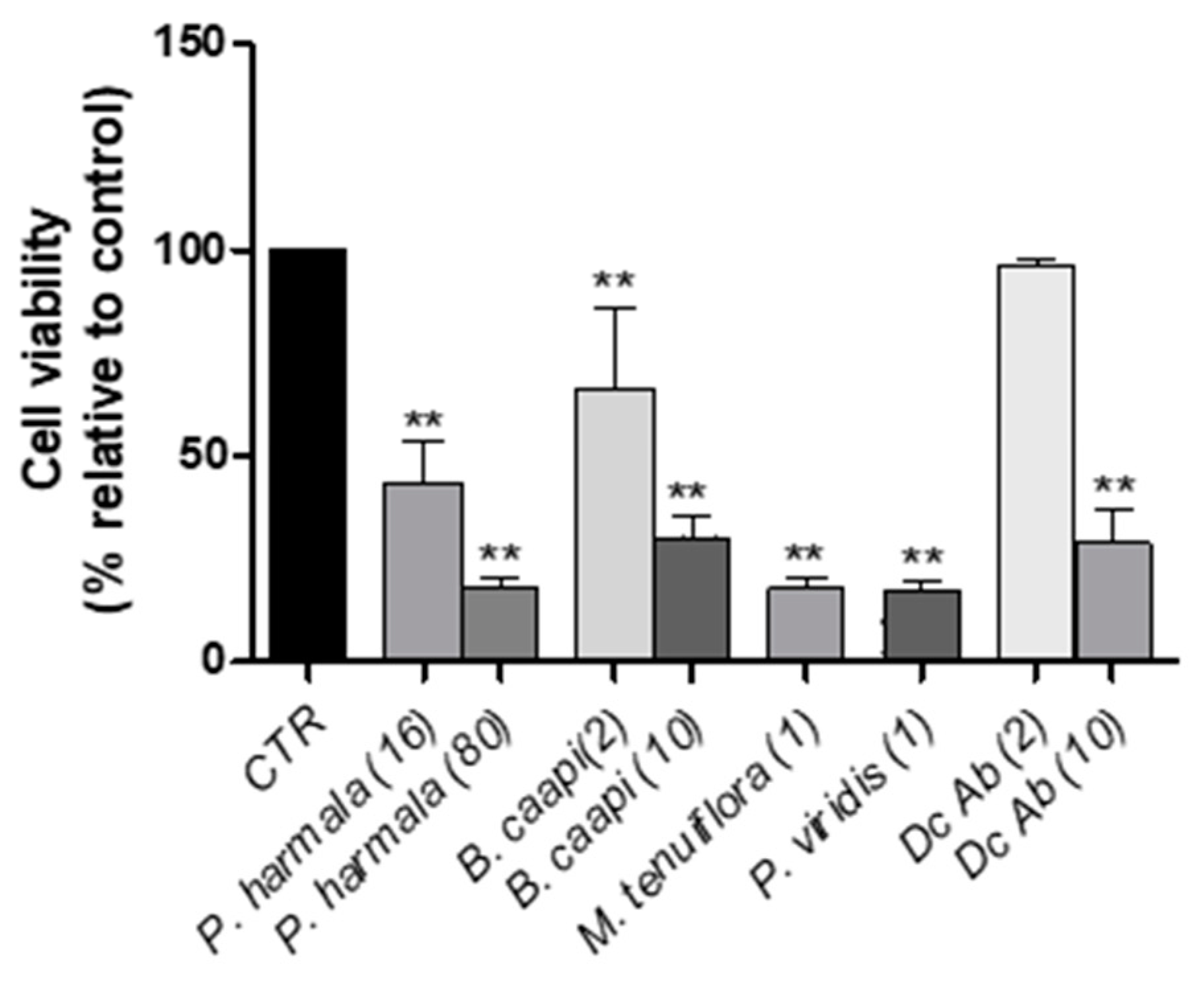
2.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
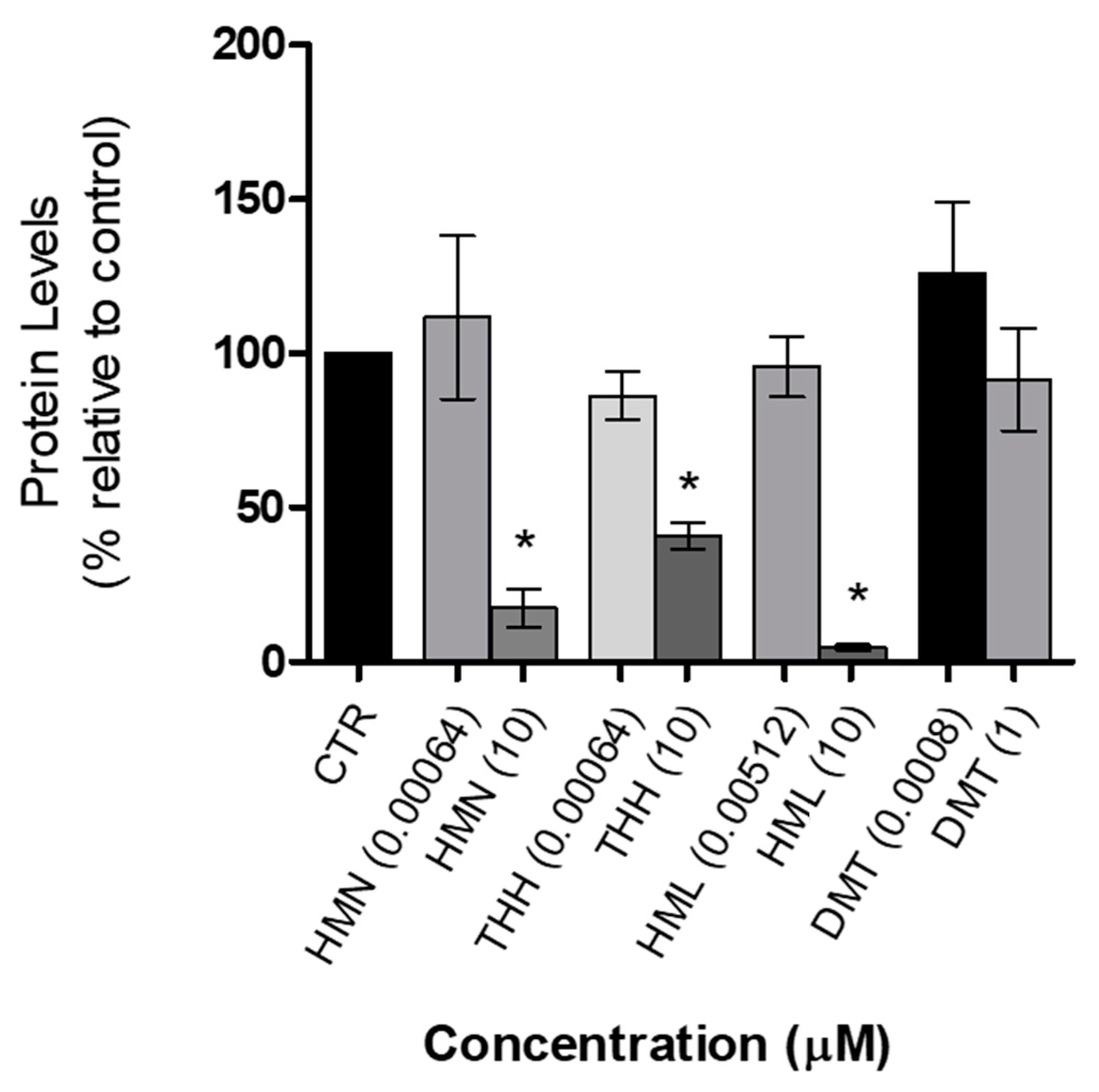
2.3. Total Protein Quantification
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. GC–MS and UHPLC-QTOF/MS Analysis
3.3. Biological Activities Evaluation
3.3.1. Cell Treatments
3.3.2. Cellular Viability Assay
3.3.3. Total Protein Extraction and Quantification
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dos Santos, R.G.; Bouso, J.C.; Hallak, J.E.C. Ayahuasca, dimethyltryptamine, and psychosis: A systematic review of human studies. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 7, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, T.S.; Oliveira, R.; Da Silva, M.L.; Von Zuben, M.V.; Grisolia, C.; Domingues, I.; Caldas, E.D.; Pic-Taylor, A.; Lopes, M. Exposure to ayahuasca induces developmental and behavioral alterations on early life stages of zebrafish. Chem. Interact. 2018, 293, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaujac, A.; Dempster, N.; Navickiene, S.; Brandt, S.D.; De Andrade, J.B. Determination of N,N-dimethyltryptamine in beverages consumed in religious practices by headspace solid-phase microextraction followed by gas chromatography ion trap mass spectrometry. Talanta 2013, 106, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labate, B.C.; Feeney, K. Ayahuasca and the process of regulation in Brazil and internationally: Implications and challenges. Int. J. Drug Policy 2012, 23, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.T.; Labate, B.C.; Meyer, M.; Tupper, K.W.; Barbosa, P.C.; Grob, C.S.; Dawson, A.; McKenna, D. Statement on ayahuasca. Int. J. Drug Policy 2012, 23, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, B.J.; Lee, K.C. Ayahuasca: An ancient sacrament for treatment of contemporary psychiatric illness? Ment. Health Clin. 2017, 7, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pic-Taylor, A.; Da Motta, L.G.; De Morais, J.A.; Junior, W.M.; Santos, A.D.F.A.; Campos, L.A.; Mortari, M.R.; Von Zuben, M.V.; Caldas, E.D. Behavioural and neurotoxic effects of ayahuasca infusion (Banisteriopsis caapi and Psychotria viridis) in female Wistar rat. Behav. Process. 2015, 118, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, J.C.; Brito, G.S.; Neves, E.S. Phytochemical analyses of Banisteriopsis caapi and Psychotria viridis. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2005, 37, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gable, R.S. Risk assessment of ritual use of oral dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and harmala alkaloids. Addiction 2006, 102, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Garcia, J.A.; Revenga, M.D.L.F.; Alonso-Gil, S.; Rodríguez-Franco, M.I.; Feilding, A.; Perez-Castillo, A.; Riba, J. The alkaloids of Banisteriopsis caapi, the plant source of the Amazonian hallucinogen Ayahuasca, stimulate adult neurogenesis in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, A.Y.; Gonçalves, J.; Duarte, A.P.; Barroso, M.; Cristovão, A.C.; Gallardo, E. Toxicological Aspects and Determination of the Main Components of Ayahuasca: A Critical Review. Medicines 2019, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, L.P.; Olson, D.E. Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT). ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2344–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, J.H. Hallucinogens and Dissociative Agents Naturally Growing in the United States. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 102, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frison, G.; Favretto, D.; Zancanaro, F.; Fazzin, G.; Ferrara, S.D. A case of β-carboline alkaloid intoxication following ingestion of Peganum harmala seed extract. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 179, e37–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklerov, J.; Levine, B.; Moore, K.A.; King, T.; Fowler, D. A Fatal Intoxication Following the Ingestion of 5-Methoxy-N,N-Dimethyltryptamine in an Ayahuasca Preparation. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2005, 29, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, D.J.; Towers, G.H.N. Biochemistry and pharmacology of tryptamines and beta-carbolines a minireview. J. Psychoact. Drugs 1984, 16, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strassman, R. DMT: The Spirit Molecule: A Doctor’s Revolutionary Research into the Biology of Near-Death and Mystical Experiences, 1st ed.; Park Street Press: Rochester, VT, USA, 2001; pp. 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, S.M. Impulsivity, compulsivity and additions. In Stahl’s Essential Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific Basis and Practical Applications, 4th ed.; Stahl, S.M., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 889–948. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, P.; Huenchuguala, S.; Paris, I.; Segura-Aguilar, J. Dopamine Oxidation and Autophagy. Park. Dis. 2012, 2012, 920953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, D.S.; Jinsmaa, Y.; Sullivan, P.; Holmes, C.; Kopin, I.J.; Sharabi, Y. Comparison of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Decreasing Production of the Autotoxic Dopamine Metabolite 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde in PC12 Cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 356, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, A.Y.; Gonçalves, J.; Caramelo, D.; Rosado, T.; Barroso, M.; Restolho, J.; Fernández, N.; Rodilla, J.; Duarte, A.P.; Cristóvão, A.C.; et al. Determination of N,N-dimethyltryptamine and beta-carbolines in plants used to prepare ayahuasca beverages by means of solid-phase extraction and gas-chromatography–mass spectrometry. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.F.; Marti, G.; Queiroz, E.F.; Marcourt, L.; Castro-Gamboa, I.; Bolzani, V.S.; Wolfender, J.-L. LC-MS/MS quantitative determination of tetrapterys mucronata alkaloids, a plant occasionally used in ayahuasca preparation. Phytochem. Anal. 2015, 26, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Cheng, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Characterization and determination of trace alkaloids in seeds extracts from Peganum harmala Linn. using LC-ESI-MS and HPLC. Acta Chromatogr. 2013, 25, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, R.T.; Locock, R.A.; Slywka, G.W.A. Mass spectra of selected beta-carbolines [β-9H-pyrido(3,4-b)indoles]. Org. Mass Spectrom. 1970, 3, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrella-Parra, E.A.; Almanza-Pérez, J.C.; Alarcón-Aguilar, F.J. Ayahuasca: Uses, Phytochemical and Biological Activities. Nat. Prod. Bioprospecting 2019, 9, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, J.; Luís, Â.; Gradillas, A.; García, A.; Restolho, J.; Fernández, N.; Domingues, F.; Gallardo, E.; Duarte, A.P. Ayahuasca beverages: Phytochemical analysis and biological properties. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhou, W.; Tian, J.; Bing, G.; Zhao, L. Effects of dimethyl sulfoxide on the morphology and viability of primary cultured neurons and astrocytes. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 128, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; Lincoln, L.; Jackson, M.J.; Abbate, V.; Jenner, P.; Hider, R.; Lees, A.; Rose, S. The effect of Banisteriopsis caapi (B. caapi) on the motor deficits in the MPTP-treated common marmoset model of Parkinson’s disease. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; Spearman, M.; Braasch, K. Monitoring cell growth, viability, and apoptosis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1104, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, G. Impact of dopamine oxidation on dopaminergic neurodegeneration. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein Degradation—The Cell—NCBI Bookshelf. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9957/ (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Valente, M.J.; Amaral, C.; Correia-Da-Silva, G.; Duarte, J.A.; Bastos, M.D.L.; Carvalho, F.; De Pinho, P.G.; Carvalho, M. Methylone and MDPV activate autophagy in human dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells: A new insight into the context of β-keto amphetamines-related neurotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3663–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acero, N.; Gradillas, A.; Beltran, M.; Garcia, A.; Mingarro, D.M. Comparison of phenolic compounds profile and antioxidant properties of different sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) varieties. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Albanchez, E.; Gradillas, A.; García, A.; García-Villaraco, A.; Gutierrez-Mañero, F.J.; Solano, B.R. Elicitation with Bacillus QV15 reveals a pivotal role of F3H on flavonoid metabolism improving adaptation to biotic stress in blackberry. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
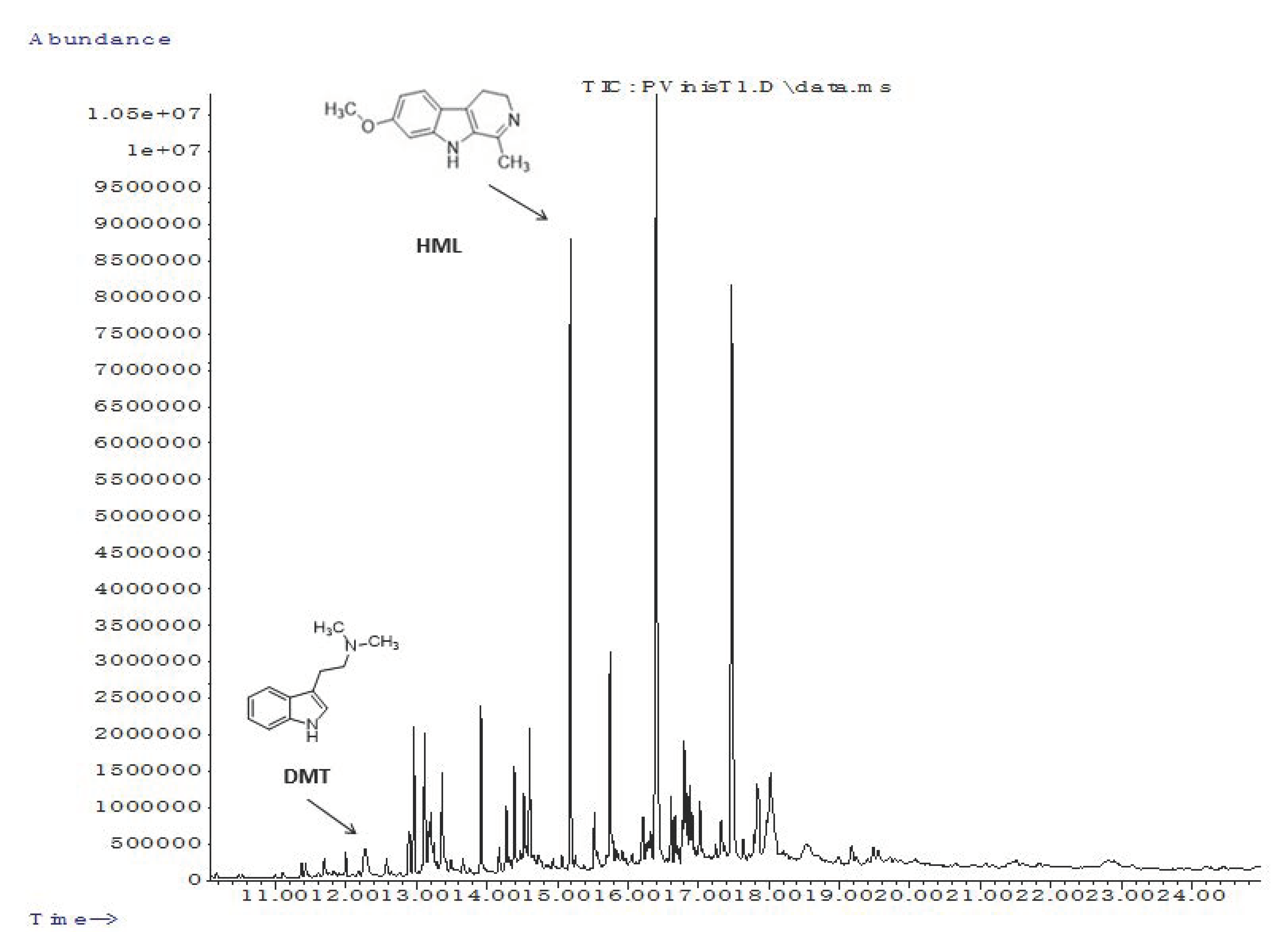
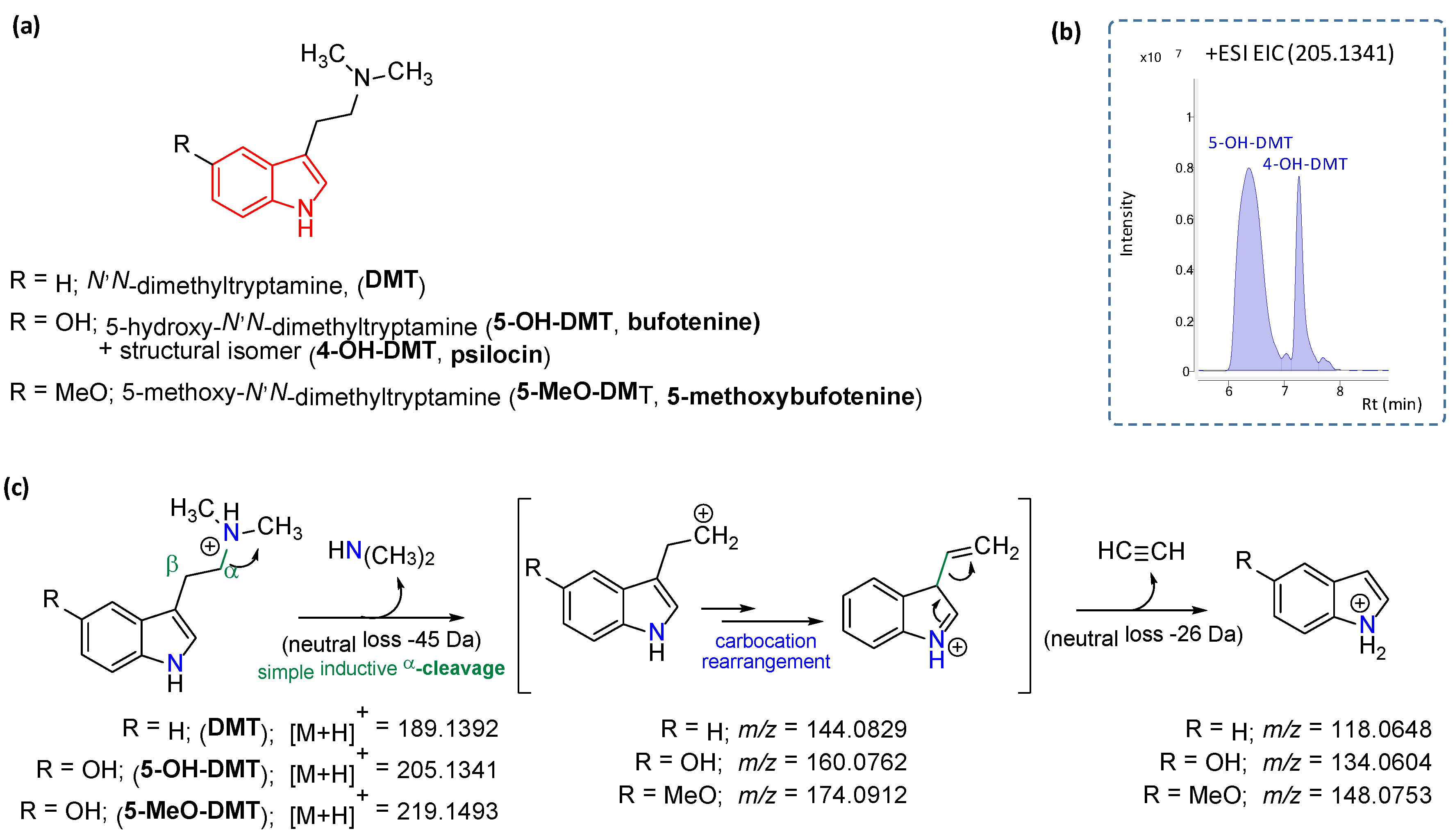


| Compounds | tR | Molecular Formula | Monoisotopic Mass | [M − H]− | [M + H]+ | In-Source Fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tryptamine Alkaloids | ||||||
| bufotenine (5-HO-DMT) | 6.4 | C12H16N2O | 204.1263 | -- | 205.1341 | 160.0762 134.0604 |
| psilocin (4-HO-DMT) | 7.3 | C12H16N2O | 204.1263 | -- | 205.1341 | 160.0762 134.0604 |
| N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) | 8.1 | C12H16N2 | 188.1313 | -- | 189.1392 | 144.0829 118.0648 |
| 5-methoxybufotenine (5-MeO-DMT) | 8.5 | C13H18N2O | 218.1419 | -- | 219.1491 | 174.0912 130.1588 |
| Harmala Alkaloids | ||||||
| tetrahydroharmol | 7.3 | C12H14N2O | 202.1106 | -- | 203.1190 | 174.0919 |
| harmalol | 8.8 | C12H12N2O | 200.0949 | -- | 201.1028 | 160.0757 |
| harmol | 9.2 | C12H10N2O | 198.0793 | -- | 199. 0960 | -- |
| tetrahydroharmine (THH) | 9.4 | C13H16N2O | 216.1263 | -- | 217.1331 | 200.0951, 188.1070 |
| harmane | 9.7 | C12H10N2 | 182.0844 | -- | 183.0941 | -- |
| harmaline (HML) | 9.8 | C13H14N2O | 214.1106 | 213.1069 | 215.1167 | 200.0943, 174.0908 |
| harmine (HMN) | 10.4 | C13H12N2O | 212.0950 | 211.0910 | 213.1037 | 198.0788, 170.0845 |
| Phenolic Compounds | ||||||
| Hydroxybenzoic Acids | ||||||
| gallic acid | 3.0 | C7H6O5 | 170.0215 | 169.0149 | -- | |
| protocatechuic acid | 6.5 | C7H6O4 | 154.0266 | 153.0201 | -- | |
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | 8.1 | C7H6O3 | 138.0317 | 137.0271 | -- | |
| gentisic acid | 8.5 | C7H6O4 | 154.0266 | 153.0197 | -- | |
| salicylic acid | 11.5 | C7H6O3 | 138.0317 | 137.0271 | -- | |
| Hydroxycinnamic Acids | ||||||
| 3-chlorogenic acid | 9.0 | C16H18O9 | 354.0951 | 353.0803 | -- | |
| 5-chlorogenic acid | 9.7 | C16H18O9 | 354.0951 | 353.0803 | -- | |
| Flavonoids-Flavanols | ||||||
| (+)-catechin | 8.6 | C15H14O6 | 290.079 | 289.0723 | -- | |
| (−)-epicatechin | 9.5 | C15H14O6 | 290.079 | 289.0723 | -- | |
| quercetin-3-O-galactoside | 10.9 | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | 463.0888 | -- | |
| quercetin-3-O-glucoside | 11.1 | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | 463.0888 | -- | |
| quercetin-3-O-rutinoside | 11.1 | C27H30O16 | 610.1534 | 609.1461 | -- | |
| kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | 11.6 | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 447.0933 | -- | |
| kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside | 11.5 | C27H30O15 | 594.1615 | 593.1542 | -- | |
| Flavonoids-Dihydrochalcone | ||||||
| phlorizin | 11.3 | C21H24O10 | 436.1369 | 435.1302 | -- | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simão, A.Y.; Gonçalves, J.; Gradillas, A.; García, A.; Restolho, J.; Fernández, N.; Rodilla, J.M.; Barroso, M.; Duarte, A.P.; Cristóvão, A.C.; et al. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Ayahuasca Beverages. Molecules 2020, 25, 5594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235594
Simão AY, Gonçalves J, Gradillas A, García A, Restolho J, Fernández N, Rodilla JM, Barroso M, Duarte AP, Cristóvão AC, et al. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Ayahuasca Beverages. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235594
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimão, Ana Y., Joana Gonçalves, Ana Gradillas, Antonia García, José Restolho, Nicolás Fernández, Jesus M. Rodilla, Mário Barroso, Ana Paula Duarte, Ana C. Cristóvão, and et al. 2020. "Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Ayahuasca Beverages" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235594
APA StyleSimão, A. Y., Gonçalves, J., Gradillas, A., García, A., Restolho, J., Fernández, N., Rodilla, J. M., Barroso, M., Duarte, A. P., Cristóvão, A. C., & Gallardo, E. (2020). Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Ayahuasca Beverages. Molecules, 25(23), 5594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235594










