The Influence of Non-Engineered Municipal Landfills on Groundwater Chemistry and Quality in Bloemfontein, South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
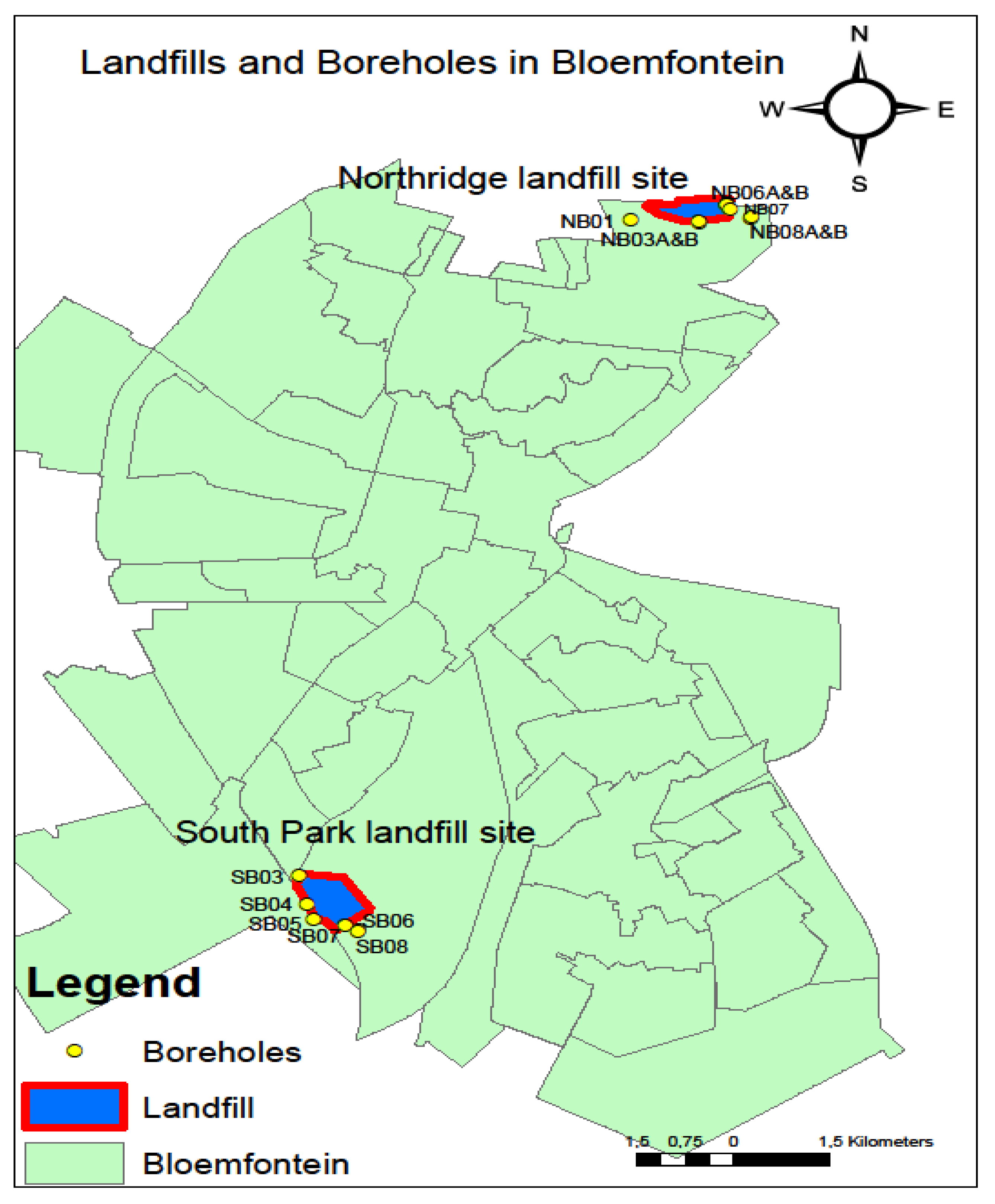
2.1. Study Area
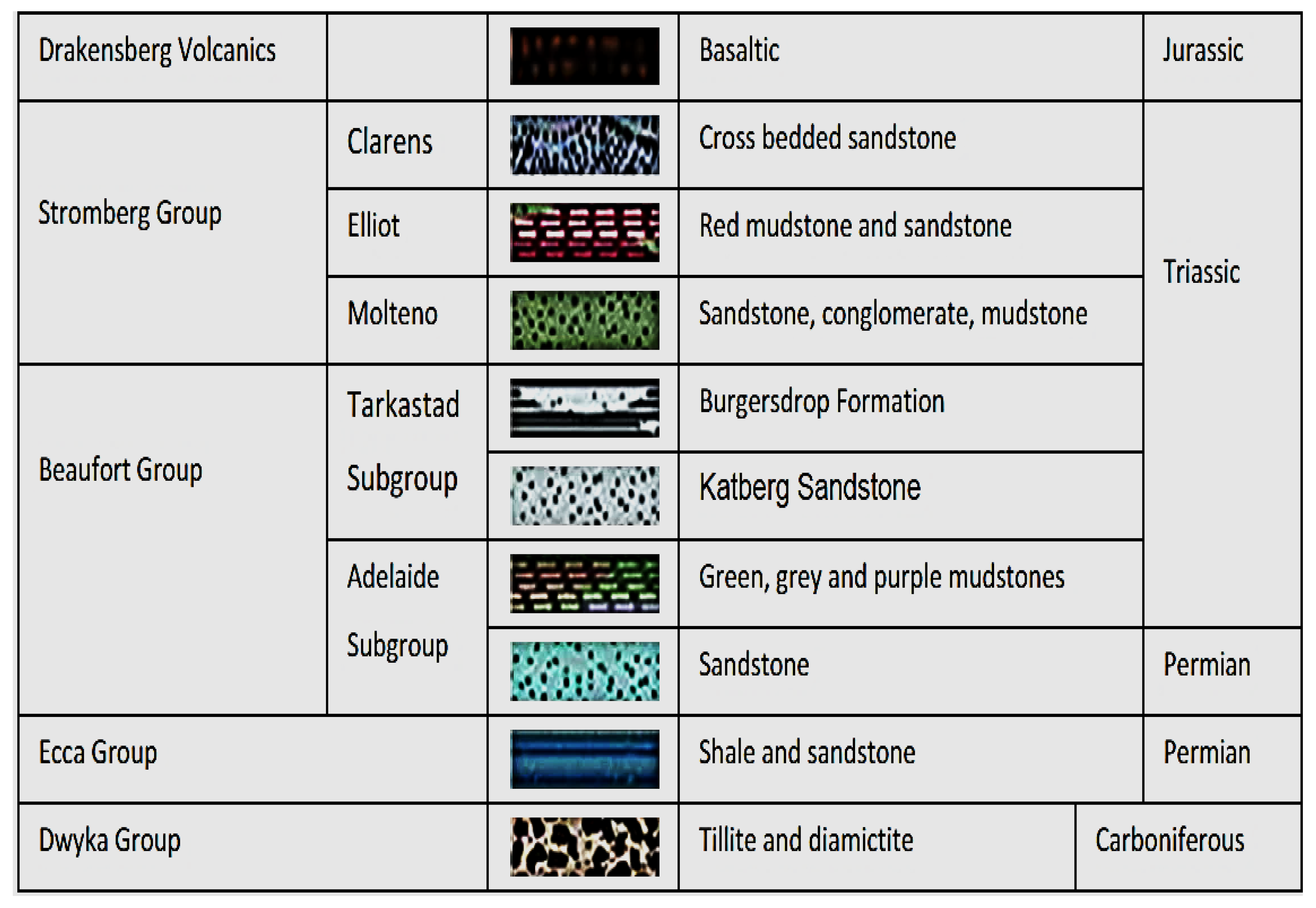
2.1.1. The Geology (Rock Types and Hydrogeology) of the Northern Landfill Site
2.1.2. The Geology (Rock Types and Hydrogeology) of the Southern Landfill Site
2.2. Groundwater Sampling
2.3. Hydrogeochemistry
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of the Groundwater Samples of the Northern and Southern Landfill Sites
3.2. Microbiological Characteristics of the Groundwater Samples from the Northern and Southern Landfill Sites
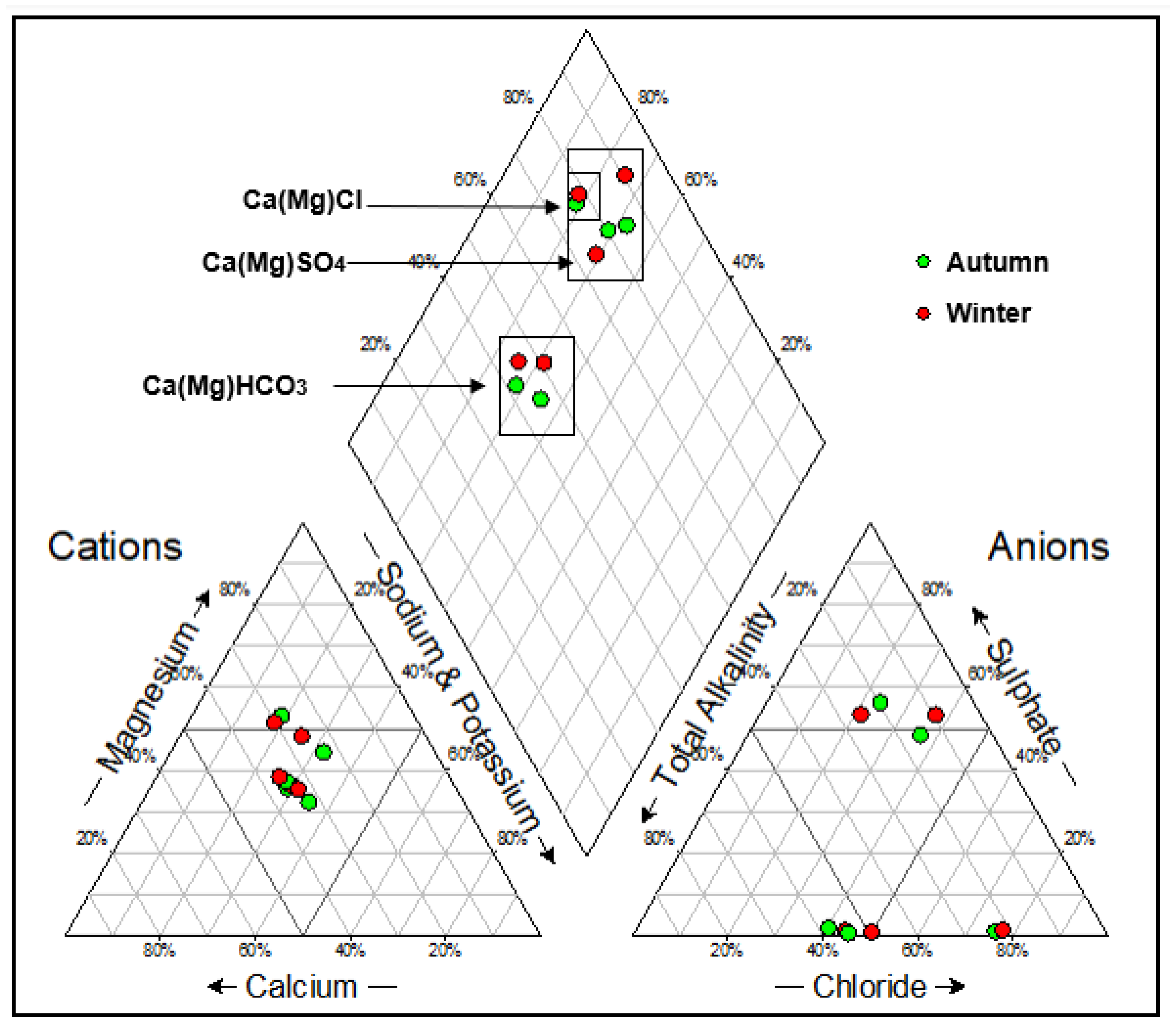
3.3. Hydrogeochemical Facies
4. Discussion
4.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of the Groundwater Samples from the Northern and Southern Landfill Sites
4.2. Microbiological Characteristics of Groundwater Samples from the Northern and Southern Landfill Sites
4.3. The Impact of Geology (Rock Types and Hydrogeology) on the Percolation of Leachate into Groundwater
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olofinlade, W.S.; Daramola, S.O.; Olabode, O.F. Hydrochemical and statistical modelling of groundwater quality in two contrasting geological terrains of southwestern Nigeria. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietersen, K.; Beekman, H.E.; Holland, M. South African Groundwater Governance Case Study; WRC Report No. KV273/11; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Palamuleni, L.; Akoth, M. Physio-chemical and microbial analysis of selected borehole water in Mahikeng, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8619–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.F.; Jones-Lee, A. Groundwater Quality Monitoring at Lined Landfills: Adequacy of Subtitle D Approaches; G. Fred Lee & Associates: El Macero, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Naveen, B.P.; Sumalatha, J.; Malik, R.K. A study on contamination of ground and surface water bodies by leachate leakage from a landfill in Bangalore, India. Int. J. Geo. Eng. 2018, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; Thirumalaisamy, S.; Lakshumanan, E. Impact of leachate on groundwater pollution due to non-engineered municipal solid waste landfill sites of erode city; Tamil Nadu, India. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng 2012, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Mittal, A.K. Toxicity analysis and public health aspects of municipal landfill leachate. A case study of Okhla landfill, Delhi. In Proceedings of the 8th World Wide Workshop for Young Environmental Scientists: Urban Waters: Resource or Risks, Arcueil, France, 2–5 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bjerg, P.L.; Kjeldsen, P.; Christensen, T.H.; Cozzarelli, I. The groundwater chemistry of waste disposal facilities. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 1st ed.; Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 579–612. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A.R.; MacCarthy, I.A.J. Geological aspects of waste disposal site selection. In Proceedings of the 1st Irish Environmental Engineering Conference, Cork, Ireland, October 1991; pp. 233–239. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271766197_Geological_aspects_of_waste_Disposal_site_selection (accessed on 26 September 2020).
- DWA. Development of Water Reconciliation Strategies for All Towns in the Central Region. Literature Review Report; Department of Water Affairs Pretoria: Pretoria, South Africa, 2011.
- Mangaung Metropolitan Municipality. Integrated Waste Management Plan: Review of Integrated Waste Management Plan; Mangaung Metropolitan Municipality: Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.J. Groundwater Pollution at Sanitary Landfill Sites: Geohydrological, Environmental Isotope and Hydrochemical Studies. Master’s Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dingaan, M.N.V.; Du Preez, P.J. Grassland communities of urban open spaces in Bloemfontein, Free State, South Africa. Koedoe 2013, 55, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hensley, M.; Le Roux, P.; Du Preez, C.; Van Huyssteen, C.; Kotze, E.; Van Rensburg, L. Soils: The Free State’s Agricultural Base. S. Afr. Geog. J. 2006, 88, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomo, M. A Groundwater-Surface Water Interaction Study of an Alluvial Channel Aquifer. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ololade, O.O.; Mavimbela, S.; Oke, S.A.; Makhadi, R. Impact of leachate from northern landfill site in Bloemfontein on water and soil quality: Implications for water and food security. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Oke, S.A. Evaluation of the Vulnerability of Selected Aquifer Systems in the Eastern Dahomey Basin, South Western Nigeria. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute for Groundwater Studies, University of Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gomo, M.; Masemola, E. Groundwater hydrogeo-chemical characteristics in rehabilitated coalmine spoils. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 116, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWA. Guidelines for Leachate Control; Department of Water Affairs: Pretoria, South Africa, 1999.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- SABS. South African National Standard 241-1: Drinking Water, Part 1: Microbiological, Physical, Aesthetic and Chemical Determinants; SABS: Pretoria, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DWAF. South African Water Quality Guidelines, 2nd ed.; Department of Water Affairs and Forestry: Pretoria, South Africa, 1996; Volume 4.
- Ngabirano, H.; Byamugisha, D.; Ntambi, E. Effects of seasonal variations in physical parameterson quality of gravity flow water in kyanamira sub county, Kabale District, Uganda. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2016, 8, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.J.S.; James, E.J. Physicochemical parameters and their sources in groundwater in the Thirupathur region, Tamil Nadu, South India. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.R.J. Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Organic Carbon in British Columbia; Ministry of Water, Land and Air Protection: Victoria, BC, Canada, 1960.
- Rusydi, A.F. Correlation between conductivity and total dissolved solid in various type of water: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, K.; Sharma, A.K. Seasonal variation in bacterial contamination of water sources with antibiotic resistant faecal coliforms in relation to pollution. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2011, 3, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisante, E.; Muzuka, A.N.N. Sources and seasonal variation of coliform bacteria abundance in groundwater around the slopes of Mount Meru, Arusha, Tanzania. Environ. Monit. Assess 2016, 188, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodford, A.C.; Chaevallier, L. Hydrogeology of the Main Karoo Basin: Current Knowledge and Future Research Needs; WRC Report No TT 179/22; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, S.S.; Kadam, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Pawar, N.J. Evaluating pollution potential of leachate from landfill site, from Pune Metropolitan City and its impact on shallow basaltic aquifers. Environ. Monit. Assess 2010, 162, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

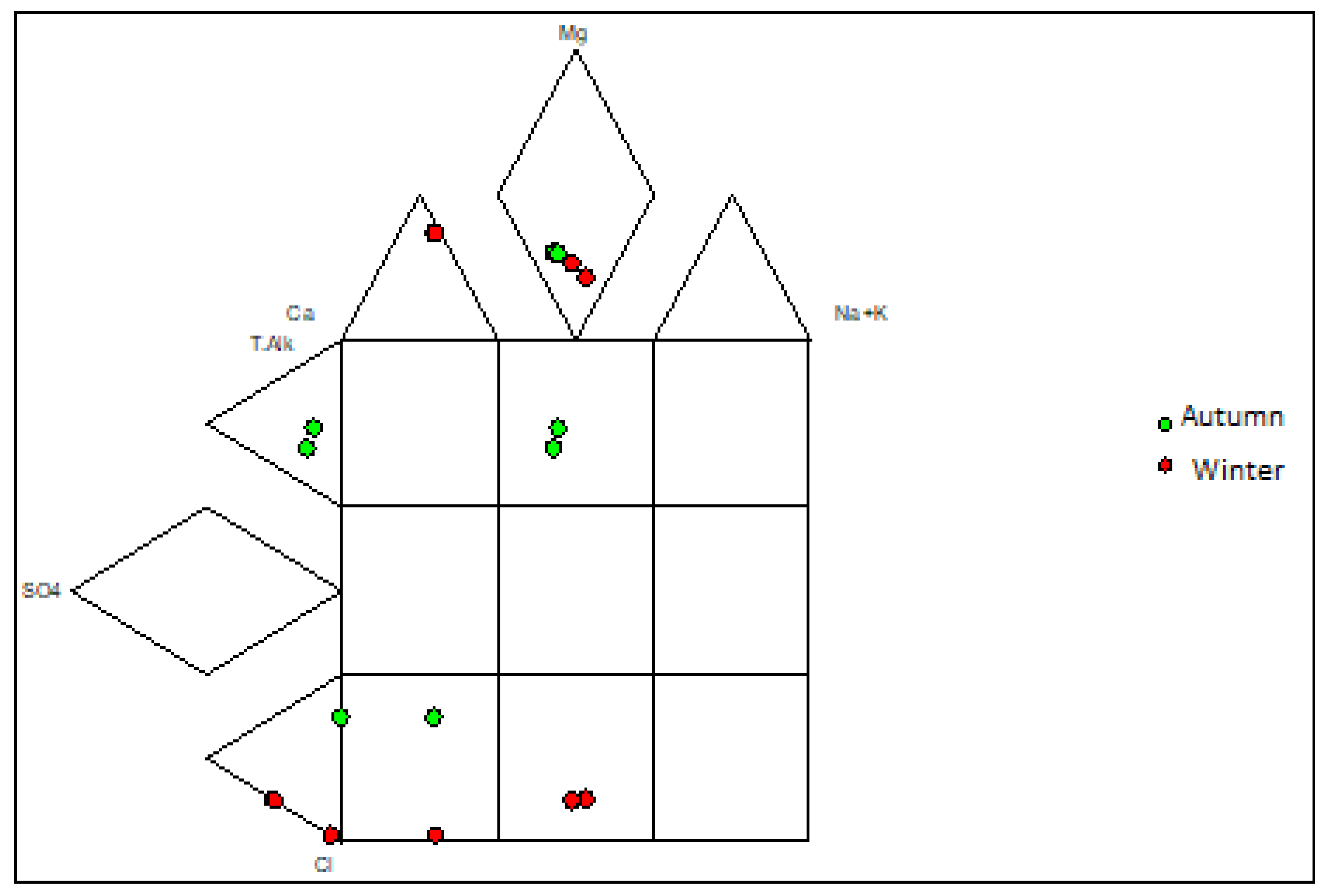
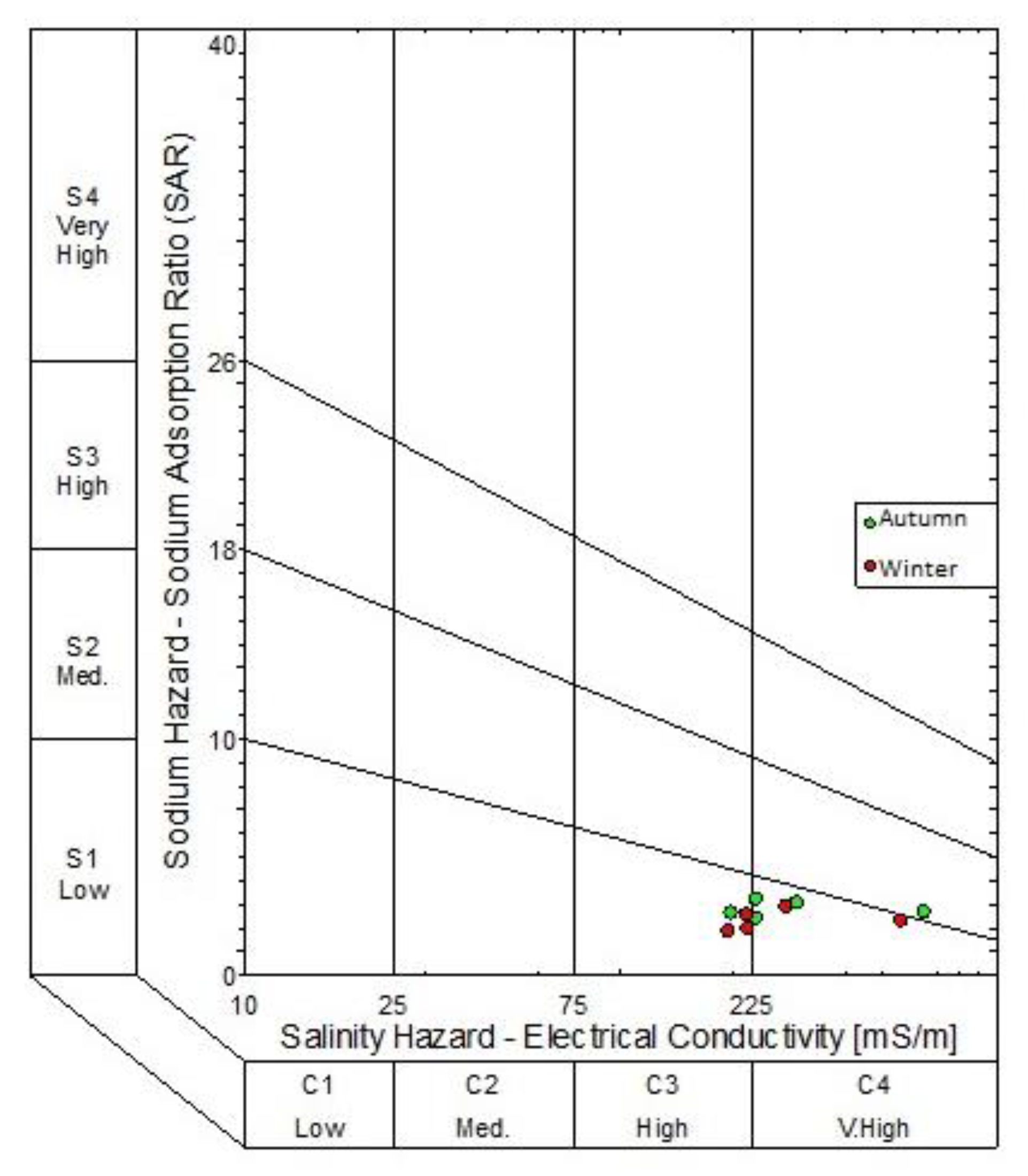



| Northern Landfill Site Autumn Season | Northern Landfill Site Winter Season | Southern Landfill Site Autumn | Southern Landfill Site Winter Season | Water Quality Guidelines | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling site | NB03A | NB03B | NB07 | NB06A | NB06B | NB03A | NB03B | NB07 | NB06A | NB06B | SB04 | SB08A | SB08B | SB04 | SB08A | SB08B | SANS 2015 | DWAF 1996 | WHO (2015) |
| pH | 7.6 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.5 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 7.5 | 8 | 7.9 | 7.0 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 5.0–9.7 | 6.5–8.4 | 6.5–8.5 |
| TDS | 1449.0 | 2435.0 | 4756.5 | 1537.0 | 1647.0 | 1364.5 | 2415.0 | 3432.0 | 1343.5 | 1417.0 | 1722.5 | 507.5 | 787.0 | 1480.0 | 597.0 | 641.5 | 1200.0 | - | 500.0 |
| EC | 1975.0 | 2950.0 | 6435.0 | 2305.0 | 2300.0 | 1930.0 | 2755.0 | 5570.0 | 2180.0 | 2165.0 | 2415.0 | 665.0 | 1105.0 | 2605.0 | 830.0 | 780.0 | 1700.0 | <40.0 | 1500.0 |
| COD | 191.5 | 96.5 | 299.5 | 72.0 | 52.0 | 37.0 | 77.0 | 261.0 | 82.0 | 51.0 | 55.0 | 17.0 | 2.5 | 77.0 | 9.0 | 16.0 | - | - | - |
| TOC | 8.3 | 18.0 | 82.7 | 11.5 | 13.0 | 8.7 | 14.6 | 77.0 | 10.0 | 12.0 | 17.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 17.5 | 2.0 | 2.8 | ≤10.0 | - | - |
| Ca | 107.0 | 282.5 | 450.5 | 180.0 | 176.0 | 103.0 | 241.0 | 391.0 | 153.0 | 150.0 | 303.0 | 57.0 | 81.0 | 260.0 | 78.0 | 75.0 | 300.0 | - | 75.0 |
| Mg | 122.5 | 171.5 | 520.0 | 117.0 | 106.0 | 112.0 | 155.0 | 405.0 | 100.0 | 97.0 | 130.5 | 20.0 | 33.0 | 110.0 | 33.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 | - | 30.0 |
| Na | 168.0 | 264.0 | 351.5 | 169.0 | 219.5 | 116.0 | 235.0 | 272.0 | 128.0 | 165.0 | 78.0 | 77.0 | 86.0 | 63.0 | 62.0 | 59.0 | ≤200. 0 | 0.0–70.0 | 200.0 |
| K | 3.0 | 4.5 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 8.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 | - | 300.0 |
| HCO3 | 174.0 | 362.5 | 939.5 | 699.5 | 708.5 | 98.0 | 478.0 | 647.0 | 596.0 | 569.0 | 621.0 | 237.0 | 276.0 | 469.0 | 259.0 | 334.0 | - | - | - |
| SO4 | 535.0 | 998.0 | 31.0 | 19.0 | 5.0 | 536.0 | 975.0 | 34.0 | 11.0 | 8.0 | 29.0 | 27.0 | 54.0 | 1.0 | 51.0 | 48.o | ≤500.0 | - | 500.0 |
| Cl | 300.0 | 318.5 | 2190.0 | 349.0 | 421.0 | 279.0 | 292.0 | 1656.0 | 347.0 | 412.0 | 540.0 | 58.0 | 123.0 | 567.0 | 80.0 | 75.0 | ≤300.0 | 0.0–105.0 | 250.0 |
| Br | 2.0 | 1.9 | 11.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 4.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | ≤3.0 | - | - |
| Mn | 0.0 | 0.9 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ≤0.4 | ≤10.0 | - |
| Cr | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.020 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 3.0 | 0.1 | 50.0 |
| Cd | 0.00 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.00 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.032 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 10.0 | 0.003 | 3.0 |
| Co | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 50.0 | 0.05 | - |
| Fe | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.6 | 0.09 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 300.0 | 5.0 | - |
| Pb | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.02 | 0.022 | 0.014 | 0.015 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.2 | - |
| Zn | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 1.0 | - |
| As | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 10.0 |
| V | 0.078 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.008 | 2.5 | 1.02 | 0.09 | 2.4 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 1.7 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 4.0 | 0.1 | - |
| Cu | 0.028 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.029 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.018 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 2.0 | 0.2 | - |
| se | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.010 | 0.02 | 40.0 |
| Total coliform | 98.5 | 2420.0 | 2420.0 | 23.0 | 517.0 | 2420.0 | 2420.0 | 3.0 | 38.5 | 36.0 | 242.0 | 1120.0 | 43.0 | 242.0 | 1300.0 | 411.0 | ≤10.0 | varies | 10.0 |
| Escherichia coli | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 307.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 6.5 | 71.5 | 7. 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Northern Landfill Site | Southern Landfill Site | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Autumn | Winter | Autumn | Winter |
| pH | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.8 | 7.4 |
| TDS | 2365.0 | 1994.7 | 1005.0 | 906.0 |
| EC | 3160.0 | 2920.0 | 1400.0 | 1400.0 |
| TOC | 27.0 | 24.0 | 6.9.0 | 7.5 |
| COD | 142.0 | 101.0 | 24.0 | 34.0 |
| Total coliform | 1095.0 | 928.0 | 1194.5 | 1377.0 |
| E. coli | 0.0 | 0.0 | 103.0 | 28.0 |
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makhadi, R.; Oke, S.A.; Ololade, O.O. The Influence of Non-Engineered Municipal Landfills on Groundwater Chemistry and Quality in Bloemfontein, South Africa. Molecules 2020, 25, 5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235599
Makhadi R, Oke SA, Ololade OO. The Influence of Non-Engineered Municipal Landfills on Groundwater Chemistry and Quality in Bloemfontein, South Africa. Molecules. 2020; 25(23):5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235599
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakhadi, Rinae, Saheed A. Oke, and Olusola O. Ololade. 2020. "The Influence of Non-Engineered Municipal Landfills on Groundwater Chemistry and Quality in Bloemfontein, South Africa" Molecules 25, no. 23: 5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235599
APA StyleMakhadi, R., Oke, S. A., & Ololade, O. O. (2020). The Influence of Non-Engineered Municipal Landfills on Groundwater Chemistry and Quality in Bloemfontein, South Africa. Molecules, 25(23), 5599. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235599






