Breath Analysis: Comparison among Methodological Approaches for Breath Sampling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Study Design
2.2. Breath Sampling into Tedlar® Bags
2.3. Breath Sampling by a ‘Mistral’ Device
2.4. Breath Sampling by ‘Respiration Collector for In Vitro Analysis’ (ReCIVA)
2.5. TD-GC-MS Analyses
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
- endogeneous and exogeneous VOCs and the ambient air contribution to VOCs’ profiles determined by collecting both whole breath and the alveolar fraction of breath in the presence and in the absence of a clean air supply system (Test 1),
- differences in VOCs’ profiles linked to the collection of lower airways expiratory breath samples and whole expiratory breath samples (Test 2),
- differences in VOCs’ profiles determined by collecting breath samples using the different investigated devices (Test 3).
3.1. Test 1: Ambient Air Contribution to Breath Sampling
3.2. Test 2: Fraction of the Breath Sampled
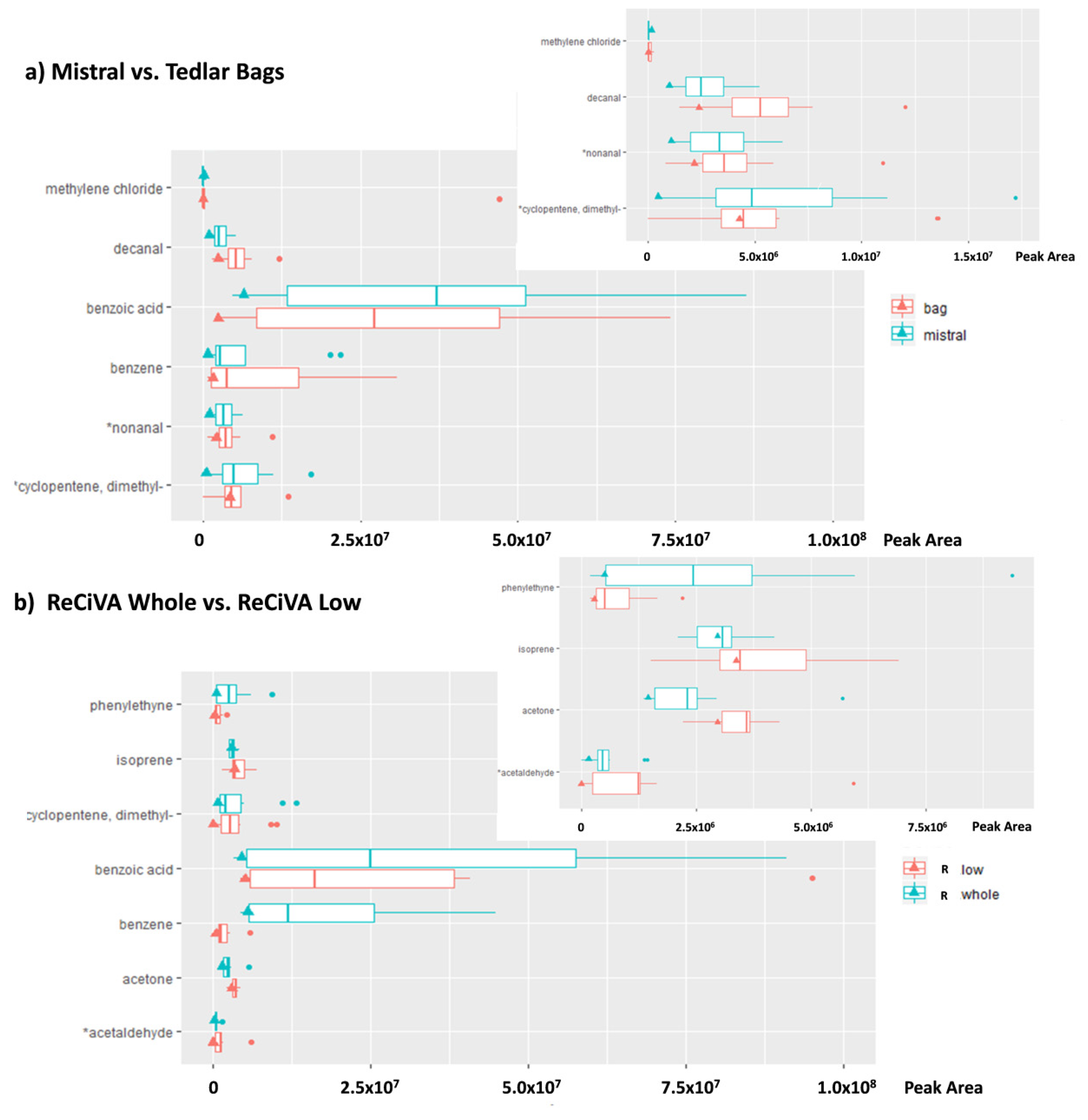
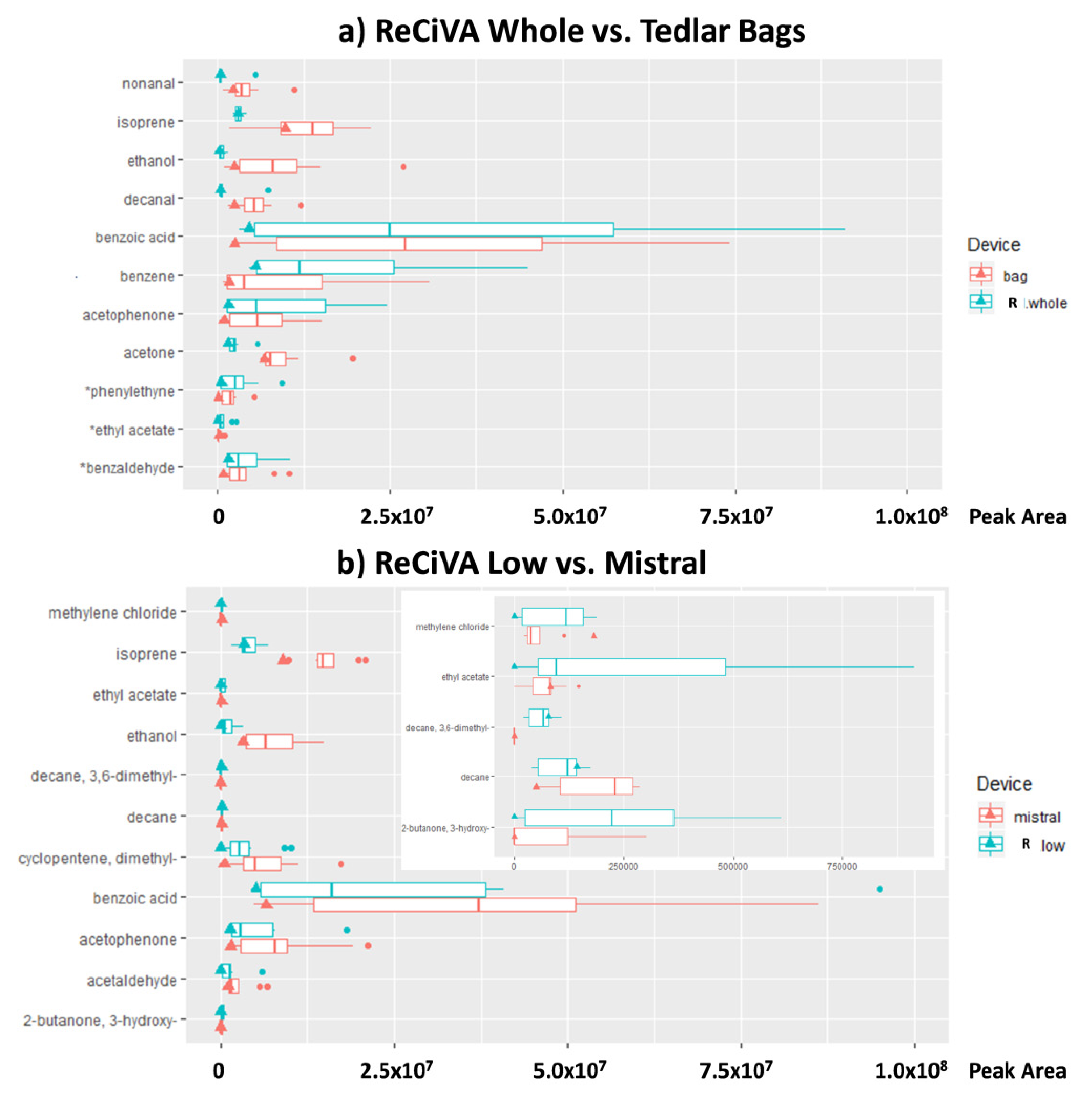
3.3. Test 3: Comparison Among Breath Sampling Devices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamote, K.; Hiddinga, B.; Van Cleemput, J.; Nackaerts, K.; Thas, O.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P. A breath test for diagnosing malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamote, K.; Vynck, M.; Thas, O.; Van Cleemput, J.; Thas, O.; Nackaerts, K.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P. Exhaled breath to screen for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A validation study. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.K.; Noeldge-Schomburg, G. Diagnostic potential of breath analysis-focus on volatile organic compounds. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 347, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catino, A.; de Gennaro, G.; Di Gilio, A.; Facchini, L.; Galetta, D.; Palmisani, J.; Porcelli, F.; Varesano, N. Breath Analysis: A Systematic Review of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Diagnostic and Therapeutic Management of Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2019, 11, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusselmans, L.; Arnouts, L.; Millevert, C.; Vandersnickt, J.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Lamote, K. Breath analysis as a diagnostic and screening tool for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A systematic review (Review). Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gennaro, G.; Dragonieri, S.; Longobardi, F.; Musti, M.; Stallone, G.; Trizio, L.; Tutino, M. Chemical characterization of exhaled breath to differentiate between patients with malignant plueral mesothelioma from subjects with similar professional asbestos exposure. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 3043–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gilio, A.; Catino, A.; Lombardi, A.; Palmisani, J.; Facchini, L.; Mongelli, T.; Varesano, N.; Bellotti, R.; Galetta, D.; de Gennaro, G.; et al. Breath Analysis for early detection of malignant pleural mesothelioma: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) determination and possible biochemical pathways. Cancers 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Kesy, M.; Ligor, T.; Amann, A. Human exhaled air analytics: Biomarkers of diseases. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Turner, C.; Španěl, P. Volatile metabolites in the exhaled breath of healthy volunteers: Their levels and distributions. J. Breath Res. 2007, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, C.; Turner, C. Breath analysis in disease diagnosis: Methodological considerations and applications. Metabolites 2014, 4, 465–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, A.; Ligor, M.; Ligor, T.; Bajtarevic, A.; Ager, C.; Pienz, M.; Denz, H.; Fiegl, M.; Hilbe, W.; Weiss, W.; et al. Analysis of exhaled breath for screening of lung cancer patients. Memo Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2010, 3, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risby, T.H.; Sehnert, S.S. Clinical application of breath biomarkers of oxidative stress status. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, K.A.; Watson, M.T.; Foster, W.M.; Sehnert, S.S.; Risby, T.H. Effects of ventilation on the collection of exhaled breath in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 1371, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbig, J.; Titzmann, T.; Beauchamp, J.; Kohl, I.; Hansel, A. Buffered end-tidal (BET) sampling-a novel method for real-time breath-gas analysis. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 037008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, A.; Miekisch, W.; Pleil, J.; Risby, T.; Schubert, J. Methodological Issues of Sample Collection and Analysis of Exhaled Breath; Maney Publishing: Leeds, UK, 2010; Volume 49, Chapter 7; pp. 96–114. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.; Hlastala, M. Breath tests and airway gas exchange. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 20, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Španěl, P.; Dryahina, K.; Smith, D. A quantitative study of the influence of inhaled compounds on their concentrations in exhaled breath. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, F.; Loccioni, C.; Fioravanti, M.; Russo, A.; Pioggia, G.; Ferro, M.; Roehrer, I.; Tabucchi, S.; Onor, M. Implementation of Fowler’s method for end-tidal air sampling. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miekisch, W.; Kischkel, S.; Sawacki, A.; Liebau, T.; Mieth, M.; Schubert, J.K. Impact of sampling procedures on the results of breath analysis. J. Breath Res. 2008, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, J.; Herbig, J.; Gutmann, R. On use of Tedlar bags for breath-gas sampling and analysis. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeker, P.; Leppert, J.; Lammers, P.S. Comparison of Odorant Losses at the ppb-Level from Sampling Bags of Nalophan (TM) and Tedlar (TM) and from Adsorption Tubes. In Proceedings of the NOSE2014: 4th International Conference on Environmental Odour Monitoring and Control; Chemical Engineering Transactions: Venice, Italy, 2014; Volume 40, pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Mochalski, P.; Wzorek, B.; Sliwka, I.; Amann, A. Suitability of different polymer bags for storage of volatile sulphur compounds relevant to breath analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.M.; McGinley, M.A. Evaluation of Background Odour in Tedlar and Nalophan Sample Bags; WEF/A&WMA Odors and Air Emissions: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2008; pp. 590–604. [Google Scholar]
- Mochalski, P.; King, J.; Unterkofler, K.; Amann, A. Stability of selected volatile breath constituents in Tedlar, Kynar and Flexfilm sampling bags. Analyst 2013, 138, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Harreveld, A. Odor concentration decay and stability in gas sampling bags. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2003, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, W.; Zellers, E. Investigation of organic vapor losses to condensed water vapor in Tedlar bags used for exhaled-breath sampling. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1996, 57, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, B.; Pleil, J.; Angrish, M.; Stiegel, M.; Risby, T.; Madden, M. Standardization of the collection of exhaled breath condensate and exhaled breath aerosol using a feedback regulated sampling device. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11, 047107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Duan, Y. Breath analysis: Technical developments and challenges in the monitoring of human exposure to volatile organic compounds. J. Chrom. B 2015, 1002, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Pellizzari, E.; Gordon, S. A linear model relating breath concentrations to environmental exposures: Application to a chamber study of four volunteers exposed to volatile organic chemicals. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1993, 3, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, L.A.; Pellizzari, E.D. Recent advances in measuring exhaled breath and estimating exposure and body burden for volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp, J. Inhaled today not gone tomorrow: Pharmacokinetics and environmental exposure of volatiles in exhaled breath. J. Breath Res. 2011, 5, 37103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshman, S.W.; Pitsch, R.L.; Davidson, C.N.; Scott, A.M.; Hill, E.M.; Smith, Z.K.; Strayer, K.E.; Schaeublin, N.M.; Wiens, T.L.; Brothers, M.C.; et al. Characterization of standardized breath sampling for off-line field use. J. Breath Res. 2020, 14, 016009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, S.W.; Pitsch, R.L.; Davidson, C.N.; Lee, E.M.; Scott, A.M.; Hill, E.M.; Mainali, P.; Brooks, Z.E.; Strayer, K.E.; Schaeublin, N.M.; et al. Evaluation of a standardized collection device for exhaled breath sampling onto thermal desorption tubes. J. Breath Res. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.A.; Thomas, P.S.; Yates, D.H. Breath analysis in asbestos-related disorders: A review of the literature and potential future applications. J. Breath Res. 2010, 4, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, M.A. Advanced Gas Chromatography-Progress in Agricultural, Biomedical and Industrial Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0298-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wypych, G. Handbook of Odors in Plastic Materials, 2nd ed.; ChemTech Publishing: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2017; ISBN 978-1-895198-98-0. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, S.; Romano, A.; Hanna, G. Optimisation of sampling parameters for standardized exhaled breath sampling. J. Breath. Res. 2018, 12, 016007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gennaro, G.; Demarinis Loiotile, A.; Fracchiolla, R.; Palmisani, J.; Saracino, M.R.; Tutino, M. Temporal variation of VOC emission from solvent and water based wood stains. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisani, J.; Di Gilio, A.; Cisternino, E.; Tutino, M.; de Gennaro, G. Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) emissions from a personal care polymer-based item: Simulation of the inhalation exposure scenario indoors under actual conditions of use. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.; Voss, D. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 112–113. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M.; Greenberg, J.; Sabas, M. Alveolar gradient of pentane in normal human breath. Free Radic. Res. 1994, 20333–20337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W.; Birken, T.; Geiger, K.; Nöldge-Schomburg, G.F.E. Impact of inspired substance concentrations on the results of breath analysis in mechanically ventilated patients. Biomarkers 2005, 10138–10152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, F.; Wolf, A.; Fink, T.; Rittershofer, B.; Heim, N.; Volk, T.; Baumbach, J. Wash-out of ambient air contaminations for breath measurements. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 027107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M. Method for the Collection and Assay of Volatile Organic Compounds in Breath. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 247, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, P.; Ferrari, C.; Persia, R.; Ghimenti, S.; Lomonaco, T.; Bellagambi, F.; Di Francescoa, F. A dual mode breath sampler for the collection of the end-tidal and dead space fractions. Med. Eng. Phys. 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, F.L.; Furne, J.K.; Springfield, J.; Levitt, M.D. Morning breath odor: Influence of treatments on sulfur gases. J. Dent. Res. 2000, 79, 1773–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangerman, A.; Winkel, E.G. Intra-and extra-oral halitosis: Finding of a new form of extra-oral blood-borne halitosis caused by dimethyl sulphide. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, J.K.; Spittler, K.H.; Braun, G.; Geiger, K.; Guttmann, J. CO2-controlled sampling of alveolar gas in mechanically ventilated patients. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, K.; Ishizaki, T. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of benzoic acid following oral administration of sodium benzoate to humans. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1991, 41, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.R.; Cox, I.J.; Walker, D.G.; North, B.V.; Patel, V.M.; Marshall, S.E.; Jewell, D.P.; Ghosh, S.; Thomas, H.J.; Teare, J.P.; et al. Characterization of inflammatory bowel disease with urinary metabolic profiling. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.; Ahmed, W.M.; Nijsen, T.M.E.; Goodacre, R.; Fowler, S.J. Exhaled breath analysis: A review of ‘breath-taking’ methods for off-line analysis. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.W. Variability of the blood: Breathal cohol ratio in vivo. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 1978, 39, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Gaude, E.; Nakhleh, M.; Patassini, S.; Boschmans, J.; Allsworth, M.; Boyle, B.; van der Schee, M. Targeted breath analysis: Exogenous volatile organic compounds (EVOC) as metabolic pathway-specific probes. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 03200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleil, J.D.; Stiegel, M.A.; Sobus, J.R. Breath biomarkers in environmental health science: Exploring patterns in the human exposome. J. Breath Res. 2011, 5, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pleil, J.D.; Stiegel, M.A.; Risby, T.H. Clinical breath analysis: Discriminating between human endogenous compounds and exogenous (environmental) chemical confounders. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 017107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Trefz, P.; Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W. Immediate effects of breath holding maneuvers onto composition of exhaled breath. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 037102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Trefz, P.; Kamysek, S.; Schubert, J.K.; Miekisch, W. Instant effects of changing body positions on compositions of exhaled breath. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 047105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, Y.; Métrailler, L.; Baumbach, J.I.; Ktaus, T. Signals in asbestos related diseases in human breath-preliminary results. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spec. 2014, 17, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajtarevic, A.; Ager, C.; Pienz, M.; Klieber, M.; Schwarz, K.; Ligor, M.; Ligor, T.; Filipiak, W.; Denz, H.; Fiegl, M.; et al. Noninvasive detection of lung cancer by analysis of exhaled breath. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligor, M.; Ligor, T.; Bajtarevic, A.; Ager, C.; Pienz, M.; Klieber, M.; Denz, H.; Fiegl, M.; Hilbe, W.; Weiss, W.; et al. Determination of volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer using solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Goldoni, M.; Caglieri, A.; Ceresa, G.; Acampa, O.; Carbognani, P.; Rusca, M.; Corradi, M. Breath analysis in non small cell lung cancer patients after surgical tumor resection. Acta. Biomed. 2008, 79, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ong, C.N.; Patra, A.; Lu, Y.; Lim, C.T.; Venkatesan, T. Detection of Lung Cancer: Concomitant Volatile Organic Compounds and Metabolomic Profiling of Six Cancer Cell Lines of Different Histological Origins. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5131–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Barash, O.; Peled, N.; Phillips, M.; Amann, A.; Haick, H. Volatile organic compounds of lung cancer and possible biochemical pathways. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5949–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponring, A.; Filipiak, W.; Mikoviny, T.; Ager, C.; Schubert, J.; Miekisch, W.; Amann, A.; Troppmair, J. Release of volatile organic compounds from the lung cancer cell line NCIH2087 in-vitro. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Patra, A.; Kutty, V.K.; Venkatesan, T. Critical Review of Volatile Organic Compound Analysis in Breath and In Vitro Cell Culture for Detection of Lung Cancer. Metabolites 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, S.; Yoav, Y.B.; Abraham, M.; Hossam, H. Profiling Single Cancer Cells with Volatolomics Approach. Science 2019, 11, 178–188. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.E.; Eyton-Jones, H.W.; Farnworth, M.J.; Gallagher, R.; Provan, W.M. Effect of intestinal microflora on the urinary metabolic profile of rats: A 1Hnuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Xenobiotica 2002, 32, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, A.W.; Mortishire-Smith, R.J.; Nicholson, J.K. NMR spectroscopic-based metabonomic studies of urinary metabolite variation in acclimatizing germ-free rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



| Step | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Tube desorption | Purge time | 3 min at 5 mL/min–trap in line |
| Desorption time | 10 min | |
| Desorption temperature | 300 °C | |
| Temperature of cold trap | 20 °C | |
| Desorption flow | 30 mL/min, no split | |
| Focusing trap desorption | Temperature of cold trap desorption | 300 °C |
| Split low | 5 mL/min | |
| Transfer Line Temperature | 200 °C | |
| GC analysis | Gas carrier | He |
| Gas flow | 1.7 mL/min | |
| Analytical column | VOCOL® (Supelco), diphenyl dimethyl polysiloxane with crosslinking moieties, 60 m × 0.25 mm ID, 1.5 μm stationary phase thickness | |
| Oven temperature | 37 °C hold for 5 min 37 °C–190 °C at 6 °C/min 190 °C–200 °C at 2 °C/min 200 °C–220 °C at 15 °C/min 220 °C hold for 3 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Gilio, A.; Palmisani, J.; Ventrella, G.; Facchini, L.; Catino, A.; Varesano, N.; Pizzutilo, P.; Galetta, D.; Borelli, M.; Barbieri, P.; et al. Breath Analysis: Comparison among Methodological Approaches for Breath Sampling. Molecules 2020, 25, 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245823
Di Gilio A, Palmisani J, Ventrella G, Facchini L, Catino A, Varesano N, Pizzutilo P, Galetta D, Borelli M, Barbieri P, et al. Breath Analysis: Comparison among Methodological Approaches for Breath Sampling. Molecules. 2020; 25(24):5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245823
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Gilio, Alessia, Jolanda Palmisani, Gianrocco Ventrella, Laura Facchini, Annamaria Catino, Niccolò Varesano, Pamela Pizzutilo, Domenico Galetta, Massimo Borelli, Pierluigi Barbieri, and et al. 2020. "Breath Analysis: Comparison among Methodological Approaches for Breath Sampling" Molecules 25, no. 24: 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245823
APA StyleDi Gilio, A., Palmisani, J., Ventrella, G., Facchini, L., Catino, A., Varesano, N., Pizzutilo, P., Galetta, D., Borelli, M., Barbieri, P., Licen, S., & de Gennaro, G. (2020). Breath Analysis: Comparison among Methodological Approaches for Breath Sampling. Molecules, 25(24), 5823. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245823











