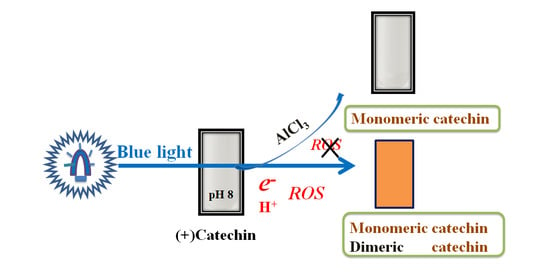
Catechin Photolysis Suppression by Aluminum Chloride under Alkaline Conditions and Assessment with Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
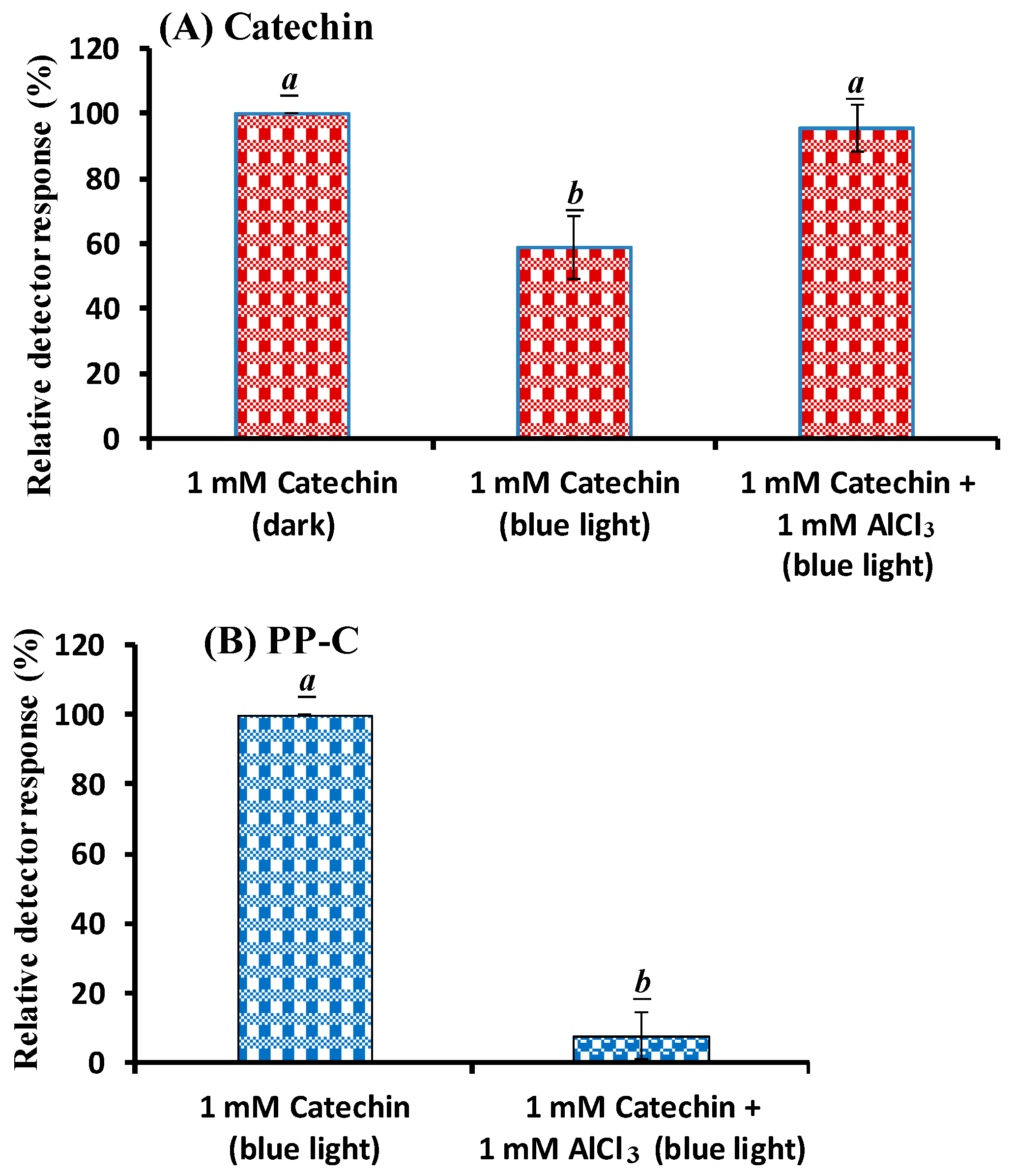
2.1. Effects of AlCl3 on Catechin Photolysis
2.2. HPLC–MS Assay of Catechin upon the Addition of AlCl3 Treated with BLI
2.3. Effects of FeCl3 on Catechin Treated with BLI
2.4. Effects of Sodium Fluoride (NaF) or Oxalic Acid on Catechin upon the Addition of AlCl3 Treated with BLI
2.5. Detection of in Catechin upon the Addition of AlCl3 Treated with BLI
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Photolytic System
4.3. The Effect of AlCl3 on Catechin Treated with BLI
4.4. The Effect of FeCl3 on Catechin Treated with BLI
4.5. The Effect of NaF or Oxalic Acid on Catechin Treated with BLI in the Presence of AlCl3
4.6. HPLC–MS Assay of Catechin upon the Addition of AlCl3 Treated with BLI
4.7. Assay of
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balasundram, N.; Sundram, K.; Samman, S. Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: Antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Niu, G.; Liu, H. Microwave-assisted extraction of tea polyphenols and tea caffeine from green tea leaves. Chem. Eng. Process. 2003, 42, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, M.; Naparlo, K.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Antioxidant properties of catechins: Comparison with other antioxidants. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Nie, Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Lu, J.L.; Liang, Y.R.; Ye, J.H. Ultraviolet B (UVB) photosensitivities of tea catechins and the relevant chemical conversions. Molecules 2016, 21, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.J.; Hung, Y.A.; Wong, T.W.; Lee, N.Y.; Yuann, J.P.; Huang, S.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, I.Z.; Liang, J.Y. Effects of blue-light-induced free radical formation from catechin hydrate on the inactivation of Acinetobacter baumannii, Iincluding a carbapenem-resistant strain. Molecules 2018, 23, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, A.; Ng, K.; Nicolazzo, J.A.; Larson, I. Effective use of reducing agents and nanoparticle encapsulation in stabilizing catechins in alkaline solution. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeiro, P.; Brett, A.M.O. Catechin electrochemical oxidation mechanisms. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 518, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Kano, K.; Ikeda, T. Kinetic analysis and mechanistic aspects of autoxidation of catechins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1569, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.B.; Ye, J.H.; Lu, J.L.; Liang, Y.R. Effects of temperature, illumination, and sodium ascorbate on browning of green tea infusion. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 932–938. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.Y.; Zhang, A.; Tsang, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Stability of Green Tea Catechins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 4624–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Liang, J.Y. Using chromatography and mass spectrometry to monitor isomerization of catechin in alkaline aqueous with thermal processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, K.; Wan, P.; Preston, C.M. Catechin and hydroxybenzhydrols as models for the environmental photochemistry of tannins and lignins. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2004, 3, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm-Mouton, A.; Bonnet, S.L.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.C.; Ferreira, D.; van der Westhuizen, J.H. Photochemistry synthesis. Part 2: Enantiomerically pure polyhydroxy-1,1,3-triarylpropan-2-ols. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2012, 227, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Hu, A.; Chen, L.Y. Photo-catalytic polymerization of catechin molecules in alkaline aqueous. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 2016, 165, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Hung, Y.A.; Yang, M.J.; Chen, I.Z.; Yuann, J.P.; Liang, J.Y. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on the stability of epicatechin in a photolytic process. Molecules 2019, 24, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torreggiani, A.; Jurasekova, Z.; Sanchez-Cortes, S.; Tamba, M. Spectroscopic and pulse radiolysis studies of the antioxidant properties of (+) catechin: Metal chelation and oxidizing radical scavenging. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 39, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exley, C. The toxicity of aluminium in humans. Morphologie 2016, 100, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, T.L.; Martin, R.B. Aluminum ion in biological systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1988, 13, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, J.I.; Rezabal, E.; Mercero, J.M.; Ruiperez, F.; Costa, D.; Ugalde, J.M.; Lopez, X. Aluminium in biological environments: A computational approach. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, e201403002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, J.R. Evidence for participation of aluminum in neurofibrillary tangle formation and growth in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 22, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, J.I.; Ruiperez, F.; Infante, I.; Ugalde, J.M.; Exley, C.; Lopez, X. Pro-oxidant activity of aluminum: Stabilization of the aluminum superoxide radical ion. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 6717–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Wang, M.K.; Huang, P.M. Catechin transformation as influenced by aluminum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.S.; Shen, S.R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, C.Y. Interaction of catechins with aluminum in vitro. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2004, 5, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.R.; Berthon, G.; Day, J.P.; Exley, C.; Flaten, T.P.; Forbes, W.F.; Kiss, T.; Orvig, C.; Zatta, P.F. Speciation of aluminum in biological systems. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1996, 48, 543–568. [Google Scholar]
- Krewski, D.; Yokel, R.A.; Nieboer, E.; Borchelt, D.; Cohen, J.; Harry, J.; Kacew, S.; Lindsay, J.; Mahfouz, A.M.; Rondeau, V. Human health risk assessment for aluminium, aluminium oxide, and aluminium hydroxide. J. Toxicol Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2007, 10 (Suppl. 1), 1–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.Y.; Chung, R.S.; Lin, H.C. Speciation of aluminum and fluorine in a blend of green tea infusion and human gastric juice by ion chromatography and 19F-NMR. Food Sci. Agric. Chem. 1999, 1, 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhabiri, M.; Carrër, C.; Marmolle, F.; Traboulsi, H. Complexation of iron (III) by catecholate-type polyphenols. Inorgan. Chim. Acta 2007, 360, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.B. The chemistry of aluminum as related to biology and medicine. Clin. Chem. 1986, 32, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.S.; Lin, X.M.; Qiao, R.Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Lu, J.L.; Ye, J.H.; Liang, Y.R. Effect of fluoride treatment on gene expression in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libert, B.; Franceschi, V.R. Oxalate in crop plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1987, 35, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Yen, C.H.; Lin, H.C. A study on aluminum species in green tea infusion by ion chromatography. J. Chin. Agric. Chem. Soc. 1998, 36, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Wu, C.C.; Tzen, J.T. Catechin content and the degree of its galloylation in oolong tea are inversely correlated with cultivation altitude. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, S.; Jurinski, N. Charge transfer complexes of aluminum chloride. Tetrahedron 1967, 23, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Lee, N.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Yang, M.J.; Hung, Y.A.; Wong, T.W.; Liang, J.Y. Effects of 462 nm light-emitting diode on the inactivation of Escherichia coli and a multidrug-resistant by tetracycline photoreaction. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.L.; Steenken, S.L. Photoionization (.lambda. = 248 or 308 nm) of triphenylmethyl radical in aqueous solution. Formation of triphenylmethyl carbocation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, A.; Wang, H. Mechanisms of oxidative browning of wine. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojwang, L.O.; Yang, L.; Dykes, L.; Awika, J. Proanthocyanidin profile of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) reveals catechin-O-glucoside as the dominant compound. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Xie, D.Y.; Sharma, S.B. Proanthocyanidins—a final frontier in flavonoid research? New Phytol. 2005, 165, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tan, H.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Qian, Y.; et al. Analysis of accumulation patterns and preliminary study on the condensation mechanism of proanthocyanidins in the tea plant [Camellia sinensis]. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagawa, M.; Shigemitsu, T.; Suyama, K. Production of hydrogen peroxide by polyphenols and polyphenol-rich beverages under quasi-physiological conditions. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumamoto, M.; Sonda, T.; Nagayama, K.; Tabata, M. Effects of pH and metal ions on antioxidative activities of catechins. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exley, C. The pro-oxidant activity of aluminum. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuzumi, S.; Ohtsu, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Itoh, S.; Imahori, H. Formation of superoxide–metal ion complexes and the electron transfer catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 226, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzumi, S. Catalytic control of electron-transfer processes. Pure Appl. Chem. 2003, 75, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzumi, S. Catalysis in electron transfer reactions: Facts and mechanistic insights. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2002, 15, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilonu, M.C.; Bonnet, S.L.; van der Westhuizen, J.H. Synthesis of proanthocyanidins. Part 1. The first oxidative formation of the interflavanyl bond in procyanidins. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Watrelot, A.A.; Addison, B.; Waterhouse, A.L. Condensed tannin reacts with SO2 during wine aging, yielding flavan-3-ol sulfonates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9259–9268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, M.; Kuwahara, Y.; Suenobu, T.; Fukuzumi, S. Oxidation mechanism of NAD dimer model compounds. Chem. Lett. 1997, 26, 567–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Yuann, J.P.; He, S.; Cheng, C.W.; Liang, J.Y. The influence of the degradation of tetracycline by free radicals from riboflavin-5’-phosphate photolysis on microbial viability. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.W.; Chen, L.Y.; Chou, C.W.; Liang, J.Y. Investigations of riboflavin photolysis via coloured light in the nitro blue tetrazolium assay for superoxide dismutase activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 148, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (aluminum chloride and catechin) are available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Liu, C.-I.; Chen, S.-H.; Chen, I.-Z.; Su, T.-C.; Yuann, J.-M.P.; Cheng, C.-W.; Huang, S.-T.; Liang, J.-Y. Catechin Photolysis Suppression by Aluminum Chloride under Alkaline Conditions and Assessment with Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 5985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245985
Yang M-J, Lee S-Y, Liu C-I, Chen S-H, Chen I-Z, Su T-C, Yuann J-MP, Cheng C-W, Huang S-T, Liang J-Y. Catechin Photolysis Suppression by Aluminum Chloride under Alkaline Conditions and Assessment with Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2020; 25(24):5985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245985
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Meei-Ju, Shwu-Yuan Lee, Chieh-I Liu, Shih-Hsuan Chen, Iou-Zen Chen, Tsung-Chen Su, Jeu-Ming P. Yuann, Chien-Wei Cheng, Shiuh-Tsuen Huang, and Ji-Yuan Liang. 2020. "Catechin Photolysis Suppression by Aluminum Chloride under Alkaline Conditions and Assessment with Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 25, no. 24: 5985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245985
APA StyleYang, M.-J., Lee, S.-Y., Liu, C.-I., Chen, S.-H., Chen, I.-Z., Su, T.-C., Yuann, J.-M. P., Cheng, C.-W., Huang, S.-T., & Liang, J.-Y. (2020). Catechin Photolysis Suppression by Aluminum Chloride under Alkaline Conditions and Assessment with Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 25(24), 5985. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25245985