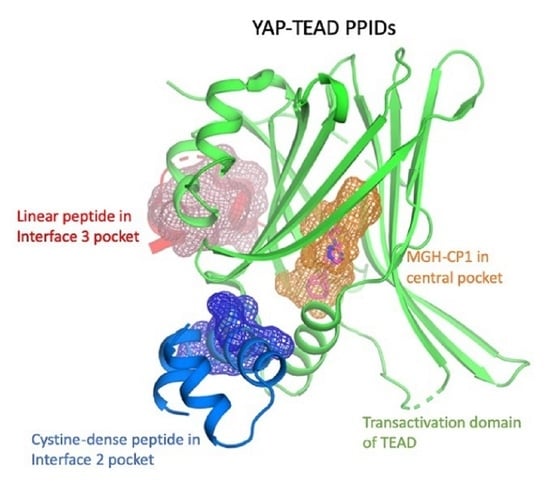
Protein-Protein Interaction Disruptors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD Transcriptional Complex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Characterization of YAP-TEAD Interaction
3. Targeting the Interface 2 Region of the YAP-TEAD Complex
4. PPIDs that Bind Interface 3
4.1. Dioxo-Benzoisothiazole Scaffold
4.2. Triazole-Carbohydrazone Scaffold
4.3. Compounds 3 and 3.1
5. Verteporfin Binds to YAP
6. Compounds That Occupy the Central Pocket
6.1. Flufenamic Acid
6.2. Non-Covalent Allosteric PPIDs
6.2.1. MGH-CP1
6.2.2. DNA-Encoded Indole-Focused Ugi-Peptidomimetics
6.2.3. Dihydropyrazolo Pyrimidines
6.3. Allosteric PPIDs That Form a Covalent Interaction
6.3.1. K-975
6.3.2. Kojic Acid Analogs
6.4. Other Central Pocket Binders
6.4.1. Compound 2
6.4.2. Vinylsulfonamides
6.4.3. Quinolinols
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 175, 598–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontaine, F.; Overman, J.; François, M. Pharmacological manipulation of transcription factor protein-protein interactions: Opportunities and obstacles. Cell Regen. 2015, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhagwat, A.S.; Vakoc, C.R. Targeting Transcription Factors in Cancer. Trends Cancer 2015, 1, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiedemann, B.; Weisner, J.; Rauh, D. Chemical modulation of transcription factors. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 1249–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibault, F.; Sturbaut, M.; Bailly, F.; Melnyk, P.; Cotelle, P. Targeting Transcriptional Enhanced Associate Domains (TEADs). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5057–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Hong, W. A combat with the YAP/TAZ-TEAD oncoproteins for cancer therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3622–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Varelas, X.; Guan, K.L. Targeting the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, S.; Dupont, S.; Cordenonsi, M. The biology of YAP/TAZ: Hippo signaling and beyond. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Luo, X. Activation mechanisms of the Hippo kinase signaling cascade. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ at the Roots of Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Yu, J.; Tomchick, D.R.; Pan, D.; Luo, X. Structural and functional analysis of the YAP-binding domain of human TEAD2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7293–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu-Chittenden, Y.; Huang, B.; Shim, J.S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, S.J.; Anders, R.A.; Liu, J.O.; Pan, D. Genetic and pharmacological disruption of the TEAD-YAP complex suppresses the oncogenic activity of YAP. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Han, X.; Hung, A.W.; Weiguang, S.; Huda, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Kang, C.; Chia, C.S.; Luo, X.; Hong, W.; et al. Targeting the Central Pocket in Human Transcription Factor TEAD as a Potential Cancer Therapeutic Strategy. Structure 2015, 23, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Hong, W. Emerging roles of TEAD transcription factors and its coactivators in cancers. Cancer Biol. 2013, 14, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huh, H.D.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, H.S.; Park, H.W. Regulation of TEAD Transcription Factors in Cancer Biology. Cells 2019, 8, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, P.; Chen, F.; Dong, Z.; Yang, H.; Guan, K.L.; Xu, Y. Structural insights into the YAP and TEAD complex. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chan, S.W.; Zhang, X.; Walsh, M.; Lim, C.J.; Hong, W.; Song, H. Structural basis of YAP recognition by TEAD4 in the hippo pathway. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.K.; Chao, S.P.; Hu, C.J. Clinical trials of new drugs for Alzheimer disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darimont, B.D.; Wagner, R.L.; Apriletti, J.W.; Stallcup, M.R.; Kushner, P.J.; Baxter, J.D.; Fletterick, R.J.; Yamamoto, K.R. Structure and specificity of nuclear receptor-coactivator interactions. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3343–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nolte, R.T.; Wisely, G.B.; Westin, S.; Cobb, J.E.; Lambert, M.H.; Kurokawa, R.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Willson, T.M.; Glass, C.K.; Milburn, M.V. Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Nature 1998, 395, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, Z.R.; Sevilla, G.P.; Friend, D.; Brusniak, M.Y.; Bandaranayake, A.D.; Clarke, M.; Gewe, M.; Mhyre, A.J.; Baker, D.; Strong, R.K.; et al. Mammalian display screening of diverse cystine-dense peptides for difficult to drug targets. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaan, H.Y.K.; Sim, A.Y.L.; Tan, S.K.J.; Verma, C.; Song, H. Targeting YAP/TAZ-TEAD protein-protein interactions using fragment-based and computational modeling approaches. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, H.C.; Yan, S.F.; Mayweg, A.V.; Xu, Z.; Qin, N.; Wong, J.C.; Rong, Y.; et al. Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Potent Cyclic Peptides Inhibiting the YAP-TEAD Protein-Protein Interaction. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhu, L.; Rong, Y.; Shen, H.; Luk, J.M.; et al. Targeting Hippo pathway by specific interruption of YAP-TEAD interaction using cyclic YAP-like peptides. Fasebj. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2015, 29, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furet, P.; Salem, B.; Mesrouze, Y.; Schmelzle, T.; Lewis, I.; Kallen, J.; Chene, P. Structure-based design of potent linear peptide inhibitors of the YAP-TEAD protein-protein interaction derived from the YAP omega-loop sequence. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 2316–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Ng, E.Y.; Li, R.; Poulsen, A.; Hill, J.; Pobbati, A.V.; Hung, A.W.; Hong, W.; Keller, T.H.; et al. Structural and ligand-binding analysis of the YAP-binding domain of transcription factor TEAD4. Biochemj. 2018, 475, 2043–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, M.C.S.; Montalbetti, C.; Spitzer, L. Preparation of new 4-(1,1-Dioxo-1,2-benzothiazol-3-yl)hydrazono]methyl]-2-methoxyphenols as Inhibitors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD Interaction and Their Use in the Treatment of Malignant Mesothelioma. WO Patent 2017064277, 20 April 2017. Inventiva. [Google Scholar]
- Gibault, F.; Coevoet, M.; Sturbaut, M.; Farce, A.; Renault, N.; Allemand, F.; Guichou, J.F.; Drucbert, A.S.; Foulon, C.; Magnez, R.; et al. Toward the Discovery of a Novel Class. of YAP(-)TEAD Interaction Inhibitors by Virtual Screening Approach Targeting YAP(-)TEAD Protein(-)Protein Interface. Cancers 2018, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.A.; Sessions, R.B.; Shoemark, D.K.; Williams, C.; Ebrahimighaei, R.; McNeill, M.C.; Crump, M.P.; McKay, T.R.; Harris, G.; Newby, A.C.; et al. Antiproliferative and Antimigratory Effects of a Novel YAP-TEAD Interaction Inhibitor Identified Using in Silico Molecular Docking. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiao, S.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Dong, A.; Zhang, W.; Song, X.; He, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. A peptide mimicking VGLL4 function acts as a YAP antagonist therapy against gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, P.; Han, X.; Zheng, B.; DeRan, M.; Yu, J.; Jarugumilli, G.K.; Deng, H.; Pan, D.; Luo, X.; Wu, X. Autopalmitoylation of TEAD proteins regulates transcriptional output of the Hippo pathway. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noland, C.L.; Gierke, S.; Schnier, P.D.; Murray, J.; Sandoval, W.N.; Sagolla, M.; Dey, A.; Hannoush, R.N.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Cunningham, C.N. Palmitoylation of TEAD Transcription Factors Is Required for Their Stability and Function in Hippo Pathway Signaling. Structure 2016, 24, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bum-Erdene, K.; Zhou, D.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, G.; Ghozayel, M.K.; Si, Y.; Xu, D.; Shannon, H.E.; Bailey, B.J.; Corson, T.W.; Pollok, K.E.; et al. Small-Molecule Covalent Modification of Conserved Cysteine Leads to Allosteric Inhibition of the TEADYap Protein-Protein Interaction. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurppa, K.J.; Liu, Y.; To, C.; Zhang, T.; Fan, M.; Vajdi, A.; Knelson, E.H.; Xie, Y.; Lim, K.; Cejas, P.; et al. Treatment-Induced Tumor Dormancy through YAP-Mediated Transcriptional Reprogramming of the Apoptotic Pathway. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 104–122 e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konradi, A.W.; Lin, T.T.L.T. Non-Fused Tricyclic Compounds. WO Patent 2018204532, 8 November 2018. Vivace Therapeutics. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jarugumilli, G.K.; Liu, S.; Dang, K.; Cotton, J.L.; Xiol, J.; Chan, P.Y.; DeRan, M.; Ma, L.; et al. Lats1/2 Sustain. Intestinal Stem Cells and Wnt Activation through TEAD-Dependent and Independent Transcription. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 675–692 e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunig, V.B.K.; Potowski, M.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Klika Skopic, M.; Dos Santos Smith, D.; Arendt, L.; Dormuth, I.; Adihou, H.; Andlovic, B.; Karatas, H.; et al. TEAD-YAP Interaction Inhibitors and MDM2 Binders from DNA-Encoded Indole-Focused Ugi Peptidomimetics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 20338–20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbieg, P.P.; Crawford, J.J. Therapeutic Compounds. WO Patent 2019232216, 22 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda, A.; Seike, T.; Uemori, T.; Myojo, K.; Aida, K.; Danjo, T.; Nakajima, T.; Yamaguchi, D.; Hamada, T.; Tsuji, Y.; et al. Discovery of a first-in-class TEAD inhibitor which directly inhibits YAP/TAZ-TEAD protein-protein interaction and shows a potent anti-tumor effect in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Prooceeding 2019, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, H.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Adihou, H.; Hahne, G.; Pobbati, A.V.; Yihui Ng, E.; Gueret, S.M.; Sievers, S.; Pahl, A.; Metz, M.; et al. Discovery of Covalent Inhibitors Targeting the Transcriptional Enhanced Associate Domain Central Pocket. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 11972–11989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, J.K.; Crawford, J.J.; Noland, C.L.; Schmidt, S.; Zbieg, J.R.; Lacap, J.A.; Zang, R.; Miller, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Beroza, P.; et al. Small Molecule Dysregulation of TEAD Lipidation Induces a Dominant-Negative Inhibition of Hippo Pathway Signaling. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Tao, H.; Xiong, H.; Lian, F.; Gao, J.; Ma, H.; Lu, T.; Zhang, D.; et al. Discovery and biological evaluation of vinylsulfonamide derivatives as highly potent, covalent TEAD autopalmitoylation inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 184, 111767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Mejuch, T.; Chakraborty, S.; Karatas, H.; Bharath, S.R.; Gueret, S.M.; Goy, P.A.; Hahne, G.; Pahl, A.; Sievers, S.; et al. Identification of Quinolinols as Activators of TEAD-Dependent Transcription. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 2909–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walensky, L.D.; Bird, G.H. Hydrocarbon-stapled peptides: Principles, practice, and progress. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6275–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Ji, L. Rational design and chemical modification of TEAD coactivator peptides to target hippo signaling pathway against gastrointestinal cancers. J. Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Chan, S.W.; Lee, I.; Song, H.; Hong, W. Structural and Functional Similarity between the Vgll1-TEAD and the YAP-TEAD Complexes. Structure 2012, 20, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesrouze, Y.; Hau, J.C.; Erdmann, D.; Zimmermann, C.; Fontana, P.; Schmelzle, T.; Chene, P. The surprising features of the TEAD4-Vgll1 protein-protein interaction. Chembiochem 2014, 15, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adihou, H.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Forster, T.; Gueret, S.M.; Gasper, R.; Geschwindner, S.; Carrillo Garcia, C.; Karatas, H.; Pobbati, A.V.; Vazquez-Chantada, M.; et al. A protein tertiary structure mimetic modulator of the Hippo signalling pathway. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N. Multiple Roles of Vestigial-Like Family Members in Tumor Development. Front Oncol. 2020, 10, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesrouze, Y.; Aguilar, G.; Bokhovchuk, F.; Martin, T.; Delaunay, C.; Villard, F.; Meyerhofer, M.; Zimmermann, C.; Fontana, P.; Wille, R.; et al. A new perspective on the interaction between the Vg/VGLL1-3 proteins and the TEAD transcription factors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Berrocal, L.; Cirri, E.; Zhang, X.; Andrini, L.; Marin, G.H.; Lebel-Binay, S.; Rebollo, A. New Therapeutic Approach for Targeting Hippo Signalling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Li, C. Fluorescence polarization assay for the identification and evaluation of inhibitors at YAP-TEAD protein-protein interface 3. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 586, 113413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibault, F.; Bailly, F.; Corvaisier, M.; Coevoet, M.; Huet, G.; Melnyk, P.; Cotelle, P. Molecular Features of the YAP Inhibitor Verteporfin: Synthesis of Hexasubstituted Dipyrrins as Potential Inhibitors of YAP/TAZ, the Downstream Effectors of the Hippo Pathway. Chem. Med. Chem. 2017, 12, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.G.; Gumbiner, B.M. Cell contact and Nf2/Merlin-dependent regulation of TEAD palmitoylation and activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9877–9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elbediwy, A.; Vincent-Mistiaen, Z.I.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Stone, R.K.; Boeing, S.; Wculek, S.K.; Cordero, J.; Tan, E.H.; Ridgway, R.; Brunton, V.G.; et al. Integrin signalling regulates YAP and TAZ to control skin homeostasis. Development 2016, 143, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.J.; Byun, M.R.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; Hong, J.H.; Jung, H.S. YAP and TAZ regulate skin wound healing. J. Investig. Derm. 2014, 134, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| No. | Molecule | Structure | Surface Pocket Validation | Molecule Type | Validation Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modalities binding to Interface 2 | ||||||
| 1. | TB2G1 | Cystine-dense peptide | Rosetta modeling | PPID | Co-IP assay | [21] |
| 2. | Fragment 1 |  | Crystal structure | PPID unlikely | GST pull-down | [22] |
| 3. | Tri-substitutedpyrazoles |  | Crystal structure | Potential PPID | ||
| Modalities binding to Interface 3 | ||||||
| 4. | Peptide 17 | YAP cyclic peptide | Molecular modeling | PPID | GST pull-down | [23] |
| 5. | Peptide 10 | YAP cyclic peptide | Crystal structure | PPID | GST pull-down | [24] |
| 6. | Peptides 9, 10 | YAP linear peptide | Crystal structure | PPID | TR-FRET assay | [25] |
| 7. | Flufenamic acid |  | Crystal structure | PPID unlikely | [13] | |
| 8. | TEAD-binding fragment |  | NMR | PPID unlikely | [26] | |
| 9. | Dioxo-benzoisothiazole Example 22 |  | NMR | PPID | AlphaLISA assay | [27] |
| 10. | Triazole carbohydrazides Hit 2 |  | Molecular modeling | Potential PPID | [28] | |
| 11. | Compound 3.1 |  | Molecular docking | PPID | Co-IP assay | [29] |
| Peptide binding to both Interfaces 2 & 3 | ||||||
| 12. | Super-TDU | YAP-VGLL4 fusion peptide | Molecular modeling | PPID | Co-IP assay | [30] |
| No. | Molecule | Structure | Binding Validation | Molecule Type | Validation Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flufenamates | ||||||
| 1. | Flufenamic acid |  | Crystal structure | Palmitoylation inhibitor | Mass Spec analysis | [13] |
| 2. | TED-347 |  | Crystal structure | Allosteric PPID | FP assay with YAP peptide | [33] |
| 3. | MYF-01-037 |  | Molecular docking | Allosteric PPID | Split luciferase assay | [34] |
| 4. | Non-fused tricyclic Compound 42 |  | unknown | PPID? | [35] | |
| 5. | FA-Palmitate fusion |  | Crystal structure | PPID? | ||
| Non-covalent allosteric PPIDs | ||||||
| 6. | MGH-CP1 |  | Crystal structure | Allosteric PPID | Co-IP assay | [36] |
| 7. | Compound 9 Indole-focused |  | Palmitate-based FP assay | Allosteric PPID | FP assay with YAP peptide | [37] |
| 8. | Dihydropyrazolo pyrimidines Compound 7 |  | unknown | AllostericPPID? | TR-FRET assay | [38] |
| Covalent allosteric PPIDs | ||||||
| 9. | K-975 |  | Crystal structure | Allosteric PPID | Co-IP assay | [39] |
| 10. | Kojic acid analogs Compound 19 |  | Thiol conjugation assay | Allosteric PPID | FP assay with YAP peptide | [40] |
| Other central pocket binders | ||||||
| 11. | Compound 2 |  | Crystal structure | Palmitoylation inhibitor | FP assay with palmitate | [41] |
| 12. | Vinylsulfonamide DC-TEADin02 |  | Molecular docking | Palmitoylation inhibitor | Competitive NMR | [42] |
| 13. | Quinolinol Q2 |  | Molecular dynamics simulations | TEAD activator | RNA-Seq | [43] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pobbati, A.V.; Rubin, B.P. Protein-Protein Interaction Disruptors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD Transcriptional Complex. Molecules 2020, 25, 6001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25246001
Pobbati AV, Rubin BP. Protein-Protein Interaction Disruptors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD Transcriptional Complex. Molecules. 2020; 25(24):6001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25246001
Chicago/Turabian StylePobbati, Ajaybabu V., and Brian P. Rubin. 2020. "Protein-Protein Interaction Disruptors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD Transcriptional Complex" Molecules 25, no. 24: 6001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25246001
APA StylePobbati, A. V., & Rubin, B. P. (2020). Protein-Protein Interaction Disruptors of the YAP/TAZ-TEAD Transcriptional Complex. Molecules, 25(24), 6001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25246001